Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Trip Circuit (Relay)
Caricato da
Shah Jay0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
7 visualizzazioni2 pagineThe document discusses the components and operation of a trip circuit for a circuit breaker. It contains a trip unit connected in parallel to a polymer element and in series with circuit breaker contacts. When a fault occurs, the polymer element changes to a high resistive state, energizing the trip unit and tripping the circuit breaker contacts. A current transformer senses high fault currents and causes a relay to close, completing the trip circuit and energizing the trip coil to open the circuit breaker and isolate the faulty part of the system.
Descrizione originale:
trip ckt
Titolo originale
Trip Circuit(Relay)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoThe document discusses the components and operation of a trip circuit for a circuit breaker. It contains a trip unit connected in parallel to a polymer element and in series with circuit breaker contacts. When a fault occurs, the polymer element changes to a high resistive state, energizing the trip unit and tripping the circuit breaker contacts. A current transformer senses high fault currents and causes a relay to close, completing the trip circuit and energizing the trip coil to open the circuit breaker and isolate the faulty part of the system.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
7 visualizzazioni2 pagineTrip Circuit (Relay)
Caricato da
Shah JayThe document discusses the components and operation of a trip circuit for a circuit breaker. It contains a trip unit connected in parallel to a polymer element and in series with circuit breaker contacts. When a fault occurs, the polymer element changes to a high resistive state, energizing the trip unit and tripping the circuit breaker contacts. A current transformer senses high fault currents and causes a relay to close, completing the trip circuit and energizing the trip coil to open the circuit breaker and isolate the faulty part of the system.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 2
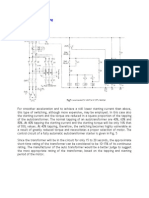
Trip circuit (Relay)
A trip unit is electrically connected in parallel with a current limiting
polymer element in series with circuit breaker contacts to function as a
shunt resistance for the polymer element. It becomes energized by
transition of the polymer element to its high resistive state for tripping the
breaker contacts. The solenoid may be particularly wound with a resistive
wire.
Here a simplified circuit of a typical relay is given. Basically the relay
circuit is a three phase circuit and the contact circuit of relays is very
much complicated. This diagram is of single phase simplified circuit to
explain the basic action of a relay. Let part A is the circuit to be
protected. The current transformer (C. T.) is connected with its primary
winding in series with the line to be protected. The secondary winding
of the current transformer is connected in series with the relay coil. The
relay contacts are the part of a trip circuit of a circuit breaker. The trip
circuit consists of a trip coil and a battery, in addition to relay contacts.
The trip circuit can operate on a. c. or d. c. If the fault occurs, Then
current through the line connected to A increases to a very high value.
Then the current transformer senses this current. Accordingly its
secondary current increases which is nothing but the current through a
relay coil. Thus the relay contacts get closed mechanically under the
influence of such a high fault current. Thus the trip circuit of a circuit
breaker gets closed and current starts flowing from battery, through trip
coil, in a trip circuit. Thus the trip coil of a circuit breaker gets
energized. This activates the circuit breaker opening mechanism,
making the circuit breaker open. This isolates the faulty part from rest
of the healthy system.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionDa EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionNessuna valutazione finora
- Relay and Circuit Breaker Term PaperDocumento4 pagineRelay and Circuit Breaker Term PaperFaiz RahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionDa EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Static Relays: Static Relays Are Superior To Electro-Magnetic Relays in The Following AspectsDocumento7 pagineStatic Relays: Static Relays Are Superior To Electro-Magnetic Relays in The Following AspectsKhaled RabeaNessuna valutazione finora
- Numerical RelayDocumento19 pagineNumerical RelayRajesh Naik Dharavath100% (1)
- Brief Disscussion On RelayDocumento24 pagineBrief Disscussion On RelayShirajul IslamNessuna valutazione finora
- Ee8602 PSG Notes - New - Unit2Documento30 pagineEe8602 PSG Notes - New - Unit2Vairaperumal KNessuna valutazione finora
- DocumentDocumento26 pagineDocumentPurbita ChakrabortyNessuna valutazione finora
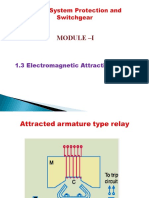
- 1.3 Electromagnetic Attraction RelaysDocumento8 pagine1.3 Electromagnetic Attraction Relays20EUEE018 - DEEPAK. MNessuna valutazione finora
