Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Density - StudenT Question
Caricato da
mirete86Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Density - StudenT Question
Caricato da
mirete86Copyright:
Formati disponibili
SCIENCE FORM 1 SET 2
STUDENT MANUAL
Learning Area
Learning Objective
:
:
Matter
Understanding the concept of density
Instructions:
1. Carry out activity and record observation with results.
2. Write a task report.
Activity Report Format.
I.
Title
: Density and buoyancy of objects
2. Aim
: To study the density of solids and liquids.
3. Apparatus / Material :...................
4. Procedure
:...................
5. Observation and results:
i)
Are cork, petrol, sand and water are matter?
ii) Based on the substances used, which are examples of :
a) solids
......................
b) liquids
......................
iii) Which substance a) float;
b) sink in water?
iv) What property do these substances have that affect their buoyancies?
v) What will happen to the cork if a nail is added to it?
6. Discussion and analysis answer the questions given.
6.1 i) Why does the substance float on water?
ii) Why does the substance sink in water?
iii) Why does the substance float/ sink in petrol?
iv) Arrange these substances in sequence of ascending order based on their
densities. Refer to table.
6.2
i)
Based on the results of the experiment, what is your inference?
ii) What can be said about the density of a substance that floats in a more dense
liquid?
iii) What can be said about the density of a substance that sinks in a less dense liquid?
Substance
,
Mercury
6.3
i)
Density [gcm-3]
13.6
Ice
0.92
Petrol
0.75
Sand
2.6
Water
1.0
Cork
0.25
Using the results obtained and the table above, predict the position of ice
and mercury if all the substances were put together in a gas jar.
ii) Draw a suitable diagram and label the substances.
6.4
i)
Based on the results and table of densities, classify the substances into two groups
based on the common property.
ii) What other criteria we can use to group them?
7.
Conclusion Do different substances have the same densities?
Activity Report Checklist
No
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Content
Title
Aim
Apparatus
Procedure
Observation & Results
Discussion & Analysis
Conclusion
Yes
1.0
EXPERIMENT 3.6
Understanding the Concept of Density
2.0
Aim
To study the density of solids and liquids.
3.0
Material
water, cork, stone, cooking oil, ice cube
Apparatus
100 ml measuring cylinder beaker
4.0
Procedure
1. I put water, petrol, stone followed by the cork into a measuring cylinder.
2. I drew what I observed about the substances in a diagram.
5.0 Observation:
C1 a, b, c, d
C1 f
C6
C8 a
i)
Cork, sand, water and petrol are matter.
ii)
Based on the substances used, examples of:
iii)
a) solid
cork, sand
b) liquid
petrol, water
C2 b
C2 a
a)
cork / petrol floats on water;
b) sand sinks in water
a)
cork floats on petrol ;
b) water/ sand sinks in petrol
iv)
The density of these substances affects their buoyancies.
v)
The cork sinks when a nail is added to it.
C1 e
C4 b
C1
3m
6.0
C4 a
Discussion and analysis.
6.1
i)
Cork floats on water because it is less dense than water.
ii) Sand sinks in water because it is more dense / denser than water.
iii) Cork float on petrol because it is less dense / Water sinks in petrol
because it is more dense / denser than petrol
iv) Sequence of densities of substances in ascending order:
Cork
6.2
i)
petrol water sand.
The buoyancy of a substance depends on its density.
ii) A less dense solid/substance floats in a more dense liquid.
iii) A denser/ more dense substance sinks in a less dense liquid.
6.3
,
Substance
Density [gcm-3]
Cork
0.25
Petrol
0.75
Ice
0.92
Water
1.0
Sand
2.6
Mercury
13.6
C8 b
C4 b
C4 c
C8 c, d
i)
Using the results and table, predict the position of ice
and mercury if all the substances were put together in a gas jar.
ii)
C4 c
Draw a suitable diagram and label the substances.
C5 a, b, c, d
if mercury is
drawn correctly!
C5 d can be
used to cover a,
b & c.
Merc
ury
6.4
i)
Based on the results and table of densities, the substances are classified into
two groups based on the common property.
Float on water
Do not float on water
Cork
Sand
Petrol
Mercury
Ice
C2 b
ii) Another criteria we can use to group the substances is buoyancy of
substance in petrol.
