Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
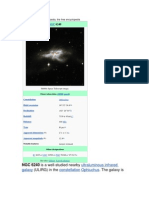
Messier 88
Caricato da
Matheus RochaCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Messier 88
Caricato da
Matheus RochaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Messier 88
Messier 88 (also known as M88 or NGC 4501) is a spiral
galaxy about 50 to 60 million light-years away[2][3][4] in
the constellation Coma Berenices. It was discovered by
Charles Messier in 1781.
Properties
M88 by Hubble space telescope
Messier 88, 24 inch telescope on Mt. Lemmon, AZ.
diameter, which has two concentration peaks. This condensation is being fed by inow from the spiral arms.[11]
M88 is one of the fteen Messier objects that belong to The supermassive black hole at the core of this galaxy has
the nearby Virgo Cluster of galaxies. It is galaxy num- 107.9 solar masses, or about 80 million times the mass of
ber 1401 in the Virgo Cluster Catalogue (VCC) of 2096 the Sun.[12]
galaxies that are candidate members of the cluster.[5]
M88 may be on a highly elliptical orbit that is carrying In 1999, supernova 1999cl was discovered in this
[13]
it toward the cluster center, which is occupied by the gi- galaxy.
ant elliptical galaxy M87. It is currently 0.30.48 million parsecs from the center and will come closest to the
core in about 200300 million years. The motion of M88 2 See also
through the intergalactic medium of the Virgo cluster is
creating ram pressure that is stripping away the outer re Messier 98
gion of neutral hydrogen. This stripping has already been
detected along the western, leading edge of the galaxy.[6]
3 References
This galaxy is inclined to the line of sight by 64.[7] It is
classied as an Sbc spiral, which lies between the Sb and
Sc categories of medium-wound and loosely wound spiral
arms, respectively. The arm structure of the spirals is very
regular and can be followed down to the galactic core.[8]
The maximum rotation velocity of the gas is 241.6 4.5
km/s.[9]
[1] Results for NGC 4501. NASA/IPAC Extragalactic
Database. California Institute of Technology. Retrieved
2006-11-14.
[2] Object Information. 20 September 2009. Retrieved 26
December 2012.
M88 is also classied as a type 2 seyfert galaxy, which
means it produces narrow spectral line emission from
highly ionized gas in the galactic nuclei.[10] In the core
region there is a central condensation with a 230 parsec
[3] Explanation. 30 January 2010. Retrieved 26 December
2012.
[4] M88. 29 June 2011. Retrieved 26 December 2012.
[5] Binggeli, B.; Sandage, A.; Tammann, G. A. (1985).
Studies of the Virgo Cluster. II A catalog of
2096 galaxies in the Virgo Cluster area. Astronomical
Journal 90: 16811759. Bibcode:1985AJ.....90.1681B.
doi:10.1086/113874.
[6] Vollmer, B.; et al. (2008). Pre-peak ram pressure stripping in the Virgo cluster spiral galaxy NGC
4501. Astronomy and Astrophysics 483 (1): 89
106. arXiv:0801.4874. Bibcode:2008A&A...483...89V.
doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078139.
[7] Tully, R. B.; Fisher, J. R. (1977).
method of determining distances to
Astronomy and Astrophysics 54 (3):
Bibcode:1977A&A....54..661T.
A new
galaxies.
661673.
[8] Mllenho, C.; Heidt, J. (2001). Surface photometry
of spiral galaxies in NIR: Structural parameters of disks
and bulges. Astronomy and Astrophysics 368 (1): 16
37. Bibcode:2001A&A...368...16M. doi:10.1051/00046361:20000335.
[9] Database for physics of galaxies.
HyperLeda.
Universit de Lyon. Retrieved 2009-09-16.
[10] L. S. Sparke; J. S. Gallagher III (2007). Galaxies in the
Universe: An Introduction. Cambridge University Press.
ISBN 978-0-521-67186-6.
[11] Onodera, S.; Sofue, Y.; Koda, J.; Nakanishi, H.; Kohno,
K. (2002). CO (J=1-0) Observations of the Non-Barred
Seyfert 2 Galaxy NGC 4501. In Ikeuchi, S.; Hearnshaw,
J.; Hanawa, T. Proceedings of the IAU 8th Asian-Pacic
Regional Meeting. Bibcode:2002aprm.conf..199O.
