Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Unit 1
Caricato da
api-282526559Descrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Unit 1
Caricato da
api-282526559Copyright:
Formati disponibili
1.
1 Everything is made of particles
Diffusion happens when particles mix by colliding against each other and bouncing off in all
directions.
Examples of diffusion in the lab:
Placing a crystal of potassium manganite in a beaker of water will cause the colour to
spread across the water and mix with it.
Placing an open gas jar upside down on an open gas jar containing a few drops of
bromine will cause the (yellowish orange) colour to spread upwards.
Evidence of diffusion outside the lab:
Cooking smells spreading everywhere
Dust and smoke dancing in the air, in bright sunlight
1.2, 1.3 Solid, Liquids and gases
Solids:
Particles arranged in fixed pattern called lattice
Strong forces hold the particles together, so they cannot leave their positions
But they do move a bit, because they vibrate
Liquids:
The particles can move about and slide past each other
The particles are quite closed to each other, but not arrange in a lattice
The forces that hold the particles together are weaker than solids
Gases:
The particles are very far apart
They move about very quickly. Almost no forces holding them together
They collide with each other and bounce of in all directions
The state of matter can be changed by altering the temperatures.
Melting:
Changing of state from a solid to a liquid
When a solid is heated the particles gain energy, so they vibrate more making the solid
expand.
The particles vibrate so much that they break away from their positions, turning into a
liquid
Boiling:
Changing of state from a liquid to gas
When a liquid is heated the particles gain energy, and move faster, causing them to
bump against each other and bounce further apart, making the liquid expand
The particles gain enough energy to overcome the forces between them, so they break
away to form a gas
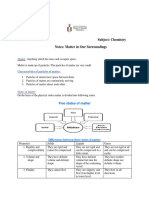
Freezing
Liqui
d
Solid
Melting
Condensati
on
Gas
Boiling
Sublimatio
n
Heating curves
In those red parts, the particles are using the energy to break the bonds between them. Time is
always on the X axis and temperature is always on the Y axis.
1.4 A closer look at gases
Gas pressure depends on 2 things:
Temperature of the gas (When you heat a gas without altering the volume, its pressure
increases.)
The volume (When a gas is compressed into a smaller space, its pressure increases.)
The rate of diffusion depends on two things:
The mass of the particles (the lower the mass of its particle, the faster a gas will diffuse.)
The temperature (the higher the temperature, the faster a gas will diffuse.)
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Y9 CH 1 & CH 2 NotesDocumento10 pagineY9 CH 1 & CH 2 NotesTeck TieNessuna valutazione finora
- The Particulate Nature of Matter 2Documento32 pagineThe Particulate Nature of Matter 2Pritam CainNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Notes 5070Documento93 pagineChemistry Notes 5070yawerakNessuna valutazione finora
- The Nature of MatterDocumento26 pagineThe Nature of MatterEsma KurtanovićNessuna valutazione finora
- FTH 4Documento14 pagineFTH 4melissaNessuna valutazione finora
- States of Matter (Key Definitations and Concepts)Documento6 pagineStates of Matter (Key Definitations and Concepts)Shruti Gorakh GadhiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry IgcseDocumento70 pagineChemistry IgcseajNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter #1 - States of MatterDocumento3 pagineChapter #1 - States of MattersurprisinglysarahytNessuna valutazione finora
- States of MatterDocumento2 pagineStates of Matteralquran.queriesNessuna valutazione finora
- 01 Structure of Matter 2009Documento6 pagine01 Structure of Matter 2009api-27085921Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry 0620 NotesDocumento192 pagineChemistry 0620 Notesmohammed mahdyNessuna valutazione finora
