Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Unit 2 Vocabulary Cards
Caricato da
api-198321679Descrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Unit 2 Vocabulary Cards
Caricato da
api-198321679Copyright:
Formati disponibili
Seventh Grade Social Studies
Unit 2: Beginnings of Human Societies
SS070202
Vocabulary
10
world history
11
prehistoric
the field study concerned
with global processes and patterns of
humanity over time.
the time or period before
recorded or written
history
Example: Studying how different societies in
different places changed to from huntergathering to farming is a global pattern that is
examined in world history.
Example: Prehistoric man used tools made of
stone.
(SS070202)
12
Stone Age
(SS070202)
13
topographical map
the earliest known
period of human
culture, marked by the creation and use
of stone tools
a type of map
characterized by
large-scale detail and contour lines
representing elevation changes.
Examples: The Stone Age lasted during the
Paleolithic and Neolithic periods because
during both humans used tools.
Example: I can tell the difference between
mountains and valleys on a topographical map.
(SS070201)
(SS070201)
14
cave paintings
15
relative dating
paintings on cave
walls and ceilings,
especially those
dating from prehistoric times.
determining the age of an object based
upon surrounding fossils and geological
deposits
Example: The Cave Paintings of Lascaux
were created in prehistoric times.
(SS070202)
Michigan Citizenship Collaborative Curriculum
Copyright 2010-2015 by Oakland Schools
Example: Through relative dating, one could
determine that the stone tools found beneath
several layers of sediment were older than the
artifacts found near the surface.
(SS070202)
Page 1 of 8
July 13, 2015
Seventh Grade Social Studies
Unit 2: Beginnings of Human Societies
SS070202
Vocabulary
16
absolute dating
(carbon dating /
radioactive dating)
17
claim
the process of determining a specific
date of an artifact based on physical or
chemical properties of the object
a statement about what
someone thinks is true,
especially when open to question
Example: The historian made a claim about
how prehistoric people used stone tools.
Example: The archaeologist used carbon
dating to determine the date of the skull found
at the site.
(SS070202)
(SS070202)
18
evidence
19
artifact
information used to support a
claim
any object made or
used by mankind.
Example: The historian used evidence such as
a fragment of Egyptian papyrus to support her Example: The archaeologist found a falcon
claim about communication patterns.
sculpture at the site.
(SS070202)
(SS070202)
21
hominid
20
human evolution
represents the
humans and their closest
evidence-based,
relatives.
scientific understanding of the origin and
development of humanity
Example: The Nakalipithecus fossil found in
Kenya thought to be the last common ancestor
between apes and humans.
Example: Humans, chimpanzees, gorillas, and
orangutans are all hominids.
(SS070203)
(SS070203)
Michigan Citizenship Collaborative Curriculum
Copyright 2010-2015 by Oakland Schools
Page 2 of 8
July 13, 2015
Seventh Grade Social Studies
Unit 2: Beginnings of Human Societies
SS070202
Vocabulary
22
biome
23
adaptation
a major
ecological
community that
corresponds to a climate and is
characterized by plants that live in that
are adapted to that environment
the process or state of
changing to fit a new
environment or different
conditions
Example: Low latitude biomes include
rainforest, savanna, and desert.
Example: Sherpas of Nepal have a higher
number of red blood cells which allow them to
live at higher Himalayan altitudes.
(SS070204)
(SS070204)
24
human
migration
The physical
movement by humans from one area to
another, sometimes over long distances
or in large groups.
Example: Homo sapiens appear to have
moved out of Africa around 70,000 years ago.
(SS070204)
26
Paleolithic Age or Era
27
foragers
the period of the Stone Age
that began about 2.5 to 2
million years ago, marked by the
earliest use of tools made of chipped
stone
Example: The Paleolithic Age is also known
as the Old Stone Age.
a group of people who survive by
hunting and gathering over a large
region
Example: Foragers spread to most parts of
the globe following large mammals.
(SS070205)
(SS070205)
Michigan Citizenship Collaborative Curriculum
Copyright 2010-2015 by Oakland Schools
Page 3 of 8
July 13, 2015
Seventh Grade Social Studies
Unit 2: Beginnings of Human Societies
SS070202
Vocabulary
28
linguistic artifacts
29
non-linguistic artifacts
artifacts that are written
language or have writing on
them
artifacts that do not have written
language like stone tools or human
remains
Example: Linguistic artifacts provide textual
information about the past.
Example: Non-linguistic artifacts like
arrowheads help us study prehistory.
(SS070205)
(SS070205)
30
lifeways
31
social institutions
the ways in which a group of
people live, find food, and behave
organizations that large groups of
humans (societies, cultures) create to help
solve social problems
Example: Foraging lifeways were
characteristic of the Paleolithic Age.
Example: Religion is one social institution
that almost every culture has.
(SS070205)
(SS070205)
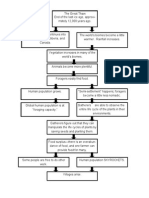
32
the Great Thaw
33
agrarian
an event that
happened about
10,000 years ago
when the Earths climate warmed and
regions of the planet became more
temperate
a type of society
or culture based
around farming
and raising livestock
Example: After the Great Thaw many plants
and animals began to flourish due to the
warmer climate.
