Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Potentiometer
Caricato da
Dileep Kumar LadiDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Potentiometer
Caricato da
Dileep Kumar LadiCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Potentiometers
Potentiometer is used for the measurement of emfs by comparison with a standard emf.
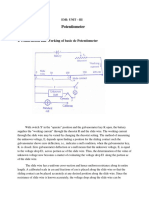
Potentiometers with Direct current:
As shown in the fig. AB is a slide wire of uniform
cross section R is a regulating resistance to limit the
current (i) through the slide wire.
B1 is a battery whose emf is to be measured
G is the DC1 galvanometer
B is the battery which supplies current to the slide
wire
Let is the (resistance / unit length) of slide wire i is the current through the slide wire when
key K is open, when the key k is closed a current will flow through the galvanometer if the volt
drop across AC slide wire is not equal to B1. The sliding contact C is adjusted till no current
flows through the galvanometer that implies the volt drop across AC is equal to B1. Let length of
AC is l 1 then volt drop is il1 it is equal to B1.
Simillarly B1 is replaced by another emf B2 and the contact point C is varied till null deflection of
galvanometer. Let the lenth is L2 then B2 = i l2
E1
emf of battery B1
E2
emf of battery B1
E1
= ir l1
E2 = i
l2
E1 l1
E2 l2
If E1 is a known emf then E2 can be calculated by measuring the length l1 & l2.
E 2 E1
l2
l1
The crompton potentiometer
Construction:
1. It consists of a graduated slide wire Ac
which is connected in series with 14
coils, each of which has a resistance
exactly equal to that of slide wire.
2. There are two moving contacts P1 & P2.
Sliding over the slide wire & studes of the
resistance coils.
3. B is the supply battery of 2v.
4. R1 & R2 are two variable resistars. R1 is for
coarse adjustment and R2 is for fine
adjustment.
5. Galvanometer G is connected in series with
a key and multi current switch by which
either the standard call on the unknown emf
is connected.
Operation:
The process of adjusting the working current so as to match the voltage drop across a portion as
standardization of sliding wire against a standard ref source is known. The potentiometer is first
standardized by connecting a standard call (Weston cell is used which volt = 1.0186). The P2
contact is placed at 1.0v and P1 at 0.0186 on the slide wire then the resistances R1 & R2 is
adjusted till null deflection of the galvanometer. Then the selection switch is switched to 1, 1 to
which an unknown emf is connected. Now P1 & P2 is adjusted till galvanometer shows null
deflection. The reading of the potentiometer will give the value of emf to be measured.
A.C Potentiometer
The principle of working of a AC potentiometer is same that of DC, only the difference is, in
d.c. only the magnitude of unknown emf and slide wire voltdrop made equal to obtained balance
but in AC the phase and magnitude of unknown volt and slide wire volt drop must be equal to
obtained balance.
There are two general type of AC potentials.
a. AC polar potentiometer - It measures the unknown voltage in polar form.
b. AC co-ordinate potentiometer It measures the rectangular co-ordinate of the voltage under
test.
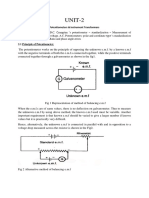
Drysdale Tinsley Polar Potentiometer
Construction: It consists of an ordinary DC potentiometer except that the resistance coils are
non-inductively wound and the source voltage is phase shifting transformer instead of a Battery.
