Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Blues
Caricato da
api-299030309Descrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Blues
Caricato da
api-299030309Copyright:
Formati disponibili
Blues
The blues originated from the African-Americans in the
Deep South in North America around the end of the
19th century. The genre is a fusion of traditional African
music and European folk music, spirituals, work
songs, field hollers, shouts and chants, and rhymed
simple narrative ballads. The blues has influenced
many other genres like jazz and rock. The first
publication of blues sheet music was in 1908 and since
then has evolved from vocal music sang by slaves into
a wide variety of styles and subgenres. Blues subgenres
include country blues, acoustic blues which evolved
into electric blues during the 1940s and rock blues
which evolved in the 1960s and 70s.
The name blues come from the saying blue devil
meaning melancholy and sadness. The lyrics to blues
songs are often describing sadness. The 12 bar
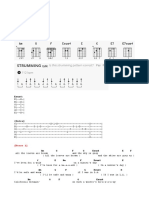
structure is a harmonic progression used in blues,
played over a 4/4 beat. The progression uses the
subtonic (1) the tonic (4) and the dominant (5).
Chords played over a 12-bar
scheme:
Chords for a blues in C:
I or IV
I7
IV
IV
I7
V or
IV
I or V
C or F
C7
C7
G or F
C or G
Reggae
The genre of Reggae was originated in the 1960s in
Jamaica. Its used in much Jamaican dance music, but
has strongly influenced much American jazz and blues
and African music. One of the most easily recognizable
elements is offbeat rhythms and staccato chords played
by a guitar or piano. The tempo of reggae is usually
slower than ska but faster than rock steady.[3] The
concept of "call and response" can be found throughout
much reggae music. The bass guitar is used a lot in
reggae and is given a thick and heavy sound. The
guitar normally plays the off beats. Reggae as a
musical term first appeared in print with the 1968 rock
steady hit "Do the Reggay" by The Maytals. Reggae is
played in 4/4, because it doesnt work musically in
other signatures like . The music emphasized the 2nd
beat and 4th beat of each bar. Reggae songs normally
use standard generic chords progressions. The concept
of "call and response" can be found throughout reggae
music, in the vocals but also in the way parts are
composed and arranged for each instrument. The
emphasis on the "third beat" of the bar also results in a
different sense of musical phrasing, with bass lines and
melody lines often emphasizing what might be
considered "pick up notes" in other genres. A standard
drum kit is generally used in reggae, but the snare
drum is often tuned very high to give it a timbales-type
sound. Some reggae drummers use an additional
timbale or high-tuned snare to get this sound. Crossstick technique on the snare drum is commonly used,
and tom-tom drums are often incorporated into the
drumbeat itself.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- BRGMIK002 JIC2 Assignment4Documento4 pagineBRGMIK002 JIC2 Assignment4Mika BurgerNessuna valutazione finora
- Book Report-2Documento18 pagineBook Report-2AmMy PenNessuna valutazione finora
- Rock-Midterm DefinitionsDocumento7 pagineRock-Midterm DefinitionsAngelica JuarezNessuna valutazione finora
- Blues - Chords, Shuffle, Crossharp - for the diatonic harmonica / BluesharpDa EverandBlues - Chords, Shuffle, Crossharp - for the diatonic harmonica / BluesharpNessuna valutazione finora
- IGCSE Music Revision NotesDocumento20 pagineIGCSE Music Revision NotesTony WongNessuna valutazione finora
- Riffs: How to Create and Play Great Guitar RiffsDa EverandRiffs: How to Create and Play Great Guitar RiffsValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (3)
- You Can Get It UpdatedDocumento4 pagineYou Can Get It UpdatedJacob MorganNessuna valutazione finora
- Bob Marley Once SaidDocumento2 pagineBob Marley Once SaidHanilen CatamaNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 Bar Blues EssayDocumento3 pagine12 Bar Blues EssayblondieajbNessuna valutazione finora
- Jonathan Butler BioDocumento5 pagineJonathan Butler BioChase CharlesNessuna valutazione finora
- Area of Study 5 Jazz Study Notes - Styles and PeopleDocumento20 pagineArea of Study 5 Jazz Study Notes - Styles and PeopleEdward McCallNessuna valutazione finora
- Zackorborg Music ReviewDocumento2 pagineZackorborg Music ReviewZachary Gabriel L. PizonNessuna valutazione finora
- Jazz and Improvisation BookletDocumento16 pagineJazz and Improvisation Bookletcharlmeatsix100% (3)
- Finley Reggae Powerpoint 1Documento21 pagineFinley Reggae Powerpoint 1api-351015803Nessuna valutazione finora
