Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Nursing Care Plan TBI
Caricato da
Chester Manalo87%(15)Il 87% ha trovato utile questo documento (15 voti)
38K visualizzazioni5 pagineHypoxia is a pathologic condition in which the body as a whole (generalize d hypoxia) or a region of the body (tissue hyoxia) is deprived of adequate oxygen supply. Following an 8-hr nursing interventio n, the client will be able to: Assessed respiratory rate.
Descrizione originale:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoHypoxia is a pathologic condition in which the body as a whole (generalize d hypoxia) or a region of the body (tissue hyoxia) is deprived of adequate oxygen supply. Following an 8-hr nursing interventio n, the client will be able to: Assessed respiratory rate.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
87%(15)Il 87% ha trovato utile questo documento (15 voti)
38K visualizzazioni5 pagineNursing Care Plan TBI
Caricato da
Chester ManaloHypoxia is a pathologic condition in which the body as a whole (generalize d hypoxia) or a region of the body (tissue hyoxia) is deprived of adequate oxygen supply. Following an 8-hr nursing interventio n, the client will be able to: Assessed respiratory rate.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 5
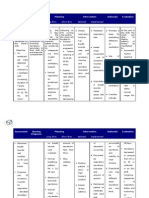
NURSING CARE PLAN
CUES NURSIN INFEREN GOAL/PL NURSING RATIONA EVALUATI
G CE AN LE ON
INTERVENTI
DIAGNO ON
SIS
No Ineffective Hypoxia is Following ♦ Assessed ♦ Provide At the end of
Subjectiv airway a an 8-hr respiratory s a basis the shift, the
e Cues clearance pathologic nursing client was
related to al interventio rate. for able to
hypoxia. condition n, the evaluati display
Objective in which client will ng patency of
: the body be able to: airway as
adequac
as a whole manifested
Dyspn (generalize Normal y of by:
ea; use d hypoxia) breathin ♦ Noted chest ventilati
Client’s
or a region g movement;
of on.
of the respirator
access pattern: use of
body y rate is
ory (tissue RR = accessory
♦ Use of within
hyoxia) is 12-20 muscles
muscle accessor normal
deprived
s for cpm during
of y range:
respira adequate respiration.
muscles RR-18
oxygen
tion: of bpm.
supply.
elevate respirati
d ♦ Auscultated on may
should breath occur in
ers. sounds; respons
noted areas e to
Increa
with ineffecti
se in
presence of ve
respira
adventitiou ventilati
tory
s sounds. on.
rate:
RR-25
cpm ♦ Crackle
s
indicate
accumul
ation of
secretio
ns and
inability
to clear
airways.
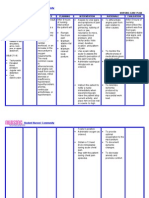
CUES NURSING INFERENC GOAL/PL NURSING RATION EVALUAT
E AN ALE ION
DIAGNOSI INTERVEN
S TION
No Ineffective Increased After 4 > Monitored > To > After 4
Subjective cerebral cardiac hours of blood know the hours of
Cues tissue output that nursing pressure base line nursing
perfusion injures the interventio every 4hours. of BP > intervention
related to endothelial n the pt > Instructed Sodium the
increased cells of the blood to have tends to bepatient’s
intracranial arteries and pressure enough rest excreted atblood
Objective: pressure the action of will on semi a faster pressure
and prostaglandi decrease fowlers rate. was
PR = 85 vasoconstri ns. from 160/ position. > decreased
bpm ction of Vasoconstri 100mmHg Instructed to from
RR = 30 blood ction occurs to eat low fat > To 160/100mm
bpm vessels and blood 120/80mm and low salt reduce Hg to
pressure Hg. diet. > edema that 140/90mm
160/100m increases. Administered may Hg.
mHg anti- activate
hypertensive renin
drug as angiotensi
ordered. n-
aldosteron
e system.
> To
control the
BP and to
avoid
other
complicati
ons.
