Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Lesson Plan Center of Gravity
Caricato da
Dora AyeCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Lesson Plan Center of Gravity
Caricato da
Dora AyeCopyright:
Formati disponibili
5 E Lesson Plan Center of Gravity
Objectives:
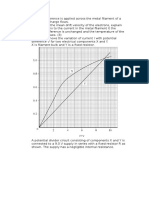
6:05 Describe and measure quantities that characterize moving objects and their interactions within a system
6.06 Investigate and analyze the real world interactions of balanced and unbalanced forces:
Engage
Balance a box on a desk or table that has weight inside that alters the center of gravity.
Ask students why doesnt the box fall off the table? Have students write their explanations in their note book.
Then record explanations on the board.
Explore
Center of Gravity Lab
Explain
Gravity is a force that pulls on all particles (the mass ) of an object. Although individual particles
throughout an object all contribute to the objects weight, the net effect is as if the total weight of the object
were concentrated in a single point--the object's center of gravity.
Center of gravity the imaginary point where all of the weight of the object is concentrated.
o Useful for designing bridges or buildings or predicting movement of an object.
o Center of gravity is a vector because it has direction as well as magnitude.
o Center of gravity is usually where things balance.
Extend
The center of gravity may or may not be the point that is exactly in the middle, distance-wise, of the object.
If you have something like a sledge hammer that is heavier on one end than the other, the center of gravity
will be much closer to the heavy end than the lighter end.
Sometimes the center of gravity isnt actually on the object.
o Boomerang example
o Fosbury Flop
Center of gravity applied to car design
o Usually low to improve cars handling
o Problems with SUVs
Center of gravity applied to airplane design
o Affects planes
Pitch
Yaw
Roll
Evaluate
Lab Rubric
Forces and Motion Unit Test
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- 5e's Lesson Plan in ScienceDocumento5 pagine5e's Lesson Plan in ScienceCAthh TherineeNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan Work Power EnergyDocumento13 pagineLesson Plan Work Power EnergyASR REDDYNessuna valutazione finora
- Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 6 I. ObjectiveDocumento3 pagineSemi Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 6 I. ObjectivePrincess Diane HerreraNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Demo Lesson Plan FINAL 1 Copy2 RepairedDocumento16 pagineFinal Demo Lesson Plan FINAL 1 Copy2 RepairedChristian DeanNessuna valutazione finora
- Knowledge: RD THDocumento6 pagineKnowledge: RD THPRAGYA SINGHNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan in Science Iii: Describe The External Parts of The Eye. Participate Actively in The Group ActivityDocumento90 pagineLesson Plan in Science Iii: Describe The External Parts of The Eye. Participate Actively in The Group ActivityLiza ValerosoNessuna valutazione finora
- Compound Machine Lesson Plan - ObservedDocumento5 pagineCompound Machine Lesson Plan - Observedapi-338531822Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ready Made Lesson PlanDocumento5 pagineReady Made Lesson Planpatrickkaye100% (2)
- Lesson Plan in Science 6Documento6 pagineLesson Plan in Science 6markNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 5 Science Lesson 8-Force, Energy and Machines Module 1Documento21 pagineGrade 5 Science Lesson 8-Force, Energy and Machines Module 1praviseNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan 6 With ReflectionDocumento15 pagineLesson Plan 6 With Reflectionapi-317701591Nessuna valutazione finora
- A Semi - Detailed Lesson Plan On Nature of ForcesDocumento5 pagineA Semi - Detailed Lesson Plan On Nature of ForcesButz GeonzonNessuna valutazione finora
- SCIENCE 5e's Lesson Plan About DistanceDocumento7 pagineSCIENCE 5e's Lesson Plan About DistanceZALVIE FERNANDO UNTUANessuna valutazione finora
