Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
ES 221: Mechanics of Solids (2016)
Caricato da
Vaibhav PalDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
ES 221: Mechanics of Solids (2016)
Caricato da
Vaibhav PalCopyright:
Formati disponibili
ES 221: Mechanics of Solids (2016)
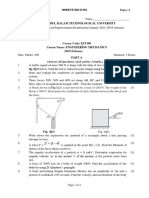
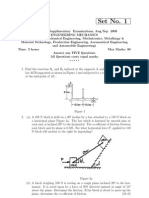
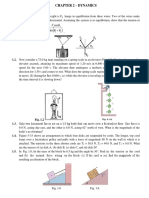
Assignment No.1 [Due on 13.1.2016]
1.1
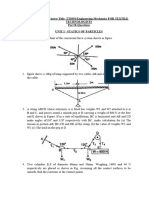
A ladder is placed at an angle of 60 to the ground. The lower end of the ladder is set in a
groove and the other end is resting on the corner of a wall. A man weighing 600N is at the
mid-height of the ladder (Fig 1.1). Determine the reactions. If the ladder is placed on a
smooth surface, what can you say about the reactions?
1.2
Two equal cylinders, each weighing 900N are placed in a box as shown in Fig1.2
.Neglecting friction between the cylinders and the box, estimate the reactions at A,B and
C.
1.3
The 1.5 kN beam AB carries a 2.5 kN load at B. The beam is held by a fixed support at A
and by cable CD which is attached to the counterweight W. (a) If W = 6.5 kN determine
the reactions at A. (b) Determine the range of W for which the magnitude of the moment
at A does not exceed 2.5 kNm.(Fig 1.3)
1.4
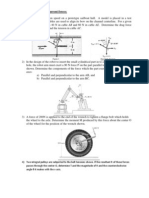
A 1.5m x 2.0m signboard of uniform density weighs 1.35 kN and is supported by a ball &
socket at A and by two cables. Determine the tension in each cable and the reaction at A.
(Fig 1.4)
Fig 1.4
1.5
An electric motor is mounted on a three-point support as shown (Fig 1.5). The motor
weighs 100N, which may be assumed to act at the center of the motor. Before starting,
the belt tensions are 140N each. When running, the motor is delivering a torque of 3Nm.
What are the reactions at supports A, B, and C when the motor is running? (Hint: Assume
the supports A, B, and C transmit no torque or moments and are frictionless. Also assume that the
mean tension in the belt remains unchanged.)
1.6
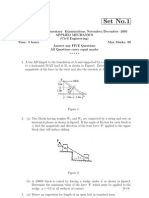
In building construction it is common to build a floor or a roof on temporary supports
which permit leveling up before setting the permanent columns in place. The sketch (Fig
1.6) shows one of the ways in which this leveling up is performed. The temporary
column C supports a weight of 10kN. Driving in the wedge at B lifts one end of the rigid
bar AB and hence lifts C by half as much. (a) Estimate the minimum force between
hammer and wedge that will cause the wedge to move farther in, assuming all
coefficients of friction are 0.3. (b) What would happen if the coefficients of frictions were
too small? What is the value of the coefficient of friction, which marks the borderline
between desirable and undesirable performance?