(SS070206)
Michigan Citizenship Collaborative Curriculum
Copyright 2010-2015 by Oakland Schools
Example: Thomas Jefferson saw the United
States as an agrarian society.
(SS070206)
Page 4 of 8
July 13, 2015
Seventh Grade Social Studies
Unit 2: Beginnings of Human Societies
SS070202
Vocabulary
34
turning point
35
Neolithic Age
or Era
an event or
occurrence which
causes a very significant change
Example: The Agricultural Revolution was a
turning point in human history.
(SS070206)
36
Agricultural
Revolution (or
Neolithic
Revolution)
a term that
means new
stone age and refers to period when
humans came to live in agricultural
communities
Example: The Neolithic Age began nearly
10,000 years ago.
(SS070206)
37
BCE
Before
Common Era
a turning point that
began about 10,000 years ago when
humans began to live in settled
communities and raise plants and
animals
Example: The development of new technology
that allowed humans to become more efficient
farmers is called the Agricultural Revolution.
a non-religious
alternative to
the use of B.C., the era of prehistory
and much of antiquity
Example: My textbook uses the annotation,
BC, but scholarly work refers to that period
as BCE.
(SS070206)
(SS070206)
Michigan Citizenship Collaborative Curriculum
Copyright 2010-2015 by Oakland Schools
Page 5 of 8
July 13, 2015
Seventh Grade Social Studies
Unit 2: Beginnings of Human Societies
38
CE
Common Era
SS070202
Vocabulary
39
region
an alternative and nonreligious method of
notation to the
traditional A.D., or Anno Domini
a geographic area
considered as a
unit for
geographical,
functional, social, or cultural reasons
Example: The period referred to CE or
AD is the time frame starting with 0 on
the Gregorian calendar.
Example: The Great Lakes region is
comprised of all the places that border
the Great Lakes.
(SS070206)
40
specialization /
division of labor
when different
people in society
take on specific roles or jobs that
require unique skill sets
Example: In healthcare, there are
specializations like surgery,
pediatrics, dentistry, and
orthodontics.
(SS070206)
41
settlement
a permanent
community where
people live
Example: Jericho, atalhyk, and
Tenta were early human
settlements.
(SS070207)
(SS070207)
Michigan Citizenship Collaborative Curriculum
Copyright 2010-2015 by Oakland Schools
Page 6 of 8
July 13, 2015
Seventh Grade Social Studies
Unit 2: Beginnings of Human Societies
42
surplus
SS070202
Vocabulary
43
social organizations /
institutions
having more than
you need (as
opposed to more
than you want).
Example: There was a surplus of
cupcakes after the party, so the class
gave the rest away to other teachers.
(SS070207)
44
domestication
an organized group
or network in a
society that exists to
help meet the long-term needs of its
people (food, clothing, shelter,
education, rules, safety).
Example: Schools are organized to
help prepare young people for adult
life and work.
(SS070207)
an approach to altering
the genetic makeup of
plants and animals to
make them more useful
to humans
Example: Humans domesticated plants
by planting seeds from individual plants
that seemed most desirable for their size,
taste, and nutrition.
(SS070207)
Michigan Citizenship Collaborative Curriculum
Copyright 2010-2015 by Oakland Schools
Page 7 of 8
July 13, 2015
Seventh Grade Social Studies
Unit 2: Beginnings of Human Societies
SS070202
Vocabulary
45
archaeological site
46
global patterns
the place of an
archaeological
investigation where
evidence of past
activity is uncovered and preserved
a frequent and
widespread
occurrences or
similar events that
happen in different
places in the world
Example: They found human remains, stone
tools, and other artifacts at the archaeological
site.
(SS070208)
Example: The transition from foraging to
agriculture is an example of a global pattern in
world history.
(SS070208)
47
technology
a branch of
knowledge that
relates to
inventions and
discoveries that help modernizing
human lifestyle and surrounding
environment
Example: Through technology humans were
able to domesticate plants and animals.