- Report Content - Digital Water MeterDocumento44 pagineReport Content - Digital Water MeteramiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Tuned Collector OscillatorDocumento3 pagineTuned Collector OscillatorHRM, BAPEXNessuna valutazione finora
- Edi Meow Exp 1Documento6 pagineEdi Meow Exp 1Jay Romar PabianiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pneumatic Based Punching MachineDocumento45 paginePneumatic Based Punching Machineraja100% (3)
- Working Principle of Distance or Impedance RelayDocumento16 pagineWorking Principle of Distance or Impedance Relayrobertovm2002Nessuna valutazione finora
- Shunt Reactor Switching Transients at High Compensation LevelsDocumento14 pagineShunt Reactor Switching Transients at High Compensation LevelsJames Ernes Llacza Carmelo100% (1)
- Single-Phase Supply Three-Phase Supply: Half-Wave RectificationDocumento7 pagineSingle-Phase Supply Three-Phase Supply: Half-Wave RectificationKhushbakht KhushiNessuna valutazione finora
- KMT#4Documento5 pagineKMT#4RomanHerreraNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 SWPDocumento2 pagine4 SWPHome automation SmartNessuna valutazione finora
- Power System Protection (Control System) : Protective RelaysDocumento29 paginePower System Protection (Control System) : Protective RelaysBagirath SwaminathanNessuna valutazione finora
- Relay Working Principle Operatin of Normal Relay Transistor Driving Ckircuit Realy Interfacig With Micro Controller RelaysDocumento8 pagineRelay Working Principle Operatin of Normal Relay Transistor Driving Ckircuit Realy Interfacig With Micro Controller RelaysGirija VaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Differential RelaysDocumento13 pagineDifferential Relayssudheerreddy115100% (4)
- CBCTDocumento14 pagineCBCTYPV TECHNICAL SERVICES100% (1)
- LC CircuitDocumento15 pagineLC CircuitKing SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Differential RelaysDocumento13 pagineDifferential RelaysJason Sonido100% (1)
- Lecture 2 Version 1 EEE 471 Switchgear and Protection - NMKHANDocumento12 pagineLecture 2 Version 1 EEE 471 Switchgear and Protection - NMKHANMortuzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Vocabulary TermDocumento3 pagineElectrical Vocabulary TermRey-an A. MorenoNessuna valutazione finora
- IUBAT-International University of Business Agriculture and TechnologyDocumento19 pagineIUBAT-International University of Business Agriculture and TechnologyMd Hasibur RahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- RELAY1Documento11 pagineRELAY1jayapriyadharshini02Nessuna valutazione finora
- Operating Principle of A Contactor:: Holds The Moving and Fixed Contacts Together. in The ProcessDocumento15 pagineOperating Principle of A Contactor:: Holds The Moving and Fixed Contacts Together. in The ProcessAnand JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Switched Mode Power Supplies.: Fig.3.0.1 Typical SMPS Block DiagramDocumento17 pagineIntroduction To Switched Mode Power Supplies.: Fig.3.0.1 Typical SMPS Block DiagramPhenias ManyashaNessuna valutazione finora
- Relay: HistoryDocumento11 pagineRelay: HistoryEngr WekiNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study of Sympathetic Interaction Between Transformers Caused by Inrush TransientsDocumento5 pagineCase Study of Sympathetic Interaction Between Transformers Caused by Inrush TransientsSven del PinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ja Assignment3Documento6 pagineJa Assignment3BookMaggotNessuna valutazione finora
- What Are Relays & How Do They Work PDFDocumento8 pagineWhat Are Relays & How Do They Work PDFdeepakNessuna valutazione finora
- 2170908Documento19 pagine2170908bhavikNessuna valutazione finora
- Abb Kab High Impedance Bus Diffrl RelayDocumento16 pagineAbb Kab High Impedance Bus Diffrl RelaymentongNessuna valutazione finora
- Relay Circuit GlobeDocumento33 pagineRelay Circuit Globevikas mauryaNessuna valutazione finora
- Single Phase Transformer Literature ReviewDocumento4 pagineSingle Phase Transformer Literature Reviewafmzodjhpxembt100% (1)
- SwitchgearDocumento6 pagineSwitchgearChayon KarmakarNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Electrical Terms and DefinitionsDocumento15 pagineBasic Electrical Terms and Definitionsilango palaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Inte Term 2 Week 6Documento6 pagineInte Term 2 Week 6Sheridan DyalNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Design and Operation: Electrically SwitchDocumento11 pagineBasic Design and Operation: Electrically SwitchAnina JacobNessuna valutazione finora
- Relay - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocumento13 pagineRelay - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediakghlkhglkghklNessuna valutazione finora
- Current Transformer Notes PDFDocumento5 pagineCurrent Transformer Notes PDFAyush SaxenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrically Switch Electromagnet Solid-State Relays: RelayDocumento8 pagineElectrically Switch Electromagnet Solid-State Relays: RelayAmiel Ohween AnayNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit II Electrical Circuits: Basic Circuit Element and Their CombinationsDocumento21 pagineUnit II Electrical Circuits: Basic Circuit Element and Their CombinationsMonte CarloNessuna valutazione finora
- Familiarization of The Electrical Machine Laboratory ApparatusDocumento5 pagineFamiliarization of The Electrical Machine Laboratory ApparatusRosalinda CondeNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is An Electric Circuit?Documento8 pagineWhat Is An Electric Circuit?Josiah ZeusNessuna valutazione finora
- Circuit Breakers-lecture-Notes 2 PDFDocumento62 pagineCircuit Breakers-lecture-Notes 2 PDFnayeemsidduNessuna valutazione finora
- The Short Line and Kilometric Fault:: Unit V Transients in Integrated Power SystemDocumento22 pagineThe Short Line and Kilometric Fault:: Unit V Transients in Integrated Power SystemJain Marshel B100% (1)
- Electrically Switch ElectromagnetDocumento16 pagineElectrically Switch ElectromagnetThamarai Kannan RamajayamNessuna valutazione finora
- Distance Relay or Impedance Relay Working Principle TypesDocumento4 pagineDistance Relay or Impedance Relay Working Principle TypesLaurence MalanumNessuna valutazione finora
- Inverter Commutation CircuitsDocumento7 pagineInverter Commutation Circuitskanor1991Nessuna valutazione finora
- Current TransformerDocumento6 pagineCurrent TransformerSwinlife WinlifeNessuna valutazione finora
- U1A1 Relays.Documento10 pagineU1A1 Relays.JESUS ALBERTO SANCHEZ GUTIERREZNessuna valutazione finora
- By: Jasper B. DeromaDocumento26 pagineBy: Jasper B. DeromaRaging Potato100% (1)
- Electrical Engineering Question and Answer - POWER SYSTEM QUESTION and ANSWERDocumento4 pagineElectrical Engineering Question and Answer - POWER SYSTEM QUESTION and ANSWERchico brilliantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Regulated DC Power SupplyDocumento15 pagineRegulated DC Power SupplynalumilanimeNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric Locomotive GlossaryDocumento6 pagineElectric Locomotive GlossaryPalade MihaelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Measurement of Earth Resistance (Three Point Method)Documento5 pagineMeasurement of Earth Resistance (Three Point Method)Shah JayNessuna valutazione finora
- Want To Learn Faster? : ONAN Cooling of TransformerDocumento4 pagineWant To Learn Faster? : ONAN Cooling of TransformerShah JayNessuna valutazione finora
- ONAF Cooling of TransformerDocumento1 paginaONAF Cooling of TransformerShah JayNessuna valutazione finora
- Cooling Methods Available For Trans Former, We Will Now Explain One by OneDocumento1 paginaCooling Methods Available For Trans Former, We Will Now Explain One by OneShah JayNessuna valutazione finora
- Starter DOLDocumento3 pagineStarter DOLShah JayNessuna valutazione finora
- DOL StarterDocumento2 pagineDOL StarterShah JayNessuna valutazione finora
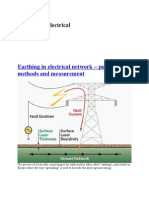
- Earthing in Electrical Network - Purpose, Methods and MeasurementDocumento12 pagineEarthing in Electrical Network - Purpose, Methods and MeasurementShah JayNessuna valutazione finora
- Why LT Motors Are Delta Connected and HT Motors Are Star Connected - 4Documento2 pagineWhy LT Motors Are Delta Connected and HT Motors Are Star Connected - 4Shah JayNessuna valutazione finora
- Lag, Lead, Lead-Lag - Compensation in Control SystemDocumento11 pagineLag, Lead, Lead-Lag - Compensation in Control SystemShah Jay100% (1)
- Hazardous Areas: Gases and VapoursDocumento10 pagineHazardous Areas: Gases and VapoursShah JayNessuna valutazione finora
- Y DDocumento6 pagineY DShah JayNessuna valutazione finora
- Ingress Protection IP Ratings - What Do They Mean?Documento1 paginaIngress Protection IP Ratings - What Do They Mean?Shah JayNessuna valutazione finora
- Autotransformer StarterDocumento1 paginaAutotransformer StarterShah JayNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Flow Diagram of Induction Motor - 5Documento1 paginaPower Flow Diagram of Induction Motor - 5Shah JayNessuna valutazione finora
- STAR DELTA Connection Diagram and Working PrincipleDocumento2 pagineSTAR DELTA Connection Diagram and Working PrinciplePrasant Kumar100% (5)
- Basics of Induction Motor - 1Documento2 pagineBasics of Induction Motor - 1Shah JayNessuna valutazione finora
- Induction MotorDocumento6 pagineInduction MotorHafidah Mohd NoorNessuna valutazione finora
- Iec CodeDocumento14 pagineIec CodeShah JayNessuna valutazione finora
- Offshore Cathodic Protection 101: What It Is and How It WorksDocumento6 pagineOffshore Cathodic Protection 101: What It Is and How It WorksSaiful ArifNessuna valutazione finora
- Transformer ProblemsDocumento4 pagineTransformer ProblemsShah JayNessuna valutazione finora
- Setting The Pickup Point - CT - PTDocumento4 pagineSetting The Pickup Point - CT - PTShah JayNessuna valutazione finora
- Iec StandardsDocumento5 pagineIec StandardsShah JayNessuna valutazione finora
