Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Harmonic Pattern
Caricato da
Shruti Thepadia0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
572 visualizzazioni8 pagineThe document discusses several harmonic patterns used in technical analysis including the AB=CD pattern, Bat pattern, Gartley pattern, and Crab pattern. For each pattern, it provides 1-3 defining characteristics and notes that they identify potential reversal zones where the flow of buying and selling may change based on alignments of Fibonacci ratios within the pattern structures. Harmonic patterns attempt to quantify areas to buy low and sell high using Fibonacci techniques.
Descrizione originale:
FOR TECHNICAL TRADING
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoThe document discusses several harmonic patterns used in technical analysis including the AB=CD pattern, Bat pattern, Gartley pattern, and Crab pattern. For each pattern, it provides 1-3 defining characteristics and notes that they identify potential reversal zones where the flow of buying and selling may change based on alignments of Fibonacci ratios within the pattern structures. Harmonic patterns attempt to quantify areas to buy low and sell high using Fibonacci techniques.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
572 visualizzazioni8 pagineHarmonic Pattern
Caricato da
Shruti ThepadiaThe document discusses several harmonic patterns used in technical analysis including the AB=CD pattern, Bat pattern, Gartley pattern, and Crab pattern. For each pattern, it provides 1-3 defining characteristics and notes that they identify potential reversal zones where the flow of buying and selling may change based on alignments of Fibonacci ratios within the pattern structures. Harmonic patterns attempt to quantify areas to buy low and sell high using Fibonacci techniques.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 8
Harmonic Pattern
The Golden Section
A simple line can illustrate the relationships of the golden ratio or
golden mean in the golden
section. Begin with drawing a line and then divide it into
segments where the ratio of one part
to the entire line is the same as the ratio of the smaller part to the
larger. The example of the
golden section is illustrated in the following table:
Whole Line A = 1 inch ( __________ )
Section B = 0.618 inches ( ______ )
Section C = 0.382 inches ( ___ )
AB=C+B=A
|-------------------|---------------|----------------|------------|
1 - 0.618 = 0.382 + 0.618 = 1
These line segments can be divided in various combinations to
manifest phi (0.618) ratios.
Ratio of A to B = 1/0.618 = 1.618
Ratio of A to C = 1/0.382 = 2.618 (1+1.618)
Ratio of B to A = 0.618/1 = 0.618
Ratio of B to C = 0.618/0.382 = 1.618
Ratio of C to A = 0.618/1 = 0.618
Ratio of C to B = 0.382/0.618 = 0.618
The golden section is closely related to the golden ratio since the
ratios have a relationship
to one another that is equal to phi (0.618) or the inverse, Phi
(1.618).
The concept of a Potential Reversal Zone (PRZ) was originally
outlined in The Harmonic
Trader:
History has proven that a convergence of Fibonacci
numbers
and price patterns provides a highly probable area for a
reversal.
This area of convergence is called the potential reversal
zone.
When three, four, or even five numbers come together
within a
specific area, you must respect the high probability for
some type
of reversal.
(The Harmonic Trader, [Nevada: HarmonicTrader.com, L.L.C.,
1999])
Specific price structures that possess three or more numbers
within a defined area are the basis for defining these harmonic
zones. It is called Potential because the defined area must be
analyzed as the price action tests the projected Reversal Zone.
Although this concept will be covered extensively later in this
material, it is imperative to understand that patterns are defined
by specific price structures that contain combinations of distinct
and consecutive Fibonacci retracements and projections. By
calculating the various Fibonacci aspects of a
specific price structure, harmonic patterns can indicate a specific
area to examine for potential
turning points in price action. Again, this area is called the
Potential Reversal Zone (PRZ). In
essence, a PRZ represents the critical areas where the flow of
buying and selling is potentially
changing. These harmonic zones attempt to identify the price
levels where imbalanced
overbought and oversold situations are reversingat a minimum
back to their respective
equilibrium level.
Any trading system attempts to be on the right side of the
marketbuying low and selling
high. Harmonic Trading techniques quantify these areas and
generate buy and sell signals
based on the price action at these turning points. Furthermore,
these techniques inherently
define and direct trading behavior as a means of anticipating
these potential changes in price
action.