- TG S5FE IVi JDocumento4 pagineTG S5FE IVi JAngela Marie SatorNessuna valutazione finora
- My Detailed Lesson Plan FinalDocumento11 pagineMy Detailed Lesson Plan FinalNovy-Ann Sancho100% (1)
- Understand What Is Force Demonstrate How To Move Objects Value The Importance of Force in Making Objects To MoveDocumento6 pagineUnderstand What Is Force Demonstrate How To Move Objects Value The Importance of Force in Making Objects To MoveReal AptitudeNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.2 Understanding Pressure in LiquidsDocumento4 pagine3.2 Understanding Pressure in LiquidsGeraldJoelBillihNessuna valutazione finora
- Sci - LP2-10 MotionDocumento7 pagineSci - LP2-10 MotionluigimanzanaresNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan No 1Documento4 pagineLesson Plan No 1hafeez ahmed0% (1)
- Demo LPDocumento5 pagineDemo LPJuMeLa SarmientoNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan QuadrilateralsDocumento1 paginaLesson Plan QuadrilateralsJonathan Robinson100% (3)
- Sound Energy Lesson PlanDocumento2 pagineSound Energy Lesson PlanWiggy31Nessuna valutazione finora
- VelocityDocumento3 pagineVelocityleizl MoncadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Plant Adaptation Lesson PlanDocumento2 paginePlant Adaptation Lesson Planapi-24727504650% (2)
- LESSON PLAN in SCIENCE V USING COLLABORATIVE LEARNING AND 5EDocumento4 pagineLESSON PLAN in SCIENCE V USING COLLABORATIVE LEARNING AND 5EAimelyn De Guzman Garalde100% (1)
- Lesson Plan in Science About MotionDocumento5 pagineLesson Plan in Science About MotionFloramae SeradorNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan Science HaysDocumento5 pagineLesson Plan Science HaysAlexie AlmohallasNessuna valutazione finora
- DLP Science7 NewDocumento7 pagineDLP Science7 NewAngel TadeoNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan Class 6 CH Magnet Day 2Documento7 pagineLesson Plan Class 6 CH Magnet Day 2Ujjwal Kr. Sinha100% (1)
- Learning Plan in Science Grade 5Documento7 pagineLearning Plan in Science Grade 5Marsha EvangelistaNessuna valutazione finora
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocumento6 pagineDetailed Lesson PlanMelanie Tagudin TrinidadNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Energy LessonPlanDocumento3 pagineElectrical Energy LessonPlanrezhablo75% (4)
- Lesson Plan Physics Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDocumento4 pagineLesson Plan Physics Magnetic Effects of Electric Currentakhil100% (1)
- Lesson Plan in Science 6 (Energy) 2Documento7 pagineLesson Plan in Science 6 (Energy) 2Kel FrancisNessuna valutazione finora
- Describing Motion: Third Quarter PhysicsDocumento26 pagineDescribing Motion: Third Quarter PhysicsRose Ann YamcoNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plans ScienceDocumento18 pagineLesson Plans Scienceapi-302425735Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson PlanDocumento4 pagineLesson PlanMary Aurielle Barroga NalusNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan in Grade 3 Science 4th QuarterDocumento4 pagineLesson Plan in Grade 3 Science 4th QuarterHazel FaelangcaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan in Science 3 LovelyDocumento3 pagineLesson Plan in Science 3 Lovelylloriane100% (1)
- Forces and Motion ActivityDocumento5 pagineForces and Motion Activityjanice alquizarNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrostatics (Lesson Plan)Documento4 pagineElectrostatics (Lesson Plan)Danastri Shahnaz100% (5)
- Color and Heat AbsorptionDocumento3 pagineColor and Heat AbsorptionPoonkodi Ramanjee Poonkodi RamanjeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Math 5 DLP 46 - Drawing 5 or MOre-Sided PolygonDocumento12 pagineMath 5 DLP 46 - Drawing 5 or MOre-Sided PolygonAnna Loraine CadaNessuna valutazione finora
- 5E Lesson Plan Template: Teacher Deonica MatthewsDocumento3 pagine5E Lesson Plan Template: Teacher Deonica Matthewsapi-532358629Nessuna valutazione finora
- Gravity Lesson Plan 4Documento3 pagineGravity Lesson Plan 4api-280622632100% (1)