- Characteristics of GenresDocumento2 pagineCharacteristics of GenresTEJONES, Ky Kiske C.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Howlin Wolf I M Leaving You PDFDocumento3 pagineHowlin Wolf I M Leaving You PDFMrPughTheMusicManNessuna valutazione finora
- Popular Song Since 1960 Revision BookletDocumento3 paginePopular Song Since 1960 Revision BookletLisa BargeNessuna valutazione finora
- Alfassy Leo Blues Hanon Traduccion AutomáticaDocumento15 pagineAlfassy Leo Blues Hanon Traduccion AutomáticaFlâneur L0% (1)
- I'm Leavin' YouDocumento4 pagineI'm Leavin' YouHashtag JoeNessuna valutazione finora
- Blues Play-a-Long and Solos Collection for Piano/Keyboards Beginner SeriesDa EverandBlues Play-a-Long and Solos Collection for Piano/Keyboards Beginner SeriesValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Rhythm 2Documento9 pagineRhythm 2Derrick MorganNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 6 50 Miles Davis QuintetDocumento5 pagineUnit 6 50 Miles Davis QuintetMax WeltonNessuna valutazione finora
- Different Types of MusicDocumento6 pagineDifferent Types of MusicZaw Ye HtikeNessuna valutazione finora
- Louis Armstrong History of JazzDocumento7 pagineLouis Armstrong History of Jazzzega5394100% (1)
- Slam Stewart:: Basic BioDocumento3 pagineSlam Stewart:: Basic BioOscarPetersonNessuna valutazione finora
- Landscape ArtDocumento2 pagineLandscape ArtAndrewjaye OcampoNessuna valutazione finora
- Number One with an Axe! A Look at the Guitar’s Role in America’s #1 HitsDa EverandNumber One with an Axe! A Look at the Guitar’s Role in America’s #1 HitsNessuna valutazione finora
- Guide MusicDocumento3 pagineGuide MusicAnonymous uCuGCvm100% (1)
- Jazz Styles ShortDocumento4 pagineJazz Styles Short8arcaNessuna valutazione finora
- Yellow BirdDocumento4 pagineYellow BirdMrPughTheMusicManNessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching Guide: Area of Study 2 - Pop Music: MelodyDocumento26 pagineTeaching Guide: Area of Study 2 - Pop Music: Melodyuq2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Music & DanceDocumento5 pagineMusic & DanceMarlon Kevin ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Jazz StylesDocumento4 pagineJazz Stylesalgo99Nessuna valutazione finora
- 37 JazzDocumento21 pagine37 JazzEdward HanNessuna valutazione finora
- Rock Music Is A Genre Of: Urban ContemporaryDocumento1 paginaRock Music Is A Genre Of: Urban ContemporaryLucia ScripcariNessuna valutazione finora
- History of MusicDocumento7 pagineHistory of MusicAdry Mateo RamonNessuna valutazione finora
- Blues Play-A-Long and Solos Collection for Piano/Keyboards Intermediate-Advanced Level: Blues Play-A-Long and Solos Collection for Intermediate-Advanced LevelDa EverandBlues Play-A-Long and Solos Collection for Piano/Keyboards Intermediate-Advanced Level: Blues Play-A-Long and Solos Collection for Intermediate-Advanced LevelValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (2)
- DOCU8000009189Documento3 pagineDOCU8000009189Sf Tep HeroNessuna valutazione finora
- The Blues Play-A-Long and Solos Collection for Guitar Beginner Series: The Blues Play-A-Long and Solos Collection Beginner SeriesDa EverandThe Blues Play-A-Long and Solos Collection for Guitar Beginner Series: The Blues Play-A-Long and Solos Collection Beginner SeriesNessuna valutazione finora
- The Blues Play-A-Long and Solos Collection for Flute Beginner Series: The Blues Play-A-Long and Solos Collection Beginner SeriesDa EverandThe Blues Play-A-Long and Solos Collection for Flute Beginner Series: The Blues Play-A-Long and Solos Collection Beginner SeriesNessuna valutazione finora
- VZM 211 Lecture 6Documento20 pagineVZM 211 Lecture 6nb7bxcmbj7Nessuna valutazione finora
- GarageBand 3 World Music Instrument TipsDocumento47 pagineGarageBand 3 World Music Instrument TipsmichaochiriumaNessuna valutazione finora
- Number One with an Axe! A Look at the Guitar’s Role in America’s #1 Hits, Volume 6, 1980-84Da EverandNumber One with an Axe! A Look at the Guitar’s Role in America’s #1 Hits, Volume 6, 1980-84Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Blues Scale for Trombone: The Blues ScaleDa EverandThe Blues Scale for Trombone: The Blues ScaleValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (2)
- Genre CharacteristicsDocumento29 pagineGenre Characteristicsspencer grahamNessuna valutazione finora
- Music Q2W1M1Documento1 paginaMusic Q2W1M1Gelia GampongNessuna valutazione finora
- Modern n5Documento51 pagineModern n5eyaoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Blues Play-A-Long and Solos Collection for Bb (tenor) sax Beginner Series: The Blues Play-A-Long and Solos Collection Beginner SeriesDa EverandThe Blues Play-A-Long and Solos Collection for Bb (tenor) sax Beginner Series: The Blues Play-A-Long and Solos Collection Beginner SeriesNessuna valutazione finora