- MATTERDocumento4 pagineMATTERRajiv BiswasNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinetic Particle Theory For Year-8 - Final ExamsDocumento17 pagineKinetic Particle Theory For Year-8 - Final ExamsJihan KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic ChemistryDocumento4 pagineBasic ChemistryEmNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch. 1 Particulate Nature of Matter 2023 Year 10Documento10 pagineCh. 1 Particulate Nature of Matter 2023 Year 10sarah awadNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics-Worksheet 1-Thermal Physics-Grade 8Documento9 paginePhysics-Worksheet 1-Thermal Physics-Grade 8dhureyaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry IGCSE Revision NotesDocumento3 pagineChemistry IGCSE Revision NotesNikhil YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Document 6Documento6 pagineDocument 6shookookie 101Nessuna valutazione finora
- States of MatterDocumento32 pagineStates of MatterKeith BansrajNessuna valutazione finora
- JYOTI Chemistry IGCSE Revision NotesDocumento16 pagineJYOTI Chemistry IGCSE Revision NotesJyoti MeenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinetic Model of MatterDocumento25 pagineKinetic Model of MatterHafiza JaweriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemisty Igcse Updated Till SyllabusDocumento97 pagineChemisty Igcse Updated Till Syllabusapi-181176018Nessuna valutazione finora
- States of MatterDocumento10 pagineStates of Matterm.umerfaizan1895Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1Documento14 pagineChapter 1dowanahamidNessuna valutazione finora
- CHEMISTRY FOR USE NotesDocumento137 pagineCHEMISTRY FOR USE NotesDavid Shitima100% (1)
- The Real Chemistry Syllabus NoteDocumento53 pagineThe Real Chemistry Syllabus NoteAbrar JawadNessuna valutazione finora
- Cambridge MsDocumento7 pagineCambridge MstaliassalimNessuna valutazione finora
- The Particulate Nature of MatterDocumento7 pagineThe Particulate Nature of Mattersakibsultan_308100% (1)
- Topic 1 The Particulate Nature of Matter NotesDocumento7 pagineTopic 1 The Particulate Nature of Matter Notessteve KingNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch-1, Cl-9, Matter in Our SurroundingDocumento37 pagineCh-1, Cl-9, Matter in Our SurroundingSoumalyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinetic Model of MatterDocumento15 pagineKinetic Model of MatterMuqarram FaisalNessuna valutazione finora
- IGCSE Chemistry Note - States of MatterDocumento8 pagineIGCSE Chemistry Note - States of MatterZahir Sher100% (2)
- 2.1.1 States of MatterDocumento10 pagine2.1.1 States of MatterDhanBahadurNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter-1 (Matter in Our Surroundings) Notes MatterDocumento9 pagineChapter-1 (Matter in Our Surroundings) Notes MatterAtharva VarshneyNessuna valutazione finora
- Class IX Matter in Our Surroundings NotesDocumento12 pagineClass IX Matter in Our Surroundings NotesInfinity InfinityNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson No. & Name-1: Matter in Our Surroundings: Chapter NotesDocumento10 pagineLesson No. & Name-1: Matter in Our Surroundings: Chapter NotesおっぱいNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch. 1 Particulate Nature of MatterDocumento10 pagineCh. 1 Particulate Nature of MatterهندNessuna valutazione finora
- O LVL Chem - Chap 1Documento3 pagineO LVL Chem - Chap 1montyredNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter: 1 Matter in Our Surroundings Class-Ix ScienceDocumento4 pagineChapter: 1 Matter in Our Surroundings Class-Ix Scienceapi-400692183Nessuna valutazione finora
- DiffusionDocumento13 pagineDiffusionImen KsibiNessuna valutazione finora
- Changes of StatesDocumento39 pagineChanges of StatesSalemah MeshalNessuna valutazione finora
- States of MatterDocumento6 pagineStates of MatterHadeel IbrahimNessuna valutazione finora
- The States of MatterDocumento26 pagineThe States of Mattertamim haqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Chapter 1Documento9 pagineChemistry Chapter 1MaticsNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter #12: States of Matter Inter-Particle ForcesDocumento49 pagineChapter #12: States of Matter Inter-Particle ForcesdNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes - Matter in Our Surroundings - ExpDocumento6 pagineNotes - Matter in Our Surroundings - Expdeborah hildaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem NotesDocumento172 pagineChem NotesTshegofatso LegadikoNessuna valutazione finora
