Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Quantum Mechanics (QM Also Known As Quantum Physics or Quantum Theory) Including
Caricato da
ripple96960 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
8 visualizzazioni1 paginaQuantum mechanics is a fundamental branch of physics that describes processes involving atoms and photons, in which physical action occurs in integer multiples of the Planck constant, which classical physics cannot explain. It arose from Max Planck's work on black-body radiation in 1900 and Albert Einstein's 1905 paper on the photoelectric effect. The modern theory was formulated in the mid-1920s using mathematical functions like the wave function to describe the probability of physical properties. It has important applications including lasers, transistors, medical imaging, and explanations of biological and physical phenomena.
Descrizione originale:
Quantum Mechanics
Titolo originale
QM
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
RTF, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoQuantum mechanics is a fundamental branch of physics that describes processes involving atoms and photons, in which physical action occurs in integer multiples of the Planck constant, which classical physics cannot explain. It arose from Max Planck's work on black-body radiation in 1900 and Albert Einstein's 1905 paper on the photoelectric effect. The modern theory was formulated in the mid-1920s using mathematical functions like the wave function to describe the probability of physical properties. It has important applications including lasers, transistors, medical imaging, and explanations of biological and physical phenomena.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato RTF, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
8 visualizzazioni1 paginaQuantum Mechanics (QM Also Known As Quantum Physics or Quantum Theory) Including
Caricato da
ripple9696Quantum mechanics is a fundamental branch of physics that describes processes involving atoms and photons, in which physical action occurs in integer multiples of the Planck constant, which classical physics cannot explain. It arose from Max Planck's work on black-body radiation in 1900 and Albert Einstein's 1905 paper on the photoelectric effect. The modern theory was formulated in the mid-1920s using mathematical functions like the wave function to describe the probability of physical properties. It has important applications including lasers, transistors, medical imaging, and explanations of biological and physical phenomena.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato RTF, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 1
Quantum mechanics (QM; also known as quantum physics or quantum
theory) including quantum field theory, is a fundamental branch ofphysics
concerned with processes involving, for example, atoms and photons. In
such processes, said to be quantized, the action has been observed to be
only in integer multiples of the Planck constant, a physical quantity that is
exceedingly, indeed perhaps ultimately, small. This is utterly inexplicable in
classical physics.
Quantum mechanics gradually arose from Max Planck's solution in 1900 to
the black-body radiation problem (reported 1859) and Albert Einstein's
1905 paper which offered a quantum-based theory to explain the
photoelectric effect (reported 1887). Early quantum theory was profoundly
reconceived in the mid-1920s.
The reconceived theory is formulated in various specially developed
mathematical formalisms. In one of them, a mathematical function, thewave
function, provides information about the probability amplitude of position,
momentum, and other physical properties of a particle.
Important applications of quantum mechanical theory include
superconducting magnets, light-emitting diodes and the laser, the transistor
andsemiconductors such as the microprocessor, medical and research
imaging such as magnetic resonance imaging and electron microscopy,
and explanations for many biological and physical phenomena.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Quantum physics and its revolution on classical physics.: Quantum physicsDa EverandQuantum physics and its revolution on classical physics.: Quantum physicsNessuna valutazione finora
- Quantum Mechanics (QM Also Known As Quantum Physics or Quantum Theory), IncludingDocumento1 paginaQuantum Mechanics (QM Also Known As Quantum Physics or Quantum Theory), Includingalokesh1982Nessuna valutazione finora
- Quantum MechanicsDocumento1 paginaQuantum MechanicsSatya ViknesrajNessuna valutazione finora
- Quantum Mechanics - DescriptionDocumento2 pagineQuantum Mechanics - DescriptionRafael Nascimento100% (1)
- Quantum MechanicsDocumento1 paginaQuantum MechanicsGuan LimNessuna valutazione finora
- Quantum Mechanics For DummiesDocumento2 pagineQuantum Mechanics For DummiesDragonsTotallyRockNessuna valutazione finora
- Quantum Mechanics - FieldDocumento10 pagineQuantum Mechanics - FieldRafael NascimentoNessuna valutazione finora
