Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Group 3 Grid de Waves With Licencing-1
Caricato da
api-194320273Descrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Group 3 Grid de Waves With Licencing-1
Caricato da
api-194320273Copyright:
Formati disponibili
WHITE, K., CHILES, C., UGOH, L., MARAIS, I., & FERNS, I.
[DOCUMENT TITLE]
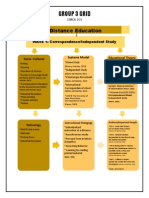
GROUP 3 GRID
OMDE 601
Distance Education
WAVE 1: Correspondence/Independent Study
Socio -Cultural
Systems Model
Educational Theory
*Mining
*Home Study
*Farming
(Moore & Kearsley, 2012)
*Education of Women
*Independent Study
*Pre-Industrial Era:
Conversational Model
Public debate is central in
learning experience
(Moore & Kearsley, 2012)
(Peters, 2001)
*Society to Encourage Study
At Home (1873) (Moore &
*Chautauqua Movement
Kearsley 2012)
(Moore & Kearsley, 2012)
*Correspondence Education
in the Armed Forces (1941)
*International
Correspondence School
(Moore & Kearsley, 2012)
(Moore & Kearsley, 2012)
*Industrial Revolution
* Mass printing
* Popular demand
* Money
Technology
* (1873) The University of
Cape Good Hope Correspondence Study
(Peters, 2001)
*Industrial Era (17501850): Teacher Model
Objective Driven. Teaching
via text. Mass production
of information (Peters, 2001)
*Victorian Era (1832-1901):
Correspondence Model
Independent study
(Peters, 2001)
Authors/Important People
Instructional Pedagogy
*1873 - Anna Eliot Ticknor
Est 1st Home Study School
(Moore, and Kearsley, 2012)
*Mail/Postal system
*Railroads
*Individualized
instruction at a distance
*Printing Press
*Asynchronous mode
*Industrial Revolution
*Personal Tone in letters
(Empathy)
*Answering Behavior
* Learning by reading
printed material
(Bates, 2001)
*1878 - Richard Moulton
Responsible for the idea of using
the mail for education
(Moore, and Kearsley, 2012)
* 1878 Bishop John H. Vincent,
started the Chautauqua Literary &
Scientific Circle, a four year
correspondence course
(Moore and Kearsley, 2012)
*1892 - William R. Harper
started the worlds first university
DE program (Moore and Kearsley, 2012)
*1941- 1943 USAFI
*Brje Holmberg - empathy, guided
pedagogic conversation
WHITE, K., CHILES, C., UGOH, L., MARAIS, I., & FERNS, I.
[DOCUMENT TITLE]
GROUP 3 GRID
OMDE 601
Distance Education
WAVE 2: Systems Approach to Education
Socio-Cultural
*Open University UK - greater
access to higher learning (Bates,
2011)
*Giving access to previously
excluded individuals (Miller,
2010)
*All support systems aimed at
non-traditional students/ social
justice mandate (Miller, 2010)
*Massification of DE where
education is a commodity to be
consumed (Shale, 2010)
*Continued low esteem of DE
(Shale, 2010)
Systems Model
*Academic tutors
Educational Theory
*Private instructors
*Andragogy: understanding
*Further industrialisation
adult learning (Bullen, 1995)
*From Industrial era to
information era (Miller, 2010)
*Transactional distance
between student and
teacher
*Dedicated DE universities
(Shale, 2010)
*Mega-universities (Shale,
2010)
*From DE to open distance
education (Shale, 2010)
*Massification of DE (Shale,
2010)
* Provide more students W/
access to education
* OU & economies of scale to
address Massification of HE
*Increase in white collar workers
* Dual mode Institutions
*Symbolic learning: learners
absorb what is taught to
them, as opposed to
situated learning where
learners are taught to make
their own meaning
(Jonassen et al., 2010).
* Labor moving to cities
Technology
*correspondence learning
*study centers (Shale, 2010)
*multimedia mix: radio, TV
*specially-designed print products
*computer-mediated
communication, collaboration, and
learning allowed for more creativity
in course design (Jonassen et al.,
1995)
*telecourses - 1st via TV then via
low-cost videos cassettes (Miller,
2010)
*Moved from local geographic
delivery via land-line delivery to
satelite delivery that removed
geographic limits (Miller, 2010)
*public broadcasters in the United
States
*Interactive tele-conferencing
(Miller,2010)
Instructional Pedagogy
*Interdisciplinary courses
*The Academics made decisions
about curriculum/teaching methods
(Bates, 2011)
*Because of computer-mediated
tech, teachers are no longer the sole
source of knowledge (Jonassen et
al., 2010)
*Collaboration and conversation
between dyads or larger groups
(Jonassen et al., 2010)
*Blended approach where
telecourse replaced classroom
lectures, but without eliminating
classroom sessions (Miller, 2010)
*Course teams: academic, graphic &
instructional designer (Shale, 2010)
Authors/Important
People
*1969 Tony Bates Open University UK
*1980 Malcom
Knowles: andragogy adult learning
*1972 Otto Peters: DE
is the most
industrialized form of
education
WHITE, K., CHILES, C., UGOH, L., MARAIS, I., & FERNS, I.