The phase shifting transformers (drysdale phase shifting) consists of a two phase station & a
single
rotor. The
position
of thetorotor can be changed by hand. A scale is provided on top
Whenphase
two phases
supply
is applied
tothese
read two
the angle
of
rotation
of
rotor
from its zero position.
phase stator wdh a Rotating
field of constant magnitude is produced
and hance an emf is induced in the rotor
wdg. The phase of it can be changed
relative to the stator
2
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Potentiometer: 1. Construction and Working of Basic DC PotentiometerDocumento11 paginePotentiometer: 1. Construction and Working of Basic DC PotentiometerKumar SanNessuna valutazione finora
- Cha:4 Potentiometers: Principal of D.C. Potentiometer Crompton's Potentiometer Application of DC PotentiometerDocumento16 pagineCha:4 Potentiometers: Principal of D.C. Potentiometer Crompton's Potentiometer Application of DC PotentiometerNirav ChauhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical and Electronics Measurement 4th Sem B.Tech.Documento41 pagineElectrical and Electronics Measurement 4th Sem B.Tech.Saksham KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Lect 4Documento37 pagineLect 4eba yohannesNessuna valutazione finora
- A.C Potentiometer1Documento22 pagineA.C Potentiometer1Kornepati SureshNessuna valutazione finora
- Slide Wire DC Potentiometer: Group MembersDocumento15 pagineSlide Wire DC Potentiometer: Group Membersanuj jainNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 3Documento6 pagineUnit 3dhub324Nessuna valutazione finora
- Slide Wire DC Potentiometer: Group MembersDocumento15 pagineSlide Wire DC Potentiometer: Group Membersanuj jainNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 2Documento19 pagineUnit 2VIDYA SAGAR KAKARLANessuna valutazione finora
- Arya Institute of Engineering Technology and Management Subject: Electrical Measurement Code: 4Ee3A Branch: Electrical EngineeringDocumento37 pagineArya Institute of Engineering Technology and Management Subject: Electrical Measurement Code: 4Ee3A Branch: Electrical EngineeringSameer GulshanNessuna valutazione finora
- Potentiometers: Nstrument Ransformers ANDDocumento26 paginePotentiometers: Nstrument Ransformers ANDDIVYA PRASOONA CNessuna valutazione finora
- Emmi LabDocumento48 pagineEmmi LabRamesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparison Methods of Measurements: UNIT-3Documento27 pagineComparison Methods of Measurements: UNIT-3jenitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Two: Ac-Dc Conversion: Uncontroled RectificationsDocumento53 pagineChapter Two: Ac-Dc Conversion: Uncontroled Rectificationsfor life100% (3)
- PotentiometerDocumento3 paginePotentiometerammuluhai333Nessuna valutazione finora
- Transformers - Chapter 2 - NewDocumento58 pagineTransformers - Chapter 2 - NewAhmet MehmetNessuna valutazione finora
- PresentationDocumento35 paginePresentationApoorva SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Q 7) Explain The Basic Principle of Control in HVDCTDocumento12 pagineQ 7) Explain The Basic Principle of Control in HVDCTrasashpujNessuna valutazione finora
- Full Wave RectifierDocumento25 pagineFull Wave RectifierSandeep KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-Iv - Ac-Measurements & Measurement of High D.C., A.C. and Impulse CurrentsDocumento39 pagineUnit-Iv - Ac-Measurements & Measurement of High D.C., A.C. and Impulse CurrentsSumaira SaifNessuna valutazione finora
- PotentiometersDocumento23 paginePotentiometersbhaskaratarun239bNessuna valutazione finora
- The Wenner PotentiometerDocumento12 pagineThe Wenner PotentiometerMirko Yanque TomasevichNessuna valutazione finora
- Potentiometers Ac PDFDocumento4 paginePotentiometers Ac PDFAdityaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ac Potentiometers: DefinitionDocumento4 pagineAc Potentiometers: DefinitionjayNessuna valutazione finora
