Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
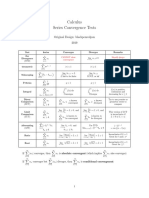
Integration Cheat Sheet
Caricato da
jieboCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Integration Cheat Sheet
Caricato da
jieboCopyright:
Formati disponibili
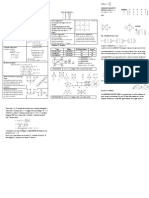
Chapter 5 Integrals I
Standard Integrals
( ax +b )n+1
( ax +b ) dx = ( n+1 ) a +C ,(n 1)
n
ax +b dx= a ln|ax+ b|+C
csc(ax+ b) cot ( ax +b ) dx=
b dx= lnb( b ) + C
x
sin ( ax +b ) dx=
1
cos ( ax +b )+ C
a
1
cos ( ax+ b ) dx= a sin ( ax +b )+C
1
tan(ax +b) dx= a ln|sec(ax+ b)|+ C
1
sec ( ax+b ) dx= a ln|sec ( ax+ b ) + tan ( ax+b )|+C
csc ( ax +b ) dx=
1
ln |csc ( ax +b )+ cot ( ax+ b )|+C
a
1
cot (ax+ b)dx= a ln|csc ( ax+ b )|+C
1
sec ( ax +b ) dx = a tan ( ax +b )+ C
2
1
csc (ax+ b)dx= a cot ( ax +b ) +C
2
1
sec ( ax+b ) tan ( ax+b ) dx= a sec ( ax +b )+ C
a ( x +b )
dx=sin1
a ( x +b )
dx=cos
Expression
x+ b=a sin
2
2
( x+a b )+C
a +( x+ b )
x+ b=a tan
2
2
( x +ba )+C
( x +b ) a
Type
( x +b ) + a
( x +b ) a
V ( x)
ax +b
( ax +b )2
a x 2+ bx+ c
b24 ac <0
Trigometr
ic
A
ax+ b
A
B
+
ax+ b ( ax +b )2
Ax +B
2
a x +bx +c
a3 +(b)3=(a+(b))(a2a(b)+ b2 )
Integration by Substitution
Substitute
cos
to simplify
integral
ax +b dx
u=ax+ b
tan1 ax +b dx
Algebraic
Partial Fractions
sin1 ax +b dx
1
Partial Fractions
Factors of
Inverse
dx=ln |( x +b ) + ( x+ b ) a |+C
2
Remark
lnax +b dx
mic
dx=ln|( x+ b ) + ( x +b ) + a |+C
2
Examples
Logarith
3
0 < <
2
2
f ' ( x ) g ( x ) dx=f ( x ) g ( x ) f ( x ) g' ( x ) dx
x+ b=a sec
Integration by Parts
1
1
x +b+ a
dx= ln
+C
2
2
2a
x+ ba
a ( x +b )
2
Domain
a ( x +b )
2
| |
ba
+C
1 dx= 21a ln| x+
x +b+ a |
( x+ b ) a
Substitution
2
( )
f (g ( x ) ) g' ( x ) dx= f (u ) du
Trigonometric Substitution
+C
2 1 2 dx = 1a tan1 x +b
a
a + ( x +b )
e ax +b dx= a eax+ b+C
1
csc ( ax+ b ) +C
a
Power functions
sin ax +b , cos ax +b , tan ax +b
Trigomet
ric
x a , polynomials
csc ax +b , sec ax +b ,
cot ax +b
Exponent
ial
ax+b
Trigonometric Identities Useful for
Integration
sec 2 1=tan 2
csc 1=cot
1
sin A cos A= sin 2 A
2
a x 2+ bx+ c dx A ff + B dx= A ln|f |+ B 1f dx
px+ q
1
cos 2 A= ( 1+cos 2 A )
2
1
sin 2 A= ( 1cos 2 A )
2
1
sin A cos B= [sin ( A + B ) +sin ( AB ) ]
2
1
cos A cos B= [ cos ( A+ B ) +cos ( AB ) ]
2
1
sin A sin B=
[ cos( A +B)cos( AB)]
2
1
i
f ( 1.
)
f ( x ) dx=lim
n
n n
0
i=1
2.
