Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Pathophysiology of Chorioamnionitis
Caricato da
jhobarryCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Pathophysiology of Chorioamnionitis
Caricato da
jhobarryCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Pathophysiology of Chorioamnionitis
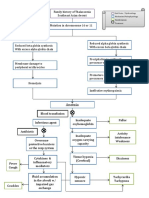
• about 5 to 10% of
infected babies
develop
Predisposing Factors: pneumonia (lung
infection) or
• young age (e.g., less than 21 years old);
bacteremia
• low socioeconomic status; (however, this is
more common in
• first pregnancy; preterm infants);
• long labor; • less than 1% of
• prolonged rupture of the membranes (bag of waters); term infants and a
slightly higher
• rupture of membranes at an early gestational age; percentage of
preterm infants
• multiple vaginal examinations during labor (only in women with
develop meningitis
ruptured membranes);
(infection of the
• pre-existing infections of the lower genital tract (bacterial vaginosis lining of the brain
and group B streptococcal infection); and and spinal cord);
and
• although death in
term babies is
very unusual, up
Chorioamnionitis usually develops when bacteria that are part of the normal vaginal flora "ascend" into the to 15% of infected
uterine cavity. The amniotic fluid and placenta, as well as the baby, become infected. E. coli, group B preterm infants die
streptococci, and anaerobic bacteria are the most common causes of chorioamnionitis, though, E. coli and because of the
group B streptococci are also the two most common causes of infection in newborns. infection or other
complications
such as
respiratory
distress syndrome
and bleeding into
Chorioamnionitis can lead to serious complications in both the brain.
mother and baby and is usually considered a medical
emergency
Fever in the mother
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- ThalassemiaDocumento1 paginaThalassemiaJobelle Fernandez-SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Adenomyosis PathophysiologyDocumento1 paginaAdenomyosis PathophysiologyZerfa NishreenNessuna valutazione finora
- Promoting Proper BreastfeedingDocumento12 paginePromoting Proper BreastfeedingAmal MUTIANessuna valutazione finora
- Midwifery Models of Care ExplainedDocumento29 pagineMidwifery Models of Care Explainedanjeline caroletti100% (2)
- Obst 5 - All Obstetrics 1 2021Documento22 pagineObst 5 - All Obstetrics 1 2021Menna KamalNessuna valutazione finora
- Prenatal Workout Plan: GlowbodyptDocumento10 paginePrenatal Workout Plan: GlowbodyptDébora BezerraNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Draft - Ectopic PregnancyDocumento7 pagineNCP Draft - Ectopic PregnancyD CNessuna valutazione finora
- Managing Premature Cervical DilatationDocumento10 pagineManaging Premature Cervical DilatationRaiden VizcondeNessuna valutazione finora
- K49 - OG - Caesarean Delivery & Peripartum HysterectomyDocumento45 pagineK49 - OG - Caesarean Delivery & Peripartum HysterectomyMonika AyuningrumNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Drug Study Group 1Documento21 pagineNCP Drug Study Group 1Cassandra Grace Muerong Dela CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Zocor (Simvastatin)Documento3 pagineZocor (Simvastatin)E100% (1)
- Nursing Assessment, Planning, Implementation and EvaluationDocumento2 pagineNursing Assessment, Planning, Implementation and EvaluationDiana MuañaNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study 1: Nicole: 1. Discuss The Significance of Nicole's Laboratory FindingsDocumento12 pagineCase Study 1: Nicole: 1. Discuss The Significance of Nicole's Laboratory FindingsClint NavarroNessuna valutazione finora
- MeaslesDocumento32 pagineMeaslesYum C100% (2)
- College of Nursing: Rifadin RifampinDocumento4 pagineCollege of Nursing: Rifadin RifampinAnika PleñosNessuna valutazione finora
- PPH Introduction 1Documento95 paginePPH Introduction 1regine maeNessuna valutazione finora
- Kaposi's SarcomaDocumento6 pagineKaposi's SarcomaveremkovichNessuna valutazione finora
- N. Bacalso Ave., Cebu City Philippines: Page 1 of 32Documento32 pagineN. Bacalso Ave., Cebu City Philippines: Page 1 of 32Joule PeirreNessuna valutazione finora
- Medications and Nursing Responsibilities for Bone HealthDocumento6 pagineMedications and Nursing Responsibilities for Bone HealthDarla JoyceNessuna valutazione finora
- Complications in PregnancyDocumento36 pagineComplications in PregnancyJADE PATEGANessuna valutazione finora
- Abruptio Placenta. Final OutputDocumento15 pagineAbruptio Placenta. Final OutputCharles Loriaga Cruz IINessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid Volume Deficit and Excess: Types, Causes, Signs and Nursing ManagementDocumento32 pagineFluid Volume Deficit and Excess: Types, Causes, Signs and Nursing ManagementAcohCChaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate: Therese M. Chapman, Jane K. Mcgavin and Stuart NobleDocumento12 pagineTenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate: Therese M. Chapman, Jane K. Mcgavin and Stuart NobleBagusHibridaNessuna valutazione finora
