Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Anatomy & Physiology Urinary System
Caricato da
Vandie MagallanesDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Anatomy & Physiology Urinary System
Caricato da
Vandie MagallanesCopyright:
Formati disponibili
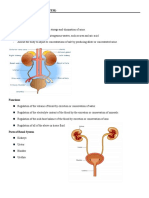
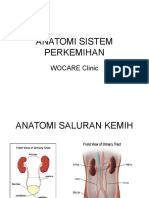
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY
URINARY SYSTEM
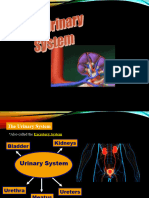
consists of two kidneys, two ureters, one urinary
bladder, one urethra
Functions of Urinary System
KIDNEYS-the kidneys regulate blood volume and
Composition, help regulate blood pressure,
synthesize glucose, release erythropoietin,
participate in Vit. D synthesis and excrete
wastes in the urine.
URETERS- transport urine from the kidneys to the
urinary bladder.
URINARY BLADDER- stores urine
URETHRA- discharges urine from the body.
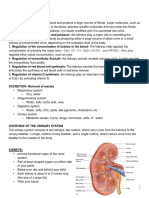
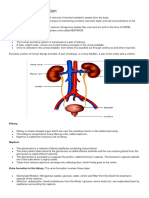
THE KIDNEY
RENAL CORTEX- The cortex is the outer
part of the kidney. This is where blood is
filtered.
RENAL MEDULLA- where the amount of
salt and water in your urine is
controlled.
RENAL CAPSULE- Smooth, transparent
sheet of irregular connective
tissue that is continuous with the outer
coat of the
ureter.
MINOR CALYX- portion of the urinary
collecting system within the kidney
that drains one renal papilla.
MAJOR CALYX- portion of the urinary
collecting system within the kidney
that drains several minor calyces
RENAL COLUMNS- are lines of the kidney
matrix which support the cortex of the
kidney. They are composed of lines of blood vessels and urinary tubes and a
fibrous, cortical material.
RENAL PYRAMID- are conical segments within the internal medulla of the
kidney. The pyramids contain the secreting apparatus and tubules.
RENAL PELVIS- This is the region of the kidney where urine collects.
RENAL PAPILLA- tip of renal pyramid projecting into a minor calyx
URETER- muscular tube that serves as the duct of the kidney to carry urine to
the bladder
URINE ELIMINATION
Increased bladder pressure
Transmit nerve impulse
Propagate to micturition Center
Trigger micturition reflex
Contraction of the detrusor muscle
And Relaxation of the internal urethral sphincter
Urination
Pathophysiology:
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Kidney Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDa EverandKidney Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiology: Urinary System (Renal System)Documento27 pagineAnatomy and Physiology: Urinary System (Renal System)dima_FlaviaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Urinary SystemDocumento19 pagineThe Urinary SystemCecil AlbaNessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary System (Renal System) Anatomy and Physiology Renal SystemDocumento3 pagineUrinary System (Renal System) Anatomy and Physiology Renal SystemAldrece CastroverdeNessuna valutazione finora
- Excretory SystemDocumento19 pagineExcretory SystemElliz DoctoraNessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary System PDFDocumento27 pagineUrinary System PDFfiona100% (3)
- Chap 18 - The Urinary SystemDocumento23 pagineChap 18 - The Urinary SystemLora Mae Delos SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary SystemDocumento10 pagineUrinary Systemapi-19824701Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 18 - The Urinary SystemDocumento22 pagineChap 18 - The Urinary SystemHATLERNessuna valutazione finora
- THE Urinary System: Charlotte R. Espiritu RN. MANDocumento25 pagineTHE Urinary System: Charlotte R. Espiritu RN. MANLenny Ronalyn QuitorianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiology-FinalDocumento4 pagineAnatomy and Physiology-FinalSlyne CenarosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary System Part 1Documento8 pagineUrinary System Part 1عبدالرحمن عدي عبدالفتاح100% (1)
- Urinary SystemDocumento29 pagineUrinary SystemTrisha AmitNessuna valutazione finora
- Script Anatomy and PhysiologyDocumento6 pagineScript Anatomy and PhysiologyEljan FernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment of Kidney and Urinary FunctionDocumento72 pagineAssessment of Kidney and Urinary Functionmoncalshareen3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Genitp Urinary SystemDocumento200 pagineGenitp Urinary SystemQuolette ConstanteNessuna valutazione finora
- BIOLOGYDocumento15 pagineBIOLOGYmanigbasrea15Nessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary System:: KidneysDocumento3 pagineUrinary System:: KidneysRochel HatagueNessuna valutazione finora