7.0
Conclusion:
C2 c
Different substances have different densities.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Etienne Szekely - The Living Atom TheoryDocumento137 pagineEtienne Szekely - The Living Atom Theorydigger257Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cosmos and Culture Final - PDF Proof 4 8 2012 PDFDocumento16 pagineCosmos and Culture Final - PDF Proof 4 8 2012 PDFzhao yiNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 2Documento8 pagineLab 2Flonja ShytiNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic and InorganicDocumento2 pagineOrganic and InorganicJudy Panguito Aralar50% (2)
- Cec 108 Prac-Geology - Soil MechnicsDocumento36 pagineCec 108 Prac-Geology - Soil MechnicsVietHungCao89% (9)
- Zodiacal Releasing - John Kerry PDFDocumento12 pagineZodiacal Releasing - John Kerry PDFAfonso FreitasNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Form 1 Set 2 Student ManualDocumento5 pagineScience Form 1 Set 2 Student ManualluvlyleaNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Form 1 Set 2 Student ManualDocumento5 pagineScience Form 1 Set 2 Student ManualNorazrina Abdul Aziz100% (1)
- Peka DensityDocumento2 paginePeka DensityupikasmarNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Form 1 Set 2 Student'S ManualDocumento9 pagineScience Form 1 Set 2 Student'S ManualbensudinNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment: 3.6 Density and Buoyancy of ObjectsDocumento8 pagineExperiment: 3.6 Density and Buoyancy of ObjectsShirlyn HeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Diagnostic Test With TOS - Q1 - Science4-Based-on-MELCSDocumento6 pagineDiagnostic Test With TOS - Q1 - Science4-Based-on-MELCSMytz PalatinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Class Notes: CHAPTER 5 - Separation of SubstancesDocumento2 pagineClass Notes: CHAPTER 5 - Separation of SubstancesUma SaravananNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Lab Activities 2020-2021Documento9 pagineScience Lab Activities 2020-2021Gretchen LaurenteNessuna valutazione finora
- ChemistryDocumento3 pagineChemistrySandeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Soil Assignment ReportDocumento14 pagineSoil Assignment ReportMUHAMMAD AKMAL MD ALINessuna valutazione finora
- Laboratory Activity 2 - Fluid Viscosity Determination - CE31S5 - AMADOR - RUSELLE - JOHNDocumento11 pagineLaboratory Activity 2 - Fluid Viscosity Determination - CE31S5 - AMADOR - RUSELLE - JOHNALDRIN JUSTADONessuna valutazione finora
- ECW231 ASSIGNMENT Questions - 20234Documento3 pagineECW231 ASSIGNMENT Questions - 20234adamNessuna valutazione finora
- Mixtures and Separation Book AnswersDocumento6 pagineMixtures and Separation Book AnswerssimplydharshiniNessuna valutazione finora
- I-Objectives: Science-CG - With-Tagged-Sci-Equipment - Revised - PDF (Deped - Gov.ph)Documento4 pagineI-Objectives: Science-CG - With-Tagged-Sci-Equipment - Revised - PDF (Deped - Gov.ph)Kent Andojar MarianitoNessuna valutazione finora
- Geotech Lab 2 TitusDocumento11 pagineGeotech Lab 2 TitusTitus HaukongoNessuna valutazione finora
- FormatDocumento5 pagineFormatEDAÑO, Justine I.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mendevil (5e's Standard Lesson Plan)Documento5 pagineMendevil (5e's Standard Lesson Plan)maganmendevilmarycrisNessuna valutazione finora
- New Horizon Public SchoolDocumento2 pagineNew Horizon Public SchoolTalented ShivaanshNessuna valutazione finora
- Hollow Blocks Out From Various ShellsDocumento23 pagineHollow Blocks Out From Various ShellsMark Ferdinand ElcanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Table of Specification: I. Multiple Choice EssayDocumento4 pagineTable of Specification: I. Multiple Choice EssayRacquel Supsup100% (1)
- Sba ChemistryDocumento19 pagineSba Chemistrykeshane JohnsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Mummy Annual Term Question PaperDocumento4 pagineMummy Annual Term Question Papersomick DasNessuna valutazione finora
- Separation of A Mixture of SolidsDocumento6 pagineSeparation of A Mixture of Solidsadrie626Nessuna valutazione finora
- Laboratory Experiment 4 Fluid MechanicsDocumento9 pagineLaboratory Experiment 4 Fluid MechanicsBAMBI SAN GABRIELNessuna valutazione finora