[12] Merloni, Andrea; Heinz, Sebastian; di Matteo, Tiziana
(2003). A Fundamental Plane of black hole activity. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 345 (4): 10571076. arXiv:astro-ph/0305261.
Bibcode:2003MNRAS.345.1057M. doi:10.1046/j.13652966.2003.07017.x.
[13] James, N. D. (1999). Supernova 1999cl in NGC 4501
(M88)". Journal of the British Astronomical Association
109 (4): 178. Bibcode:1999JBAA..109..178J.
External links
Spiral Galaxy M88 @ SEDS Messier pages
Messier 88 on WikiSky: DSS2, SDSS, GALEX,
IRAS, Hydrogen , X-Ray, Astrophoto, Sky Map,
Articles and images
Coordinates:
12h 31m 59.2s , +14 25 14
EXTERNAL LINKS
Text and image sources, contributors, and licenses
5.1
Text
Messier 88 Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Messier_88?oldid=722813522 Contributors: Bryan Derksen, SimonP, Ahoerstemeier,
Danceswithzerglings, Jyril, JamesHoadley, Joseph Dwayne, Aranel, RJHall, Ardric47, WilliamKF, Palica, Rjwilmsi, Sumanch, RobyWayne, Chobot, YurikBot, Ve3, Tony1, Uber nemo, American2, Hurricane Devon, SmackBot, Eskimbot, Chris the speller, Bluebot,
OrphanBot, Van helsing, ShelfSkewed, Friendlystar, Cydebot, Clh288, SeventyThreeBot, Kozuch, Thijs!bot, Headbomb, SGGH, Z10x,
Escarbot, Nine9s, Dr. Submillimeter, JEH, Altamel, JAnDbot, .anacondabot, Glen, Kheider, CommonsDelinker, McSly, STBotD, Idiomabot, VolkovBot, TXiKiBoT, A4bot, Rei-bot, SieBot, KGyST, Finetooth, ImageRemovalBot, Jschulman555, Hewholooks, Arianewiki1,
Addbot, DOI bot, Sebagr, Luckas-bot, Yobot, Ptbotgourou, Amirobot, Guy1890, Citation bot, Fabian RRRR, Anna Frodesiak, GrouchoBot, Mnmngb, Fotaun, Telescopi, D'ohBot, Citation bot 1, Tom.Reding, MastiBot, Jauhienij, DixonDBot, Dinamik-bot, Miracle Pen,
RjwilmsiBot, EmausBot, IndvTbot, AvicBot, ZroBot, StringTheory11, GermanJoe, ClueBot NG, Ngc1535, Helpful Pixie Bot, Bibcode
Bot, BG19bot, Vagobot, JYBot, Exoplanetaryscience, Spideratseds and Anonymous: 13
5.2
Images
File:Celestia.png Source: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/8/83/Celestia.png License: GPL Contributors: ? Original
artist: ?
File:Charles_Messier.jpg Source: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/a/a4/Charles_Messier.jpg License: Public domain
Contributors: Stoyan R. et al. Atlas of the Messier Objects: Highlights of the Deep Sky. Cambridge: Cambridge Univercity Press, 2008.
P. 15. Original artist: Ansiaume (17291786)
File:Commons-logo.svg Source: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/4/4a/Commons-logo.svg License: CC-BY-SA-3.0 Contributors: ? Original artist: ?
File:Folder_Hexagonal_Icon.svg Source: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/4/48/Folder_Hexagonal_Icon.svg License: Cc-bysa-3.0 Contributors: ? Original artist: ?
File:M88HunterWilson.jpg Source: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/3/34/M88HunterWilson.jpg License: CC BYSA 3.0 Contributors: Own work Original artist: Hewholooks
File:M88s.jpg Source: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/7/7c/M88s.jpg License: CC BY-SA 3.0 us Contributors: http:
//www.caelumobservatory.com/gallery/m88.shtml Original artist: Credit Line and Copyright Adam Block/Mount Lemmon SkyCenter/University of Arizona
File:NGC_4501.png Source: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/8/80/NGC_4501.png License: CC BY-SA 3.0 Contributors: datale from http://hla.stsci.edu/hlaview.html Original artist: Own work
File:Portal-puzzle.svg Source: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/f/fd/Portal-puzzle.svg License: Public domain Contributors: ?