Force
1
n
f ( x )=a x +bx +c
2) Find
f ' ( x)
3) Find
and
B by fitting
out first
( ni )=f ( x)
i=1
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
b
FTC
1
f (x)dx=F ( b )F (a)
FTC
2
d
f (t )dt=f ( u ( x ) ) u' ( x )f ( v ( x ) ) v ' (x )
dx v(x)
u(x)
Miscellaneous
into
px+ q
a
f (x) dx= f (ax) dx
0
lim f ( x )
g ( x)
=exp ( lim g ( x ) ln f (x ) )
Examples
f ' (0)
2x
3+ x
f ( x )=
dt
1 1+ln t
2x
( 3+ x )
1
e
with1
1+ln t
dt
2x
1
1
f ( x )=( 3+ x )
2 e 2 x +
dt
1+2 x
1 1+ ln t
'
ba
ba
lim (
f (a+ i (
)
f ( x)dx n
)
n
n )
f'
Take out term
Express as
f
b
'
A f f+ B dx= A 2 f + B 1f dx
Find exact value of
Riemann Sums
a x 2 +bx +c
dx
FTC
Chapter 6 Integrals II
px+q
1) Let
1
cos A sin B= [sin ( A + B )sin ( AB ) ]
2
'
1
f ( 0 )=3 2+
dt
1 1+ ln t
'
Product Rule + FTC,
dont touch integral
part
Chapter 7 Applications of Integrals I
Area on xaxis
A= f ( x )g(x) dx
a
Area on yaxis
A= f ( y )g( y )dy
c
Disk Method
Shell Method
V = ( f ( x ) ) dx
a
V = ( f ( y ) ) dy
c
f (b )
f ( x ) dx=b f ( b )a f ( a ) f
a
g ( X )= g ( t ) f ( t ) dt
( x ) dx
a
b
f ( a)
1
sec t=cos
1
t
1
t
csc t=sin
cot t=tan
E ( X )= t f ( t ) dt E
1
t
Values of ab depends on question
Arc Length
d
V =2 x |f (x)|dx
a
dy 2
1+
dx
dx
( )
V =2 x |f ( x )g( x)|dx
OR
When
cont. on
dx 2
dy
dy
( )
1+
[c,d] ,
works on
First Order Ordinary Differential Equations
Separable
1
dy= f ( x) dx
ODE
g( y)
f > 0f <0
on one side,
on other
dy
+ P ( x ) y=Q ( x )
dx
Linear ODE
Chapter 8 Applications of Integrals II
Probability Density Function
I ( x )=exp ( P ( x ) dx )
Probability > 0
f ( x ) 0 for all x
y I ( x )= Q ( x ) I ( x ) dx
Total Probability
=1
f ( t) dt=1
V =2 y |f ( y )| dy
c
V =2 y |f ( y )g( y )|dy
c
dy
=
dx
2) Check separability
x2
iii.
P ( x1 X x 2 )= f (t) dt
iv.
P ( X=x )=0
x1
Inverse Functions
Use on Inverse trigo and logs
1) Set
Probability =
area under
curve
3)
1
dy=f ( x ) dx
g( y)
OR
dy
+ P ( x ) y=Q(x )
dx
x
x
P ( X x )=P ( X < x )= f (t) dt
4a) Integrate both sides
I ( x )=exp P( x )dx
Cumulative Distribution Function
P (X x )
x
F ( x )= f ( t ) dt
4b) Find
5a) Add arbitrary
constant, C
Expected Value (Mean)
6a) Combine
ln
5b)
ALWAYS
y I ( x )= Q ( P(
x ) XI (x )z)
dx
6b)
y I ( x )=+C
7b)
y=
terms
7a)
y=
Geometry
Law of Sines
Law of
Cosines
Area of
triangle
sin A sin B sinC
=
=
a
b
c
2
c =a + b 2 ab cos C
1
base height
2
1
ab sin C
2
s (sa)( sb)(sc)
where
1
s= (a+b+ c)
2
Solid
Cone
Volume
Surface Area
1 2
r h
3
r r 2 +h2
Cylinder
r 2h
2 rh
Sphere
4 3
r
3
4 r2
Cumulative Distribution Function
F ( x )= dt
DF
Basically just wants to
find area under curve
in
Riemann Sums
n
i= n2 (n+1)
i=0
i2= n6 (n+1)(2 n+1)
i=0
n
i =
i=0
n2
2
( n+ 1 )
4
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Dynamical Systems Method for Solving Nonlinear Operator EquationsDa EverandDynamical Systems Method for Solving Nonlinear Operator EquationsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Differentiation Cheat SheetDocumento15 pagineDifferentiation Cheat SheetjieboNessuna valutazione finora
- X X X X Ecx Ecx: Tan - Sec Sec Cot - Cos CosDocumento4 pagineX X X X Ecx Ecx: Tan - Sec Sec Cot - Cos Cossharanmit2039Nessuna valutazione finora
- Vector Calculus Cheat SheetDocumento1 paginaVector Calculus Cheat SheetAyisha A. GillNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 2 - Complex IntegrationDocumento43 pagineModule 2 - Complex IntegrationRathnaNessuna valutazione finora
- PRINT5 - Integrals Cheat Sheet - SymbolabDocumento2 paginePRINT5 - Integrals Cheat Sheet - SymbolabPamela Ricaforte100% (1)
- Eee Formula Sheet PDFDocumento143 pagineEee Formula Sheet PDFKiran Patil0% (1)
- Euler Substitution and Ostrogardsky Integration Method For Proper Rational FunctionsDocumento5 pagineEuler Substitution and Ostrogardsky Integration Method For Proper Rational FunctionsKeith Lester Mallorca100% (1)