- Homeostasis 1Documento23 pagineHomeostasis 1mandimutsiradoreen8Nessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary SystemDocumento18 pagineUrinary Systemwmaximoff426Nessuna valutazione finora
- KIDNEYSDocumento9 pagineKIDNEYSAnamNessuna valutazione finora
- Expelling (Getting Rid Of) Any Undigested Food Eliminates Undigested MaterialsDocumento12 pagineExpelling (Getting Rid Of) Any Undigested Food Eliminates Undigested MaterialscamilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary System FinalDocumento7 pagineUrinary System Finalapi-341176984Nessuna valutazione finora
- Review of AnaphysioDocumento8 pagineReview of AnaphysioDizerine Mirafuentes RolidaNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Homeostasis?: Body Cells Work Best If They Have The Correct EnvironmentDocumento45 pagineWhat Is Homeostasis?: Body Cells Work Best If They Have The Correct EnvironmentNatty ChikumbaNessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary SystemDocumento17 pagineUrinary SystemShiela Mae SagayoNessuna valutazione finora
- Excretory SystemDocumento61 pagineExcretory Systemalayca cabatanaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Urinary System NotesDocumento3 pagineThe Urinary System NoteselyyNessuna valutazione finora
- General Structure and Functions of Urinary System-Week 11Documento49 pagineGeneral Structure and Functions of Urinary System-Week 11Reentsha EllyNessuna valutazione finora
- UrinaryDocumento2 pagineUrinaryMario BagesbesNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 6Documento3 pagineChapter 6John ErickNessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary System: Yudha Bayu FirmansyahDocumento4 pagineUrinary System: Yudha Bayu FirmansyahYudha Bayu FirmansyahNessuna valutazione finora
- Excretory SystemDocumento37 pagineExcretory SystemPatrick DeeNessuna valutazione finora
- KidneyDocumento85 pagineKidneyIshita SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- 07 Urinary SystemDocumento92 pagine07 Urinary SystemcelynjasminegNessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary SystemDocumento6 pagineUrinary SystemAubrey Yu JaneaNessuna valutazione finora
- ExcretionDocumento26 pagineExcretionfatima zahraNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity 10 Urinary SystemDocumento5 pagineActivity 10 Urinary SystemKristine Claire GalaceteNessuna valutazione finora
- Excretory System: Group Members - Ronit, Saumya, Yash, Ishan, Arnav, Amaan, Sanil Grade - 7 Section - ADocumento9 pagineExcretory System: Group Members - Ronit, Saumya, Yash, Ishan, Arnav, Amaan, Sanil Grade - 7 Section - AAmaan KaziNessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary SystemDocumento2 pagineUrinary SystemCharlayne AnneNessuna valutazione finora
- The Excretory SystemDocumento31 pagineThe Excretory Systemapi-3759646100% (12)
- Anatomy and Patho of PyelonephritisDocumento3 pagineAnatomy and Patho of PyelonephritisMonica Melo HernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- ScriptDocumento3 pagineScriptAnghelNessuna valutazione finora
- System UriDocumento48 pagineSystem UriStef FieNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomi Sistem Perkemihan: WOCARE ClinicDocumento11 pagineAnatomi Sistem Perkemihan: WOCARE ClinicMangiwa InartryNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Urinary SystemDocumento18 pagineWhat Is Urinary Systemwmaximoff426Nessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary SystemDocumento14 pagineUrinary SystemCharli ParachinniNessuna valutazione finora
- Bped 65 Urinary SystemDocumento26 pagineBped 65 Urinary SystemDollie May Maestre-TejidorNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy & Physiology of The Urinary System.: Presented By:-Mr. Saihou Sanneh RN, RM, BSN&RH, FwacnDocumento70 pagineAnatomy & Physiology of The Urinary System.: Presented By:-Mr. Saihou Sanneh RN, RM, BSN&RH, Fwacnflex gyNessuna valutazione finora
- Renal Physiology 1 1aDocumento88 pagineRenal Physiology 1 1afentaw melkieNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 4 Excretory SystemDocumento18 pagineLecture 4 Excretory Systembabaaijaz01Nessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction and Assessment of The Renal - Urological SystemDocumento182 pagineIntroduction and Assessment of The Renal - Urological SystemValerie Suge-Michieka100% (1)
- Urinary SystemDocumento22 pagineUrinary Systemapi-288754676Nessuna valutazione finora