Original artist: ?
File:Symbol_book_class2.svg Source: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/8/89/Symbol_book_class2.svg License: CC
BY-SA 2.5 Contributors: Mad by Lokal_Prol by combining: Original artist: Lokal_Prol
5.3
Content license
Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Space TravelerDocumento73 pagineSpace TravelerBobapatatasNessuna valutazione finora
- Abushattal - 2019 - J. - Phys. - Conf. - Ser. - 1258 - 012018Documento8 pagineAbushattal - 2019 - J. - Phys. - Conf. - Ser. - 1258 - 012018AliNessuna valutazione finora
- JWST Primer v20Documento32 pagineJWST Primer v20ganeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Manuel Linares, Scott Ransom, Alessandro Papitto, Slavko Bogdanov, Enrico Bozzo, Nanda Rea, Domingo Garc Ia-Senz, Paulo Freire, and Ingrid StairsDocumento26 pagineManuel Linares, Scott Ransom, Alessandro Papitto, Slavko Bogdanov, Enrico Bozzo, Nanda Rea, Domingo Garc Ia-Senz, Paulo Freire, and Ingrid Stairsm tNessuna valutazione finora
- Two Directly Imaged, Wide-Orbit Giant Planets Around The Young, Solar Analog TYC 8998-760-1Documento10 pagineTwo Directly Imaged, Wide-Orbit Giant Planets Around The Young, Solar Analog TYC 8998-760-1TobakilNessuna valutazione finora
- Short Introduction To The Physics of Neutron StarsDocumento8 pagineShort Introduction To The Physics of Neutron StarsKEERTHANA RAJAN LNessuna valutazione finora
- 2303 12102Documento4 pagine2303 12102Hrvoje KNessuna valutazione finora
- AsteroidsDocumento14 pagineAsteroidscvelmanNessuna valutazione finora
- 2017 Bensby - Chemical Evolution of The Galactic BulgeDocumento34 pagine2017 Bensby - Chemical Evolution of The Galactic BulgeInflatableOkapiNessuna valutazione finora
- Planet Hunters X. KIC 8462852 - Where's The Flux?Documento15 paginePlanet Hunters X. KIC 8462852 - Where's The Flux?MohaMuñozNessuna valutazione finora
- Space Physics: 6.1 Earth and The Solar System The EarthDocumento4 pagineSpace Physics: 6.1 Earth and The Solar System The EarthRaahilNessuna valutazione finora
- Nssc22' Cs Round 2 PsDocumento8 pagineNssc22' Cs Round 2 PsJeya SionaNessuna valutazione finora
- Thesis Master PhysicsDocumento18 pagineThesis Master Physicsyehia.j21Nessuna valutazione finora
- Science EssayDocumento12 pagineScience Essayapi-295808543Nessuna valutazione finora
- Py 101 Stars and Galaxies Practice Test 2 (CHAPTERS 19-20)Documento4 paginePy 101 Stars and Galaxies Practice Test 2 (CHAPTERS 19-20)Alli ANessuna valutazione finora
- Earth ScienceDocumento10 pagineEarth ScienceRhea Mae PatatagNessuna valutazione finora
- BoruckiDocumento28 pagineBoruckilagensahoo2003Nessuna valutazione finora
- Planets in The Galactic Bulge: Results From The SWEEPS ProjectDocumento8 paginePlanets in The Galactic Bulge: Results From The SWEEPS ProjectViktor RadovićNessuna valutazione finora
- Solar System RQDocumento2 pagineSolar System RQAyaan MajidNessuna valutazione finora
- Chen 2016 ApJL 827 L24Documento5 pagineChen 2016 ApJL 827 L24Saba ChkuaseliNessuna valutazione finora
- Py 101 Stars and Galaxies Practice Test 1 (CHAPTERS 19-20)Documento4 paginePy 101 Stars and Galaxies Practice Test 1 (CHAPTERS 19-20)Alli ANessuna valutazione finora
- Abstract. The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) Is A Large (6.6 M), Cold (Documento122 pagineAbstract. The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) Is A Large (6.6 M), Cold (pumpkinpewterNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT - 5 & UNIT - 6 NotesDocumento7 pagineUNIT - 5 & UNIT - 6 Notessharkfin1403Nessuna valutazione finora
- Zechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 1Documento1 paginaZechmeister Et Al. 2013 Page 1Pierre-Cécil KönigNessuna valutazione finora
- G. Nelemans Et Al - The Astrophysics of Ultra-Compact BinariesDocumento8 pagineG. Nelemans Et Al - The Astrophysics of Ultra-Compact BinariesMremefNessuna valutazione finora