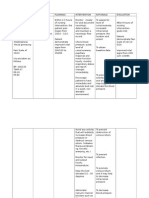
CUES NURSING INFEREN GOAL/PL NURSING RATIONA EVALUATI
CE AN LE ON
DIAGNO INTERVENTI
SIS ON
No Risk for Brain After 3 Monitor •To assess After 3 hours
Subjecti injury damage or hours of peripheral baseline of nursing
ve Cues related to "brain nursing pulses and data intervention,
brain injury" interventio vital signs, the client
damage. (BI); n, the client especially the •To assist verbalized
means the will be able heart rate client to understandin
destruction to verbalize every hour to reduce or g of
Objectiv or understandi every four correct individual
e: degenerati ng of hours individual factors that
on of brain individual depending on risk factor. contribute to
T: 36.7 cells, often factors that the client’s possibility of
PR: 65 with an contribute condition. injury and
bpmRR: implication to take steps to
that the possibility • correct
18
cpmBP: loss is of injury Provide situations.Go
120/70 significant and take information al was met
mmHg in terms of steps to regarding
functionin correct disease/conditi
g or situations on that may
conscious result in
experience increased risk
. It is a of injury.
common
and very
broad in
scope,
such that
in
medicine a
vast range
of specific
diagnoses
exist.
Brain
injuries
occur due
to a wide
range of
internal
and
external
factors. A
common
category
with the
greatest
number of
injuries is
traumatic
brain
injury
(TBI)
following
physical
trauma or
head injury
from an
outside
source, and
the term
acquired
brain
injury
(ABI) is
used in
appropriate
circles, to
differentiat
e brain
injuries
occurring
after birth
from
injury due
to a
disorder or
congential
malady.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Gastroesopageal Reflux DiseaseDocumento6 pagineGastroesopageal Reflux Diseasecory kurdapya100% (1)
- Nursing Diagnosis Diabetic KetoacidosisDocumento11 pagineNursing Diagnosis Diabetic Ketoacidosismonisha50% (4)
- 5 Altered Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements Chronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlansDocumento3 pagine5 Altered Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements Chronic Renal Failure Nursing Care Plansjustin_sane40% (5)
- Nursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento7 pagineNursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway Clearancearlee marquez96% (118)
- "Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction, Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, and Community Acquired Pneumonia" Nursing Care PlansDocumento21 pagine"Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction, Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, and Community Acquired Pneumonia" Nursing Care PlansCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For ESRDDocumento8 pagineNursing Care Plan For ESRDChester Manalo94% (17)
- RESPIRATORYDocumento10 pagineRESPIRATORYVikash Kushwaha100% (2)
- NCP TbiDocumento4 pagineNCP TbiWyen CabatbatNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP AnginaDocumento3 pagineNCP AnginaShie LA100% (1)
- NCP Head InjuryDocumento3 pagineNCP Head InjuryEdelou Alegria Jumawan67% (3)
- Fluid Volume Excess (CRF)Documento4 pagineFluid Volume Excess (CRF)NursesLabs.com100% (1)
- SchistosomiasisDocumento92 pagineSchistosomiasisIvan Juan75% (4)
- Case Presentation of Hemorrhagic Stroke Subarachnoid HemorrhageDocumento69 pagineCase Presentation of Hemorrhagic Stroke Subarachnoid HemorrhageShin FerranculloNessuna valutazione finora
- Myocarditis NCP 2Documento8 pagineMyocarditis NCP 2astro_aaron117375% (4)
- Activity Intolerance Related To AmeniaDocumento1 paginaActivity Intolerance Related To AmeniaSiti Syazana Mohamad MogriNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan Impaired AdjustmentDocumento1 paginaNursing Care Plan Impaired Adjustmentderic100% (2)
- NURSING CARE PLAN For Myocardial InfarctionDocumento16 pagineNURSING CARE PLAN For Myocardial InfarctionFreisanChenMandumotan100% (1)
- NCP Head InjuryDocumento3 pagineNCP Head InjuryAngel Mae Alsua100% (2)
- Med Surge 2 - RESP SYSTEM NOTESDocumento26 pagineMed Surge 2 - RESP SYSTEM NOTESlorrainenxumalo75% (4)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Evaluation No Subjective Cues ObjectiveDocumento3 pagineAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Evaluation No Subjective Cues ObjectiveMaverick LimNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment Explanation Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Objective: STG: STGDocumento11 pagineAssessment Explanation Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Objective: STG: STGGrape JuiceNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Near DrowningDocumento1 paginaNCP Near Drowningchristine louise bernardoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocumento2 pagineIneffective Tissue Perfusionsyderman999Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento13 pagineNursing Care PlanCris Solis33% (3)
