Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
NFV
Caricato da
SaurabhDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
NFV
Caricato da
SaurabhCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Can be customer location
or provider PoP
Location
WAN Accelerator
Deep Packet Inspection
( DPI)
vE-CPE
Multiple Functions can be
virtualized
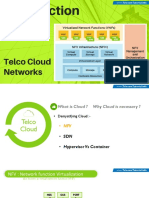
NFV aims at virtualizing Network Element or certain function of of Network Element in
Service Provider network by using commodity machines like x86 servers.
What is NFV
Intrusion Detection/
Prevention System
Both E-CPE ( Enterprise Access Router) and
PE ( Provider Edger) can be virtualized
Virtualization of E-CPE
and PE
Faisal Khan
NFV Mindmap V 2.0
Telecomlighthouse.com
QoS
V-PE
NG-Firewall
NFV Use Cases
Layer 2 or layer 3
capabilities
Standard IT virtualization technologies ( Cloud
Computing)
Use standard servers and commodity switches to reduce costs.
Start here, Move Clock Wise
Or
Jump to the topic
Firewall
Can also host some or all of
the functions of Ve-CPE
Technology Motivated
from
Innovate and rollout Services
quickly
Motivations/
Drivers of NFV
Reduce Power and space usage by using
commodity servers
Standardized and Open
interfaces
SGW
Serving Gateway
Mobile Core and
IMS
4G
Operation innovation through
common tools
PGW
Packet data network
gateway
Intrusion
Detection System
Security
Serving GPRS
support node
SGSN
Firewall
Basic Concepts
3G
Gateway GPRS
support node
GGSN
Call session
control function
CSCF
Mobile Base
station
Node B, eNodeB
Mobile Network
Elements
IMS
MME
Mobile Core
Media Gateway
Control function
Many Types of
Equipment
MGCF
Benefits
GGSN, SGSN
Target Areas of NFV
"Commoditiazation"
Setup Box
Elasticity, Flexibility,
Quick reconfiguration
Home
Enivronment
The following functions are virtualized:
Baseband radio processing unit, Phy, MAC, RLC, RRC
Complete base station or part
of base station is virtualized
Two Models
HLR, RNC
Home Router
Mobile Base
Station
For C-RAN, above functions ( in BBU) and also
switching/load balancing is virtualized
CPE
CG-NAT
These functions include but not limited to
Firewall, DHCP,NAT and VPN
Many functions of CPE are taken
to service provider cloud
Virtual CPE
Virtualization of Home
environment
Switching
BNG
Routing
SDN was originated in labs by Academia.
Differences and
Similarities
Both refers to software centric network
Virtual Network
Function
VNF
Virtualizes a Network Element or some
function of a network element
Example includes VNF for
Router, Switch, Base Station etc
SDN emphasizes separation of data and control plane; NFV aims at
virtualizing network hardware gear.
VNF Manager
Both refers to commoditization. Commoditization is a by-product of
SDN but the main focus of NFV
NFV
Use Cases
Service, VNF &
Infrastructure
Description
ic
NFV
NFV
Infrastructure
Compute, Memory and Network
Resources
Different Blocks
EMS 1
EMS 2
EMS 3
Complete hardware and software
environment in which VNFs are deployed
For example-Physical resources like
x86/Commodity Server and Virtual resources
The physical part of
of NFVI
For example
Commodity servers
New Topic
Ve-Vnfm
VNF Manager
VNF 2
Or-Vi
VNF 3
Vn-Nf
I
FV
N truc
ras
Inf
V
NF
e
tur
Arc
hite
ctu
re
Virtual
Compute
NFVI
Vi-Vnfm
Virtual
Memory
Virtual
Network
Virtualization Layer
NF-Vi
Vi-Ha
Compute
Memory
Virtualization Layer
Virtual Compute, Memory and
Network
Network
VIM
VNF
What is VNF?
Responsible for decoupling hardware
resource from software resource
Abstracts hardware resource
into software resource
Example:
HyperVisor
VIM-Virtualized
Infrastructure
Manager
The result of abstraction of
hardware resources
Virtualization
Infrastructure Manager
VNF (Virtual Network Function) represents
the function to be virtualized.
