Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Case Study Pcos
Caricato da
api-315331895Descrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Case Study Pcos
Caricato da
api-315331895Copyright:
Formati disponibili
Scholarly Assignment
1
Scholarly Assignment
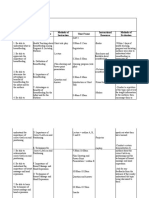
Concept Map:
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
Mark Kevin D. Sadiamona
N01036081
NURS 252
Vasanthy Harananan
March 14, 2016
Scholarly Assignment
Case Study
The scenario is all about a 28 year old Female client that arrives at wellness clinic
complaining about amenorrhea. The client is anxious and states that she and her husband have
been married for two years and want to start a family. The client has a medical history of
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS). Vital signs taken: T-36.8, P-88, R-22, BP-112/62, O2 Sat
99% on room air and has a CBG of 9.3.
Introduction
There are many important information that are given in the scenario, as a nurse I must
identify the most relevant priority data for the client. The resident was complaining about having
amenorrhea and according to the case study, she has a past medical history of Polycystic Ovarian
Syndrome (PCOS). Due to having history of PCOS, amenorrhea could be one of its symptoms
(Wang, 2008). Another information that is alarming is the clients complete blood glucose level
of 9.3mmol/L. The normal range for blood glucose is between 4-7mmol/L (Lewis, 2014). A 9.3
mmol/L is high for a normal person. But Insulin resistance is also one of the clinical
manifestations for PCOS (Wang, 2008). This could be one of the reasons why her blood sugar is
higher than the normal range. Another concern of the client is she wanted to start a family after
her 2 years of marriage with her husband. In her situation, it is hard for them to start a family
because women with PCOS have difficulties in ovulation because of their irregular or sometimes
absent menstruation (Wang, 2008). Another main concern is the client being anxious. Anxiety
can be harmful if not treated or prevented but in my opinion, Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome has a
higher priority than anxiety.
Scholarly Assignment
Body
Pathophysiology
The highest priority highlighted in my concept map is Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
(PCOS). I chose it as a priority over anxiety because it has variety of clinical manifestations that
are very important such as insulin resistance, excess androgens in the body, and irregular or
absent menstruation. These manifestations of PCOS can lead into so many complications like
diabetes and deferred ovulation process. Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome is a common endocrine
disorder among women who are of reproductive age. It affects womans menstrual cycle, ability
to have children, hormones, heart, blood vessels, and physical appearance. According to
womens health Canada, 1 in 10 childbearing women in Canada has PCOS (Stein, 2006). It is
almost 10% of women population in Canada alone. It is a serious condition that leads into so
many complications. Hormonal balance is a main underlying problem in PCOS (Gardner, 2009).
Production of insulin is one of the biggest problems in PCOS. It is a hormone that controls sugar,
starches, and other food energy in our body. (Lewis, 2014). Patients with PCOS have excessive
amount of insulin in their bodies because they have problems using it. Producing too much
insulin appears to increase production of androgen. Androgen levels can lead to unnecessary hair
growth, problem in ovulation, and acne. The main complication that excessive production of
insulin causes is Diabetes.
Clinical Manifestation
There are so many manifestations of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS), but the main
important one is insulin resistance. As what I have said in the pathophysiology, hormonal balance
is the main underlying problem in PCOS. Women with PCOS do not have control in their insulin
Scholarly Assignment
which causes uncontrolled sugar levels. Due to this, complications such as diabetes arises.
Diabetes is chronic and sometimes fatal disease which a persons body either cannot use the
insulin properly or cannot produce insulin. According to Canadian Diabetes Association, there
are more than 20 Million Canadians living with diabetes. I highlighted the risk of developing
diabetes in my concept map as the highest priority because the complete blood glucose level of
the client is higher than the normal range. It is an important piece of information because it gives
idea that she could develop diabetes mellitus type 2. Especially she is only 28 years old which is
the least age group of people having type 2 diabetes mellitus. According to Canadian Diabetes
Association, 45-64 years old are the most diagnosed age group for diabetes. It is important to
intervene the development of diabetes mellitus type 2 for the client as soon as possible. If the
development of diabetes continues, it will lead to so many complications such as; chronic kidney
disease, stroke, heart attack, and risk for infections. These diabetes-related complications are
serious and even life threatening. It is a priority and should be prevented.