(SS070208)
Michigan Citizenship Collaborative Curriculum
Copyright 2010-2015 by Oakland Schools
Page 8 of 8
July 13, 2015
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- 2016 Djhs Track and Field RecordsDocumento1 pagina2016 Djhs Track and Field Recordsapi-198321679Nessuna valutazione finora
- Account Analysis FormDocumento1 paginaAccount Analysis Formapi-198321679Nessuna valutazione finora
- 7th Ss - Primary-Secondary Sample AnswersDocumento6 pagine7th Ss - Primary-Secondary Sample Answersapi-198321679Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 3 VocabularyDocumento8 pagineUnit 3 Vocabularyapi-198321679Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4 VocabularyDocumento8 pagineUnit 4 Vocabularyapi-198321679Nessuna valutazione finora
- Learning TargetsDocumento1 paginaLearning Targetsapi-198321679Nessuna valutazione finora
- Farming To Foraging DiagramDocumento1 paginaFarming To Foraging Diagramapi-198321679Nessuna valutazione finora
- Jared Diamond and The Theory of Geographic LuckDocumento2 pagineJared Diamond and The Theory of Geographic Luckapi-198321679Nessuna valutazione finora
- Learning TargetsDocumento2 pagineLearning Targetsapi-198321679Nessuna valutazione finora
- Capitalism II Website DocumentDocumento1 paginaCapitalism II Website Documentapi-198321679Nessuna valutazione finora
- Test ReviewDocumento18 pagineTest Reviewapi-198321679Nessuna valutazione finora
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- 120 Days Planner For Prelims 2021 DAY 11 Prehistoric PeriodDocumento10 pagine120 Days Planner For Prelims 2021 DAY 11 Prehistoric PeriodAllindiatestNessuna valutazione finora
- World CivilizationDocumento75 pagineWorld Civilizationodin3zNessuna valutazione finora
- World CivilizationDocumento224 pagineWorld CivilizationRommel Villaroman Esteves100% (1)
- Chap 3 - Reading Essentials Nicholas CeballosDocumento5 pagineChap 3 - Reading Essentials Nicholas CeballosNicholasNessuna valutazione finora
- Bargas TIMELINE PDFDocumento20 pagineBargas TIMELINE PDFBargas, Mia Kazandra Loren L.100% (2)
- Prehistoric ArchitectureDocumento5 paginePrehistoric ArchitectureDino Amiel Bancaso Bongcayao0% (1)
- Liam de Paor - The Peoples of Ireland From Prehistory To Modern Times (1986)Documento360 pagineLiam de Paor - The Peoples of Ireland From Prehistory To Modern Times (1986)Nigel Elworthy100% (1)
- UCSP Chapter 3Documento17 pagineUCSP Chapter 3Agent09Nessuna valutazione finora
- 01 Prehistoric EgyptianDocumento140 pagine01 Prehistoric EgyptianChabilita AndresNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 2. Science and Technology During Pre Historic TimesDocumento8 pagineLesson 2. Science and Technology During Pre Historic TimesKing HarlequinNessuna valutazione finora
- An Early Neolithic Village in GreeceDocumento13 pagineAn Early Neolithic Village in GreeceJoeNessuna valutazione finora
- Ap 9Documento3 pagineAp 9Miriam VillegasNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 1Documento8 pagineChap 1Reza FalevyNessuna valutazione finora
- Static GK Theory FinalDocumento387 pagineStatic GK Theory FinalRahul NkNessuna valutazione finora
- History Vol-1 EM PDFDocumento216 pagineHistory Vol-1 EM PDFAbhishek Krishna ChandraNessuna valutazione finora
- Science, Technoloy and Society Prelim ExamDocumento14 pagineScience, Technoloy and Society Prelim ExamIman Official (Em-J)Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Birth of The Gods and The Origins of Agriculture, ReviewDocumento20 pagineThe Birth of The Gods and The Origins of Agriculture, ReviewSamuel100% (1)
- Prehistoric Religion: General CharacteristicsDocumento10 paginePrehistoric Religion: General CharacteristicsLord PindarNessuna valutazione finora
- Wuolah Free TODOS LOS APUNTES DE CULTURADocumento89 pagineWuolah Free TODOS LOS APUNTES DE CULTURAThalia SalvadorNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction of HumanalityDocumento8 pagineIntroduction of HumanalityBùi Yến NhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Art in Early CivilizationDocumento36 pagineArt in Early CivilizationCrisha Joy Delos SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Economic History of Ancient India (Santosh Kumar Das, 1944)Documento363 pagineEconomic History of Ancient India (Santosh Kumar Das, 1944)Srini KalyanaramanNessuna valutazione finora
- Periodic Test-UCSP - WITH KEYDocumento4 paginePeriodic Test-UCSP - WITH KEYMaricris Atienza100% (1)
- Ancient Civilizations DBQDocumento2 pagineAncient Civilizations DBQStanley ZhuNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer The Succeeding Guide Questions.: Ucsp Week 4 Offline Activity: Article Reading 101Documento3 pagineAnswer The Succeeding Guide Questions.: Ucsp Week 4 Offline Activity: Article Reading 101Ruby Ann Agulto-CabreraNessuna valutazione finora
- Chronotypic Tension in Bulgarian PrehistDocumento20 pagineChronotypic Tension in Bulgarian PrehistХристо ИвановNessuna valutazione finora
- Geographical FactorsDocumento6 pagineGeographical FactorsKrishna GopaliyaNessuna valutazione finora
- A Problem of The Earliest Horse Domestication - Data From The Neolithic Camp Ayakagytma, Uzbekistan - ImportantDocumento10 pagineA Problem of The Earliest Horse Domestication - Data From The Neolithic Camp Ayakagytma, Uzbekistan - ImportantimmchrNessuna valutazione finora
- Technology (FromDocumento10 pagineTechnology (FromvyasmusicNessuna valutazione finora