- Difference Between Classical Physics and Modern PhysicsDocumento7 pagineDifference Between Classical Physics and Modern PhysicsSyed Qassam Mustafa SadiqullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Quantum Mechanics: For A Generally Accessible and Less Technical Introduction To The Topic, SeeDocumento2 pagineQuantum Mechanics: For A Generally Accessible and Less Technical Introduction To The Topic, Seenelkon505Nessuna valutazione finora
- Quantum Optics: An Introduction: Min Raj LamsalDocumento4 pagineQuantum Optics: An Introduction: Min Raj Lamsalhelen shumyeNessuna valutazione finora
- Quantum in EdDocumento9 pagineQuantum in EdmoonthinkerNessuna valutazione finora
- Quantum Mechanics (QM Also Known Theory), Including Quantum Field TheoryDocumento26 pagineQuantum Mechanics (QM Also Known Theory), Including Quantum Field TheoryRojas UnmsmNessuna valutazione finora
- It Is A New Set of Ideas That Explain Physical Processes Incomprehensible To ObjectsDocumento10 pagineIt Is A New Set of Ideas That Explain Physical Processes Incomprehensible To ObjectsEva BarojasNessuna valutazione finora
- Text I: Classical Mechanics Describes The Motion of Macroscopic Objects, From Projectiles ToDocumento22 pagineText I: Classical Mechanics Describes The Motion of Macroscopic Objects, From Projectiles ToCaraiman GeorgeNessuna valutazione finora
- The Concept of The PhotonDocumento10 pagineThe Concept of The PhotonDouglas Delgado de SouzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Modern PhysicsDocumento1 paginaModern PhysicsMarko MarićNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction of Quantum MechanicsDocumento2 pagineIntroduction of Quantum MechanicsAnand Verma0% (1)
- Quantum MechanicsDocumento2 pagineQuantum MechanicsfloresprincereisterNessuna valutazione finora
- Quantum Mechanics (QM Also Known As Quantum Physics, Quantum Theory, The Wave Mechanical Model and Matrix Mechanics), IncludingDocumento1 paginaQuantum Mechanics (QM Also Known As Quantum Physics, Quantum Theory, The Wave Mechanical Model and Matrix Mechanics), IncludingkamolkanonNessuna valutazione finora
- Classical Physics Versus Quantum PhysicsDocumento10 pagineClassical Physics Versus Quantum Physicsjoff_grNessuna valutazione finora
- Application of Quantum Mechanics ProjectDocumento10 pagineApplication of Quantum Mechanics Projectpraiseharrison419Nessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment OriginalDocumento14 pagineAssignment OriginalSunilNessuna valutazione finora
- Classical Physcisvs Quantum PhysicsDocumento8 pagineClassical Physcisvs Quantum PhysicsIchlasulNessuna valutazione finora
- Classical Mechanics - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocumento13 pagineClassical Mechanics - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediad_richard_dNessuna valutazione finora
- Quantum TheoryDocumento5 pagineQuantum TheoryagileengrNessuna valutazione finora
- Quantum TheoryDocumento2 pagineQuantum TheoryJaspreet Singh ChopraNessuna valutazione finora
- Quantum Field Theory - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocumento18 pagineQuantum Field Theory - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaShiva MohammadzadehNessuna valutazione finora
- Quantum Mechanics - Britannica Online Encyclopedia PDFDocumento29 pagineQuantum Mechanics - Britannica Online Encyclopedia PDFMahesh MaheshwariNessuna valutazione finora
- Quantum Field Theory - WikipediaDocumento167 pagineQuantum Field Theory - WikipediaOzhenNessuna valutazione finora
- Quantum MechanicsDocumento6 pagineQuantum MechanicsJehison ManquilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Quantum MeachanicsDocumento1 paginaIntroduction To Quantum MeachanicsShashi SolankiNessuna valutazione finora
- Wave Trough: Electric ForceDocumento12 pagineWave Trough: Electric ForcemichsantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Particle & Quantum PhysicsDocumento2 pagineParticle & Quantum PhysicsSudhanshu SrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- Third LawDocumento8 pagineThird LawChristeen GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocumento9 pagineNew Microsoft Word DocumentAritra SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- One Hundred Years of Quantum Physics: Daniel Kleppner and Roman Jackiw Massachusetts Institute of TechnologyDocumento12 pagineOne Hundred Years of Quantum Physics: Daniel Kleppner and Roman Jackiw Massachusetts Institute of TechnologytestNessuna valutazione finora
- From The MarsDocumento3 pagineFrom The Marswaboce1918Nessuna valutazione finora
- Etymology and Discovery: Quantum QuantaDocumento2 pagineEtymology and Discovery: Quantum QuantaMasterclassNessuna valutazione finora
- Etymology and Discovery: Quantum QuantaDocumento2 pagineEtymology and Discovery: Quantum QuantaMasterclassNessuna valutazione finora
- Name-Arpit Goyal REG. NO.-20BIT0054 Course Code-Phy1701: TOPIC: Importance of Quantum Mechanics in The Modern WorldDocumento5 pagineName-Arpit Goyal REG. NO.-20BIT0054 Course Code-Phy1701: TOPIC: Importance of Quantum Mechanics in The Modern WorldarpitNessuna valutazione finora