Nursing Interventions
In order to prevent the development of diabetes, a nurse must plan interventions. I as a
nurse to the given scenario, I provided series of interventions. First intervention is to instruct the
client to monitor glucose levels with glucometer at regular intervals to identify and respond early
to fluctuation in glucose levels that occur outside the normal parameters (4-7mmol/L) (Sparks,
2014). This first intervention helps to monitor the sugar levels in timely manner so that if ever
sugar levels go high or low, actions such as providing orange juice for a low sugar level and
administering insulin for high sugar level will be implemented right away. Another intervention
is to assess for underlying cause of elevated serum glucose levels including PCOS, dietary
intake, and lifestyle(Sparks, 2014). It is important to do this to prevent future episodes and to
Scholarly Assignment
know what triggers the high or low sugar levels. The third intervention is to assess the clients
knowledge of hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia to ensure adequate management and prevent
future episode. It is important if the client knows what and how to do if ever hyperglycemia or
hypoglycemia occurs. Assessing the clients knowledge give an idea to the nurse if the client has
a self-care deficit. If a client has lack of knowledge, she might have some problems taking care
of herself especially if administering insulin. The fourth intervention is to teach the patient to
follow a diet that is low in simple sugars, low in fat, and high in fiber and whole grains to control
cholesterol and triglycerides (Sparks, 2014). Following a healthy diet provides so many benefits
in the body. Controlling cholesterol and triglycerides in the body can prevent diabetes related
complications like myocardial infarction. Lastly, Promote exercise routine. Working muscles
more often improves insulin use and absorb glucose.
Conclusion
There are so many important information given in the case study and it is imperative to
use critical thinking. Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome is the main priority in the scenario because it
could trigger so many complications and one of them is diabetes. Diabetes is the most important
clinical manifestation of PCOS because it can be chronic or life-long disease. Interventions such
as monitoring sugar levels, assessing elevated serum levels, assessing patients knowledge
regarding diabetes, and maintaining a healthy diet are necessary to prevent the development of
diabetes.
Scholarly Assignment
References:
Azziz R., Carmina E., Dewailly D, et al. The Androgen Excess and PCOS Society criteria for the
polycystic ovary syndrome:the complete task force report. Fertil Steril. 2009
Feb.91(2):456-88
Wang JG, Lobo RA. The complex relationship between hypothalamic amenorrhea and
polycystic ovary syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008 Apr. 93(4):1394-7.
Stein F., Leventhal M. Amenorrhea associated with bilateral polycystic ovaries
Am J Obstet Gynecol, 29 (1935), pp. 181191.
Lewis, S. L. (2014). Medical-Surgical Nursing in Canada, 3rd Edition.
[VitalSource Bookshelf Online]. Retrieved from
https://pageburstls.elsevier.com/#/books/978-1-926648-70-5/.
Gardner, J. (2011). Hormonal Imbalance in Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome.
Greenspan's Basic andClinical Endocrinology. 9th edition New York: McGraw-Hill.
Sparks, S. (2014). Risk for Unstable Blood Glucose Level. Nursing Diagnosis Pocket Guide 2nd
Edition. Sparks & Taylor, pp. 31-32.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Pre-eclampsia, (Pregnancy with Hypertension And Proteinuria) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDa EverandPre-eclampsia, (Pregnancy with Hypertension And Proteinuria) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNessuna valutazione finora
- Pcos Case Study For Human DiseasesDocumento6 paginePcos Case Study For Human Diseasesapi-273353925Nessuna valutazione finora
- Xiii. Discharge Planning: Carbohydrates NutrientsDocumento4 pagineXiii. Discharge Planning: Carbohydrates Nutrientsgroupbsection1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Gary Fending For HimselfDocumento3 pagineGary Fending For HimselfPrincess Levie CenizaNessuna valutazione finora