Harmonic Trading Ratios
Primary Ratios:
(Directly derived from the Fibonacci Number Sequence)
0.618 = Primary Ratio
1.618 = Primary Projection
Primary Derived Ratios:
0.786 = Square root of the 0.618 ( )
0.886 = Fourth root of 0.618 or
Square root of the 0.786 ( )
1.13 = Fourth root of 1.618 or
Square root of the 1.27 ( )
1.27 = Square root of the 1.618 ( )
Complementary Derived Ratios:
0.382 = (1-0.618) or 0.6182
0.50 = 0.7072
0.707 = Square root of 0.50 ( )
1.41 = Square root of 2.0 ( )
2.0 = (1+1)
2.24 = Square root of 5 ( )
2.618 = 1.6182
3.14 = Pi (See later section The Importance of Pi (3.14) in
Harmonic
Trading)
3.618 = (1+2.618)
The AB=CD Pattern Summary
Although the basic AB=CD structure may possess a variety of
Fibonacci ratios, the concept of
support or resistance at the completion of two distinct and
consecutive price legs is the
essence of all harmonic patterns.
Alternate AB=CD patterns underscore the importance of using the
basic structure to define
the completion of specific patterns. In either AB=CD, the BC
projection should complement the
completion point of the pattern. It is important to remember the
reciprocal relationships of the
C point to the BC projection. A perfect AB=CD utilizes the 0.618
retracement and 1.618 extension,
as the most harmonic alignment of Fibonacci ratios for the
pattern. I believe that this
pattern should possess specific characteristics to be a valid
harmonic structure and to define
a trading opportunity:
1. Minimum AB=CD completion where each price leg is
equivalent.
2. C point retracement can vary between a 0.382 to a
0.886, although 0.618 is
preferred.
3. BC projection can vary from 1.13 to 3.618 and depends
upon the C point
retracement.
4. Alternate AB=CD patterns exist.
It is important to mention that many Fibonacci-related analysts
have oversimplified this pattern
in recent years. The idea of trading every AB=CD that completes
is absurd. Many people
who present this pattern as the end-all-be-all price structure fail
to understand that AB=CDs
require many other considerations to confirm and complement
the completion point. Preferably,
the structure should possess other Fibonacci retracements or
projections. However, the most
important concept is that the AB=CD is the basic structure of all
harmonic patterns.
The Bat Pattern Summary
The Bat pattern is a precise harmonic pattern that frequently
yields exact and sharp reversals.
The 0.886 retracement is a powerful completion point and the
defining limit within the PRZ.
Although a 0.50 or 0.382 retracement is preferred, any B point
that is less than a 0.618 will
define a valid Bat structure. The Bat pattern incorporates a
minimum AB=CD completion to
validate the structure, as well. However, an Alternate 1.27 AB=CD
is most common and is
a defining element in the Perfect Bat structure. Furthermore, the
BC projection should
complement the other numbers in the PRZ, and it must be at least
a 1.618 extension.
1. B point retracement of the XA leg must be less than
0.618 with a 0.50 or 0.382
retracement preferred.
2. Precise 0.886 D point retracement of the XA leg as the
defining limit within
the PRZ.
3. Minimum 1.618 BC projection with extreme extensions
(2.02.618) possible.
4. Minimum AB=CD completion, although an Alternate
1.27 AB=CD is more common
and preferred.
5. C point retracement can vary between a 0.382 to an
0.886.
The Bat pattern is probably the best harmonic pattern of them all!
Bat structures represent
powerful corrective signals that identify excellent trading
opportunities that are retesting
significant levels of support or resistance. The best structures
typically are distinct and
possess a precise alignment of Fibonacci ratios to validate the
pattern.
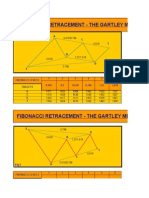
Gartley Pattern Summary
The Gartley pattern is a controversial pattern. Despite the varying
interpretations within
The Great Gartley Controversy, the most harmonic Gartley
pattern possesses distinct
characteristics at all points within the structural rules were
originally outlined in The Harmonic
Trader.
The 0.618 B point retracement is critical in defining a valid
Gartley structure. Although the
0.786 XA retracement is an important element of the structure,
the equivalent AB=CD within
the pattern is the most critical completion point in the Potential
Reversal Zone (PRZ).
Furthermore, the AB=CD completion is a mandatory minimum
requirement for all valid Gartley
patterns.
1. Precise 0.618 B point retracement of the XA leg.
2. Precise 0.786 D point retracement of the XA leg in the
PRZ.
3. 1.27 or 1.618 BC projection.
4. Equivalent AB=CD.
5. C point retracement can vary between a 0.382 to a
0.886.