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Same Virtus: Alarm ListDocumento23 pagineSame Virtus: Alarm ListLacatusu Mircea100% (1)
- Question Bank Engg. MechanicsDocumento18 pagineQuestion Bank Engg. MechanicsSakendra Kumar0% (2)
- Examples MomentumDocumento9 pagineExamples Momentumettypasewang0% (1)
- Prob Set 1Documento3 pagineProb Set 1Joery Jr Esperon50% (2)
- GNG 1105 Final Exam 2000Documento3 pagineGNG 1105 Final Exam 2000Stefano MazzaNessuna valutazione finora
- ESO 202A/204: Mechanics of Solids (2016-17 II Semester) Assignment No. - 1Documento3 pagineESO 202A/204: Mechanics of Solids (2016-17 II Semester) Assignment No. - 1HNessuna valutazione finora
- ESO 202A/204: Mechanics of Solids (2016-17 II Semester) Assignment No. - 1Documento3 pagineESO 202A/204: Mechanics of Solids (2016-17 II Semester) Assignment No. - 1Asim KatakwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Correl 2 Until MidtermsDocumento23 pagineCorrel 2 Until MidtermsKimberly TacaisanNessuna valutazione finora
- EST100-engineering MechanicsDocumento4 pagineEST100-engineering MechanicsclintNessuna valutazione finora
- Model QSTN Paper 1-Be100Documento5 pagineModel QSTN Paper 1-Be100nanduNessuna valutazione finora
- FE Statics PDFDocumento6 pagineFE Statics PDFMiguel Analuisa0% (1)
- FE StaticsDocumento6 pagineFE StaticsJaime CorralesNessuna valutazione finora
- Question Bank & Bit BankDocumento20 pagineQuestion Bank & Bit BankKomma HemaNessuna valutazione finora
- Infant Jesus College of Engineering: PART A (10 X 2 20 Marks)Documento4 pagineInfant Jesus College of Engineering: PART A (10 X 2 20 Marks)Robinston Jeyasingh KNessuna valutazione finora
- rr10105 Applied MechanicsDocumento13 paginerr10105 Applied MechanicsSRINIVASA RAO GANTANessuna valutazione finora
- R05010105-APPLIED-MECHANICS apr/may 2007 ExCluSiVe ~ ∂ℑ я.ß.⊂™Documento12 pagineR05010105-APPLIED-MECHANICS apr/may 2007 ExCluSiVe ~ ∂ℑ я.ß.⊂™badboy_rockssNessuna valutazione finora
- Question BankDocumento9 pagineQuestion Bankpragash100% (1)
- r05010302 Engineering MechanicsDocumento11 paginer05010302 Engineering MechanicsSRINIVASA RAO GANTANessuna valutazione finora
- Btes103 203 em QBDocumento10 pagineBtes103 203 em QBSurajNessuna valutazione finora
- Extra Problem Phys 1 CH 2Documento2 pagineExtra Problem Phys 1 CH 2Quỳnh NguyễnNessuna valutazione finora
- CENG 198 Problem Set 1 Part1 QuestionsDocumento1 paginaCENG 198 Problem Set 1 Part1 QuestionsBryan Christian MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5: Work, Energy and Power: DirectionDocumento1 paginaChapter 5: Work, Energy and Power: DirectionlynnadzNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer All Questions. Each Question Carries 5 Marks: B1C008 Total Pages:3Documento3 pagineAnswer All Questions. Each Question Carries 5 Marks: B1C008 Total Pages:3Srikanth KodothNessuna valutazione finora
- Categories of Equilibrium: Problem 1.1Documento33 pagineCategories of Equilibrium: Problem 1.1Suresh NatarajanNessuna valutazione finora
- Part B Question BankDocumento9 paginePart B Question BankSriram SrinivasanNessuna valutazione finora
- CENG198 CE Competency Appraisal IllDocumento4 pagineCENG198 CE Competency Appraisal IllJeric DinglasanNessuna valutazione finora
- Rr10105 Applied MechanicsDocumento13 pagineRr10105 Applied MechanicsSrinivasa Rao GNessuna valutazione finora
- 1111-110010-Mech - of SolidsDocumento4 pagine1111-110010-Mech - of SolidsjaydeepNessuna valutazione finora
- Question Paper Code: X10561: (10×2 20 Marks)Documento5 pagineQuestion Paper Code: X10561: (10×2 20 Marks)NISHANTH KNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 ReviewDocumento3 pagineChapter 2 ReviewFlora DongNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 3Documento8 pagineModule 3VenkatNessuna valutazione finora
- r5100105 Applied MechanicsDocumento2 paginer5100105 Applied MechanicssivabharathamurthyNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering MechanicsDocumento8 pagineEngineering MechanicsNanna ShivuNessuna valutazione finora
- r5100105 Applied MechanicsDocumento2 paginer5100105 Applied MechanicssivabharathamurthyNessuna valutazione finora
- Candidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarksDocumento4 pagineCandidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarksManish Shrestha100% (1)
- EMech Prob Set II EqulibriumDocumento3 pagineEMech Prob Set II Equlibriumsubhafkt.2005Nessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment Questions For All UnitsDocumento10 pagineAssignment Questions For All UnitsPiyush BhandariNessuna valutazione finora
- Practise Problems Set05Documento8 paginePractise Problems Set05rohit kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanics: Graph Paper Is Available in The Examination RoomDocumento6 pagineMechanics: Graph Paper Is Available in The Examination RoomIoana BoilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 6-2Documento3 pagineTutorial 6-2Chandrali DasNessuna valutazione finora
- General Physics (Phys 1011) : Worksheet 3Documento3 pagineGeneral Physics (Phys 1011) : Worksheet 3MeklitNessuna valutazione finora
- nov/dec 2005 ExCluSiVe ~ ∂ℑ я.ß.⊂Documento14 paginenov/dec 2005 ExCluSiVe ~ ∂ℑ я.ß.⊂badboy_rockssNessuna valutazione finora
- APL104 F23 Tutorial 1Documento5 pagineAPL104 F23 Tutorial 1md osamaNessuna valutazione finora
- EMech Prob Set IV FrictionDocumento3 pagineEMech Prob Set IV FrictionSamrat SadhukhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic of Mechanical Engineering - Assignment IDocumento3 pagineBasic of Mechanical Engineering - Assignment ISreenuNessuna valutazione finora
- MechanicsDocumento9 pagineMechanicsHarshal Dengle100% (1)
- Applied Dynamics QuestionsDocumento5 pagineApplied Dynamics QuestionsKritamMaharjanNessuna valutazione finora
- Practise Problems Set01Documento7 paginePractise Problems Set01rohit kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Applied MechanicsDocumento13 pagineApplied Mechanicsapi-26349602100% (1)
- Me 2151 e MechDocumento22 pagineMe 2151 e Mechkalirajgurusamy33% (3)
- Model-EM-29 5 13Documento2 pagineModel-EM-29 5 13rkumaravelanNessuna valutazione finora
- 07a10101 Applied MechanicsDocumento11 pagine07a10101 Applied MechanicsSRINIVASA RAO GANTANessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 1Documento5 pagineAssignment 1mohityaav0% (1)
- Sheet Two Chapter Three The Laws of MotionDocumento24 pagineSheet Two Chapter Three The Laws of MotionTony AtefNessuna valutazione finora
- Ass 3 An Rem EMDocumento4 pagineAss 3 An Rem EMAbhay Singh ChauhanNessuna valutazione finora
- EM Coaching QBDocumento10 pagineEM Coaching QBsaravananNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 - DynamicsDocumento8 pagineChapter 2 - DynamicsTHIÊN LÊ TRẦN THUẬNNessuna valutazione finora
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Da EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Phy Lab Exp NewDocumento6 paginePhy Lab Exp NewVaibhav PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Phy Lab Exp NewDocumento5 paginePhy Lab Exp NewVaibhav PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Phy Lab Exp NewDocumento5 paginePhy Lab Exp NewVaibhav PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Phy Lab Exp NewDocumento6 paginePhy Lab Exp NewVaibhav PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Phy Lab Exp NewDocumento5 paginePhy Lab Exp NewVaibhav PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Phy Lab Exp NewDocumento5 paginePhy Lab Exp NewVaibhav PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Phy Lab Exp NewDocumento5 paginePhy Lab Exp NewVaibhav PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Phy Lab Exp NewDocumento5 paginePhy Lab Exp NewVaibhav PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Phy Lab Exp NewDocumento5 paginePhy Lab Exp NewVaibhav PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Phy Lab Exp NewDocumento5 paginePhy Lab Exp NewVaibhav PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Phy Lab Exp NewDocumento5 paginePhy Lab Exp NewVaibhav PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Phy Lab Exp NewDocumento5 paginePhy Lab Exp NewVaibhav PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment No. 1 Planck'S Constant: ObjectiveDocumento5 pagineExperiment No. 1 Planck'S Constant: ObjectiveVaibhav PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment No. 1 Planck'S Constant: ObjectiveDocumento5 pagineExperiment No. 1 Planck'S Constant: ObjectiveVaibhav PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment No. 1 Planck'S Constant: ObjectiveDocumento5 pagineExperiment No. 1 Planck'S Constant: ObjectiveVaibhav PalNessuna valutazione finora