- Lesson Plan On Sound: (Loudness, Pitch and Quality)Documento6 pagineLesson Plan On Sound: (Loudness, Pitch and Quality)Frician Bernadette Muyco50% (2)
- Work and Energy 062719Documento5 pagineWork and Energy 062719IRISNessuna valutazione finora
- Contact and Non-Contact Lesson PlanDocumento3 pagineContact and Non-Contact Lesson Planapi-28334474583% (6)
- DistanceDocumento4 pagineDistanceleizl MoncadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Celestial Bodies Lesson PlanDocumento5 pagineCelestial Bodies Lesson Planapi-247664759Nessuna valutazione finora
- G10 Lesson Plan On Energy TransformationDocumento2 pagineG10 Lesson Plan On Energy TransformationChristianNessuna valutazione finora
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science VI (GRavity)Documento7 pagineDetailed Lesson Plan in Science VI (GRavity)Azia GoniloamusNessuna valutazione finora
- Rocks Lesson PlanDocumento7 pagineRocks Lesson Planapi-241268840Nessuna valutazione finora
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Physics UAMDocumento5 pagineA Detailed Lesson Plan in Physics UAMNikka KayeNessuna valutazione finora
- DLL Science 3rd Week 1 Day 1-5Documento10 pagineDLL Science 3rd Week 1 Day 1-5Elmalyn BernarteNessuna valutazione finora
- Copy of Science Lesson Plan Luminous and Non-Luminous ObjectsDocumento9 pagineCopy of Science Lesson Plan Luminous and Non-Luminous ObjectsOcania WalkerNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Lesson Plan Grade XDocumento27 paginePhysics Lesson Plan Grade Xarief1271618880% (5)
- I. Objectives: Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade 9 Science (Force, Motion, and Energy)Documento7 pagineI. Objectives: Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade 9 Science (Force, Motion, and Energy)JEREMAEH DELOSANessuna valutazione finora
- Lab No-14Documento13 pagineLab No-14ShahZaib AnwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Center of Gravity Lab ReportDocumento3 pagineCenter of Gravity Lab ReportHarlynn Joy Salmeo13% (8)
- Waves Lesson PlanDocumento4 pagineWaves Lesson PlanDora Aye0% (1)
- O Level QuizDocumento2 pagineO Level QuizDora AyeNessuna valutazione finora
- Reading Text IDocumento3 pagineReading Text ILakshitaNessuna valutazione finora
- InductionDocumento2 pagineInductionDora AyeNessuna valutazione finora
- Circular Motion WorksheetDocumento2 pagineCircular Motion WorksheetJonathan Teng0% (2)
- A Level PhysicsDocumento2 pagineA Level PhysicsDora AyeNessuna valutazione finora
- Sankey Diagrams WorksheetDocumento4 pagineSankey Diagrams WorksheetDora Aye100% (1)
- Physics PressureDocumento4 paginePhysics PressureDora AyeNessuna valutazione finora
- PhysicsDocumento1 paginaPhysicsDora AyeNessuna valutazione finora
- Alevel PhysicsDocumento4 pagineAlevel PhysicsDora AyeNessuna valutazione finora
- ConvectionDocumento2 pagineConvectionDora AyeNessuna valutazione finora
- WorksheetDocumento1 paginaWorksheetDora AyeNessuna valutazione finora
- A Level QuizDocumento2 pagineA Level QuizDora AyeNessuna valutazione finora
- EnergyDocumento6 pagineEnergyDora AyeNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment o LevlDocumento1 paginaExperiment o LevlDora AyeNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 Jun 00Documento11 pagine5 Jun 00Riya MalikNessuna valutazione finora
- ThermalDocumento7 pagineThermalDora AyeNessuna valutazione finora
- Convection CurrentDocumento1 paginaConvection CurrentDora AyeNessuna valutazione finora
- TestDocumento3 pagineTestDora AyeNessuna valutazione finora
- Fossil FuelsDocumento16 pagineFossil FuelsDora AyeNessuna valutazione finora
- Energy TransferDocumento12 pagineEnergy TransferAnga PutraborneoNessuna valutazione finora
- EvaporationDocumento18 pagineEvaporationDora AyeNessuna valutazione finora
- Nuclear PhysicsDocumento5 pagineNuclear PhysicsDora AyeNessuna valutazione finora
- O Level Wave MCDocumento6 pagineO Level Wave MCDora AyeNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermometer MCDocumento3 pagineThermometer MCDora AyeNessuna valutazione finora
- GCE Past PaperDocumento2 pagineGCE Past PaperDora Aye0% (1)