- Quantum Field TheoryDocumento24 pagineQuantum Field TheoryYolanda DidouNessuna valutazione finora
- Tarasov QMDocumento272 pagineTarasov QMmarceloNessuna valutazione finora
- ND Less Technical Introduction To The...Documento6 pagineND Less Technical Introduction To The...Ashwani KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Quantum Causality, Decoherence, Trajectories and InformationDocumento75 pagineQuantum Causality, Decoherence, Trajectories and InformationshiravandNessuna valutazione finora
- Quantum MechanicsDocumento21 pagineQuantum MechanicsRahul SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Modern Physics: Modern Physics History of Special Relativity History of Quantum MechanicsDocumento2 pagineModern Physics: Modern Physics History of Special Relativity History of Quantum MechanicsSjhon Miguel PerolinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanics QuantumDocumento1 paginaMechanics QuantumStardragonNessuna valutazione finora
- 7419 Et Et PDFDocumento19 pagine7419 Et Et PDFPuja NepalNessuna valutazione finora
- Cabang Ilmu Fisika (Pertemuan 2)Documento22 pagineCabang Ilmu Fisika (Pertemuan 2)alfi_hamidahNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics EssayDocumento2 paginePhysics EssayAmirtha VarshiniNessuna valutazione finora
- New Approach To Quantum Electrodynamics: Special ReportDocumento35 pagineNew Approach To Quantum Electrodynamics: Special ReportbehsharifiNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocumento15 paginePhysics: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaSammy JoshuaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Methodology of PhysicsDocumento3 pagineThe Methodology of Physicsnikita bajpaiNessuna valutazione finora
- PhotonDocumento2 paginePhotonfunmastiNessuna valutazione finora
- QM Lecture Notes 1Documento41 pagineQM Lecture Notes 1Dhruv DesaiNessuna valutazione finora
- College of Science: Physics DepartmentDocumento3 pagineCollege of Science: Physics DepartmentMaryam Al KathiriNessuna valutazione finora
- Field of PhysicDocumento5 pagineField of PhysicutpNessuna valutazione finora
- Quantum Chemistry ReviewDocumento7 pagineQuantum Chemistry ReviewElizabeth NagedNessuna valutazione finora
- Keys 2 Cognition - Cognitive ProcessesDocumento2 pagineKeys 2 Cognition - Cognitive Processesripple9696Nessuna valutazione finora
- Stoicism PDFDocumento16 pagineStoicism PDFripple9696Nessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus PACS10 Fa10Documento8 pagineSyllabus PACS10 Fa10ripple9696Nessuna valutazione finora
- Jacek MDocumento1 paginaJacek Mripple9696Nessuna valutazione finora
- Paul Wittgenstein Early LifeDocumento1 paginaPaul Wittgenstein Early Liferipple9696Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ans Sheet Chemical 23111Documento96 pagineAns Sheet Chemical 23111Aejaz MujawarNessuna valutazione finora
- Real Time EvaluationDocumento3 pagineReal Time Evaluationأيوب علاءNessuna valutazione finora
- Wel-Come: Heat Treatment Process (TTT, CCT & CCR)Documento14 pagineWel-Come: Heat Treatment Process (TTT, CCT & CCR)atulkumargaur26Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Zombie in The Brain and The Woman Who Died LaughingDocumento40 pagineThe Zombie in The Brain and The Woman Who Died Laughingcory_ruda100% (1)
- Sail ProjectDocumento28 pagineSail ProjectShahbaz AlamNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 3 Passive Heating 8.3.18Documento63 pagineModule 3 Passive Heating 8.3.18Aman KashyapNessuna valutazione finora
- Parle G ReportDocumento7 pagineParle G ReportnikhilNessuna valutazione finora
- Nama Anggota: Dede Wiyanto Endri Murni Hati Rukhi Hasibah Tugas: Bahasa Inggris (Narrative Text)Documento3 pagineNama Anggota: Dede Wiyanto Endri Murni Hati Rukhi Hasibah Tugas: Bahasa Inggris (Narrative Text)Wiyan Alwaysfans CheLseaNessuna valutazione finora
- UntitledDocumento8 pagineUntitledapi-86749355Nessuna valutazione finora
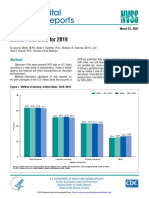
- National Vital Statistics Reports: Births: Final Data For 2019Documento51 pagineNational Vital Statistics Reports: Births: Final Data For 2019Simon ReichNessuna valutazione finora
- Leadership Roles and Management Functions in Nursing Theory and ApplicationDocumento2 pagineLeadership Roles and Management Functions in Nursing Theory and Applicationivan0% (3)
- Rev C Diagnostic Repair Manual AC Evolution 1.0 2.0 50 60 HZDocumento254 pagineRev C Diagnostic Repair Manual AC Evolution 1.0 2.0 50 60 HZVariACK100% (1)
- Monthly Hse Report Nhai Org inDocumento12 pagineMonthly Hse Report Nhai Org inPhilip S. GongarNessuna valutazione finora
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocumento1 paginaDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesAre Em GeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Tokyo Fact SheetDocumento17 pagineTokyo Fact Sheethoangnguyen2401Nessuna valutazione finora