- Intergalactic Filaments Spin: Qianli Xia, Mark C. Neyrinck, Yan-Chuan Cai, Miguel A. Arag On-CalvoDocumento21 pagineIntergalactic Filaments Spin: Qianli Xia, Mark C. Neyrinck, Yan-Chuan Cai, Miguel A. Arag On-CalvoMilan StepanovNessuna valutazione finora
- Wright 2010Documento14 pagineWright 2010OstpohlNessuna valutazione finora
- Contour Comet Nucleus Tour Launch Press KitDocumento27 pagineContour Comet Nucleus Tour Launch Press KitBob AndrepontNessuna valutazione finora
- Galaxy Zoo Green Peas: Discovery of A Class of Compact Extremely Star-Forming GalaxiesDocumento15 pagineGalaxy Zoo Green Peas: Discovery of A Class of Compact Extremely Star-Forming GalaxiesVicky UngariuddanieNessuna valutazione finora
- As Troj Kippin Get AlDocumento16 pagineAs Troj Kippin Get AlAnonymous b2k9ABe7eNessuna valutazione finora
- LITTLETHINGS DatapaperDocumento29 pagineLITTLETHINGS DatapaperSarthak DasadiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Artikel MekanikaDocumento22 pagineArtikel MekanikaWidii Nugrahaa AadyNessuna valutazione finora
- NGC 6240 Is A Well-Studied Nearby: Ultraluminous Infrared Galaxy Constellation OphiuchusDocumento26 pagineNGC 6240 Is A Well-Studied Nearby: Ultraluminous Infrared Galaxy Constellation OphiuchusAtticus ChristensenNessuna valutazione finora
- 2022 GCU Astronomy NightDocumento12 pagine2022 GCU Astronomy NightJean EtnyreNessuna valutazione finora
- Orosz 2019 AJ 157 174Documento46 pagineOrosz 2019 AJ 157 174Vitor BeloNessuna valutazione finora
- France - 2023 - AJ - 165 - 63 - The Colorado Ultraviolet Transit Experiment Mission OverviewDocumento9 pagineFrance - 2023 - AJ - 165 - 63 - The Colorado Ultraviolet Transit Experiment Mission OverviewyiduannNessuna valutazione finora
- General Exam Part III: 180 Astrophysics Questions: α CrucisDocumento14 pagineGeneral Exam Part III: 180 Astrophysics Questions: α CrucisİlaydaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2017 Santos - Characterisation of Exoplanet Host Stars - A Window Into Planet FormationDocumento10 pagine2017 Santos - Characterisation of Exoplanet Host Stars - A Window Into Planet FormationInflatableOkapiNessuna valutazione finora
- The Pristine Inner Galaxy Survey (PIGS) VIII: Characterising The Orbital Properties of The Ancient, Very Metal-Poor Inner Milky WayDocumento24 pagineThe Pristine Inner Galaxy Survey (PIGS) VIII: Characterising The Orbital Properties of The Ancient, Very Metal-Poor Inner Milky WayjtNessuna valutazione finora
- UY Scuti - WikipediaDocumento35 pagineUY Scuti - WikipediaGoten HarrysonNessuna valutazione finora
- Stellaspecta Aug '11Documento4 pagineStellaspecta Aug '11Dayasagar VSNessuna valutazione finora
- Venturini Et Al. 2020Documento23 pagineVenturini Et Al. 2020OBXONessuna valutazione finora
- J. Stenger Et Al - Spin Domains in Ground-State Bose-Einstein CondensatesDocumento4 pagineJ. Stenger Et Al - Spin Domains in Ground-State Bose-Einstein CondensatesPomac232Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Compositional Structure of The Asteroid Belt: Massachusetts Institute of TechnologyDocumento49 pagineThe Compositional Structure of The Asteroid Belt: Massachusetts Institute of TechnologyPNessuna valutazione finora
- 2008SerAJ 176 1IDocumento13 pagine2008SerAJ 176 1IViktor RadovićNessuna valutazione finora
- The Maggie Filament Physical Properties of A GiantDocumento19 pagineThe Maggie Filament Physical Properties of A Giantthedigital blendNessuna valutazione finora
- Soler Mpia Hifilaments PreprintDocumento29 pagineSoler Mpia Hifilaments PreprintJuan Carlos MolinaNessuna valutazione finora
- The TRAPPIST Survey of Southern Transiting Planets: Astronomy AstrophysicsDocumento15 pagineThe TRAPPIST Survey of Southern Transiting Planets: Astronomy AstrophysicsbbteenagerNessuna valutazione finora
- Fedele 2008Documento17 pagineFedele 2008Anonymous 0HOs3CANessuna valutazione finora
- Milky WayDocumento41 pagineMilky Way呂布Nessuna valutazione finora
- Worksheet-Space PhysicsDocumento8 pagineWorksheet-Space PhysicsMohammad Wajeeh MohsinNessuna valutazione finora