- Persuasive Speech - RenielDocumento5 paginePersuasive Speech - RenielIsaiah Solano0% (1)
- Professional Gatekeeping As A Function of Role FidelityDocumento2 pagineProfessional Gatekeeping As A Function of Role FidelityNURSETOPNOTCHER100% (3)
- Thinking UpstreamDocumento1 paginaThinking UpstreamDONITA DALUMPINESNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of HyperbilirubinemiaDocumento3 paginePathophysiology of Hyperbilirubinemiaapi-434682657Nessuna valutazione finora
- Maternal and Child Check Up TestDocumento12 pagineMaternal and Child Check Up TestDENNIS N. MUÑOZNessuna valutazione finora
- Doh ProgramDocumento8 pagineDoh ProgramSheril Sularte CasanesNessuna valutazione finora
- PREECLAMPSIA Case ScenarioDocumento2 paginePREECLAMPSIA Case Scenariosabao kizuiteNessuna valutazione finora
- Gestational Diabetes MellitusDocumento73 pagineGestational Diabetes Mellitusreniere lagazoNessuna valutazione finora
- NCM 107 LecDocumento16 pagineNCM 107 LecSheila May SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1: Introduction To Community Health Nursing Chapter 1: Fundamental Concepts of Community Health NursingDocumento140 pagineUnit 1: Introduction To Community Health Nursing Chapter 1: Fundamental Concepts of Community Health NursingChevelle Valenciano-GaanNessuna valutazione finora
- The Importance of Nursing Clinical JudgmentDocumento6 pagineThe Importance of Nursing Clinical Judgmentapi-545692127Nessuna valutazione finora
- Gerontologic Health Promotion ActivityDocumento3 pagineGerontologic Health Promotion ActivityCorinne50% (2)
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii Hemophilia: St. Paul College of Ilocos SurDocumento1 paginaNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii Hemophilia: St. Paul College of Ilocos SurCharina AubreyNessuna valutazione finora
- Brent Hospital and Colleges IncorporatedDocumento4 pagineBrent Hospital and Colleges Incorporateddaniel gariandoNessuna valutazione finora
- Concept MapDocumento2 pagineConcept Mapantherchio100% (2)
- COMMUNITY HEALTH NURSING CONCEPTS Topic 2Documento25 pagineCOMMUNITY HEALTH NURSING CONCEPTS Topic 2Ciedelle Honey Lou DimaligNessuna valutazione finora
- Case StudyDocumento4 pagineCase StudyYdynn Parejas GavinaNessuna valutazione finora
- CASE STUDY Labor and DeliveryDocumento2 pagineCASE STUDY Labor and DeliveryAprodite Sumod-ong100% (1)
- Neuro Vital SignsDocumento3 pagineNeuro Vital SignsKrissa Lei Pahang Razo100% (1)
- Birthing Beliefs in The PhilippinesDocumento2 pagineBirthing Beliefs in The PhilippinesJeeyan DelgadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Micronutrients and Pregnancy Outcome: A Review of The LiteratureDocumento1 paginaMicronutrients and Pregnancy Outcome: A Review of The LiteratureDenisse Shazz Mae MaretNessuna valutazione finora
- CP Preeclampsia RevisedDocumento32 pagineCP Preeclampsia RevisedTessa Grace PugonNessuna valutazione finora
- Severe PreeclampsiaDocumento84 pagineSevere PreeclampsiaJm Bernardo50% (2)
- Gestational Diabetes Mellitus - NISALDocumento7 pagineGestational Diabetes Mellitus - NISALKevin de SilvaNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Renal FailureDocumento1 paginaAcute Renal FailureSonia Letran Singson100% (1)
- Learning Packet in Level 2 RLE - RED: College of Nursing School Year 2020-2021Documento28 pagineLearning Packet in Level 2 RLE - RED: College of Nursing School Year 2020-2021Nur SetsuNessuna valutazione finora
- A Case Analysis OnDocumento27 pagineA Case Analysis Onbunso padillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing ReflectionDocumento5 pagineNursing Reflectionvrunda patelNessuna valutazione finora
- Soapie, Assessment and NCP On PAINDocumento7 pagineSoapie, Assessment and NCP On PAINAna100% (2)
- Diabetes Mellitus (Case Study)Documento13 pagineDiabetes Mellitus (Case Study)Narie TungpalanNessuna valutazione finora
- PPH Introduction 1Documento95 paginePPH Introduction 1regine maeNessuna valutazione finora
