Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Automatic Control (Mech 305) : Saturated Refrigerant To The Evaporator
Caricato da
Peter Owusu0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
7 visualizzazioni1 paginaControl
Titolo originale
Automatic Control
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoControl
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
7 visualizzazioni1 paginaAutomatic Control (Mech 305) : Saturated Refrigerant To The Evaporator
Caricato da
Peter OwusuControl
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 1
UE20028713
AUTOMATIC CONTROL (MECH 305)
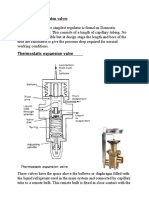
Thermostatic expansion valve is a device designed to regulate (controller) the rate
at which liquid refrigerant (working fluid) flows into the evaporator of refrigerator or
an air conditioning system and also maintains a constant superheat in the
evaporator.
The thermostatic expansion valve as a controller receives and responds to two main
signals. These are;
1. The temperature of the refrigerant as it leaves the evaporator.
2. The pressure in the evaporator itself
The thermostatic expansion valve is installed in the liquid line at the inlet of the
evaporator. A thermal bulb from the evaporator is connected to the thermostatic
expansion valve. The thermal expansion valve consists of;
1. Valve body: Provides means to connect valve to the piping circuit and also has
inlet screen to stop any small particulate matter from entering the valve
2. Diaphragm: Moves the needle in and out of the seat in response to system load
changes. Flexes down to open the valve and upward to close the valve. It is
located at the top of the valve.
3. Needle and seat: Control refrigerant flow through the valve. It is pushed into the
seat to reduce refrigerant flow to the evaporator by the diaphragm.
4. Spring: Acts to push the needle into the seat, causing the valve to close. The
spring pressure determines the evaporator superheat.
5. Adjustable and packing gland
6. Sensing bulb and transmission tube: It senses temperature at the end of the
evaporator which is converted into a pressure and is transmitted to the top of
the diaphragm. The bulb pressure is the only opening pressure that controls the
valve.
As the thermostatic expansion valve regulates the rate at which liquid refrigerant
flows into the evaporator, it maintains a proper supply of refrigerant by matching
this flow rate against how quickly the refrigerant evaporates in the evaporator coil.
If the evaporator superheat is high, the bulb pressure increases and the valve will
open. This ensures that no liquid refrigerant leaves the evaporator. However, low
superheat increases the net refrigerant effect.
Thermal Bulb
Transmission Line
Valve body
Saturated refrigerant to the evaporator
Liquid refrigerant from condenser receiver
Superheat spring adjusting screw
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Expansion ValveDocumento23 pagineExpansion Valvemahmoud EissaNessuna valutazione finora
- Expansion ValvesDocumento19 pagineExpansion ValvesMostafa ZaytounNessuna valutazione finora
- metering_devices_Documento8 paginemetering_devices_Kudzai ManyanyeNessuna valutazione finora
- AC TECHNOLOGY PART 12: AUTOMATIC AND ELECTRONIC EXPANSION VALVESDocumento3 pagineAC TECHNOLOGY PART 12: AUTOMATIC AND ELECTRONIC EXPANSION VALVESAhmed AzadNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of EXPANSION DEVICES (RAC)Documento3 pagineTypes of EXPANSION DEVICES (RAC)Parshant RawatNessuna valutazione finora
- Expansion Valves - Working PrincipleDocumento3 pagineExpansion Valves - Working PrinciplePradeep Sukumaran100% (1)
- Environmental Control SystemDocumento16 pagineEnvironmental Control SystemAlaye AkpanaNessuna valutazione finora
- HVAC Unit 1&2Documento22 pagineHVAC Unit 1&2LOYOLA RS 200Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1,2 - Unit 1Documento137 pagine1,2 - Unit 1Saran T SNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermostatic expansion valves explainedDocumento4 pagineThermostatic expansion valves explainedSwarg VibhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Design and Analysis of Forged Thermostatic Expansion Valve by Using FEADocumento5 pagineDesign and Analysis of Forged Thermostatic Expansion Valve by Using FEARajat JunejaNessuna valutazione finora
- Parts of A Refrigeration SystemDocumento8 pagineParts of A Refrigeration SystemRay RavelNessuna valutazione finora
- Air Conditioning BasicsDocumento2 pagineAir Conditioning BasicsLaurice Ortiz LuisNessuna valutazione finora
- The Thermostatic Expansion ValveDocumento2 pagineThe Thermostatic Expansion ValveMark Anthony Sibayan100% (1)
- Basic Refrigeration Systems Chapter Describes TypesDocumento7 pagineBasic Refrigeration Systems Chapter Describes TypesVijay RajaindranNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Air Conditioning Guide in 38 CharactersDocumento37 pagineBasic Air Conditioning Guide in 38 CharacterscspolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Back Pressure ValveDocumento3 pagineBack Pressure ValveAnkur SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Household RefrigerationDocumento23 pagineHousehold RefrigerationsureshNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 24 Expansion DevicesDocumento49 pagineUnit 24 Expansion DevicesJanice Winkle100% (2)
- Refrigeration System: ComponentsDocumento31 pagineRefrigeration System: ComponentsMae CaspeNessuna valutazione finora
- Heat Pump TrainerDocumento6 pagineHeat Pump TrainerAfzaal FiazNessuna valutazione finora