- Integration CheatSheetDocumento4 pagineIntegration CheatSheetahmet mNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter-1: Integration Indefinite Integrals Definite IntegralsDocumento11 pagineChapter-1: Integration Indefinite Integrals Definite IntegralsEverything What U Want100% (1)
- Integral Calculus - ExercisesDocumento34 pagineIntegral Calculus - ExercisesVillamorchard0% (2)
- Cheat SheetDocumento2 pagineCheat SheetdeepfriedcatsNessuna valutazione finora
- Techniques of Integration Thomas FinneyDocumento6 pagineTechniques of Integration Thomas FinneyVineet TannaNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculus 1 Analytic Geometry Cheat SheetDocumento1 paginaCalculus 1 Analytic Geometry Cheat SheetStephanie DulaNessuna valutazione finora
- Convergence of Taylor Series (Sect. 10.9) PDFDocumento7 pagineConvergence of Taylor Series (Sect. 10.9) PDFTu ShirotaNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculus 2 Cheat SheetDocumento1 paginaCalculus 2 Cheat SheetB SotoNessuna valutazione finora
- BasicsDocumento2 pagineBasicsmadcow_scribdNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Calculus Test QuestionsDocumento13 pagineAdvanced Calculus Test QuestionsRyan BaleNessuna valutazione finora
- CPSC Algorithms Cheat SheetDocumento6 pagineCPSC Algorithms Cheat SheetRya KarkowskiNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 12th Maths WorksheetDocumento7 pagineGrade 12th Maths WorksheetABCD 1234Nessuna valutazione finora
- LA Cheat SheetDocumento1 paginaLA Cheat SheetMuhammad RizwanNessuna valutazione finora
- List of Logarithmic IdentitiesDocumento7 pagineList of Logarithmic IdentitiesMuhammedNayeemNessuna valutazione finora
- CALCUL - Applications of Partial Differentiation PDFDocumento28 pagineCALCUL - Applications of Partial Differentiation PDFOctav MiranorNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To IntegrationDocumento34 pagineIntroduction To IntegrationSanaullah Baloch100% (1)
- STUDY182@248298Documento26 pagineSTUDY182@248298Siddha FasonNessuna valutazione finora
- Vector Calculus Cheat SheetDocumento1 paginaVector Calculus Cheat SheetdeskfanNessuna valutazione finora
- Real Analysis Cheat SheetDocumento8 pagineReal Analysis Cheat SheetJoannaWilliamsNessuna valutazione finora
- Multiple IntegralsDocumento133 pagineMultiple Integralsmanasa raajheshNessuna valutazione finora
- Math - Complex Numbers RefresherDocumento5 pagineMath - Complex Numbers Refresherhelixate100% (2)
- Integration TechniquesDocumento18 pagineIntegration Techniquesஏம்மனுஎல்லெ செலேச்டினோNessuna valutazione finora
- Inverse Trigonometry Theory - eDocumento20 pagineInverse Trigonometry Theory - ethinkiitNessuna valutazione finora
- 15 Multiple IntegralsDocumento8 pagine15 Multiple IntegralsChristian J SebellinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculus Cheat Sheet LimitsDocumento2 pagineCalculus Cheat Sheet Limitstasos_rex3139Nessuna valutazione finora
- Calculus: So You Think You Can Take The Derivative? (Practice #3)Documento4 pagineCalculus: So You Think You Can Take The Derivative? (Practice #3)FernandoNessuna valutazione finora
- MA 201 (Complex Analysis) Lecture - 01Documento33 pagineMA 201 (Complex Analysis) Lecture - 01dab111Nessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis I Cheatsheet PDFDocumento11 pagineAnalysis I Cheatsheet PDFLogan BleysNessuna valutazione finora
- HKUST Math1013 NotesDocumento10 pagineHKUST Math1013 NotesJessicaLiNessuna valutazione finora
- Anti DerivativesDocumento21 pagineAnti DerivativesHanna GalatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculus Indefinite IntegralDocumento9 pagineCalculus Indefinite Integralnicusor.iacob5680Nessuna valutazione finora