- Gender Dysphoria NCPDocumento1 paginaGender Dysphoria NCPSeann LorescoNessuna valutazione finora
- NCPDocumento9 pagineNCPTracy Camille EscobarNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan For Acute Head InjuryDocumento4 pagineNursing Care Plan For Acute Head InjuryAngie Mandeoya67% (3)
- Aneurysm NCPDocumento4 pagineAneurysm NCPAnneUXD100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Risk For ConstipationDocumento4 pagineNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Risk For Constipationkenneth_bambaNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP AneurysmDocumento4 pagineNCP AneurysmJanielle Christine Monsalud100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento22 pagineNursing Care PlanjamNessuna valutazione finora
- Case: Liver Cirrhosis Assessment:: Nursing InferenceDocumento7 pagineCase: Liver Cirrhosis Assessment:: Nursing InferenceLovelyn GanirNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan Renal FailureDocumento11 pagineNursing Care Plan Renal Failurenosevad88850% (2)
- NCP ChoreaDocumento4 pagineNCP Choreanj_pink081794100% (2)
- Ards NCPDocumento5 pagineArds NCPgopscharanNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Impaired Skin IntegrityDocumento1 paginaNCP Impaired Skin Integritysinister17Nessuna valutazione finora
- San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesDocumento3 pagineSan Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, Philippineskuro hanabusaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrocephalus N C P BY BHERU LALDocumento1 paginaHydrocephalus N C P BY BHERU LALBheru LalNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP - Excess Fluid Volume (Aortic Stenosis)Documento3 pagineNCP - Excess Fluid Volume (Aortic Stenosis)Daniel Vergara Arce100% (3)
- NCPDocumento3 pagineNCPJezza RequilmeNessuna valutazione finora
- Nanda NCP BasedDocumento14 pagineNanda NCP Baseddeliejoyce100% (1)
- Subdural HematomaDocumento4 pagineSubdural Hematomarodamel gundanNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Impaired Gas Exhange CHEST INJURYDocumento4 pagineNCP Impaired Gas Exhange CHEST INJURYMa. Elaine Carla Tating100% (2)
- NCP Epidural HemDocumento32 pagineNCP Epidural HemKatrina PonceNessuna valutazione finora
- Head Injury .Documento26 pagineHead Injury .Lenjun100% (4)
- NCPDocumento7 pagineNCPChris Denver BancaleNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan: Fluid Volume Deficit R/T Active Fluid Loss (Increased Urine Output)Documento9 pagineNursing Care Plan: Fluid Volume Deficit R/T Active Fluid Loss (Increased Urine Output)Gayu Patel100% (2)
- NCP - Tissue Perfusion (Cerebral)Documento2 pagineNCP - Tissue Perfusion (Cerebral)moodlayers50% (6)
- NCP - Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion R/T Space Occupying Lesion (Neuroblastoma On Frontal Lobe)Documento4 pagineNCP - Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion R/T Space Occupying Lesion (Neuroblastoma On Frontal Lobe)Carl Elexer Cuyugan Ano100% (4)
- Sample NCPDocumento1 paginaSample NCPemrith100% (5)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento10 pagineAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationJobelle AcenaNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP For DM1Documento2 pagineNCP For DM1Pau Hipol MadriagaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocumento1 paginaIneffective Tissue PerfusionRhae RaynogNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento4 pagineNursing Care Planapi-309251523Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento4 pagineNursing Care PlanAdreanah Martin RañisesNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan (Bronchiectasis)Documento4 pagineNursing Care Plan (Bronchiectasis)Leah QuiñanolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento8 pagineNursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearancemishyjayNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento7 pagineNursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway Clearancepeter_degamo20000% (1)
- Athero NCP 3Documento2 pagineAthero NCP 3Quinonez Anna MarieNessuna valutazione finora
- IndependentDocumento2 pagineIndependentQuinonez Anna MarieNessuna valutazione finora
- NCPDocumento27 pagineNCPcuakialyannaNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP For TBDocumento3 pagineNCP For TBNelle Agni100% (1)
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Related To Accumulation of Fluid in The LungsDocumento3 pagineIneffective Breathing Pattern Related To Accumulation of Fluid in The LungsEdem LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology Schizo by ChestermanaloDocumento1 paginaPathophysiology Schizo by ChestermanaloChester ManaloNessuna valutazione finora