- HPV Virus Causes Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis in BoyDocumento21 pagineHPV Virus Causes Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis in BoyDaffa IbnurasyNessuna valutazione finora
- Malignant Mixed Mullerian Tumor Arising From The UDocumento5 pagineMalignant Mixed Mullerian Tumor Arising From The UAmin IsmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Thyroid Lobectomy and IsthmusectomyDocumento12 pagineThyroid Lobectomy and IsthmusectomyAgustina100% (1)
- NCP AnxietyDocumento6 pagineNCP AnxietyRaijenne VersolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Journal For MEdical WardDocumento8 pagineJournal For MEdical WardValcrist BalderNessuna valutazione finora
- Abruptio Placenta Risks, Signs, and TreatmentDocumento10 pagineAbruptio Placenta Risks, Signs, and TreatmentDoc DudayNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP On Preterm LaborDocumento2 pagineNCP On Preterm LaborAngelica Malacay RevilNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study: Brokenshire College Madapo, Davao CityDocumento1 paginaDrug Study: Brokenshire College Madapo, Davao CityHera Pamela Buelis BatoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Suppositories: Abenol (CAN)Documento2 pagineSuppositories: Abenol (CAN)Mikko McDonie VeloriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocumento3 pagineIneffective Tissue PerfusionJulie Marie PavadoraNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento8 pagineDrug StudyJay-ar Batara SorianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Vulva HeamatomaDocumento16 pagineVulva Heamatomaabeer saadNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP PTBDocumento9 pagineNCP PTBecbarticanNessuna valutazione finora
- Transient Tachypnea of The NewbornDocumento6 pagineTransient Tachypnea of The NewbornTarquin TomadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary of Clinical RotationDocumento2 pagineSummary of Clinical RotationbulikakoNessuna valutazione finora
- Risk For Falls As Evidence by Loss of BalanceDocumento4 pagineRisk For Falls As Evidence by Loss of BalanceAlexandrea MayNessuna valutazione finora
- SN: Charisse D. Bulalaque Family Nursing Care PlanDocumento2 pagineSN: Charisse D. Bulalaque Family Nursing Care PlanZee EedNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 12 ContempoDocumento5 pagineModule 12 ContempoJericho CunananNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction RevisionDocumento50 pagineIntroduction RevisionGracie S. VergaraNessuna valutazione finora
- De Guzman NCP GDMDocumento4 pagineDe Guzman NCP GDMCameron De GuzmanNessuna valutazione finora
- NALAM 106 Ass. AntibioticsDocumento6 pagineNALAM 106 Ass. AntibioticsBeth100% (1)
- Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Pathology of NeuroblastomaDocumento21 pagineEpidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Pathology of NeuroblastomaHandre PutraNessuna valutazione finora
- Guide in Making The FCA 1Documento18 pagineGuide in Making The FCA 1Zedrake CaraanNessuna valutazione finora
- Neonatal SepsisDocumento39 pagineNeonatal SepsisBryan KernsNessuna valutazione finora
- Effect of BCG Vaccination Against Mycobacterium: Tuberculosis Infection in ChildrenDocumento2 pagineEffect of BCG Vaccination Against Mycobacterium: Tuberculosis Infection in ChildrennissieNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan for Subarachnoid HemorrhageDocumento46 pagineNursing Care Plan for Subarachnoid HemorrhageShitaljit IromNessuna valutazione finora
- Module4 Promabortion Week 8Documento21 pagineModule4 Promabortion Week 8Emmy Flor ValmoriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Review of Related LiteratureDocumento2 pagineReview of Related LiteratureAlexa MurielNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology Biliary AtresiaDocumento1 paginaPathophysiology Biliary AtresiaPATHOSHOPPENessuna valutazione finora
- Uterine AtonyDocumento4 pagineUterine AtonyJohn Cenas100% (1)
- Assesment Diagnosis Inference Objective Intervention Raionale Evaluation Subjective: Objective: Long Term Goal: Goal MetDocumento2 pagineAssesment Diagnosis Inference Objective Intervention Raionale Evaluation Subjective: Objective: Long Term Goal: Goal MetChaeL90Nessuna valutazione finora
- NCP of Endometrical CancerDocumento2 pagineNCP of Endometrical CancerFrando kennethNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan for a Patient with Hemorrhagic StrokeDocumento5 pagineNursing Care Plan for a Patient with Hemorrhagic StrokeKhim BalcitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Drugs and NCPDocumento4 pagineDrugs and NCPApril Anne CostalesNessuna valutazione finora