- Wise Detections of Dust in The Habitable Zones of Planet-Bearing StarsDocumento6 pagineWise Detections of Dust in The Habitable Zones of Planet-Bearing Starsanhntran4850Nessuna valutazione finora
- Horizons Exploring The Universe Enhanced 13Th Edition Seeds Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocumento30 pagineHorizons Exploring The Universe Enhanced 13Th Edition Seeds Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFconatusimploded.bi6q100% (10)
- Escape of Asteroids From The Main Belt: Astronomy AstrophysicsDocumento13 pagineEscape of Asteroids From The Main Belt: Astronomy AstrophysicsViktor RadovićNessuna valutazione finora
- The Large-Scale Structure of The UniverseDocumento22 pagineThe Large-Scale Structure of The Universefernando romeroNessuna valutazione finora
- RocketSTEM Issue 9 2014Documento84 pagineRocketSTEM Issue 9 20143582Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cosmic EtherDocumento24 pagineCosmic Ethertherm000Nessuna valutazione finora
- Modem Astronomy - Startling FactsDocumento184 pagineModem Astronomy - Startling FactsRiaz Ur Rehman Khalid100% (6)
- NikonosDocumento8 pagineNikonosMatheus RochaNessuna valutazione finora
- Wikipedia:Random: See AlsoDocumento3 pagineWikipedia:Random: See AlsoMatheus RochaNessuna valutazione finora
- Alastair Donaldson: ReferencesDocumento1 paginaAlastair Donaldson: ReferencesMatheus RochaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bruno CarrièreDocumento1 paginaBruno CarrièreMatheus RochaNessuna valutazione finora
- Multiple-Criteria Decision AnalysisDocumento12 pagineMultiple-Criteria Decision AnalysisMatheus RochaNessuna valutazione finora
- Click-Fit A4!23!07 LRDocumento12 pagineClick-Fit A4!23!07 LRMatheus RochaNessuna valutazione finora
- Association Des Galeries D'art Contemporain (AGAC)Documento4 pagineAssociation Des Galeries D'art Contemporain (AGAC)Matheus RochaNessuna valutazione finora
- Henry Ashurst (Merchant)Documento2 pagineHenry Ashurst (Merchant)Matheus RochaNessuna valutazione finora
- Is Entropy Associated With Time's ArrowDocumento30 pagineIs Entropy Associated With Time's ArrowMatheus RochaNessuna valutazione finora
- LorymanaDocumento1 paginaLorymanaMatheus RochaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chamber of Commerce Building (Baltimore, Maryland)Documento2 pagineChamber of Commerce Building (Baltimore, Maryland)Matheus RochaNessuna valutazione finora
- Command & Conquer - Tiberian SeriesDocumento9 pagineCommand & Conquer - Tiberian SeriesMatheus RochaNessuna valutazione finora
- Max AlvaradoDocumento3 pagineMax AlvaradoMatheus RochaNessuna valutazione finora
- Reflexogenous ZoneDocumento1 paginaReflexogenous ZoneMatheus RochaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bob Haworth: 1 ReferencesDocumento2 pagineBob Haworth: 1 ReferencesMatheus RochaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pesto (Album)Documento2 paginePesto (Album)Matheus RochaNessuna valutazione finora
- Inermaegocidnus ElongatusDocumento1 paginaInermaegocidnus ElongatusMatheus RochaNessuna valutazione finora
- Britten-Pears School For Advanced Musical StudiesDocumento2 pagineBritten-Pears School For Advanced Musical StudiesMatheus RochaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bent Ho CometesDocumento2 pagineBent Ho CometesMatheus RochaNessuna valutazione finora
- RAB11FIP1Documento4 pagineRAB11FIP1Matheus RochaNessuna valutazione finora
- Saskatchewan Highway 16B: 1 Intersections From East To WestDocumento2 pagineSaskatchewan Highway 16B: 1 Intersections From East To WestMatheus RochaNessuna valutazione finora
- Andrijana JanevskaDocumento4 pagineAndrijana JanevskaMatheus RochaNessuna valutazione finora
- Perrine's Bridge: 1 ReferencesDocumento2 paginePerrine's Bridge: 1 ReferencesMatheus RochaNessuna valutazione finora