- STUDY NOTES-The Urinary SystemDocumento3 pagineSTUDY NOTES-The Urinary Systempeterneil75% (4)
- Urinary SystemDocumento40 pagineUrinary SystemAlyssa AlferezNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 18 Anaphy TransesDocumento5 pagineChapter 18 Anaphy TransesHoly HaeinNessuna valutazione finora
- Curs 11. Sistemul ExcretorDocumento66 pagineCurs 11. Sistemul ExcretorDobrincu MirelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Excretion NOTESDocumento2 pagineExcretion NOTESabhinavsinghbaliyanraghuvanshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary SystemDocumento2 pagineUrinary SystemShehzadi KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary System: by Marie Cris AmerilaDocumento22 pagineUrinary System: by Marie Cris AmerilaZilocke Gelera AmerilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanical VentilatoradwawdDocumento1 paginaMechanical VentilatoradwawdVandie MagallanesNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiology Uti Adawdiasdfkuhasdlukfhalkfjashdkljfahrguilahrluihadfkljnxj, CnalksefhauehDocumento4 pagineAnatomy and Physiology Uti Adawdiasdfkuhasdlukfhalkfjashdkljfahrguilahrluihadfkljnxj, CnalksefhauehVandie MagallanesNessuna valutazione finora
- Vandie P. Magallanes, RNDocumento3 pagineVandie P. Magallanes, RNVandie MagallanesNessuna valutazione finora
- FormsDocumento1 paginaFormsVandie MagallanesNessuna valutazione finora
- Demand LetterDocumento2 pagineDemand LetterVandie MagallanesNessuna valutazione finora
- Appendix 1Documento2 pagineAppendix 1Vandie MagallanesNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Method of Family PlanningDocumento2 pagineChemical Method of Family PlanningVandie MagallanesNessuna valutazione finora
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Da EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Valutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (1)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedDa EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (82)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityDa EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (32)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionDa EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (404)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDDa EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (3)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsDa EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNessuna valutazione finora
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsDa EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsDa EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (4)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDa EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeDa EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeValutazione: 2 su 5 stelle2/5 (1)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDa EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (42)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Da EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (110)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeDa EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (254)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsDa EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (170)
- Manipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesDa EverandManipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (1412)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaDa EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- To Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceDa EverandTo Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (51)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossDa EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (6)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryDa EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (46)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlDa EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (60)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessDa EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (328)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityDa EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (6)
- How to ADHD: The Ultimate Guide and Strategies for Productivity and Well-BeingDa EverandHow to ADHD: The Ultimate Guide and Strategies for Productivity and Well-BeingValutazione: 1 su 5 stelle1/5 (1)