- Origins of Pop MusicDocumento2 pagineOrigins of Pop Musicapi-589780132Nessuna valutazione finora
- Genres of Popular MusicDocumento6 pagineGenres of Popular MusicNelson TongNessuna valutazione finora
- From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia: CompingDocumento10 pagineFrom Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia: CompingJginer RiusNessuna valutazione finora
- MasterClass - Cantieri - Handout Drums Lessons PDFDocumento16 pagineMasterClass - Cantieri - Handout Drums Lessons PDFeliasabboud22100% (1)
- Fake Platcis TreesDocumento1 paginaFake Platcis Treesapi-299030309Nessuna valutazione finora
- Back To BlackDocumento1 paginaBack To Blackapi-299030309Nessuna valutazione finora
- BattlesDocumento1 paginaBattlesapi-299030309Nessuna valutazione finora
- HysteriaDocumento1 paginaHysteriaapi-299030309Nessuna valutazione finora
- Listening GuideDocumento2 pagineListening Guideapi-299030309100% (1)
- Listening GuideDocumento2 pagineListening Guideapi-299030309100% (1)
- Interlude in BB For Clarinet Solo and Orchestra byDocumento46 pagineInterlude in BB For Clarinet Solo and Orchestra byCarlo Rossi100% (1)
- The Fairly OddParents: "My Shiny Teeth and Me"Documento12 pagineThe Fairly OddParents: "My Shiny Teeth and Me"Ian DavisNessuna valutazione finora
- TuxGuitar Minor SwingDocumento8 pagineTuxGuitar Minor SwingGiorgio SalbegoNessuna valutazione finora
- Curriculum Project Muse 375Documento19 pagineCurriculum Project Muse 375api-354623976Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 Melody: Musical Line 1. Defining MelodyDocumento7 pagineChapter 1 Melody: Musical Line 1. Defining MelodyJorge Molina MonsivaisNessuna valutazione finora
- Pentatonica Mayor PDFDocumento2 paginePentatonica Mayor PDFJames LeandroNessuna valutazione finora
- I'm Calling You PartitionDocumento2 pagineI'm Calling You PartitionBento67% (3)
- Mike TomoroDocumento16 pagineMike TomoroEJimenez86100% (4)
- The First NoelDocumento2 pagineThe First NoelSteven Roox100% (1)
- Emmanuel Satb 02 Choral+ScoreDocumento9 pagineEmmanuel Satb 02 Choral+ScoreSixtusNessuna valutazione finora
- 43 Real BooksDocumento1 pagina43 Real Booksmazza241126% (47)
- ANZCA Singing Syllabus 2018-20Documento93 pagineANZCA Singing Syllabus 2018-20Eka Setiawati100% (1)
- Open G Tuning - Chord ChartsDocumento3 pagineOpen G Tuning - Chord ChartsHud McClanahan100% (1)
- The Anthem William Murphy Key of DDocumento1 paginaThe Anthem William Murphy Key of DJessica Kenney67% (3)
- Pe 112 - Lo11Documento4 paginePe 112 - Lo11Nikkaa XOXNessuna valutazione finora
- Come in Alone ChordsDocumento1 paginaCome in Alone ChordsKarlo Marco CletoNessuna valutazione finora
- Romantic PeriodDocumento63 pagineRomantic Periodvkris71100% (1)
- California Dreamin ChordsDocumento2 pagineCalifornia Dreamin ChordsMaurizioNessuna valutazione finora
- Vocal Choral Techniques Fairfield UDocumento14 pagineVocal Choral Techniques Fairfield UJason TiongcoNessuna valutazione finora
- Music Check SheetDocumento5 pagineMusic Check Sheetandyedwards73Nessuna valutazione finora
- Eduqas Ko AfricaDocumento1 paginaEduqas Ko AfricaJ FrancisNessuna valutazione finora
- Approaching Renaissance Music Using Tane PDFDocumento24 pagineApproaching Renaissance Music Using Tane PDFAntonio Peña Fernández100% (1)
- The Art of Crafting Your Time Feel Vol 1Documento22 pagineThe Art of Crafting Your Time Feel Vol 1aingerutNessuna valutazione finora
- Cadenza Doppia and 5 Cool Things U Can Do With It For Chapman StickDocumento5 pagineCadenza Doppia and 5 Cool Things U Can Do With It For Chapman StickRoy VergesNessuna valutazione finora
- The Influence of Different Structural Features On Felt Musical TensionDocumento15 pagineThe Influence of Different Structural Features On Felt Musical TensionLorenzo CapostagnoNessuna valutazione finora
- I'm A BelieverDocumento11 pagineI'm A BelieverJosieNessuna valutazione finora
- Dep Ed Music Grade 9 2nd QuarterDocumento28 pagineDep Ed Music Grade 9 2nd QuarterRiz MonterolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Stamp Method Friedman StanleyDocumento4 pagineStamp Method Friedman StanleyWilliam Flores100% (1)
- University of Illinois Press, Council For Research in Music Education Bulletin of The Council For Research in Music EducationDocumento12 pagineUniversity of Illinois Press, Council For Research in Music Education Bulletin of The Council For Research in Music Educationchua0726Nessuna valutazione finora
- Autumn Leaves With ArpeggiosDocumento7 pagineAutumn Leaves With ArpeggiosLuis ArmestoNessuna valutazione finora