Example-Virtual
Machine
Manages NFVI
Resource management of
Compute, Memory and Network
Creates end to end
services among VNFs
Virtual Network
Function
Orchestration
Two functions
Manages resources to be utilized among among VIMs
in case there are multiple VIMs in network
VNFC
NFVI
NFVI is the totality of all software and
hardware on which VNFs are built up
NFVI
Manages VNF- This can
be proprietry
Se-Ma
Or-Vi
NFV
Network Functions
Virtualization
SDN can be said as enabler for NFV
Element Management
System
Orchestration
VNF 1
SDN can make communication between Management/
Orchestration and VNFs more flexible and efficient.
EMS
Os-Ma
OSS/BSS
s s
Ba ition
fin
How SDN can
help NFV
Management through Open
Interface
NFV Management
& Orchestration
De
SDN makes it more efficient and flexible for VMs/VNFs to
communicate within same host or distributed host architecture
NF
Vr
wit elati
h S on
DN
SDN does not need NFV for its implementation and vice versa; but
if implemented together can synergize each other
Manages VNF
Virtual Network
Function Component
VNF can be composed of multiple
functions that together make the VNF
Functional View
of VNF
Some vendors may implement network element
as one VNF, others as collection of VNFCs
Five different types of
interfaces
Stands for NFV
Infrastructure
SWA-1
With other VNFs
SWA-2
Between VNFCs
SWA-3
Between VNF
Manager and VNFC
SWA-4
With element
Management system
SWA-5
With NFV
Infrastructure
Has three main
domains
Computational and
Storage resources
Direct vs Indirect
communication
Hypervisor communicate with NIC through vSwitch,
this could by severe performance issue
Hypervisor abstracts physical resources of compute domain
to virtual domain( virtual machine)
VNFC to VNFC communication if they
are geographically separated
Responsibility of different
communication like
Scenario 1
Compute domain
Hypervisor
domain
How VNFCs communicate
with one another
Description
Network Infrastructure
domain
There are
multiple ways
Through Hardware switch
Scenario 2
Through vSwitch in Hypervisor
Scenario 3
Through vSwitch enhanced in
performance by DPDK
Scenario 4 &5
Through eSwtich embedded in
NIC
Scenario 6
Direct serial bus
communication
Different ways to
communicate
VNF
Communication of Orch. And
Management with VNF/VNFC
Communication channel
between different VNFs
Virtual Machine
VNF is fully deployable on COTS
By COTS type
Virtual machine is the virtualization
container in which VNF/VNFC runs
COTS mean Commercial Off the
Shelf. For example x86 Server
Two types
Some VNFC still needs some
specialized hardware
Virtual Machine has processor, memory and NIC as a physical machine
has-Hypervisor creates virtual machine from physical machine
Hypervisor
Agnostic
By Virtualization
Environment ( By Hypervisor
and Container)
Broad network
access of NFVI
VNF depends on the hypervisor
environment it runs on
Hypervisor
dependant
On demand self
service in NFVI
End to End service should be possible through variaty of transport
media and through different networks
Higher layer container
dependant
5 essential characteristics of cloud
applied to NFVI ( as per NIST)
Not Elastic
NFVI should be able to support VNF of other operators-Multi Tenancy
Elastic up/down
Performance can be increased (up)
or decreased ( down)
Elastic in/out
VNFC can be added (in) or removed
(out)
By Elastic Nature
Rapid Elasticity of
NFVI
VNF is dependent on higher layer
container, for example Java environment
References
Types of VNF
Resource Pooling
Upscale, downscale of computing, storage and network resources
should be possible because of service load or power consumption
VNF can run in any
hypervisor
environment
1. ETSI GS NFV 002 V1.2.1 (2014-12)-NFV Architectural Framework
2. ETSI GS NFV-SWA 001 V1.1.1 (2014-12)- Virtual Network Functions Architecture
3. ETSI GS NFV-INF 001 V1.1.1 (2015-01)- Infrastructure Overview
4. ETSI GS NFV 001 V1.1.1 (2013-10)- Use Cases
Full Elastic