- Abruptio Placenta FullDocumento10 pagineAbruptio Placenta FullChester ManaloNessuna valutazione finora
- Management of Angina PectorisDocumento5 pagineManagement of Angina PectorisChester ManaloNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetics of Rheumatic DiseaseDocumento3 pagineGenetics of Rheumatic DiseaseChester ManaloNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of DM ESRD HPNDocumento1 paginaPathophysiology of DM ESRD HPNChester ManaloNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology TBIDocumento1 paginaPathophysiology TBIChester ManaloNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction On ESRDDocumento2 pagineIntroduction On ESRDChester ManaloNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study On ESRD DrugsDocumento5 pagineDrug Study On ESRD DrugsChester ManaloNessuna valutazione finora
- Hypoxic Ischemic EncephalopathyDocumento10 pagineHypoxic Ischemic EncephalopathyPadmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cellular Adaptation: Pathophysiology: The Cell Is The Fundamental Unit of DiseaseDocumento51 pagineCellular Adaptation: Pathophysiology: The Cell Is The Fundamental Unit of DiseaseJerneth Nyka FloresNessuna valutazione finora
- 18 - Trauma in ElderlyDocumento18 pagine18 - Trauma in ElderlyIman KadeNessuna valutazione finora
- 03 Hazards of Oxygen TherapyDocumento21 pagine03 Hazards of Oxygen TherapysandeeppupuNessuna valutazione finora
- Hypothyroidism Concept MapDocumento5 pagineHypothyroidism Concept Mapnursing concept maps0% (1)
- NURSING CARE PLAN (Ineffective Breathing Pattern)Documento4 pagineNURSING CARE PLAN (Ineffective Breathing Pattern)annie kolandjianNessuna valutazione finora
- Hummingbird PDE1Documento3 pagineHummingbird PDE1Galia DeitzNessuna valutazione finora
- The Physiologic Basis of High-Altitude DiseasesDocumento12 pagineThe Physiologic Basis of High-Altitude DiseasesMario LosadaNessuna valutazione finora
- NCPDocumento11 pagineNCPRyan Dela CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- High Altitude Environment Physiology, Adaptations, and IllnessDocumento3 pagineHigh Altitude Environment Physiology, Adaptations, and IllnessJoseph AmeerNessuna valutazione finora
- 1949 Normal Respiratory and Circulatory PathwaysDocumento8 pagine1949 Normal Respiratory and Circulatory PathwaysvitaarfianaNessuna valutazione finora
- 597 MCQs Legal Med Answer Key by DR - Abet Rebosa Updated by DR - Jessica SanchezDocumento86 pagine597 MCQs Legal Med Answer Key by DR - Abet Rebosa Updated by DR - Jessica SanchezTrisNessuna valutazione finora
- Hemorrhagic ShockDocumento5 pagineHemorrhagic ShockGhina RahmadiantiNessuna valutazione finora
- Placenta CirculationDocumento11 paginePlacenta CirculationJason Jimmy Lee PillayNessuna valutazione finora
- Dec - ProbableCause - Burbank-05272021081756Documento21 pagineDec - ProbableCause - Burbank-05272021081756Law of Self DefenseNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell and Tissue Injury: Francisco G. La Rosa, MDDocumento8 pagineCell and Tissue Injury: Francisco G. La Rosa, MDCakradenta Yudha PoeteraNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Cyanotic Congenital Heart DefectsDocumento16 paginePathophysiology of Cyanotic Congenital Heart Defectsbonar46Nessuna valutazione finora
- Our Lady of Lourdes HospitalDocumento19 pagineOur Lady of Lourdes HospitalJerald Oliver MacabayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Paediatric Respiratory Assessment Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocumento1 paginaPaediatric Respiratory Assessment Cheat Sheet: by ViaReihann N. EdresNessuna valutazione finora
- DR Anu Sachdeva Rational Use of Oxygen in NeonatesDocumento11 pagineDR Anu Sachdeva Rational Use of Oxygen in NeonatesBhoomika PandeyNessuna valutazione finora
- (Jean Champagnat Monique Denavit-Saubie Gilles F PDFDocumento330 pagine(Jean Champagnat Monique Denavit-Saubie Gilles F PDFFashionaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Blue Book 2019 2Documento173 pagineBlue Book 2019 2MNessuna valutazione finora
- Respiratory SystemDocumento10 pagineRespiratory SystemFahd Abdullah100% (2)
- Administering Oxygen by Cannula/Face Mask/Face TentDocumento4 pagineAdministering Oxygen by Cannula/Face Mask/Face TentLixa Mae Cawal-oNessuna valutazione finora
- Kangen Miracle Water 2021Documento47 pagineKangen Miracle Water 2021ajaypal100% (1)
- Coma - Types, Causes, Treatments, PrognosisDocumento3 pagineComa - Types, Causes, Treatments, PrognosisgcsNessuna valutazione finora
- Physiology Haq 2nd EdDocumento19 paginePhysiology Haq 2nd Edsathvikamothe0103Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pulmonary Insufficiency:: Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocumento72 paginePulmonary Insufficiency:: Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromeJannen CasasNessuna valutazione finora