- A Drug Study On FansidarDocumento7 pagineA Drug Study On FansidarCasey EmellanoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Story of GregorioDocumento2 pagineThe Story of GregorioKelly LegaspiNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing DiagnosisDocumento16 pagineNursing DiagnosisShemie TutorNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Chorioamnionitis: Predisposing FactorsDocumento1 paginaPathophysiology of Chorioamnionitis: Predisposing FactorsJane Ann AlolodNessuna valutazione finora
- Livret MF GB21Documento20 pagineLivret MF GB21mary15eugNessuna valutazione finora
- Cho Rio Amnion It IsDocumento24 pagineCho Rio Amnion It IsKristaRicaAbayabayNessuna valutazione finora
- Viral Exanthems in Childhood ÔÇô Infectious (Direct) Exanthems. Part 2 Other Viral ExanthemsDocumento5 pagineViral Exanthems in Childhood ÔÇô Infectious (Direct) Exanthems. Part 2 Other Viral Exanthemsraymundo lopez silvaNessuna valutazione finora
- Abnormal Labor Diagnosis and ManagementDocumento14 pagineAbnormal Labor Diagnosis and ManagementPreeti Joan BuxaniNessuna valutazione finora
- COMPLICATIONS OF LABOR AND BIRTHDocumento6 pagineCOMPLICATIONS OF LABOR AND BIRTHAmethystNessuna valutazione finora
- Jurnal Posisi Kala II PartusDocumento10 pagineJurnal Posisi Kala II Partusichsan gamingNessuna valutazione finora
- Filipino Culture and Beliefs Related to Maternal and Child CareDocumento35 pagineFilipino Culture and Beliefs Related to Maternal and Child CareRica MariaeNessuna valutazione finora
- Management of Breech PresentationDocumento27 pagineManagement of Breech Presentationapi-370504683% (6)
- The Four Stages of LaborDocumento12 pagineThe Four Stages of LaborEdrea Aquino MendezNessuna valutazione finora
- Amokrane2016 PDFDocumento5 pagineAmokrane2016 PDFRaditya TaslimNessuna valutazione finora
- Stages of LaborDocumento12 pagineStages of LabortejaNessuna valutazione finora
- CR Poli Obs 11-05-18 EditDocumento133 pagineCR Poli Obs 11-05-18 EditRyan IlhamNessuna valutazione finora
- Reduce Childbirth Injuries With Perineal MassageDocumento2 pagineReduce Childbirth Injuries With Perineal MassageFarid NurdiansyahNessuna valutazione finora
- SWAZILAND DAIRY BORD DOCUMENT ON CATTLE DISEASESDocumento14 pagineSWAZILAND DAIRY BORD DOCUMENT ON CATTLE DISEASESLaddi SandhuNessuna valutazione finora
- EENC (Early Essential Newborn Care) BREATHING BABY. Preparation Stage Not Done Partially Done Done 0 1 2Documento2 pagineEENC (Early Essential Newborn Care) BREATHING BABY. Preparation Stage Not Done Partially Done Done 0 1 2Trevor UratelNessuna valutazione finora
- OBSTETRICS Enhancement - FINAL COPY 1Documento17 pagineOBSTETRICS Enhancement - FINAL COPY 1Jan Joseph BanzuelaNessuna valutazione finora
- St. Martin de Porres Catholic School of Guiguinto Poblacion, Guiguinto 3015 BulacanDocumento2 pagineSt. Martin de Porres Catholic School of Guiguinto Poblacion, Guiguinto 3015 BulacanJoshua GuiriñaNessuna valutazione finora
- Telaah Jurnal Dyah Retno (0801163141)Documento5 pagineTelaah Jurnal Dyah Retno (0801163141)Dn DesainNessuna valutazione finora
- Midwives' Role in Empowering WomenDocumento6 pagineMidwives' Role in Empowering WomennurvalahNessuna valutazione finora
- Physiotherapy Following Caesarean SectionDocumento26 paginePhysiotherapy Following Caesarean SectionsarikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Implementasi Asuhan Kebidanan Berkontinuitas Mengurangi BBLRDocumento7 pagineImplementasi Asuhan Kebidanan Berkontinuitas Mengurangi BBLRNafisha HaifaNessuna valutazione finora
- Kajian Metode Persalinan Normal Dengan Bantuan Cermin Pada Persalinan Kala Ii Ibu PrimigravidaDocumento8 pagineKajian Metode Persalinan Normal Dengan Bantuan Cermin Pada Persalinan Kala Ii Ibu Primigravidaridani 13Nessuna valutazione finora
- Induction and Augmentation of Labor - Williams ObDocumento3 pagineInduction and Augmentation of Labor - Williams ObAria IndrabrataNessuna valutazione finora
- Vaccum DeliveryDocumento24 pagineVaccum DeliveryBezawit TesfahunNessuna valutazione finora
- Ultrasound Report for 33 Week PregnancyDocumento1 paginaUltrasound Report for 33 Week PregnancyAUSTRIAN DIAGNOSTIC CENTERNessuna valutazione finora
- 1091223產科晨會報告ver3Documento58 pagine1091223產科晨會報告ver3peipeipoorNessuna valutazione finora
- ICOEDocumento2 pagineICOEmeutia wardhanie ganieNessuna valutazione finora
- Case 1Documento9 pagineCase 1Saketha Rama ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Using A Simplified Bishop Score To Predict VaginalDocumento7 pagineUsing A Simplified Bishop Score To Predict Vaginalmasyarakatsampah10Nessuna valutazione finora