- North Sails Brochure 2007 enDocumento24 pagineNorth Sails Brochure 2007 ennorthsailsNessuna valutazione finora
- Decision-Making Under Risk and Uncertainty: OutcomesDocumento21 pagineDecision-Making Under Risk and Uncertainty: OutcomesprabodhNessuna valutazione finora
- GMS60CSDocumento6 pagineGMS60CSAustinNessuna valutazione finora
- Ug CR RPTSTDDocumento1.014 pagineUg CR RPTSTDViji BanuNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 07 Self-Test Chemistry Self TestDocumento2 pagineUnit 07 Self-Test Chemistry Self TestOluwatusin Ayo OluwatobiNessuna valutazione finora
- Flexenclosure Esite Brochure PDFDocumento5 pagineFlexenclosure Esite Brochure PDFajdCruiseNessuna valutazione finora
- Ticket Eater - User Manual 2006Documento24 pagineTicket Eater - User Manual 2006tokio2424Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bootloader3 PDFDocumento18 pagineBootloader3 PDFsaravananNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical Report Guideline EEE250Documento8 paginePractical Report Guideline EEE250MOHD ASYRAAF BIN SAIDINNessuna valutazione finora
- JZ990D43501 eDocumento6 pagineJZ990D43501 eМаксим ПасичникNessuna valutazione finora
- VT300 User ManualDocumento21 pagineVT300 User ManualLuvNessuna valutazione finora
- Sentinel Visualizer 6 User GuideDocumento227 pagineSentinel Visualizer 6 User GuideTaniaNessuna valutazione finora
- GS (2006) Vol 2 Rev20 S15 Steel ReinforcementDocumento14 pagineGS (2006) Vol 2 Rev20 S15 Steel ReinforcementLap Chun TUNGNessuna valutazione finora
- A Tutorial On Spectral Sound Processing Using Max/MSP and JitterDocumento16 pagineA Tutorial On Spectral Sound Processing Using Max/MSP and Jittertramazio0% (1)
- SPE-183743-MS Maintaining Injectivity of Disposal Wells: From Water Quality To Formation PermeabilityDocumento19 pagineSPE-183743-MS Maintaining Injectivity of Disposal Wells: From Water Quality To Formation PermeabilityAminNessuna valutazione finora
- Fiber SyllabusDocumento1 paginaFiber SyllabusPaurav NayakNessuna valutazione finora
- Teleprotection Over IP MPLS Network White PaperDocumento23 pagineTeleprotection Over IP MPLS Network White PaperLakshmi Kiran100% (1)
- RRB JE CBT-2 Electronics Tech Paper With Key 31-8-2019 1st ShiftDocumento55 pagineRRB JE CBT-2 Electronics Tech Paper With Key 31-8-2019 1st ShiftKuldeep SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- 5R55W-S Repair DiagnosisDocumento70 pagine5R55W-S Repair Diagnosisaxallindo100% (2)
- PistonDocumento7 paginePistongauravarora93100% (1)
- Biomechanic of Foot PDFDocumento8 pagineBiomechanic of Foot PDFMichealowen BabygoalNessuna valutazione finora
- OK Flux 231 (F7AZ-EL12) PDFDocumento2 pagineOK Flux 231 (F7AZ-EL12) PDFborovniskiNessuna valutazione finora
- Ergonomic DesignDocumento132 pagineErgonomic DesignErin WalkerNessuna valutazione finora
- Wavetek Portable RF Power Meter Model 1034A (1499-14166) Operating and Maintenance Manual, 1966.Documento64 pagineWavetek Portable RF Power Meter Model 1034A (1499-14166) Operating and Maintenance Manual, 1966.Bob Laughlin, KWØRLNessuna valutazione finora
- 1400 CFM TDocumento3 pagine1400 CFM TmahmadwasiNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Electronics Circuits Devices and Applications by Muhammad H RashidDocumento602 paginePower Electronics Circuits Devices and Applications by Muhammad H Rashidkartik balojiNessuna valutazione finora
- Body Deassembly 9 Interior TrimDocumento7 pagineBody Deassembly 9 Interior TrimCarlos TecnicNessuna valutazione finora
- Fractal Cities - A Geometry of Form and Function PDFDocumento432 pagineFractal Cities - A Geometry of Form and Function PDFDavid Diaz100% (1)
- 1SFC132367M0201 PSE Internal Modbus RTUDocumento22 pagine1SFC132367M0201 PSE Internal Modbus RTUAhmed OsmanNessuna valutazione finora