The Gartley pattern must include these specific conditions to
define the best harmonic
structures. Although the Gartley may resemble a Bat, the
Fibonacci ratios utilized in the setup
are unique to this pattern. In addition, the pattern should be quite
distinct and possess ideal
symmetry.
The Crab Pattern Summary
Although the structural variations of the Crab may seem to define
the same pattern, the
alignment of Fibonacci ratios clearly differentiates each type as a
unique situation. The Crab
typically defines extreme overbought and oversold situations, as
the 1.618 XA leg is the most
important Fibonacci measurement of the pattern and it represents
the most critical number in
the Potential Reversal Zone (PRZ).
Unlike the other patterns within the Harmonic Trading approach,
the AB=CD is not as critical
at the completion point. Although it is important to differentiate
the AB=CD possibilities for each
variation, the Alternate 1.618 AB=CD pattern is the preferred
structure in most Crab patterns.
However, the 1.27 AB=CD pattern is typically found in the original
version, while it is not
unusual for the Deep Crab to possess an equivalent AB=CD.
The extreme BC projectionusually a 2.618, 3.14, or 3.618
extensionunderscores the
nature of this structure. Although the Deep Crab permits a wider
range of BC possibilities, this
projection should converge closely with the 1.618 XA.
1. Precise 0.618 B point retracement or less of the XA leg.
(.382 and 0.50 are
common B points in the structure.)
2. Extreme 2.618, 3.14 or 3.618BC projection. (Sometimes
2.24 BC projections form
in the structure.)
3. Minimum AB=CD completion. Alternate 1.27 AB=CD or
1.618 AB=CD patterns are
most common.
4. C point retracement can vary between a 0.382 to an
0.886.
5. This is an extreme pattern!
The volatile nature of this pattern must be emphasized. Reversals
from these PRZs can be
sharp and possess extreme price action. The Crab is a distinctive
pattern and possesses
unique qualities that identify remarkable harmonic opportunities.
The differentiation of this
pattern is critical to define each variation.
From a harmonic perspective, valid Crab structures identify
extreme oversold or overbought
conditions. These patterns usually offer some type of reaction on
the initial test of the
Potential Reversal Zone. The price action frequently responds to
extreme Fibonacci projection
combinations within the Crab pattern of the 1.618 XA leg and the
2.618 or greater BC leg.
The Crab is an incredibly accurate and consistently effective
pattern within the Harmonic
Trading arsenal to identify critical turning points in the markets.
The Butterfly Pattern Summary
The Butterfly is a specific 5-point extension structure that
possesses a distinct alignment of
Fibonacci ratios to validate the pattern. The primary determining
element of the pattern is a
precise 0.786 B point retracement of the XA leg. The Butterfly
utilizes only a 1.27 XA projection
as the most critical number in the PRZ. Furthermore, the
equivalent AB=CD pattern serves as
a minimum requirement for the patterns completion. But, the
Alternate 1.27 AB=CD pattern is
more common to the structure. The BC projection is another
defining element of the pattern, as
it must be at least a 1.618 extension. However, the BC projection
is not as extreme in the
Butterfly as it is in the Crab.
1. Minimum AB=CD completion with Alternate 1.27 AB=CD
pattern most common.
2. C point retracement can vary between a 0.382 to an
0.886, although 0.618 is
preferred.
3. BC projection can vary from 1.13 to 3.618 and depends
upon the C point
retracement.
4. Alternate AB=CD patterns are common within the
structure.
The Butterfly is similar to the Gartley because it requires a
specific alignment of Fibonacci
ratiosespecially a precise B pointto validate the structure.