Both up/down and in/out is possible
Measured service in
NFVI
Increasing VNF
resilience
Distributed VNFs or VNFCs on
different hosts
For scalability and redundancy
purposes
Typically VNFs need layer 2 connectivity from
infrastructure , layer 3 is provided by VNF themselves
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Bio-Gro HyperGrowth Lean Mass FinalDocumento17 pagineBio-Gro HyperGrowth Lean Mass FinalMarcelo Calderón Cruz80% (5)
- The Order of Melchizedek by Francis Myles (Myles, Francis)Documento382 pagineThe Order of Melchizedek by Francis Myles (Myles, Francis)cap4090% (10)
- GOLDEN DAWN 1 10 The Banishing Ritual of HexagramDocumento4 pagineGOLDEN DAWN 1 10 The Banishing Ritual of HexagramF_RC86% (7)
- Implementation and Design Pfsense Based Intrusion Detection and Prevention System by Using SuricataDocumento32 pagineImplementation and Design Pfsense Based Intrusion Detection and Prevention System by Using SuricataYasir MehmoodNessuna valutazione finora
- Learning OpenStack Networking (Neutron) - Second EditionDa EverandLearning OpenStack Networking (Neutron) - Second EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Cisco NX-OS Software ArchitectureDocumento69 pagineCisco NX-OS Software ArchitectureBakre21100% (1)
- IPv6: Compare Cisco NAT-PT Vs NAT64. With Configuration Examples and DNS64.Documento40 pagineIPv6: Compare Cisco NAT-PT Vs NAT64. With Configuration Examples and DNS64.Gianrico Fichera100% (2)
- Wso2 Pricing Eur 2019 - 08 - 01Documento18 pagineWso2 Pricing Eur 2019 - 08 - 01MrProkeska100% (1)
- Sd-Wan Velocloud by VmwareDocumento8 pagineSd-Wan Velocloud by VmwareDenis OuNessuna valutazione finora
- OSI Layers Model Network AssociatesDocumento1 paginaOSI Layers Model Network Associatesacademy100% (15)
- LLM01v5 0Documento12 pagineLLM01v5 0Alan LeungNessuna valutazione finora
- CHAPTER VI-Design of Stair, Ramp & Lift CoreDocumento15 pagineCHAPTER VI-Design of Stair, Ramp & Lift CoreMahmudul HasanNessuna valutazione finora
- LearnAbout NFVDocumento10 pagineLearnAbout NFVAhmed SharifNessuna valutazione finora
- Mastering Python Network Automation: Automating Container Orchestration, Configuration, and Networking with Terraform, Calico, HAProxy, and IstioDa EverandMastering Python Network Automation: Automating Container Orchestration, Configuration, and Networking with Terraform, Calico, HAProxy, and IstioNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Sdns and NFV: Jorge Bernal Bernabe, PHDDocumento50 pagineIntroduction To Sdns and NFV: Jorge Bernal Bernabe, PHDMelwin SyafrizalNessuna valutazione finora
- 01 ENSP Study GuideDocumento45 pagine01 ENSP Study GuidesatourismNessuna valutazione finora
- Avaya One X Communicator 6Documento66 pagineAvaya One X Communicator 6malar1900Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mistral Introduction OpenStack MeetupDocumento18 pagineMistral Introduction OpenStack MeetupArun SomashekarNessuna valutazione finora
- Virtualization Technologies in Networking: ITP4111 Open Standards NetworkingDocumento88 pagineVirtualization Technologies in Networking: ITP4111 Open Standards NetworkingdieloNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To NFVDocumento14 pagineIntroduction To NFVToure VacabaNessuna valutazione finora
- Riverbed SD-WAN: Ricky Lin, CCIE#7469, MBA Deputy CTODocumento26 pagineRiverbed SD-WAN: Ricky Lin, CCIE#7469, MBA Deputy CTOjmbrhnNessuna valutazione finora
- vEPC Solutions Guide 10.0 PDFDocumento16 paginevEPC Solutions Guide 10.0 PDFvallala venkateshNessuna valutazione finora
- L2VPN Docsis PDFDocumento63 pagineL2VPN Docsis PDFTiago SoaresNessuna valutazione finora
- ETSI Worshop - Huawei - Marcelo BrazaoDocumento27 pagineETSI Worshop - Huawei - Marcelo BrazaoAbdullah N. DwairyNessuna valutazione finora
- NFV-Thesis Kalliosaari Metropolia-V2 PDFDocumento55 pagineNFV-Thesis Kalliosaari Metropolia-V2 PDFJuanMateoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cisco Overlay TechnologyDocumento19 pagineCisco Overlay TechnologyRajatNessuna valutazione finora