- Dysfunctional Labor and BirthDocumento167 pagineDysfunctional Labor and BirthKristel Joy Sarmiento AsuncionNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity 6 Case Study ONCOLOGY DUTYDocumento6 pagineActivity 6 Case Study ONCOLOGY DUTYSitty Aizah MangotaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Pres A1-RhdDocumento11 pagineCase Pres A1-RhdCharm TanyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Factors That Affect Normal Functioning of The Older PersonsDocumento7 pagineFactors That Affect Normal Functioning of The Older Personslouie john abilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Discharge PlanningDocumento2 pagineDischarge PlanningAthena Irish LastimosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pre EclampsiaDocumento45 paginePre EclampsiaYuri Iranda100% (1)
- CHAPTER 4-Atty AliboghaDocumento48 pagineCHAPTER 4-Atty AliboghaPaul EspinosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Family Health Assessment - EditedDocumento6 pagineFamily Health Assessment - EditedOnkwani DavidNessuna valutazione finora
- Care of Adults 26 Endocrine ManagementDocumento26 pagineCare of Adults 26 Endocrine ManagementGaras AnnaBerniceNessuna valutazione finora
- Far Eastern University: Evidence Based NursingDocumento5 pagineFar Eastern University: Evidence Based NursingandreaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Influence of Meal Frequency and Timing On Health in Humans: The Role of FastingDocumento19 pagineThe Influence of Meal Frequency and Timing On Health in Humans: The Role of FastingJosé Eduardo Zaragoza LópezNessuna valutazione finora
- The Program Proposal - DiabetesDocumento11 pagineThe Program Proposal - DiabetesRifa'atul Mahmudah100% (2)
- NCP 1Documento7 pagineNCP 1NataCo100% (1)
- 104-3 Journaling EssayDocumento6 pagine104-3 Journaling Essayapi-288504264Nessuna valutazione finora
- Learning Objectives Content Outline Methods of Instruction Time Frame Instructional Resources Methods of EvaluationDocumento3 pagineLearning Objectives Content Outline Methods of Instruction Time Frame Instructional Resources Methods of EvaluationteuuuuNessuna valutazione finora
- Madeleine Leininger and The Transcultural Theory of NursingDocumento8 pagineMadeleine Leininger and The Transcultural Theory of Nursingratna220693Nessuna valutazione finora
- NCP RenalDocumento22 pagineNCP Renalمحمود على ما تفرجNessuna valutazione finora
- RLE-level-2-packet-week-12-requirement (SANAANI, NUR-FATIMA, M.)Documento26 pagineRLE-level-2-packet-week-12-requirement (SANAANI, NUR-FATIMA, M.)Nur SanaaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Pre Term LaborDocumento3 paginePre Term LaborHazel Marie Echavez100% (1)
- Activity 2Documento7 pagineActivity 2Karen T. CeletariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gordon'S Functional Health Pattern Prior To Admission During Hospitalization Health Perception and Health ManagementDocumento3 pagineGordon'S Functional Health Pattern Prior To Admission During Hospitalization Health Perception and Health ManagementJordz PlaciNessuna valutazione finora
- Diabetes MellitusDocumento13 pagineDiabetes Mellitusdreneavalentinstefan100% (1)
- DM Type IiDocumento5 pagineDM Type IiKay Clarice G. TimosaNessuna valutazione finora
- COMMUNITY HEALTH NURSE: Passbooks Study GuideDa EverandCOMMUNITY HEALTH NURSE: Passbooks Study GuideNessuna valutazione finora
- Craigslist Cover LetterDocumento1 paginaCraigslist Cover Letterapi-315331895Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nurs 208 Fall 15 FinalDocumento25 pagineNurs 208 Fall 15 Finalapi-315331895Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nurs217 Ethics Course OutlineDocumento27 pagineNurs217 Ethics Course Outlineapi-315331895Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nurs 252 Course Outlines - Jan 4 2016 1 - 3Documento21 pagineNurs 252 Course Outlines - Jan 4 2016 1 - 3api-315331895Nessuna valutazione finora
- Winrer 2016 Course Outline Pregrad Nurs 253 1Documento20 pagineWinrer 2016 Course Outline Pregrad Nurs 253 1api-315331895Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cerebral Palsy Theory 3 EssayDocumento7 pagineCerebral Palsy Theory 3 Essayapi-315331895Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reflective PracticeDocumento7 pagineReflective Practiceapi-315331895Nessuna valutazione finora