- After The Storm (1915 Film)Documento2 pagineAfter The Storm (1915 Film)Matheus RochaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pink Floyd PigsDocumento4 paginePink Floyd PigsMatheus RochaNessuna valutazione finora
- Méjico Máxico: 1 Track ListingDocumento2 pagineMéjico Máxico: 1 Track ListingMatheus RochaNessuna valutazione finora
- Richard Upjohn LightDocumento2 pagineRichard Upjohn LightMatheus RochaNessuna valutazione finora
- George Oliver (Historian)Documento3 pagineGeorge Oliver (Historian)Matheus RochaNessuna valutazione finora
- World Record (Lower Than Atlantis Album)Documento5 pagineWorld Record (Lower Than Atlantis Album)Matheus RochaNessuna valutazione finora
- Untes Chiller HEDocumento5 pagineUntes Chiller HEAnarNessuna valutazione finora
- 2017 Lecture 3 Metal Carbonyls PDFDocumento28 pagine2017 Lecture 3 Metal Carbonyls PDFMahnoor FatimaNessuna valutazione finora
- 118 - Package Boiler BrochureDocumento8 pagine118 - Package Boiler BrochureBayu Pramana PutraNessuna valutazione finora
- 19eec42 - Generation Transmission and DistributionDocumento3 pagine19eec42 - Generation Transmission and DistributionKarunakaran M,47Nessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Marine MachineriesDocumento13 pagineIntroduction To Marine MachineriessrcattozziNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.2 Substation Components, Functions & RatingsDocumento57 pagine1.2 Substation Components, Functions & Ratings021804Nessuna valutazione finora
- of Gatorade..Documento29 pagineof Gatorade..Jay ThakkarNessuna valutazione finora
- IEC 61869 Replacing IEC 60044Documento2 pagineIEC 61869 Replacing IEC 60044josevil79Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ehad Hussainabad HvacDocumento4 pagineEhad Hussainabad Hvacashar jafferyNessuna valutazione finora
- Touareg Supplementary HeatingDocumento32 pagineTouareg Supplementary HeatingAnonymous t1FCvPRSaNessuna valutazione finora
- TP30Documento9 pagineTP30abelmonte_geotecniaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bearcat Bc80xlt ManualDocumento32 pagineBearcat Bc80xlt Manualjwyatt4155Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Effect of Financial Development On Renewable Energy Consumption. A Panel Data ApproachDocumento9 pagineThe Effect of Financial Development On Renewable Energy Consumption. A Panel Data ApproachArnawan Hasibuan, ST., MT Arnawan Hasibuan, ST., MTNessuna valutazione finora
- Urban - Visions - SUP2ER Project 8 - PlannerDocumento14 pagineUrban - Visions - SUP2ER Project 8 - Plannersamanisbest553Nessuna valutazione finora
- Kush Nir 2019Documento6 pagineKush Nir 2019Gustavo FloresNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit - Ii Switching TransientsDocumento42 pagineUnit - Ii Switching Transientsshree100% (5)
- TC FLS Sihi Leh 1200 1500 1800 enDocumento10 pagineTC FLS Sihi Leh 1200 1500 1800 enGustavo ZavalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cost of Capital Project PDFDocumento50 pagineCost of Capital Project PDFPreet PreetNessuna valutazione finora
- LPG Co-MinglingDocumento17 pagineLPG Co-MinglingderhgawenrahulNessuna valutazione finora
- Catalog Series 212 Composite Asco Global en 3674082Documento5 pagineCatalog Series 212 Composite Asco Global en 3674082LuisNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 1. Introduction To Farm Power and EnergyDocumento30 pagineLecture 1. Introduction To Farm Power and EnergyMaureen Joy Cascayan EspirituNessuna valutazione finora
- NBC Gear Info.Documento8 pagineNBC Gear Info.GLOCK35Nessuna valutazione finora
- RippleTankSE Key PDFDocumento10 pagineRippleTankSE Key PDFYesi Setyo Ningrum100% (1)
- Full Product Line Catalogue 2018 2270Documento232 pagineFull Product Line Catalogue 2018 2270kingreadyNessuna valutazione finora
- Alkylation PDFDocumento7 pagineAlkylation PDFVasthadu Vasu Khanan DLNessuna valutazione finora
- Science F3 C8-PPT-Part I Dynamo and GeneratorDocumento36 pagineScience F3 C8-PPT-Part I Dynamo and GeneratorRebecca Choong Xin Hui100% (2)
- TwingoDocumento26 pagineTwingoDumitru-Lucian PurcaruNessuna valutazione finora