[DOCUMENT TITLE]
GROUP 3 GRID
OMDE 601
Distance Education
WAVE 3:
Socio-Cultural
Systems Model
Educational Theory
*Learning in a Knowledge
Building Community
(Moore & Kearsley, 2012)
*Community of Inquiry:
educational experience
influeced by social, teacher
and cognitive presence
*Virtual Universities
(Anderson, 2008)
* Technological
Affordances
*Home Schooling
*Social Constructivist &
Inquiry oriented
approaches (ClevelandInnes & Garrison, 2010,
p.109)
*Open Universities
*Learning Equivalancy
Theory: interaction between
teacher, student, content
(Anderson, 2010)
*Globalization
Technology
*Consortia (Networks of
universities and colleges)
*K-12 Virtual Schools
*Dual Mode Institutions
* For Profit Virtual
Institutions
Instructional Pedagogy
*Constructivism: building
knowledge through
discussion (Anderson & Dron,
2011)
Authors/Important
People
*Laptops
*Online Education
*Smart Phones
*2003 - Anderson, T.
*Massice Open Online
Courses (MOOCs)
Learning Equivalency
Theorem
*Tablets
*Desk Tops
*Learning Management
Systems
*Multimedia Integration
*Course Authoring
Software
* Collaborative Tools
(Google Drive, Discussion
Boards, Chats, E-Mails,
Text Messaging)
*Digitized learning
environments: learning
through hypertext and
hypermedia (Peters,
2010)
*Computer Conferences
*2013 - Akyol, Z.
Community of Inquiry
*2000 - Otto Peters:
First Pedagogical
Analysis
WHITE, K., CHILES, C., UGOH, L., MARAIS, I., & FERNS, I.
[DOCUMENT TITLE]
GROUP 3 GRID
OMDE 601
Distance Education
CURRENT TRENDS:
Socio-Cultural
*Powerful yet low-cost
communication
(Anderson, 2010)
*move from content scarcity
to abandunce (Anderson,
2010)
*Ability to synthesize &
curate large quantities of
data by autonomous agents
(Anderson, 2010)
*Massive open online
learning courses (Schwier,
2011)
Technology
*The semantic web
*The Internet
*Web2.0 and 3.0 tools
*Social media
*Smart-phones, smart
watches, e-readers etc.
*Learning Management
Systems
*Learning analytics (Schwier,
2011)
Systems Model
* Learner-centric view:
Students play a
significant role in the
learning process (Hase &
Kenyon, 2011)
*Knowledge economy:
endless opportunities to
learn and apply new
skills
(Blaschke, 2012)
Instructional Pedagogy
* Network infused
environments (Anderson,
2010)
*Blended and online
learning
*Connectivism
*Learner-centered
learning (Hase & Kenyon,
2000)
Educational Theory
*Connectivism: networked
learning (Anderson &
Dron, 2011)
*Heutagogy: selfdetermined learning (Hase
& Kenyon, 2011)
*Complexity theory:
(Anderson, 2010)
*Pedagogy of nearness
(Anderson, 2010)
*Net-centric learning
theories (Anderson, 2010)
Authors/Important
People
* George Siemens Connectivism, Learning
Analytics
* Terry Anderson - Interaction
Equivalency Theory
* Lisa Blaschke - Life Long
Learning
* Hase & Kenyon- Heutagogy
* Stephen Downes Connectivism, MOOCs
* Otto Peters - Importance of
digitized environments
WHITE, K., CHILES, C., UGOH, L., MARAIS, I., & FERNS, I.
[DOCUMENT TITLE]
References
Akyol, Z. & Garrison, D.R. (2013). The Community of Inquiry theoretical framework. In
M.G.Moore (Ed.), The handbook of distance education. New York, NY: Routledge.
Anderson, T. (2008). The theory and practice of online learning. Edmonton, AB: AU Press,
Athabasca University.
Anderson, T. (2010). Theories for learning with emerging technologies. In G. Veletsianos (Ed.),
Emerging technologies in distance education (pp. 23-40). Canada: Athabasca University
Press. Retrieved from,
http://www.aupress.ca/books/120177/ebook/99Z_Veletsianos_2010Emerging_Technologies_in_Distance_Education.pdf
Anderson, T. & Dron, J. (2011, March). Three generations of distance education pedagogy.