- IGCSE Chemistry Note (9-1) On States of MatterDocumento4 pagineIGCSE Chemistry Note (9-1) On States of MatterMd. Saif Ullah Bari100% (3)
- Worldofmatter 130724204531Documento16 pagineWorldofmatter 130724204531patmadasdasNessuna valutazione finora
- Solids: Notes 1 Chapter 1: The Particulate Nature of Matter Solids, Liquids and GasesDocumento7 pagineSolids: Notes 1 Chapter 1: The Particulate Nature of Matter Solids, Liquids and GasesQfkjfksNessuna valutazione finora
- States of MatterDocumento9 pagineStates of Mattervidya pmNessuna valutazione finora
- Csec Chemistry Chapter 1 - States of MatterDocumento8 pagineCsec Chemistry Chapter 1 - States of Matterchelsea AlexandriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Year 10 Book 2015Documento188 pagineYear 10 Book 2015api-317749980Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1 States of MatterDocumento7 pagine1 States of MatterAiman SanobarNessuna valutazione finora
- States of MatterDocumento5 pagineStates of MattertasneemNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 - The Particulate Nature of MatterDocumento3 pagineChapter 2 - The Particulate Nature of MatterMahad AsimNessuna valutazione finora
- Conduction, Convection, RadiationDocumento4 pagineConduction, Convection, RadiationChloe LiewNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4 ContDocumento6 pagineUnit 4 Contapi-282526559Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 2 1-2 3Documento5 pagineUnit 2 1-2 3api-282526559Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4Documento13 pagineUnit 4api-282526559Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 2 31-2 38Documento12 pagineUnit 2 31-2 38api-282526559Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 2 4-2 16Documento4 pagineUnit 2 4-2 16api-282526559Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 2 17Documento3 pagineUnit 2 17api-282526559Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 2 23-2 26Documento9 pagineUnit 2 23-2 26api-282526559Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1Documento14 pagineUnit 1api-282526559Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 12Documento10 pagineUnit 12api-282526559Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 13Documento7 pagineUnit 13api-282526559Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 8Documento3 pagineUnit 8api-282526559Nessuna valutazione finora
- W TheoryDocumento8 pagineW Theoryapi-282526559Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 7Documento3 pagineUnit 7api-282526559Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 11Documento14 pagineUnit 11api-282526559Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 3Documento3 pagineUnit 3api-282526559Nessuna valutazione finora
- TableDocumento2 pagineTableapi-282526559Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4Documento13 pagineUnit 4api-282526559Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 6Documento2 pagineUnit 6api-282526559Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 5Documento5 pagineUnit 5api-282526559Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2.1 Mixtures, Solutions and Solvents: Solvent It DissolvesDocumento6 pagine2.1 Mixtures, Solutions and Solvents: Solvent It Dissolvesapi-282526559Nessuna valutazione finora
- EarthquakesDocumento5 pagineEarthquakesapi-282526559Nessuna valutazione finora
- TestsDocumento3 pagineTestsapi-282526559Nessuna valutazione finora
- Geography Case StudyDocumento2 pagineGeography Case Studyapi-282526559Nessuna valutazione finora
- DefinitionsDocumento5 pagineDefinitionsapi-282526559Nessuna valutazione finora
- RasputinDocumento2 pagineRasputinapi-282526559Nessuna valutazione finora
- TheoryDocumento19 pagineTheoryapi-282526559Nessuna valutazione finora
- TableDocumento3 pagineTableapi-282526559Nessuna valutazione finora
- SyllDocumento5 pagineSyllapi-282526559Nessuna valutazione finora
- Depth Study NotesDocumento18 pagineDepth Study Notesapi-282526559100% (1)