- Pce Che 20-07-2023Documento1 paginaPce Che 20-07-2023mehdi.mehdi15121472Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ch-3 Elements, Compounds and Mixtures: Class 7 (Chemistry)Documento6 pagineCh-3 Elements, Compounds and Mixtures: Class 7 (Chemistry)Antony PaulrajNessuna valutazione finora
- SUBJECT: Science Test Yourself Worksheet Class: Ix Subject Code-086Documento6 pagineSUBJECT: Science Test Yourself Worksheet Class: Ix Subject Code-086Vedant SinghalNessuna valutazione finora
- Worksheet Class Ix - ScienceDocumento38 pagineWorksheet Class Ix - Sciencemegha21decNessuna valutazione finora
- Technological Institute of The Philippines: Experiment # 4 Determination of The Density of A FluidDocumento13 pagineTechnological Institute of The Philippines: Experiment # 4 Determination of The Density of A FluidRoselle Gene Celin AgpaloNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson PlanDocumento7 pagineLesson PlanAldrich SuarezNessuna valutazione finora
- Joseph and Mary Academy: Multiple ChoicesDocumento4 pagineJoseph and Mary Academy: Multiple ChoicesAlyssa Mae DapadapNessuna valutazione finora
- Mock Biology P4 (New)Documento14 pagineMock Biology P4 (New)Abdul SamadNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Properties of GasesDocumento4 pagine1 Properties of GasesCris CorsinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem LabDocumento24 pagineChem Laberey4968Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mini Project Ecg263: Muhammad Najmi Najhan Bin Mohd Azhan J4EC1104A2 2020488778 Wan Syarizawani Binti Wan ChikDocumento13 pagineMini Project Ecg263: Muhammad Najmi Najhan Bin Mohd Azhan J4EC1104A2 2020488778 Wan Syarizawani Binti Wan ChikMUHAMMAD AKMAL MD ALINessuna valutazione finora
- SCIENCE 3 First QUARTER ExamDocumento5 pagineSCIENCE 3 First QUARTER ExamJenny CanoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade: Third Grade Unit Title: Matter Course/Subject: Science Approximate Time Required: 1 WeekDocumento6 pagineGrade: Third Grade Unit Title: Matter Course/Subject: Science Approximate Time Required: 1 Weekapi-272854858Nessuna valutazione finora
- Diffusion MMDocumento4 pagineDiffusion MMbsscience.departmentNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Gr2 Final RevDocumento6 pagineScience Gr2 Final Revezzeldin3khaterNessuna valutazione finora
- Integrated Science Assessment 1Documento22 pagineIntegrated Science Assessment 1MARICEL MIRANDANessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1 Q1 Gen Chem I v.2Documento17 pagineModule 1 Q1 Gen Chem I v.2Gweneth BenjaminNessuna valutazione finora
- Methods of Analysis of Sewage Sludge Solid Wastes and CompostDocumento49 pagineMethods of Analysis of Sewage Sludge Solid Wastes and Compostsantu bardhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry LabsDocumento28 pagineChemistry LabsJayson cheekNessuna valutazione finora
- Ceramic Technology - 2 PDFDocumento90 pagineCeramic Technology - 2 PDFFA Ay50% (2)
- CBSE Worksheet-12 Class - VI Science (Sorting Materials Into Groups)Documento3 pagineCBSE Worksheet-12 Class - VI Science (Sorting Materials Into Groups)AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Ap 10 Ps em PW Total PDFDocumento6 pagineAp 10 Ps em PW Total PDFtalluri raj mohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Expt 1 ScreeningDocumento22 pagineExpt 1 ScreeningEzekielNessuna valutazione finora
- Group3 Lab Report1Documento22 pagineGroup3 Lab Report1Jerome MoriNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 StoichiometryDocumento6 pagine10 StoichiometryCas TielNessuna valutazione finora
- Soil Report#3Documento8 pagineSoil Report#3zeinabNessuna valutazione finora
- Separation TechniqueDocumento8 pagineSeparation TechniqueachoeyzNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes Scy5 Unit 8 MatterDocumento9 pagineNotes Scy5 Unit 8 MatterMARIAYEE A/P PERUMAL MoeNessuna valutazione finora
- La GeotekDocumento22 pagineLa GeotekI2OI5OOI8Cintya Agnessa SitorusNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan Guide Final 3Documento3 pagineLesson Plan Guide Final 3api-563430348Nessuna valutazione finora
- ThesisDocumento95 pagineThesisAper ZavaNessuna valutazione finora
- STD 9 CH 1Documento9 pagineSTD 9 CH 1HIRAL SOLANKINessuna valutazione finora
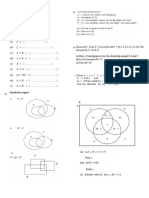
- Coordinate FORM 3Documento1 paginaCoordinate FORM 3mirete86Nessuna valutazione finora
- Form 4 :setsDocumento2 pagineForm 4 :setsmirete86Nessuna valutazione finora
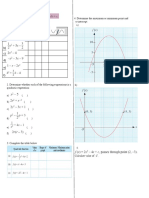