- Permatex, Inc - Ultra Gasket Sealant 1ozDocumento3 paginePermatex, Inc - Ultra Gasket Sealant 1ozjaredf@jfelectric.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Competency Competency Multiple Choice Multiple Choice ComputationDocumento4 pagineCompetency Competency Multiple Choice Multiple Choice ComputationAaron James LicoNessuna valutazione finora
- Doppler EffectDocumento47 pagineDoppler EffectLouies UngriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Anatomy and Physiology ReviewDocumento20 pagineBlood Anatomy and Physiology ReviewStacey CamilleNessuna valutazione finora
- Refuse Chute PPT 01Documento11 pagineRefuse Chute PPT 01sanika shindeNessuna valutazione finora
- Key Nursing SkillsDocumento359 pagineKey Nursing Skillsmordanga100% (6)
- Pathology SEQ Answers - Adaptive Responses & Cell InjuryDocumento7 paginePathology SEQ Answers - Adaptive Responses & Cell InjurysugandiNessuna valutazione finora
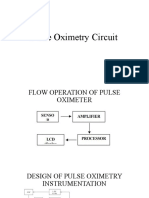
- Pulse Oximetry CircuitDocumento19 paginePulse Oximetry Circuitنواف الجهنيNessuna valutazione finora
- Treeleaf Basic Zazen InstructionsDocumento16 pagineTreeleaf Basic Zazen InstructionsFaisal sarhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Fire CodeDocumento1 paginaFire CodeShainette VillarazaNessuna valutazione finora
- Textile Chemical Brochure 8.6.22 - 031Documento1 paginaTextile Chemical Brochure 8.6.22 - 031NIKESH PRAKASHNessuna valutazione finora
- Marpappa EASADocumento5 pagineMarpappa EASAAshley SamNessuna valutazione finora
- WW.04.05 Contraction Stress Test (Oxytocin Challenge Test) PDFDocumento3 pagineWW.04.05 Contraction Stress Test (Oxytocin Challenge Test) PDFDiah Kurniawati100% (1)
- 200 State Council Members 2010Documento21 pagine200 State Council Members 2010madhu kanna100% (1)
- Indian Income Tax Return Acknowledgement: Do Not Send This Acknowledgement To CPC, BengaluruDocumento1 paginaIndian Income Tax Return Acknowledgement: Do Not Send This Acknowledgement To CPC, BengaluruDrsex DrsexNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingDa EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (5)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesDa EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (2193)
- Giza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyDa EverandGiza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyNessuna valutazione finora
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseDa EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (69)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldDa EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (64)
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceDa EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (51)
- The Beauty of Falling: A Life in Pursuit of GravityDa EverandThe Beauty of Falling: A Life in Pursuit of GravityNessuna valutazione finora
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayDa EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (125)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessDa EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (6)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Da EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (157)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterDa EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (410)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceDa EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (5)
- Vibration and Frequency: How to Get What You Want in LifeDa EverandVibration and Frequency: How to Get What You Want in LifeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (13)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldDa EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (54)
- The 60 Minute Quantum Physics Book: Science Made Easy For Beginners Without Math And In Plain Simple EnglishDa EverandThe 60 Minute Quantum Physics Book: Science Made Easy For Beginners Without Math And In Plain Simple EnglishValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (4)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowDa EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (49)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldDa EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (60)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeDa EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeNessuna valutazione finora
- The Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityDa EverandThe Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (78)
- Let There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessDa EverandLet There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (57)
- The Illustrated Theory of Everything: The Origin and Fate of the UniverseDa EverandThe Illustrated Theory of Everything: The Origin and Fate of the UniverseValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidDa EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1396)
- AP Physics 1 Premium, 2024: 4 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeDa EverandAP Physics 1 Premium, 2024: 4 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeNessuna valutazione finora