Although such a strict definition
reduces the number of possible trading opportunities, this
precision reduces those invalid
situations that may appear similar but fail to yield consistently
accurate setups.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Fibonacci Retracement - The Gartley Method (Bullish Ascent) : A C T Fig 1Documento14 pagineFibonacci Retracement - The Gartley Method (Bullish Ascent) : A C T Fig 1brijeesh0% (1)
- Patterns: The Three Drives PatternDocumento10 paginePatterns: The Three Drives PatternRABENAIVONessuna valutazione finora
- Fib ClusterDocumento3 pagineFib ClusterSPIMYSNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5 - Rate of ChangeDocumento37 pagineChapter 5 - Rate of ChangeNAJWA SYAKIRAH MOHD SHAMSUDDINNessuna valutazione finora
- Sunil KaleDocumento57 pagineSunil Kalevenkata sivaram posaNessuna valutazione finora
- Zones Trading StrateDocumento15 pagineZones Trading StratePetter ZapataNessuna valutazione finora
- TradeBuilder - Classic Edition MANUALDocumento19 pagineTradeBuilder - Classic Edition MANUALGabriel BlakeNessuna valutazione finora
- 30 Min Simple SystemDocumento2 pagine30 Min Simple SystemRayzwanRayzmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Decision Making-Stock TradingDocumento17 pagineDecision Making-Stock TradingGayathri BNessuna valutazione finora
- 27 Aug Risk Management Theory NotesDocumento5 pagine27 Aug Risk Management Theory NotesChitranjan SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- ZSCOREDocumento9 pagineZSCORENitin Govind BhujbalNessuna valutazione finora
- The Empowered Forex Trader: Strategies to Transform Pains into GainsDa EverandThe Empowered Forex Trader: Strategies to Transform Pains into GainsNessuna valutazione finora
- Price Breaks ThroughDocumento34 paginePrice Breaks Throughpb41Nessuna valutazione finora
- Support Resistance Volume BasedDocumento12 pagineSupport Resistance Volume BasedVinod KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Better Volume IndicatorDocumento7 pagineBetter Volume IndicatorMrugenNessuna valutazione finora
- Intraday 890 PDFDocumento3 pagineIntraday 890 PDFharishvasanth1982100% (1)
- Orderblock Trading StrategyDocumento12 pagineOrderblock Trading Strategynahuel.bourdichon100% (1)
- Trader PyramidDocumento12 pagineTrader Pyramidramji3115337Nessuna valutazione finora
- Disadvantages of Harmonic by ArunDocumento14 pagineDisadvantages of Harmonic by ArunMark PangantihonNessuna valutazione finora
- Wagza FX Order Blocks V1Documento24 pagineWagza FX Order Blocks V1ProuserNessuna valutazione finora
- Rsi 5 PDFDocumento9 pagineRsi 5 PDFManoj RaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Falling WedgeDocumento3 pagineFalling Wedgekarthick sudharsanNessuna valutazione finora
- PRZ Backtesting With Harmonic Pattern Plus - v1.0Documento11 paginePRZ Backtesting With Harmonic Pattern Plus - v1.0Jafar SultanNessuna valutazione finora
- Nifty Doctor Simple SystemDocumento5 pagineNifty Doctor Simple SystemPratik ChhedaNessuna valutazione finora
- Al Brooks - Trading Price Action Ranges-7Documento2 pagineAl Brooks - Trading Price Action Ranges-7André Vitor Favaro Medes de Oliveira0% (2)
- Head and Shoulders Pattern GuideDocumento8 pagineHead and Shoulders Pattern GuidejeevandranNessuna valutazione finora
- NVS StrategyDocumento5 pagineNVS StrategyParameswaran ShanmugamNessuna valutazione finora
- SwingTrading Pro - Screeners Examples Z6v7ywDocumento3 pagineSwingTrading Pro - Screeners Examples Z6v7ywjamshidNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Tutorial en PDFDocumento35 pagineTechnical Tutorial en PDFsnehachandan91Nessuna valutazione finora
- 30 Min Strategy PDFDocumento14 pagine30 Min Strategy PDFThe red RoseNessuna valutazione finora
- Bitcoin Pro Trader StudyDocumento2 pagineBitcoin Pro Trader StudyGozgo22Nessuna valutazione finora
- 06 - Class 06 - Trade SetupsDocumento12 pagine06 - Class 06 - Trade SetupsChandler BingNessuna valutazione finora
- Trading Strategies From Technical Analysis - 6Documento19 pagineTrading Strategies From Technical Analysis - 6GEorge StassanNessuna valutazione finora
- Combining RSI With RSIDocumento39 pagineCombining RSI With RSIwayansiagaNessuna valutazione finora
- 01 - The Truth About Support and ResistanceDocumento11 pagine01 - The Truth About Support and ResistanceIv AnNessuna valutazione finora