- Openstack & Object Intro: Chesapeake Regional Ses Feb 2015Documento19 pagineOpenstack & Object Intro: Chesapeake Regional Ses Feb 2015netapp000444Nessuna valutazione finora
- PCRF Information Gateway 2015 Issue 03 (Cell Congestion Feature)Documento1 paginaPCRF Information Gateway 2015 Issue 03 (Cell Congestion Feature)firasibraheemNessuna valutazione finora
- 3D Cisco Icon Library v3.1Documento27 pagine3D Cisco Icon Library v3.1Karl KugelhagelNessuna valutazione finora
- Vmware Vcloud NFV Solution Brief - 49528 PDFDocumento15 pagineVmware Vcloud NFV Solution Brief - 49528 PDFkallolshyam.roy2811Nessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Cloud ComputingDocumento21 pagineWhat Is Cloud ComputinganilkarriiNessuna valutazione finora
- VeloCloud Metzler Mock SD-WAN RFIDocumento11 pagineVeloCloud Metzler Mock SD-WAN RFIeleazar_lostNessuna valutazione finora
- Ebook SDWAN When The Internet Becomes The Network 2Documento14 pagineEbook SDWAN When The Internet Becomes The Network 2Razvan FilipNessuna valutazione finora
- Learning OpenStack Networking (Neutron) Sample ChapterDocumento18 pagineLearning OpenStack Networking (Neutron) Sample ChapterPackt PublishingNessuna valutazione finora
- Design and Deployment of The ASR5500 PDFDocumento51 pagineDesign and Deployment of The ASR5500 PDFsafyh2005Nessuna valutazione finora
- SDN and NFV - Affirmed NetworksDocumento4 pagineSDN and NFV - Affirmed NetworkshelbakouryNessuna valutazione finora
- BRKSPM 2074Documento74 pagineBRKSPM 2074dembi86Nessuna valutazione finora
- Does Your PCRF Have What It Takes For VoLTE - WhitepaperDocumento10 pagineDoes Your PCRF Have What It Takes For VoLTE - WhitepaperJordan RashevNessuna valutazione finora
- Sflow Technology White Paper: Huawei Technologies Co., LTDDocumento11 pagineSflow Technology White Paper: Huawei Technologies Co., LTDLeo LimaNessuna valutazione finora
- NFV Management and OrchestrationDocumento14 pagineNFV Management and OrchestrationMasood SabriNessuna valutazione finora
- Core Network Migration PathsDocumento3 pagineCore Network Migration PathsGGSNNessuna valutazione finora
- Designing and Building A Campus Wireless Network 2012 v2Documento13 pagineDesigning and Building A Campus Wireless Network 2012 v2ulexoxNessuna valutazione finora
- 05 - SecurityDocumento59 pagine05 - SecurityashooNessuna valutazione finora
- NANOG32 BGP Multihoming PDFDocumento282 pagineNANOG32 BGP Multihoming PDFNixbie (Pemula yg serba Kepo)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cisco SD-WAN Application BRKRST-2514Documento47 pagineCisco SD-WAN Application BRKRST-2514Aaron Reyes SanchezNessuna valutazione finora
- Cisco SD-WAN: Securely Connect Any User To Any Application Across Any Platform, All With A Consistent User ExperienceDocumento7 pagineCisco SD-WAN: Securely Connect Any User To Any Application Across Any Platform, All With A Consistent User ExperienceSayed Ashraf Husaini Kazi100% (1)
- Cloud Service Concept and ValueDocumento86 pagineCloud Service Concept and ValueMarco MarcoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ie HQ DCF LLD V12Documento111 pagineIe HQ DCF LLD V12gebruNessuna valutazione finora
- B1 - Overlay Virtual Networking and SDDCDocumento278 pagineB1 - Overlay Virtual Networking and SDDCdownloadpostaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cisco Switch 9300 - DatasheetDocumento61 pagineCisco Switch 9300 - DatasheetJose RojasNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding Carrier Ethernet ThroughputDocumento22 pagineUnderstanding Carrier Ethernet Throughputexplorenet7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Asr9k NCS5000Documento17 pagineAsr9k NCS5000RobertAlSafiNessuna valutazione finora
- MSTP Network DesignDocumento86 pagineMSTP Network Designshahramkarimi76100% (1)