- MaltreatmentDocumento7 pagineMaltreatmentapi-315331895Nessuna valutazione finora
- Student Project: Cutaneous Discoid LupusDocumento28 pagineStudent Project: Cutaneous Discoid LupusFaradilla Novita AnggreiniNessuna valutazione finora
- Anes PDFDocumento91 pagineAnes PDFBarda GulanNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment and Management of Patients With Hearing and Balance DisorderDocumento77 pagineAssessment and Management of Patients With Hearing and Balance DisorderKevin Dolok SaribuNessuna valutazione finora
- Efektifitas Spiritual Leadership Terhadap Kualitas Mutu Pelayanan KesehatanDocumento6 pagineEfektifitas Spiritual Leadership Terhadap Kualitas Mutu Pelayanan KesehatanHanifah DiahNessuna valutazione finora
- CEDH Syllabus - FinalDocumento8 pagineCEDH Syllabus - Finaldipgang7174Nessuna valutazione finora
- Zambia Study Dec 2019Documento9 pagineZambia Study Dec 2019AbiodunOlaiyaPaulNessuna valutazione finora
- Nurse ResumesDocumento4 pagineNurse ResumesPrincess Aira Bucag CarbonelNessuna valutazione finora
- The 1932 Cancer Cure - by Joseph GallgherDocumento9 pagineThe 1932 Cancer Cure - by Joseph GallgherJoseph Gallagher100% (3)
- H Dip Fam Med (SA) Past Papers - 2016 2nd Semester 24-1-2017Documento2 pagineH Dip Fam Med (SA) Past Papers - 2016 2nd Semester 24-1-2017matentenNessuna valutazione finora
- Running Head: Social Media and The Modern Impact of Informatics 1Documento3 pagineRunning Head: Social Media and The Modern Impact of Informatics 1danielNessuna valutazione finora
- I. LearningsDocumento5 pagineI. LearningsMarie Kelsey Acena MacaraigNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan: This Study Resource WasDocumento6 pagineNursing Care Plan: This Study Resource WasCristina BernardoNessuna valutazione finora
- Breastfeeding TPDocumento3 pagineBreastfeeding TPAndrea Mae SanchezNessuna valutazione finora
- DIABETES InfographicDocumento1 paginaDIABETES InfographicDail Xymere YamioNessuna valutazione finora
- Family Planning MethodDocumento4 pagineFamily Planning MethodJohn Patrick G. GuevarraNessuna valutazione finora
- Karwatzky ActivatorDocumento8 pagineKarwatzky ActivatorSankhyaNessuna valutazione finora
- GTD Case StudyDocumento9 pagineGTD Case StudyZnarf Izlah Sadanreb100% (1)
- M E W S: Mews (Odified Arly Arning Ystem) 3 2 1 0 1 2 3 ScoreDocumento1 paginaM E W S: Mews (Odified Arly Arning Ystem) 3 2 1 0 1 2 3 ScoreMimi SunaryantiNessuna valutazione finora
- Health Facilities and Services Regulatory Bureau: Republic of The Philippines Department of HealthDocumento1 paginaHealth Facilities and Services Regulatory Bureau: Republic of The Philippines Department of HealthPANACEE DIAGNOSTIC CENTERNessuna valutazione finora
- Air Borne DiseasesDocumento3 pagineAir Borne DiseasesMuhammad Anwar GulNessuna valutazione finora
- Books For Mrcog Part1Documento2 pagineBooks For Mrcog Part1srini100% (3)
- The Pre-Travel Consultation: An OverviewDocumento4 pagineThe Pre-Travel Consultation: An OverviewintanNessuna valutazione finora
- Why We Need Health Information Technology For Maintaining and Accessing Health Care Information 2157 7420.1000e103Documento2 pagineWhy We Need Health Information Technology For Maintaining and Accessing Health Care Information 2157 7420.1000e103Jake PendonNessuna valutazione finora
- Competency Assessment For Practicum Design RefDocumento7 pagineCompetency Assessment For Practicum Design RefEmmanuel OpiyoNessuna valutazione finora
- Mercy Drugs AbuseDocumento10 pagineMercy Drugs Abuseyaji ezraNessuna valutazione finora
- CIGNA Prior Approval FormDocumento1 paginaCIGNA Prior Approval FormDimitar FilevskiNessuna valutazione finora
- Health G7 Q4 SLM2Documento14 pagineHealth G7 Q4 SLM2arlene villenaNessuna valutazione finora
- My Personal Fitness Plan ProjectDocumento15 pagineMy Personal Fitness Plan Projectapi-568256870Nessuna valutazione finora
- Facial Nerve Palsy: Dr. Saud AlromaihDocumento74 pagineFacial Nerve Palsy: Dr. Saud AlromaihChandra ManapaNessuna valutazione finora
- HealthDocumento6 pagineHealthДария КоваленкоNessuna valutazione finora