- Compensator Design Using Bode PlotDocumento24 pagineCompensator Design Using Bode PlotShah JayNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Phase Transformer - 1Documento6 pagine3 Phase Transformer - 1Shah JayNessuna valutazione finora
- DC Generator ProjectDocumento10 pagineDC Generator ProjectMuhammad Asif Iqbal43% (7)
- All Day Efficiency and Regulation - 5Documento8 pagineAll Day Efficiency and Regulation - 5Shah JayNessuna valutazione finora
- Autotransformer 6Documento5 pagineAutotransformer 6Shah JayNessuna valutazione finora
- Approximate Equivalent Circuits & Test - 3Documento6 pagineApproximate Equivalent Circuits & Test - 3Shah JayNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical Transformer 2Documento4 paginePractical Transformer 2Shah JayNessuna valutazione finora
- XCDocumento5 pagineXCPhuong PhamNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Production Decline Analysis and ApplicationDa EverandAdvanced Production Decline Analysis and ApplicationValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (4)
- A Practical Handbook for Drilling Fluids ProcessingDa EverandA Practical Handbook for Drilling Fluids ProcessingNessuna valutazione finora
- Flow Analysis for Hydrocarbon Pipeline EngineeringDa EverandFlow Analysis for Hydrocarbon Pipeline EngineeringNessuna valutazione finora
- Asphaltene Deposition Control by Chemical Inhibitors: Theoretical and Practical ProspectsDa EverandAsphaltene Deposition Control by Chemical Inhibitors: Theoretical and Practical ProspectsNessuna valutazione finora
- Well Integrity for Workovers and RecompletionsDa EverandWell Integrity for Workovers and RecompletionsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (3)
- Internal Combustion: How Corporations and Governments Addicted the World to Oil and Subverted the AlternativesDa EverandInternal Combustion: How Corporations and Governments Addicted the World to Oil and Subverted the AlternativesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (2)
- Practical Reservoir Engineering and CharacterizationDa EverandPractical Reservoir Engineering and CharacterizationValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- Abrasive Water Jet Perforation and Multi-Stage FracturingDa EverandAbrasive Water Jet Perforation and Multi-Stage FracturingNessuna valutazione finora
- Hybrid Enhanced Oil Recovery Using Smart WaterfloodingDa EverandHybrid Enhanced Oil Recovery Using Smart WaterfloodingNessuna valutazione finora
- Well Control for Completions and InterventionsDa EverandWell Control for Completions and InterventionsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (10)
- Casing and Liners for Drilling and Completion: Design and ApplicationDa EverandCasing and Liners for Drilling and Completion: Design and ApplicationValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (3)
- Pocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataDa EverandPocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (22)
- Machine Learning Guide for Oil and Gas Using Python: A Step-by-Step Breakdown with Data, Algorithms, Codes, and ApplicationsDa EverandMachine Learning Guide for Oil and Gas Using Python: A Step-by-Step Breakdown with Data, Algorithms, Codes, and ApplicationsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (4)
- Well Testing Project Management: Onshore and Offshore OperationsDa EverandWell Testing Project Management: Onshore and Offshore OperationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Guide to the Practical Use of Chemicals in Refineries and PipelinesDa EverandGuide to the Practical Use of Chemicals in Refineries and PipelinesValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Fundamentals and Applications of Bionic Drilling FluidsDa EverandFundamentals and Applications of Bionic Drilling FluidsNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Studies of Material Corrosion Prevention for Oil and Gas ValvesDa EverandCase Studies of Material Corrosion Prevention for Oil and Gas ValvesNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas and Oil Reliability Engineering: Modeling and AnalysisDa EverandGas and Oil Reliability Engineering: Modeling and AnalysisValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (6)
- Heat Exchanger Equipment Field Manual: Common Operating Problems and Practical SolutionsDa EverandHeat Exchanger Equipment Field Manual: Common Operating Problems and Practical SolutionsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (6)
- Advanced Biomass Gasification: New Concepts for Efficiency Increase and Product FlexibilityDa EverandAdvanced Biomass Gasification: New Concepts for Efficiency Increase and Product FlexibilityValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (2)
- The Petroleum Engineering Handbook: Sustainable Operations: Sustainable OperationsDa EverandThe Petroleum Engineering Handbook: Sustainable Operations: Sustainable OperationsValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (5)
- Acquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic DataDa EverandAcquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic DataValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (4)