- Form4 Quadratic ExpressionDocumento1 paginaForm4 Quadratic Expressionmirete86Nessuna valutazione finora
- PendulumDocumento1 paginaPendulummirete86Nessuna valutazione finora
- Form 1 Math Mid Year 2010Documento8 pagineForm 1 Math Mid Year 2010mirete86Nessuna valutazione finora
- Math Tahun 5Documento7 pagineMath Tahun 5mirete86Nessuna valutazione finora
- HS Catch: Kertas Soalan Ramalan 2010Documento18 pagineHS Catch: Kertas Soalan Ramalan 2010Quarda DohnyNessuna valutazione finora
- SPM AddMath - Integration ExerciseDocumento9 pagineSPM AddMath - Integration Exercisehasnitajb100% (1)
- Year 9 Maths Answers Level 6Documento21 pagineYear 9 Maths Answers Level 6TheMJCG100% (2)
- 12510637Documento78 pagine12510637Unnamed PoolNessuna valutazione finora
- Static Torque PDFDocumento43 pagineStatic Torque PDFlylyho91Nessuna valutazione finora
- Jauhiainen Thesis PDFDocumento296 pagineJauhiainen Thesis PDFNell-Marcos SilvaNessuna valutazione finora
- Y6/AS Physics Final Exam 11 - 12 Unit 1 - AnswersDocumento21 pagineY6/AS Physics Final Exam 11 - 12 Unit 1 - AnswersPaul Burgess100% (2)
- Carbon 14Documento41 pagineCarbon 14doxorubicin100% (1)
- Grade12 Lesson 1Documento3 pagineGrade12 Lesson 1cris silvanoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Seven Stages of ConsciousnessDocumento10 pagineThe Seven Stages of ConsciousnessSon of Rizq100% (1)
- BBC FocusDocumento116 pagineBBC FocusNorbert Mifsud100% (1)
- Soho 1 PDFDocumento9 pagineSoho 1 PDFhcdmelloNessuna valutazione finora
- (9789047430568 - The World As Active Power) The World As Active Power PDFDocumento356 pagine(9789047430568 - The World As Active Power) The World As Active Power PDFbenhjorthNessuna valutazione finora
- Philosophy of The ScriptureDocumento27 paginePhilosophy of The ScripturesnigdhaprasadNessuna valutazione finora
- Aryabhata The ElderDocumento5 pagineAryabhata The Elderapi-240974857Nessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Assignment 4th SemesterDocumento11 paginePhysics Assignment 4th SemesterMuzaffar SalikNessuna valutazione finora
- Peters Greek Philosophical Terms A Historical Lexicon New York University Press 1967pdf PDF FreeDocumento124 paginePeters Greek Philosophical Terms A Historical Lexicon New York University Press 1967pdf PDF FreeLIZA NEREYDA PIÑA RUBIONessuna valutazione finora
- Leo - Sign of Creative Self-ExpressionDocumento7 pagineLeo - Sign of Creative Self-ExpressionReiki Master0% (1)
- Summary of English Grammar For 3rd YearsDocumento4 pagineSummary of English Grammar For 3rd YearsMouni MounNessuna valutazione finora
- An Introduction To Semilinear Evolution Equations Thierry Cazenave Alain Haraux Yvan Martel PDFDocumento198 pagineAn Introduction To Semilinear Evolution Equations Thierry Cazenave Alain Haraux Yvan Martel PDFCristobal Valenzuela MusuraNessuna valutazione finora
- Prashna Jyotish (PDFDrive) - p0005Documento1 paginaPrashna Jyotish (PDFDrive) - p0005pragnesh thakkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Who or What Is The Arcturian ProtectorateDocumento1 paginaWho or What Is The Arcturian ProtectorateG.n.o.d.e.100% (1)
- ESP & Mental Telepathy Research Documents Before I Learned My In-Depth Knowledge of U.S. Sponsored Mind Control September 10, 2007Documento141 pagineESP & Mental Telepathy Research Documents Before I Learned My In-Depth Knowledge of U.S. Sponsored Mind Control September 10, 2007Stan J. CaterboneNessuna valutazione finora
- Conversational ImplicatureDocumento27 pagineConversational ImplicatureSiti Dwi RukmannurNessuna valutazione finora
- The Big Bang TheoryDocumento13 pagineThe Big Bang TheoryHilary YvonneNessuna valutazione finora
- Mage The Awakening - Imperial MysteriesDocumento84 pagineMage The Awakening - Imperial MysteriesMadon_Stormeyes100% (4)
- Geographic l1Documento86 pagineGeographic l1Raaja ShekharNessuna valutazione finora
- Solusi Soal Ganjil Pada Buku Arthur Beiser Edisi Ke 8Documento194 pagineSolusi Soal Ganjil Pada Buku Arthur Beiser Edisi Ke 8AshabulMukhtarNessuna valutazione finora
- H. Bateman - The Structure of The AetherDocumento11 pagineH. Bateman - The Structure of The AetherOppekeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Cavagna On Energy Efficiency of Walking and RunningDocumento19 pagineCavagna On Energy Efficiency of Walking and RunningLaboratory in the WildNessuna valutazione finora