- Phy 104 - 1 PDFDocumento132 paginePhy 104 - 1 PDFVictor Afolabi100% (1)
- Analog Measuring InstrumentsDocumento43 pagineAnalog Measuring Instrumentsmuvvala charithaNessuna valutazione finora
- Full WaveDocumento17 pagineFull WaveSandeep KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit IV Ac MeasurementsDocumento40 pagineUnit IV Ac MeasurementsKhánh NguyễnNessuna valutazione finora
- Potentiometers: DefinitionDocumento4 paginePotentiometers: DefinitionjayNessuna valutazione finora
- Duo Range Type PotentiometerDocumento19 pagineDuo Range Type Potentiometersaikarthick023Nessuna valutazione finora
- EE536 ManualDocumento67 pagineEE536 Manualciraj123456Nessuna valutazione finora
- Constant Voltage Constant Current DC Power SupplyDocumento56 pagineConstant Voltage Constant Current DC Power SupplySeven HillsNessuna valutazione finora
- 03 TheoryDocumento8 pagine03 TheoryRathankar RaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Eee 2205 AssingmentDocumento3 pagineEee 2205 AssingmentDavid Ochieng'Nessuna valutazione finora
- Trans Lab ManualDocumento76 pagineTrans Lab ManualSanthosh Kumar100% (1)
- Measurement of High A.C. and Impulse VoltagesDocumento24 pagineMeasurement of High A.C. and Impulse VoltagesSumaira SaifNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT IV Part 1 PotentometersDocumento12 pagineUNIT IV Part 1 PotentometersmahiNessuna valutazione finora
- Appendix Chapter For Transformer StandardDocumento28 pagineAppendix Chapter For Transformer StandardHabib SimorangkirNessuna valutazione finora
- E1.08 (2016) Single Phase TransformerDocumento5 pagineE1.08 (2016) Single Phase TransformerDalilahNessuna valutazione finora
- PEC Lecture Slide Inverter TurkceDocumento43 paginePEC Lecture Slide Inverter Turkcemdur67Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nouveau Document Microsoft WordDocumento7 pagineNouveau Document Microsoft WordAbdelkarim MessaoudiNessuna valutazione finora
- BEEE Precise NotesDocumento56 pagineBEEE Precise Noteskurubamailagani ravaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4 Electrical BridgesDocumento9 pagineUnit 4 Electrical Bridgesazhar3303Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 3Documento30 pagineUnit 3Jebas ManovaNessuna valutazione finora
- Full Wave RectifierDocumento10 pagineFull Wave Rectifierdheerajguptaandro20% (5)
- Physics Practicals Experiment: PotentiometerDocumento14 paginePhysics Practicals Experiment: PotentiometerdeoNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit - V InvertersDocumento11 pagineUnit - V InvertersSukhpal SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 1: DC Multimeter Measurements: ObjectiveDocumento11 pagineLab 1: DC Multimeter Measurements: ObjectiveAli AdnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 07Documento13 paginePower Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 07Syed AfzalNessuna valutazione finora
- Measurement of ResistanceDocumento96 pagineMeasurement of ResistancePraveena BNessuna valutazione finora
- DC-DC Converter SimulationDocumento3 pagineDC-DC Converter SimulationMThe StrokesNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter4 28wheatstonebridge 29Documento26 pagineChapter4 28wheatstonebridge 29Amirul SyazwanNessuna valutazione finora
- DC Choke Inductance MeasurementDocumento8 pagineDC Choke Inductance MeasurementAnonymous vKD3FG6RkNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Lab - Rectification and Smoothing of An A.C. VoltageDocumento8 paginePhysics Lab - Rectification and Smoothing of An A.C. Voltageaben100% (1)
- Chapter 3Documento46 pagineChapter 3Tewodros ShegawNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3Documento46 pagineChapter 3Tewodros ShegawNessuna valutazione finora
- 19EEE181 ReportDocumento14 pagine19EEE181 ReportabcdNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Machines TransformersDocumento53 pagineElectrical Machines TransformersYoshua DylanNessuna valutazione finora