- Dynamic Zone RSIDocumento2 pagineDynamic Zone RSIMiner candNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Analysis TutorialDocumento34 pagineTechnical Analysis TutorialFahimNessuna valutazione finora
- Hidden Divergence: New TechniquesDocumento5 pagineHidden Divergence: New Techniquesbrijendra singhNessuna valutazione finora
- 1-2-3 Trend Change PatternDocumento4 pagine1-2-3 Trend Change PatternHaichu100% (1)
- E-Book GaryDocumento19 pagineE-Book GaryRenganathan VenkatavaradhanNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Predict Markets Catch The MoveDocumento35 pagineHow To Predict Markets Catch The MoveOswaldo SuarezNessuna valutazione finora
- Options Open Interest AnalysisDocumento19 pagineOptions Open Interest AnalysisManish SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Japanese Candlesticks: Strategy GuideDocumento3 pagineJapanese Candlesticks: Strategy GuideJean Claude DavidNessuna valutazione finora
- Fibonacci Trading TechniquesDocumento9 pagineFibonacci Trading TechniquesmuradhashimNessuna valutazione finora
- Atma Publication PDFDocumento28 pagineAtma Publication PDFSanjay RaghuvanshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Analysis HarshitDocumento84 pagineTechnical Analysis Harshitrahul_mhabde20059812100% (1)
- Tech AnalysisDocumento19 pagineTech AnalysisjatingediaNessuna valutazione finora
- MACD (Moving Average Convergence/Divergenc E) : Reference: SPDocumento11 pagineMACD (Moving Average Convergence/Divergenc E) : Reference: SPLiew Fook SinNessuna valutazione finora
- XM8 Introduction To Trend Reversal Patterns enDocumento31 pagineXM8 Introduction To Trend Reversal Patterns enConstantino L. Ramirez IIINessuna valutazione finora
- Gann Master Forex Course 4Documento51 pagineGann Master Forex Course 4Trader RetailNessuna valutazione finora
- Daily Day Trading PlanDocumento10 pagineDaily Day Trading PlanlowtarhkNessuna valutazione finora
- Indicator 675 % This Macd + RSI + Stochastic Trading Strategy ?? Gives +675% ReturnsDocumento4 pagineIndicator 675 % This Macd + RSI + Stochastic Trading Strategy ?? Gives +675% ReturnsAbbas MuhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- Abcd NsepayDocumento18 pagineAbcd NsepayroughimNessuna valutazione finora
- Tbar BreakotsDocumento8 pagineTbar Breakotssmksp1Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Dow Theory PrinciplesDocumento9 pagineThe Dow Theory Principlesjcfchee2804Nessuna valutazione finora
- G5-T7 How To Use WilliamsDocumento4 pagineG5-T7 How To Use WilliamsThe ShitNessuna valutazione finora
- The Basics of Bollinger Bands® PDFDocumento8 pagineThe Basics of Bollinger Bands® PDFangkiongbohNessuna valutazione finora
- Trends & TrendlinesDocumento23 pagineTrends & TrendlinesBlue Bird0% (1)
- Chronicles of a Million Dollar Trader: My Road, Valleys, and Peaks to Final Trading VictoryDa EverandChronicles of a Million Dollar Trader: My Road, Valleys, and Peaks to Final Trading VictoryNessuna valutazione finora
- Pring PeaksAndTrophs PDFDocumento5 paginePring PeaksAndTrophs PDFbillthegeekNessuna valutazione finora
- Report On MarutiDocumento1 paginaReport On MarutiShruti ThepadiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Money Classic Research: Total Profit Till DateDocumento9 pagineMoney Classic Research: Total Profit Till DateShruti ThepadiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bobokus Style FibonacciDocumento6 pagineBobokus Style FibonacciVincent SampieriNessuna valutazione finora
- Global Recession To Global Recovery With OpportunityDocumento9 pagineGlobal Recession To Global Recovery With OpportunityShruti ThepadiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Money Maker Research PVT LTD Total Profit Till Date: Track SheetDocumento100 pagineMoney Maker Research PVT LTD Total Profit Till Date: Track SheetShruti ThepadiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Industrial NewsDocumento11 pagineIndustrial NewsShruti ThepadiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Guidelines For Economics ProjectDocumento1 paginaGuidelines For Economics ProjectShruti ThepadiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Finance Ki ProfileDocumento2 pagineFinance Ki ProfileShruti ThepadiaNessuna valutazione finora