- Math 38 UPLB Taylor Series ExpansionDocumento8 pagineMath 38 UPLB Taylor Series ExpansionKennypherneliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Differential Calculus: Engr. Joeydann M. TelinDocumento41 pagineDifferential Calculus: Engr. Joeydann M. TelinJoey TelinNessuna valutazione finora
- Math 257-316 PDE Formula Sheet - Final Exam: M It It M It ItDocumento3 pagineMath 257-316 PDE Formula Sheet - Final Exam: M It It M It Itjokes NerdNessuna valutazione finora
- Networking Essentials Exam NotesDocumento6 pagineNetworking Essentials Exam NotesHelen Shi100% (1)
- IntegralsDocumento27 pagineIntegralssudersanaviswanathanNessuna valutazione finora
- Series Convergence Tests BlackpenredpenDocumento1 paginaSeries Convergence Tests BlackpenredpenKarolina Padilla ValdezNessuna valutazione finora
- Cheat Sheet PDFDocumento11 pagineCheat Sheet PDFsergeNessuna valutazione finora
- Differential Equations Problems and SolutionsDocumento19 pagineDifferential Equations Problems and SolutionsBrian McCannNessuna valutazione finora
- Complex Variables & Transforms (20A54302) : Lecture NotesDocumento263 pagineComplex Variables & Transforms (20A54302) : Lecture NotesAl AminNessuna valutazione finora
- ODE Cheat SheetDocumento2 pagineODE Cheat SheetMuhammad Rizwan88% (8)
- 3D Analytical GeometryDocumento3 pagine3D Analytical GeometryMaths Home Work 123100% (1)
- Integration Formulas Solved ProblemsDocumento26 pagineIntegration Formulas Solved ProblemsWinona Marquez Vinluan100% (1)
- Worksheet On Vector Valued FunctionsDocumento6 pagineWorksheet On Vector Valued FunctionsvietboiiNessuna valutazione finora
- A2 Reference Sheet 01Documento5 pagineA2 Reference Sheet 01rajbmohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics Integral MCQ PDFDocumento11 pagineMathematics Integral MCQ PDFBilalAzamNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics FormulasDocumento2 pagineMathematics FormulasgopalmyneniNessuna valutazione finora
- Cs421 Cheat SheetDocumento2 pagineCs421 Cheat SheetJoe McGuckinNessuna valutazione finora
- Matlab Cheat Sheet PDFDocumento3 pagineMatlab Cheat Sheet PDFKarishmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Integration Fact SheetDocumento1 paginaIntegration Fact Sheetbala1307Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cong Thuc Tich Phan 2banDocumento1 paginaCong Thuc Tich Phan 2banTrà BùiNessuna valutazione finora
- F C D I: Ormulario de Álculo Iferencial E NtegralDocumento2 pagineF C D I: Ormulario de Álculo Iferencial E Ntegralpaz_aranibarNessuna valutazione finora
- IS4241 - RevisionDocumento13 pagineIS4241 - RevisionjieboNessuna valutazione finora
- SSA2211 - Evolution of A Global City-StateDocumento19 pagineSSA2211 - Evolution of A Global City-StatejieboNessuna valutazione finora
- IS2103 - SummaryDocumento22 pagineIS2103 - SummaryjieboNessuna valutazione finora
- GEK2013 Real Estate FinanceDocumento20 pagineGEK2013 Real Estate FinanceUnknown uploaderNessuna valutazione finora
- Creating Teams With An EdgeDocumento8 pagineCreating Teams With An EdgejieboNessuna valutazione finora
- CS1231 Cheat Sheet Part 1Documento1 paginaCS1231 Cheat Sheet Part 1jieboNessuna valutazione finora
- CS1231 Cheat Sheet 2Documento2 pagineCS1231 Cheat Sheet 2jieboNessuna valutazione finora
- ST1131 Cheat Sheet Page 2Documento1 paginaST1131 Cheat Sheet Page 2jieboNessuna valutazione finora
- ST1131 Cheat Sheet Page 1Documento1 paginaST1131 Cheat Sheet Page 1jiebo0% (1)
- ACC1002X Cheat Sheet 1Documento2 pagineACC1002X Cheat Sheet 1jieboNessuna valutazione finora
- ACC1002X Cheat Sheet 2Documento1 paginaACC1002X Cheat Sheet 2jieboNessuna valutazione finora
- Christena Nippert-Eng - Watching Closely - A Guide To Ethnographic Observation-Oxford University Press (2015)Documento293 pagineChristena Nippert-Eng - Watching Closely - A Guide To Ethnographic Observation-Oxford University Press (2015)Emiliano CalabazaNessuna valutazione finora