International Review of Research on Open and Distance Learning, 12(3). Retrieved from
http://www.irrodl.org/index.php/irrodl/article/view/890/1826
Bates, A. W. (2011, November). The second wave of distance education and history of the Open
University United Kingdom [Online video]. Available from http://vimeo.com/32292234
(Transcript: http://www.box.com/s/cvygk4334sub0i6atrn8)
Blaschke, L.M. (2012). Heutagogy and lifelong learning: A review of heutagogical practice and
self-determined learning. International Review of Research in Open and Distance
Learning, 13(1), 56-71. Retrieved from:
http://www.irrodl.org/index.php/irrodl/article/view/1076/2113
Bullen, M. (1995, June). Andragogy and university distance education. Paper presented to the
17th conference on the International Council for Open and Distance Education,
Birmingham, UK. Available from http://www.box.com/s/ap4nq2zf1jujkyo65pz0
WHITE, K., CHILES, C., UGOH, L., MARAIS, I., & FERNS, I.
[DOCUMENT TITLE]
Garrison, D.R., Cleveland-Innes (2010). Teaching and Learning In Post-Industrial Distance
Education. In M. F. An introduction to distance education: Understanding teaching and
learning in a new era (p. 109). New York & London: Routledge.
Hase, S., & Kenyon, C. (2000). From andragogy to heutagogy. In UltiBase Articles. Retrieved
from http://pandora.nla.gov.au/nphwb/20010220130000/http://ultibase.rmit.edu.au/Articles/dec00/hase2.htm
Jonassen, D., Davidson, M., Collins, M., Campbell, J., & Bannan Haag, B. (1995).
Constructivism and computer-mediated communication in distance education. The
American Journal of Distance Education, 9(2), 7-26. Available from
http://www.box.com/s/i9y1f17cii6zmb0pi4qd
Miller, G. E. (2010). Organization and technology of distance education. In M. F. ClevelandInnes & D. R. Garrison (Eds.), An introduction to distance education: Understanding
teaching and learning in a new era (pp. 26-45). New York & London: Routledge.
Moore, G.M., Kearsley, G. (2012). The Historical Context. In Mark Kerr & Genevieve Allen
(Eds.), Distance Education: A Systems View of Online Learning (pp. 23-29). Belmont
CA: Wadsworth.
Peters, O. (2001) Distance and Proximity. In Fred Lockwood (Eds.), Learning & Teaching In
Distance Education: Analysis And Interpretations From An International Perspective
(pp.19-25). Sterling VA: Stylus Publishing Inc.
Peters, O. (2010). Digitized learning environments: New chances and opportunities. In O.
Peters, Distance education in transition: Developments and issues (5th edition) (pp. 141153). Oldenburg, Germany: BIS-Verlag der Carl von Ossietzky Universitt Oldenburg.
Available from http://www.box.com/shared/ktx7ipccetotqrr11mct
WHITE, K., CHILES, C., UGOH, L., MARAIS, I., & FERNS, I.
[DOCUMENT TITLE]
Schwier, R. (2011). Connectivism. 30 minute video interview with George Siemens. Retrieved
from http://rickscafe.wordpress.com/2011/08/05/interview-with-george-siemens-aboutconnectivism/
Shale, D. (2010). Beyond boundaries: The evolution of distance education. In M. F. ClevelandInnes & D. R. Garrison (Eds.), An introduction to distance education: Understanding
teaching and learning in a new era (pp. 91-107). New York & London: Routledge.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Business Analytics Capstone Project TemplateDocumento13 pagineBusiness Analytics Capstone Project TemplateChristopher Lam100% (4)
- Storyboard TemplateDocumento11 pagineStoryboard Templateapi-194320273Nessuna valutazione finora
- Year 9 WwiDocumento28 pagineYear 9 Wwiapi-318829239Nessuna valutazione finora
- Psychology in The Real WorldDocumento3 paginePsychology in The Real WorldEmily EvensonNessuna valutazione finora
- Zlaps Overview StoryboardDocumento11 pagineZlaps Overview Storyboardapi-194320273Nessuna valutazione finora
- Jira Process To Change OverviewDocumento14 pagineJira Process To Change Overviewapi-194320273Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bibliography Omde601Documento2 pagineBibliography Omde601api-194320273Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reflectionwave 3Documento2 pagineReflectionwave 3api-194320273Nessuna valutazione finora