- NmatsampletestDocumento9 pagineNmatsampletestAshank DubeyNessuna valutazione finora
- INVESTOPEDIA Stockpicking PDFDocumento36 pagineINVESTOPEDIA Stockpicking PDFelisaNessuna valutazione finora
- Study On Performance Characteristic of Medium Consistency Pump - AMEDocumento13 pagineStudy On Performance Characteristic of Medium Consistency Pump - AMELeonardo TerraNessuna valutazione finora
- Icwa Foundation - Maths-Latest PDFDocumento242 pagineIcwa Foundation - Maths-Latest PDFVijay NivasNessuna valutazione finora
- DLP - Week 1 - MathDocumento19 pagineDLP - Week 1 - MathAnnaliza MayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Summative Test in Math 6 2nd Quarter EditedDocumento5 pagineSummative Test in Math 6 2nd Quarter EditedShare LayNessuna valutazione finora
- Solving For A Variable: Useful TipDocumento14 pagineSolving For A Variable: Useful TipIvan Darryl LopezNessuna valutazione finora
- Math5 q1 w5 CM, LP, LasDocumento11 pagineMath5 q1 w5 CM, LP, LasHerynadel AdvinculaNessuna valutazione finora
- Handout 35 Ratio and ProportionDocumento7 pagineHandout 35 Ratio and Proportionrajesh duaNessuna valutazione finora
- Numerical Ability Answer Key Set 5Documento16 pagineNumerical Ability Answer Key Set 5KylaNessuna valutazione finora
- CM PlacementTestDocumento11 pagineCM PlacementTestlynlyn101Nessuna valutazione finora
- @MedicalBooksStore 2017 Pharmaceutical PDFDocumento469 pagine@MedicalBooksStore 2017 Pharmaceutical PDFeny88% (8)
- Ratio Proportion and Variation - ProblemsDocumento15 pagineRatio Proportion and Variation - ProblemsJeevan GonaNessuna valutazione finora
- 3D OBC Seismic Survey Geometry OptimizationDocumento9 pagine3D OBC Seismic Survey Geometry OptimizationIn SeNessuna valutazione finora
- MOST EXPECTED Ratio ProportionDocumento13 pagineMOST EXPECTED Ratio ProportionChannabasava YadramiNessuna valutazione finora
- 7th Grade Mathematics Curriculum MapDocumento6 pagine7th Grade Mathematics Curriculum MapMarcos ShepardNessuna valutazione finora
- Department of Education: Balagtas Central School Table of Specification in Mathematics 5 4Th Summative Test For 2 QuarterDocumento2 pagineDepartment of Education: Balagtas Central School Table of Specification in Mathematics 5 4Th Summative Test For 2 Quarterarnel pascuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Carnival ProjectDocumento16 pagineCarnival Projectapi-397509742Nessuna valutazione finora
- Intergration of Plane and Solid GeometryDocumento27 pagineIntergration of Plane and Solid GeometryAbdussamad MusaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pget For MBADocumento17 paginePget For MBAZoheb Ali KNessuna valutazione finora
- Module Overview: Mathematics As The Study of Patterns)Documento15 pagineModule Overview: Mathematics As The Study of Patterns)hi ilyNessuna valutazione finora
- Philpott 1953 Determination Volatile FattyDocumento15 paginePhilpott 1953 Determination Volatile FattyDCNessuna valutazione finora
- Carolyn Boroden Trading Markets How I Use Fibonacci To Identify Key Support and Resistance Levels PDFDocumento5 pagineCarolyn Boroden Trading Markets How I Use Fibonacci To Identify Key Support and Resistance Levels PDFJose Leonardo PoloNessuna valutazione finora
- Cement Concrtet Mix Design of M-20 Grade For RCC WorkDocumento7 pagineCement Concrtet Mix Design of M-20 Grade For RCC WorkSandip Roy100% (1)
- Math5 Q3 V1Documento88 pagineMath5 Q3 V1Hermel ClapisNessuna valutazione finora
- A. Directions: Choose The Letter of The Correct Answer and ENCIRCLE Your AnswerDocumento4 pagineA. Directions: Choose The Letter of The Correct Answer and ENCIRCLE Your AnswerRodessa Marie Canillas LptNessuna valutazione finora
- Orion Flat Slab Design TrainingDocumento134 pagineOrion Flat Slab Design TrainingAdigwe George Chima100% (4)
- Act m1 Algebra For PayhipDocumento65 pagineAct m1 Algebra For PayhipCecília de SousaNessuna valutazione finora
- DLL Math 6 Q2 Week 4-1Documento7 pagineDLL Math 6 Q2 Week 4-1Astro0% (1)
- Business Math - 1st Quarter ExamDocumento3 pagineBusiness Math - 1st Quarter ExamKelly ChengNessuna valutazione finora
- Direct Proportion ProblemsDocumento11 pagineDirect Proportion ProblemsMarivic Echaveria Depala100% (1)
- Population Pyramid IndiaDocumento4 paginePopulation Pyramid India18maneeshtNessuna valutazione finora