- Thermal MCDocumento5 pagineThermal MCDora AyeNessuna valutazione finora
- Energy ResourcesDocumento16 pagineEnergy ResourcesDora AyeNessuna valutazione finora
- Cog MCDocumento2 pagineCog MCDora AyeNessuna valutazione finora
- Commissioning LectureDocumento59 pagineCommissioning Lecturemuaz_aminu1422Nessuna valutazione finora
- SSC Je 2024 Electrical Engineering Solved Papers Technical and NonDocumento688 pagineSSC Je 2024 Electrical Engineering Solved Papers Technical and NonDIPAYAN MAHAPTRANessuna valutazione finora
- Impulse and MomentumDocumento18 pagineImpulse and MomentumIjal HaizalNessuna valutazione finora
- Modeling of SVC For Load Flow Analysis: BackgroundDocumento2 pagineModeling of SVC For Load Flow Analysis: BackgroundRajat RK KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Open System (1) ThermodynamicDocumento38 pagineOpen System (1) ThermodynamicSakinah KamalNessuna valutazione finora
- Saab 2000 ElectricalDocumento17 pagineSaab 2000 ElectricalAndrewNessuna valutazione finora
- Catalogo Switchgear BrochureDocumento2 pagineCatalogo Switchgear BrochureSergio PediconiNessuna valutazione finora
- Viscosity and Density (Metric SI Units)Documento3 pagineViscosity and Density (Metric SI Units)malith kmlNessuna valutazione finora
- ESR Metru Nou Cu Posibilitati de CalibrareDocumento6 pagineESR Metru Nou Cu Posibilitati de Calibraremsicoie1851Nessuna valutazione finora
- BJBJBJBJBDocumento10 pagineBJBJBJBJBFarah AmrNessuna valutazione finora
- T3 ME Performance Record Jan TemplateDocumento5 pagineT3 ME Performance Record Jan TemplateMuhd Khir RazaniNessuna valutazione finora
- KBP200G 2010 Puente RectificadorDocumento3 pagineKBP200G 2010 Puente RectificadorEnriqueEMontenegroNessuna valutazione finora
- Nepal Aviation Authority 8Documento5 pagineNepal Aviation Authority 8Janup PokharelNessuna valutazione finora
- 08-08-19 Sri Chaitanya-Jr - Chaina-I Jee-Adv (2014 P2) WTA-13 Q.PDocumento28 pagine08-08-19 Sri Chaitanya-Jr - Chaina-I Jee-Adv (2014 P2) WTA-13 Q.PPRANITH REDDYNessuna valutazione finora
- Worksheet X PhysicsDocumento31 pagineWorksheet X PhysicsGuru PrasannaNessuna valutazione finora
- Generator and MotorDocumento19 pagineGenerator and Motortrihandoko1631Nessuna valutazione finora
- Wiring Diagrams - 12 Volt Planet Knowledge CentreDocumento2 pagineWiring Diagrams - 12 Volt Planet Knowledge CentreLong JidinNessuna valutazione finora
- Catalogo General de Productos EPCOS 2013Documento96 pagineCatalogo General de Productos EPCOS 2013aresmecanicoNessuna valutazione finora
- 12th Physics - Practical - 2021 - 22 Term 1 Term 2Documento12 pagine12th Physics - Practical - 2021 - 22 Term 1 Term 2NAYAN DARYANINessuna valutazione finora
- 544892main PS2 InertiaAndFriction C2 PDFDocumento3 pagine544892main PS2 InertiaAndFriction C2 PDFJohn David RamosNessuna valutazione finora
- Alternating Current: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocumento18 pagineAlternating Current: Multiple Choice QuestionsUrja MoonNessuna valutazione finora
- Transmission TowerDocumento11 pagineTransmission TowerSantosh Rai100% (3)
- 38,202 - Renewable ProjectDocumento40 pagine38,202 - Renewable ProjectAnas AyubNessuna valutazione finora
- Transient Recovery Voltage Requirements Associated With The Application of Current-Limiting Series ReactorsDocumento6 pagineTransient Recovery Voltage Requirements Associated With The Application of Current-Limiting Series ReactorsDante FilhoNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Data Sheet Mx21Fga 200-220/220-230V 50/60Hz 1 R404ADocumento4 pagineTechnical Data Sheet Mx21Fga 200-220/220-230V 50/60Hz 1 R404AFreddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Reading Motion Graphs PracticeDocumento4 pagineReading Motion Graphs PracticeRachel WilliamsonNessuna valutazione finora
- JEST 2012 Question-AnswerDocumento13 pagineJEST 2012 Question-Answertduality100% (1)
- Separation Theory For Palmkernel and Shell MixtureDocumento8 pagineSeparation Theory For Palmkernel and Shell MixturekilankoNessuna valutazione finora