- Printed Circuit Board AssembliesDocumento9 paginePrinted Circuit Board AssembliespcbamanufacturerNessuna valutazione finora
- Multilin: Synchronism Check EquipmentDocumento26 pagineMultilin: Synchronism Check EquipmentĐức Nguyễn XuânNessuna valutazione finora
- EE21 Lecture 1Documento32 pagineEE21 Lecture 1R SuyaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Power SupplyDocumento29 paginePower SupplyJaved MaralitNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronics Theory AssignmentDocumento2 pagineElectronics Theory AssignmentShakeel Ahmad KasuriNessuna valutazione finora
- ANSI MV Bridges Polymer Disconnect Flyer enDocumento2 pagineANSI MV Bridges Polymer Disconnect Flyer enbarukomkssNessuna valutazione finora
- Megger S1-552 - 2 5KV Insulation Tester DescriptionDocumento5 pagineMegger S1-552 - 2 5KV Insulation Tester DescriptionBenabidNessuna valutazione finora
- Philips EnduraLED T8 Tube LED Light Installation GuideDocumento3 paginePhilips EnduraLED T8 Tube LED Light Installation GuideGreen SupplyNessuna valutazione finora
- Resistivity of Wire Electricity Conductor - Dana Santika - Physics - Ganesha University of EducationDocumento16 pagineResistivity of Wire Electricity Conductor - Dana Santika - Physics - Ganesha University of EducationI Gede Dana SantikaNessuna valutazione finora
- EIM 11 10 MultitesterDocumento14 pagineEIM 11 10 MultitesterJorge PeraltaNessuna valutazione finora
- DB hrc800 e 9498-737-38613 PDFDocumento4 pagineDB hrc800 e 9498-737-38613 PDFpradeepchennai10_959Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ee 2022Documento9 pagineEe 2022LATIGAR, JEFFERSON 0.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapiter3 - Mig Mag Welding50931Documento22 pagineChapiter3 - Mig Mag Welding50931Augusto SoaresNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 SuperjunctionDocumento5 pagine3 SuperjunctionharibadriNessuna valutazione finora
- Esquematico Karate PlusDocumento37 pagineEsquematico Karate PlusAmir FarukNessuna valutazione finora
- Iso 1042Documento43 pagineIso 1042mar_barudjNessuna valutazione finora
- Series: Aluminum Electrolytic CapacitorsDocumento4 pagineSeries: Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitorsyo mismoNessuna valutazione finora
- NH360QM-D-2XR - Omni Commscope (SC 2019)Documento3 pagineNH360QM-D-2XR - Omni Commscope (SC 2019)Paulo L. MuñozNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Specification of Fire Alarm EquipmentDocumento1 paginaTechnical Specification of Fire Alarm EquipmentRaton121 RahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- MSETCL - Approved Vendor ListDocumento11 pagineMSETCL - Approved Vendor ListNavaneetha KrishnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Micro SteppingDocumento4 pagineMicro SteppingDobai SzilardNessuna valutazione finora
- DC MachinesDocumento17 pagineDC MachinessatyaNessuna valutazione finora
- ETEL61Documento2 pagineETEL61Claudio CalabreseNessuna valutazione finora
- NBM-Probes DataSheetDocumento4 pagineNBM-Probes DataSheetMarcelo Hernan LaurettiNessuna valutazione finora
- Design and Development of Small Active and Passive Loop Antennas For Measurement of Shielding Effectiveness Per IEEE Std.299Documento5 pagineDesign and Development of Small Active and Passive Loop Antennas For Measurement of Shielding Effectiveness Per IEEE Std.299Andrea QuadriNessuna valutazione finora
- KSE-LIGHTS Lamps KS-8600 and KS-8700: Zone 0, Permission D2 For Dust and M1Documento1 paginaKSE-LIGHTS Lamps KS-8600 and KS-8700: Zone 0, Permission D2 For Dust and M1Dan StrideNessuna valutazione finora
- Experimental Verification of Network Theorems, UGC Practical - Physics - S - PaulDocumento8 pagineExperimental Verification of Network Theorems, UGC Practical - Physics - S - PaulspNessuna valutazione finora
- A Review of LCC-HVDC and VSC-HVDC Technologies and Applications - 2016Documento7 pagineA Review of LCC-HVDC and VSC-HVDC Technologies and Applications - 2016M8ow6fNessuna valutazione finora