- Deployment Case Study of SDN and NFV TransformationDocumento25 pagineDeployment Case Study of SDN and NFV Transformationhector_ninoskaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nokia Mobile Packet Backbone Network White PaperDocumento8 pagineNokia Mobile Packet Backbone Network White PaperR.s. FélixNessuna valutazione finora
- Cisco Preferred Arch For Enterprise Collab 12.0 CVDDocumento402 pagineCisco Preferred Arch For Enterprise Collab 12.0 CVDMuhammad ShahzadNessuna valutazione finora
- Networking 201-400 Practice Questions - PDF + Online Practice TestDocumento11 pagineNetworking 201-400 Practice Questions - PDF + Online Practice TestDumps LandNessuna valutazione finora
- <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <HTML><HEAD><META HTTP-EQUIV="Content-Type" CONTENT="text/html; charset=iso-8859-1"> <TITLE>ERROR: The requested URL could not be retrieved</TITLE> <STYLE type="text/css"><!--BODY{background-color:#ffffff;font-family:verdana,sans-serif}PRE{font-family:sans-serif}--></STYLE> </HEAD><BODY> <H1>ERROR</H1> <H2>The requested URL could not be retrieved</H2> <HR noshade size="1px"> <P> While trying to process the request: <PRE> TEXT http://www.scribd.com/titlecleaner?title=4gwireless-100512064142-phpapp02.ppt HTTP/1.1 Host: www.scribd.com Proxy-Connection: keep-alive Proxy-Authorization: Basic bWFuaXNoYTpxd2VydHk= Accept: */* Origin: http://www.scribd.com X-CSRF-Token: 8444de8a4418e0bef1686d64a1ce88a986cb9f10 User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.31 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/26.0.1410.43 Safari/537.31 X-Requested-With: XMLHttpRequest Referer: htDocumento31 pagine<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <HTML><HEAD><META HTTP-EQUIV="Content-Type" CONTENT="text/html; charset=iso-8859-1"> <TITLE>ERROR: The requested URL could not be retrieved</TITLE> <STYLE type="text/css"><!--BODY{background-color:#ffffff;font-family:verdana,sans-serif}PRE{font-family:sans-serif}--></STYLE> </HEAD><BODY> <H1>ERROR</H1> <H2>The requested URL could not be retrieved</H2> <HR noshade size="1px"> <P> While trying to process the request: <PRE> TEXT http://www.scribd.com/titlecleaner?title=4gwireless-100512064142-phpapp02.ppt HTTP/1.1 Host: www.scribd.com Proxy-Connection: keep-alive Proxy-Authorization: Basic bWFuaXNoYTpxd2VydHk= Accept: */* Origin: http://www.scribd.com X-CSRF-Token: 8444de8a4418e0bef1686d64a1ce88a986cb9f10 User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.31 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/26.0.1410.43 Safari/537.31 X-Requested-With: XMLHttpRequest Referer: htPrerna LakhotiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Secure Data Center Design Piotr Wojciechowski Ccie 25543Documento66 pagineSecure Data Center Design Piotr Wojciechowski Ccie 25543Javed HashmiNessuna valutazione finora
- Network Functions Virtualization (NFV) With A Touch of SDNDocumento1 paginaNetwork Functions Virtualization (NFV) With A Touch of SDNJuanKNessuna valutazione finora
- HCIA-Cloud Service V2.2 Lab Guide1Documento206 pagineHCIA-Cloud Service V2.2 Lab Guide1RCM LoaderNessuna valutazione finora
- Troubleshooting Cisco 3800 Series RoutersDocumento14 pagineTroubleshooting Cisco 3800 Series RouterskalemgiNessuna valutazione finora
- Cisco Netflow ConfigurationDocumento19 pagineCisco Netflow Configurationfabio almeidaNessuna valutazione finora
- Eudemon Basic Function and Configuration: Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. All Rights ReservedDocumento32 pagineEudemon Basic Function and Configuration: Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. All Rights ReservedCarlos Carlinhos100% (3)
- SDN Wan Orchestration Principles and Solutions: Ciscolive 2015 - San Diego Tecmpl-3200Documento195 pagineSDN Wan Orchestration Principles and Solutions: Ciscolive 2015 - San Diego Tecmpl-3200trbvmsNessuna valutazione finora
- CFM TutorialDocumento56 pagineCFM TutorialSaurabhNessuna valutazione finora
- PCSDocumento11 paginePCSSaurabhNessuna valutazione finora