- Group 3 Grid Finalrevision 10 10 15Documento4 pagineGroup 3 Grid Finalrevision 10 10 15api-194320273Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ottopetersindustrializationpt 2Documento1 paginaOttopetersindustrializationpt 2api-194320273Nessuna valutazione finora
- Business Enterprise Simulation NotesDocumento12 pagineBusiness Enterprise Simulation NotesShakira Leslene StonecypherNessuna valutazione finora
- Purposive CommunicationDocumento1 paginaPurposive CommunicationArt Lloyd DatahanNessuna valutazione finora
- How Do You Show Your Respect Toward People Whose Opinions Are Different From Yours?Documento2 pagineHow Do You Show Your Respect Toward People Whose Opinions Are Different From Yours?Jonela LazaroNessuna valutazione finora
- Psychology 11th Edition Wade Test BankDocumento35 paginePsychology 11th Edition Wade Test Bankvoleryremurmur560v5100% (27)
- Research Paper (20 PTS) - GuidelinesDocumento1 paginaResearch Paper (20 PTS) - GuidelinesjasonmscofieldNessuna valutazione finora
- Essential Research Skills For Teens Unit - Sheet1 2Documento9 pagineEssential Research Skills For Teens Unit - Sheet1 2api-642237718Nessuna valutazione finora
- III Quarter-Math 7 DLLDocumento6 pagineIII Quarter-Math 7 DLLKM Laysa GonzalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment Instructions The QuestionsDocumento1 paginaAssignment Instructions The QuestionsMellaniNessuna valutazione finora
- MBODocumento16 pagineMBODr. Rakshit SolankiNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 4 Q2 2022-2023 Budgeted Lesson MAPEH 4 - MGA - 1Documento8 pagineGrade 4 Q2 2022-2023 Budgeted Lesson MAPEH 4 - MGA - 1Dian G. MateoNessuna valutazione finora
- Reading Comprehension StrategiesDocumento3 pagineReading Comprehension StrategiesMeni PappaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sleeping For Exam Success - TranscriptDocumento2 pagineSleeping For Exam Success - TranscriptAmir AslanNessuna valutazione finora
- Fraser 2016Documento4 pagineFraser 2016Loan TrầnNessuna valutazione finora
- Masa Depan Profesi Akuntansi Dalam Revolusi Industri 4.0: Analisis Meta-Sintesis AbstrakDocumento15 pagineMasa Depan Profesi Akuntansi Dalam Revolusi Industri 4.0: Analisis Meta-Sintesis AbstrakHoàng Hải QuyênNessuna valutazione finora
- Elt 305Documento9 pagineElt 305Almira Menson-MakalingkangNessuna valutazione finora
- ETFO Internal Memo On New CurriculumDocumento2 pagineETFO Internal Memo On New CurriculumCityNewsTorontoNessuna valutazione finora
- Etd9534 ACant PDFDocumento228 pagineEtd9534 ACant PDFDiana PopNessuna valutazione finora
- An Intercultural CLT Model For EFL LearnersDocumento16 pagineAn Intercultural CLT Model For EFL LearnersDG AnnNessuna valutazione finora
- PSYCH 101 Motivation, Values and Purpose AssignDocumento4 paginePSYCH 101 Motivation, Values and Purpose AssignLINDA HAVENSNessuna valutazione finora
- Feral Child ShortDocumento4 pagineFeral Child ShortGrigoras Laura IoanaNessuna valutazione finora
- A Study On Preference of Learning Style in Relation To Academic Achievement in Commerce Among Higher Secondary School StudentsDocumento9 pagineA Study On Preference of Learning Style in Relation To Academic Achievement in Commerce Among Higher Secondary School StudentsEditor IJTSRDNessuna valutazione finora
- Impact of Emotional Intelligence On Academic Performance of Engineering Students (2019) 7p (Fakhar Et Al.)Documento7 pagineImpact of Emotional Intelligence On Academic Performance of Engineering Students (2019) 7p (Fakhar Et Al.)Wei LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Talent System Assessment Tool (TSAT)Documento4 pagineTalent System Assessment Tool (TSAT)inaisaaqNessuna valutazione finora
- Speech According To Manner of DeliveryDocumento19 pagineSpeech According To Manner of DeliveryPerfect BeanNessuna valutazione finora
- Soalan Lerning SkillsDocumento22 pagineSoalan Lerning SkillsKhairul NizamNessuna valutazione finora
- Fin-Edl221 S-LV-C Grade 7 DemoDocumento3 pagineFin-Edl221 S-LV-C Grade 7 DemoDanna Mae Terse YuzonNessuna valutazione finora
- May 24 Art PcupDocumento3 pagineMay 24 Art Pcupaanyadhingra94Nessuna valutazione finora