- Report On Expansion Devices: Icemake Refrigeration Pvt. LTDDocumento31 pagineReport On Expansion Devices: Icemake Refrigeration Pvt. LTDmalayNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of ChillerDocumento13 pagineTypes of Chillerzakaria masud sonyNessuna valutazione finora
- Boiler Operation Made Easy: Procedure For Starting and Stopping A BoilerDocumento24 pagineBoiler Operation Made Easy: Procedure For Starting and Stopping A BoilerBanshi Lal MaanNessuna valutazione finora
- Refrigeration System Components"The provided title "TITLE Refrigeration System ComponentsDocumento14 pagineRefrigeration System Components"The provided title "TITLE Refrigeration System ComponentsRizwan SaeedNessuna valutazione finora
- Tech Tips For Thermostatic Expansion ValvesDocumento9 pagineTech Tips For Thermostatic Expansion ValvesAnonymous UhM8o52cNessuna valutazione finora
- Water Cooling System ExplainedDocumento9 pagineWater Cooling System ExplainedRANDY JR. LANGUIDONessuna valutazione finora
- RefrigerationDocumento65 pagineRefrigerationyassinNessuna valutazione finora
- Safety Devices in Air Conditioning and Refrigeration PlantsDocumento11 pagineSafety Devices in Air Conditioning and Refrigeration PlantsQOBITNessuna valutazione finora
- Expansion DevicesDocumento26 pagineExpansion DevicesYogesh Yadav100% (1)
- Description: Cooling SystemDocumento2 pagineDescription: Cooling SystemvixentdNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 2 Basic Refrigerationsystem and ComponentsDocumento25 pagineGroup 2 Basic Refrigerationsystem and ComponentsVipin VetriNessuna valutazione finora
- COC ORAL EXAM GUIDE ON REFRIGERATION AND AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEMSDocumento105 pagineCOC ORAL EXAM GUIDE ON REFRIGERATION AND AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEMSAshok Kumar0% (1)
- Refrigeration SystemDocumento3 pagineRefrigeration SystemCamillus GulimNessuna valutazione finora
- Brass Thermostatic Expansion Valve: ApplicationDocumento14 pagineBrass Thermostatic Expansion Valve: ApplicationVeera Pandian100% (1)
- Expansion Devices: Figures Are From Stoecker and Jones, Refrigeration and Air Conditioning, 2 Ed., Mcgraw HillDocumento5 pagineExpansion Devices: Figures Are From Stoecker and Jones, Refrigeration and Air Conditioning, 2 Ed., Mcgraw HillGonKilNessuna valutazione finora
- RAC D Expansion DevicesDocumento21 pagineRAC D Expansion DevicesSohaib IrfanNessuna valutazione finora
- 2-COMPRESSIONDocumento28 pagine2-COMPRESSIONVijay RajaindranNessuna valutazione finora
- Heat PumpDocumento1 paginaHeat PumpmikhailNessuna valutazione finora
- Refregeration UnitDocumento24 pagineRefregeration UnitEZWANNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Introduction To CompressorsDocumento12 pagineLesson Introduction To Compressorsmister pogiNessuna valutazione finora
- BG4Documento26 pagineBG4Mandeep MalikNessuna valutazione finora
- A Report On Boiler Feed WaterDocumento11 pagineA Report On Boiler Feed WaterAustin UdofiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Created by Ankur Sharma, Gurudayal Srivastava, Vikram Singh, Sanket TamhaneDocumento12 pagineCreated by Ankur Sharma, Gurudayal Srivastava, Vikram Singh, Sanket TamhaneSankash SoodNessuna valutazione finora
- PPTDocumento16 paginePPTShrvan HirdeNessuna valutazione finora
- Condensers EtcDocumento7 pagineCondensers Etcsmartleo_waloNessuna valutazione finora
- Refrigeration Lab SheetDocumento6 pagineRefrigeration Lab SheetShan aliNessuna valutazione finora
- Expansion in a-WPS OfficeDocumento2 pagineExpansion in a-WPS OfficeMalecha SebastianNessuna valutazione finora
- 03 Expansion Devices Refrigerants 06Documento13 pagine03 Expansion Devices Refrigerants 06scarpredator5Nessuna valutazione finora
- Heat Pump Lab ReportDocumento11 pagineHeat Pump Lab ReportPrecisionetica63% (8)
- Six Types Refrigerant ControlsDocumento47 pagineSix Types Refrigerant Controlssasi taranNessuna valutazione finora
- The Refrigerator - How Does It Work?: Michelle Gettle Eng202C - Section 033 October 19, 2011Documento7 pagineThe Refrigerator - How Does It Work?: Michelle Gettle Eng202C - Section 033 October 19, 2011michellegettleNessuna valutazione finora
- Refrigeration Unit Lab Report FKKDocumento28 pagineRefrigeration Unit Lab Report FKKKicauan KataNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineer Exam Refrigeration Systems GuideDocumento20 pagineEngineer Exam Refrigeration Systems GuideDennis ErminoNessuna valutazione finora
- Air Condition How Does It Works?Documento10 pagineAir Condition How Does It Works?Gwapong CrisNessuna valutazione finora
- Everything You Need To Know About TX ValvesDocumento6 pagineEverything You Need To Know About TX Valvescalishe1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Liquid Cooled SystemsDocumento9 pagineLiquid Cooled Systemsananth k rNessuna valutazione finora
- List of ExperimentsDocumento25 pagineList of Experiments24sandeep24Nessuna valutazione finora
- Marvel Carbureter and Heat Control: As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SDa EverandMarvel Carbureter and Heat Control: As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SNessuna valutazione finora
- Oral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseDa EverandOral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseNessuna valutazione finora
- Design and Analysis of Belt DrivesDocumento44 pagineDesign and Analysis of Belt DrivesPeter Owusu50% (2)
- WeldingDocumento4 pagineWeldingPeter OwusuNessuna valutazione finora
- ECON204Documento29 pagineECON204Peter OwusuNessuna valutazione finora
- Consumer Choice or Behaviour TheoryDocumento4 pagineConsumer Choice or Behaviour TheoryPeter OwusuNessuna valutazione finora