- PCSDocumento11 paginePCSSaurabhNessuna valutazione finora
- NFVDocumento1 paginaNFVSaurabhNessuna valutazione finora
- VT Cac ChecksDocumento4 pagineVT Cac ChecksSaurabhNessuna valutazione finora
- Eye Pattern AgilentDocumento13 pagineEye Pattern AgilentSaurabhNessuna valutazione finora
- Extreme Broadband Testing: The Adtech AX/4000 Broadband Test SystemDocumento17 pagineExtreme Broadband Testing: The Adtech AX/4000 Broadband Test SystemSaurabhNessuna valutazione finora
- Testing Fire-ProtectionDocumento2 pagineTesting Fire-Protectionmia murciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz13 130630200754 Phpapp02Documento10 pagineQuiz13 130630200754 Phpapp02anukrititiwaNessuna valutazione finora
- i1000SR System Quick Troubleshooting GuideDocumento2 paginei1000SR System Quick Troubleshooting GuideEarliNessuna valutazione finora
- Product Analysis Certificate: Propanol-2 (Iso-Propanol) A.RDocumento1 paginaProduct Analysis Certificate: Propanol-2 (Iso-Propanol) A.RAMMARNessuna valutazione finora
- User Manual For Emvólio: WWW - Blackfrog.InDocumento22 pagineUser Manual For Emvólio: WWW - Blackfrog.InmariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Samyung SI-30 ManualDocumento2 pagineSamyung SI-30 ManualYan Naing0% (1)
- Practice Tests - Tiếng Anh 7 I-learn Smart World TestDocumento9 paginePractice Tests - Tiếng Anh 7 I-learn Smart World TestnghiepNessuna valutazione finora
- Stephane Moses The Angel of History Rosenzweig Benjamin Scholem PDFDocumento196 pagineStephane Moses The Angel of History Rosenzweig Benjamin Scholem PDFlivehuman100% (3)
- Advent of SkyscrapersDocumento27 pagineAdvent of SkyscrapersJoshua AlboNessuna valutazione finora
- 1965 Elio R. Freni - Electrolytic Lead Refining in SardiniaDocumento9 pagine1965 Elio R. Freni - Electrolytic Lead Refining in SardiniaGeorgettaNessuna valutazione finora
- D 5431 - 93 Rdu0mzetotmDocumento4 pagineD 5431 - 93 Rdu0mzetotmJuanNessuna valutazione finora
- Drugs and Tinnitus - Neil Bauman PHD - April '09Documento2 pagineDrugs and Tinnitus - Neil Bauman PHD - April '09DownTheTheRabbitHole108Nessuna valutazione finora
- Daniel Madison - BreachDocumento8 pagineDaniel Madison - Breachmrbookman3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Proposed Revisions To Usp Sterile Product - Package Integrity EvaluationDocumento56 pagineProposed Revisions To Usp Sterile Product - Package Integrity EvaluationDarla Bala KishorNessuna valutazione finora
- Harmonization of HR Policies - RoughDocumento119 pagineHarmonization of HR Policies - RoughFrancis SoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Serial Interface RS485 (RS422) Configuration InstructionsDocumento20 pagineSerial Interface RS485 (RS422) Configuration Instructionsyana sopian hidayatNessuna valutazione finora
- Reading Week 13Documento6 pagineReading Week 13Quy PhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Nature Generator (Emtech Concept Paper)Documento3 pagineNature Generator (Emtech Concept Paper)Min SugaNessuna valutazione finora
- GTE LAB MANUAL Ver 4 - 1Documento135 pagineGTE LAB MANUAL Ver 4 - 1akhilaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Guardian Weekly 9-02-2024-2Documento64 pagineThe Guardian Weekly 9-02-2024-2krris.galNessuna valutazione finora
- PVC Duct DesignDocumento10 paginePVC Duct DesigncitramuaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Sustainability Schematic ReportDocumento5 pagineSustainability Schematic ReportsakhrNessuna valutazione finora
- Risk Assesment FOR PIPING WORKDocumento1 paginaRisk Assesment FOR PIPING WORKsunil100% (2)
- Business Description: Apollo TyresDocumento4 pagineBusiness Description: Apollo TyresSrijit SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Maximizing Bass Reflex System Performance Through Optimization ofDocumento32 pagineMaximizing Bass Reflex System Performance Through Optimization ofGilberto MontaniNessuna valutazione finora