- TAS-331DG Data Sheet 4921220036 UKDocumento8 pagineTAS-331DG Data Sheet 4921220036 UKAkhilNessuna valutazione finora
- Compact Substation KioskDocumento2 pagineCompact Substation Kiosk4usangeetNessuna valutazione finora
- Differentiated Reading for Comprehension, Grade 1Da EverandDifferentiated Reading for Comprehension, Grade 1Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- The Reading Mind: A Cognitive Approach to Understanding How the Mind ReadsDa EverandThe Reading Mind: A Cognitive Approach to Understanding How the Mind ReadsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Uncovering the Logic of English: A Common-Sense Approach to Reading, Spelling, and LiteracyDa EverandUncovering the Logic of English: A Common-Sense Approach to Reading, Spelling, and LiteracyNessuna valutazione finora
- The Read-Aloud Family: Making Meaningful and Lasting Connections with Your KidsDa EverandThe Read-Aloud Family: Making Meaningful and Lasting Connections with Your KidsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (205)
- Teach Reading with Orton-Gillingham: 72 Classroom-Ready Lessons to Help Struggling Readers and Students with Dyslexia Learn to Love ReadingDa EverandTeach Reading with Orton-Gillingham: 72 Classroom-Ready Lessons to Help Struggling Readers and Students with Dyslexia Learn to Love ReadingValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- The Artful Read-Aloud: 10 Principles to Inspire, Engage, and Transform LearningDa EverandThe Artful Read-Aloud: 10 Principles to Inspire, Engage, and Transform LearningValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (2)
- Empires of the Word: A Language History of the WorldDa EverandEmpires of the Word: A Language History of the WorldValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (236)
- Reading Comprehension Practice, Grades 7 - 8Da EverandReading Comprehension Practice, Grades 7 - 8Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- ESL Reading Activities For Kids (6-13): Practical Ideas for the ClassroomDa EverandESL Reading Activities For Kids (6-13): Practical Ideas for the ClassroomValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- Guided Word Building: Systematic, Sequential Phonics LessonsDa EverandGuided Word Building: Systematic, Sequential Phonics LessonsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (3)
- Differentiated Reading for Comprehension, Grade 2Da EverandDifferentiated Reading for Comprehension, Grade 2Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Making Words, Grade 2: Lessons for Home or SchoolDa EverandMaking Words, Grade 2: Lessons for Home or SchoolValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Harry Potter and the Chamber of Secrets (Novel Study)Da EverandHarry Potter and the Chamber of Secrets (Novel Study)Valutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (6)
- Reading Comprehension Practice, Grade 5Da EverandReading Comprehension Practice, Grade 5Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (10)
- The Book Whisperer: Awakening the Inner Reader in Every ChildDa EverandThe Book Whisperer: Awakening the Inner Reader in Every ChildValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (56)
- Honey for a Child's Heart Updated and Expanded: The Imaginative Use of Books in Family LifeDa EverandHoney for a Child's Heart Updated and Expanded: The Imaginative Use of Books in Family LifeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (106)
- Proven Speed Reading Techniques: Read More Than 300 Pages in 1 Hour. A Guide for Beginners on How to Read Faster With Comprehension (Includes Advanced Learning Exercises)Da EverandProven Speed Reading Techniques: Read More Than 300 Pages in 1 Hour. A Guide for Beginners on How to Read Faster With Comprehension (Includes Advanced Learning Exercises)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (9)
- Wild and Free Book Club: 28 Activities to Make Books Come AliveDa EverandWild and Free Book Club: 28 Activities to Make Books Come AliveValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)