- Raman Spectral NotesDocumento4 pagineRaman Spectral NotesswethasNessuna valutazione finora
- Guia SupacDocumento44 pagineGuia SupacMario Vazquez BNessuna valutazione finora
- SDT Series User Manual (With Tigo)Documento15 pagineSDT Series User Manual (With Tigo)Manimaran MaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingDa EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (5)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldDa EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (64)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseDa EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (69)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesDa EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (2193)
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceDa EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (51)
- The Creator and the Cosmos: How the Latest Scientific Discoveries Reveal GodDa EverandThe Creator and the Cosmos: How the Latest Scientific Discoveries Reveal GodValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (4)
- Under Alien Skies: A Sightseer's Guide to the UniverseDa EverandUnder Alien Skies: A Sightseer's Guide to the UniverseValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (17)
- When the Earth Had Two Moons: Cannibal Planets, Icy Giants, Dirty Comets, Dreadful Orbits, and the Origins of the Night SkyDa EverandWhen the Earth Had Two Moons: Cannibal Planets, Icy Giants, Dirty Comets, Dreadful Orbits, and the Origins of the Night SkyValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (7)
- Giza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyDa EverandGiza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyNessuna valutazione finora
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldDa EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (60)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessDa EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (6)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidDa EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1395)
- Too Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldDa EverandToo Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (8)
- The Beauty of Falling: A Life in Pursuit of GravityDa EverandThe Beauty of Falling: A Life in Pursuit of GravityNessuna valutazione finora
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterDa EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (410)
- The Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectDa EverandThe Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (20)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldDa EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (54)
- Excel Essentials: A Step-by-Step Guide with Pictures for Absolute Beginners to Master the Basics and Start Using Excel with ConfidenceDa EverandExcel Essentials: A Step-by-Step Guide with Pictures for Absolute Beginners to Master the Basics and Start Using Excel with ConfidenceNessuna valutazione finora
- Believing Is Seeing: A Physicist Explains How Science Shattered His Atheism and Revealed the Necessity of FaithDa EverandBelieving Is Seeing: A Physicist Explains How Science Shattered His Atheism and Revealed the Necessity of FaithValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (32)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeDa EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeNessuna valutazione finora
- When the Heavens Went on Sale: The Misfits and Geniuses Racing to Put Space Within ReachDa EverandWhen the Heavens Went on Sale: The Misfits and Geniuses Racing to Put Space Within ReachValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (27)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1108)
- Cosmos and Psyche: Intimations of a New World ViewDa EverandCosmos and Psyche: Intimations of a New World ViewValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (7)