- Geotechnical Aspects of Open Stope Design at BHP Cannington: G C StreetonDocumento7 pagineGeotechnical Aspects of Open Stope Design at BHP Cannington: G C StreetonJuan PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- Villamaria JR Vs CADocumento2 pagineVillamaria JR Vs CAClarissa SawaliNessuna valutazione finora
- BioremediationDocumento21 pagineBioremediationagung24864Nessuna valutazione finora
- Discovery and Integration Content Guide - General ReferenceDocumento37 pagineDiscovery and Integration Content Guide - General ReferencerhocuttNessuna valutazione finora
- Redirection & PipingDocumento16 pagineRedirection & PipingPraveen PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- What Says Doctors About Kangen WaterDocumento13 pagineWhat Says Doctors About Kangen Waterapi-342751921100% (2)
- Innovativ and Liabl :: Professional Electronic Control Unit Diagnosis From BoschDocumento28 pagineInnovativ and Liabl :: Professional Electronic Control Unit Diagnosis From BoschacairalexNessuna valutazione finora
- Cad Data Exchange StandardsDocumento16 pagineCad Data Exchange StandardskannanvikneshNessuna valutazione finora
- Mule 4 Error Handling DemystifiedDocumento8 pagineMule 4 Error Handling DemystifiedNicolas boulangerNessuna valutazione finora
- List of The Legend of Korra Episodes - Wikipedia PDFDocumento27 pagineList of The Legend of Korra Episodes - Wikipedia PDFEmmanuel NocheNessuna valutazione finora
- Terminal Blocks: Assembled Terminal Block and SeriesDocumento2 pagineTerminal Blocks: Assembled Terminal Block and SeriesQuan Nguyen TheNessuna valutazione finora
- A Review of Mechanism Used in Laparoscopic Surgical InstrumentsDocumento15 pagineA Review of Mechanism Used in Laparoscopic Surgical InstrumentswafasahilahNessuna valutazione finora
- Ac221 and Ac211 CourseoutlineDocumento10 pagineAc221 and Ac211 CourseoutlineLouis Maps MapangaNessuna valutazione finora
- UnixDocumento251 pagineUnixAnkush AgarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Schneider Contactors DatasheetDocumento130 pagineSchneider Contactors DatasheetVishal JainNessuna valutazione finora
- AstmDocumento5 pagineAstmyanurarzaqaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nestlé CASEDocumento3 pagineNestlé CASEAli Iqbal CheemaNessuna valutazione finora
- ARC-232, Material Construction 2Documento4 pagineARC-232, Material Construction 2danishali1090Nessuna valutazione finora
- Business CombinationsDocumento18 pagineBusiness Combinationszubair afzalNessuna valutazione finora
- Zygosaccharomyces James2011Documento11 pagineZygosaccharomyces James2011edson escamillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Benko Gambit-Jacobs and Kinsman, 1999Documento163 pagineBenko Gambit-Jacobs and Kinsman, 1999johnson Greker100% (3)
- Activity Evaluation Form: "Where Children Come First"Documento1 paginaActivity Evaluation Form: "Where Children Come First"TuTitNessuna valutazione finora
- The Minimum Means of Reprisal - China's S - Jeffrey G. LewisDocumento283 pagineThe Minimum Means of Reprisal - China's S - Jeffrey G. LewisrondfauxNessuna valutazione finora
- Formal Letter LPDocumento2 pagineFormal Letter LPLow Eng Han100% (1)
- Internal Analysis: Pertemuan KeDocumento15 pagineInternal Analysis: Pertemuan Kekintan utamiNessuna valutazione finora
- Code ExplanantionDocumento4 pagineCode ExplanantionVivek JadiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Explore The WorldDocumento164 pagineExplore The WorldEduardo C VanciNessuna valutazione finora
- Sistine Chapel Ceiling Lesson PlanDocumento28 pagineSistine Chapel Ceiling Lesson PlannivamNessuna valutazione finora