Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
The Engineers Toolbox 1
Caricato da
kmmansaf0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
39 visualizzazioni1 paginaThis document provides information on the densities, strength limits, and stiffness of common engineering materials including:
- Concrete has a normal density of 2.4 t/m3 and light weight of 1.9 t/m3. Its compressive strength is around 30% of its ultimate strength of 40 N/mm2 for beams and 40-60 N/mm2 for columns.
- Structural steel has a working compressive stress of around 150 N/mm2, shear stress of 100 N/mm2, and tensile stress of 225 N/mm2.
- Timber has a working compressive or tensile strength along the grain of 8-10 N/mm2. Glulam timber
Descrizione originale:
Toolbox
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoThis document provides information on the densities, strength limits, and stiffness of common engineering materials including:
- Concrete has a normal density of 2.4 t/m3 and light weight of 1.9 t/m3. Its compressive strength is around 30% of its ultimate strength of 40 N/mm2 for beams and 40-60 N/mm2 for columns.
- Structural steel has a working compressive stress of around 150 N/mm2, shear stress of 100 N/mm2, and tensile stress of 225 N/mm2.
- Timber has a working compressive or tensile strength along the grain of 8-10 N/mm2. Glulam timber
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
39 visualizzazioni1 paginaThe Engineers Toolbox 1
Caricato da
kmmansafThis document provides information on the densities, strength limits, and stiffness of common engineering materials including:
- Concrete has a normal density of 2.4 t/m3 and light weight of 1.9 t/m3. Its compressive strength is around 30% of its ultimate strength of 40 N/mm2 for beams and 40-60 N/mm2 for columns.
- Structural steel has a working compressive stress of around 150 N/mm2, shear stress of 100 N/mm2, and tensile stress of 225 N/mm2.
- Timber has a working compressive or tensile strength along the grain of 8-10 N/mm2. Glulam timber
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 1
THE ENGINEERS TOOLBOX
Materials
Densities
Strength and
stress limits
Stiffness
1 t/m3 = 10 kN/m3
Water
1 t/m3
Concrete
2.4 t/m3 normal weight
1.9 t/m3 light weight
Steel
7.8 t/m3
Timber
0.8 t/m3
Carbon fibre
1.5 t/m3
Aluminium
2.7 t/m3
Snow
0.1 to 0.3 t/m3
Sand/gravel
About 1.8 t/m3 moist
Rock
About 2.8 t/m3
Concrete (ult)
Work at about 30% fcu
Slabs/beams use fccu = 40 N/mm2
Columns use fcu = 40 to 60 N/mm2
Shear stress:
v = say 2.0 N/mm2 for beams
v = say 0.7 N/mm2 for slabs and walls
Structural steel Grade 50
(working)
Compressive stress: about
150 N/mm2 unless slenderness governs
Shear: about 100 N/mm2
Tension: about 225 N/mm2
Steel cables (working)
Use 500 N/mm2 for concept design
Aluminium (working)
Use 80 N/mm2
Timber (working)
8 to 10 N/mm2 compression or
tension (along the grain)
Glulam timber (working)
About 12 N/mm2
Carbon fibre (working)
Use about 200 N/mm2 (but brittle!!)
Masonry (working)
215 brick wall: about 200 kN/m run
Bolts for steelwork (working)
Grade 8.8 16 mm bolt will carry
about 4 tonnes (working) in single
shear
Welds for steelwork (working)
6 mm fillet weld will carry
0.48 kN per mm
Bolts for timber (working)
12 mm diameter in 50 mm timber
about 1 kN (100kg)
Concrete
28 kN/mm2 (short term)
14 kN/mm2 (long term)
Steel
205 kN/mm2
Timber
6 kN/mm2
Aluminium
70 kN/mm2
Carbon fibre
120 kN/mm2
Sands and gravels
25 mm settlement at normal bearing
capacity
Double the depth
At least quadruple the stiffness
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Engineers ToolboxDocumento6 pagineThe Engineers ToolboxStefan-Paul DobreNessuna valutazione finora
- The Engineer'S Toolbox: MaterialsDocumento6 pagineThe Engineer'S Toolbox: MaterialsSandy KavitakeNessuna valutazione finora
- 200 THK Slab-Span Upto 3500 MM: Short Term PropertiesDocumento2 pagine200 THK Slab-Span Upto 3500 MM: Short Term Propertiesaldert_pathNessuna valutazione finora
- Ultimate Tensile StrengthDocumento7 pagineUltimate Tensile StrengthAgung Pratama JuniantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Super PassageDocumento5 pagineSuper PassageSamir Rawat0% (1)
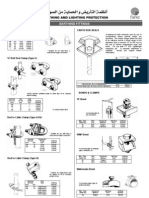
- Air Terminals and Fixings: Taper Pointed Air RodDocumento8 pagineAir Terminals and Fixings: Taper Pointed Air RodIgho AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Sub Sec 1 To 9Documento7 pagineSub Sec 1 To 9khan4luvNessuna valutazione finora
- Materials Engineering Review TablesDocumento8 pagineMaterials Engineering Review Tablesxyza1234100% (1)
- Curtain RodDocumento4 pagineCurtain RodAnonymous 9b8vCz1WNessuna valutazione finora
- SlabDocumento3 pagineSlabLeanna Abdul WahabNessuna valutazione finora
- Bentang 30 Sni BaruDocumento1 paginaBentang 30 Sni Barumang juhaiNessuna valutazione finora
- GTP For TowersDocumento7 pagineGTP For Towersabhi_akNessuna valutazione finora
- Civil Engineers GuideDocumento46 pagineCivil Engineers GuideSrinivasan Reddy88% (17)
- Composite DeckDocumento5 pagineComposite DeckvkagarwaNessuna valutazione finora
- GENERAL NOTES of Structure ElementsDocumento9 pagineGENERAL NOTES of Structure ElementsOmar TariqNessuna valutazione finora
- N2Xfgby 2 X (1.5-300) MM 0.6/1 KVDocumento4 pagineN2Xfgby 2 X (1.5-300) MM 0.6/1 KVfasa9009Nessuna valutazione finora
- Non Factored Design (Geology Deign)Documento6 pagineNon Factored Design (Geology Deign)Nguyen Trong NhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Typical Weights of Building MaterialsDocumento7 pagineTypical Weights of Building Materialshakimrahim91100% (1)
- Tabla Cutata SMD - DAT - .119.V11-SMD-Technical-Data-Sheet-TR80+Documento3 pagineTabla Cutata SMD - DAT - .119.V11-SMD-Technical-Data-Sheet-TR80+Monica Adriana PopescuNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculate Number of Plate / Pipe EarthingDocumento36 pagineCalculate Number of Plate / Pipe EarthingPhanhai KakaNessuna valutazione finora
- Earth BarDocumento1 paginaEarth BarYoussef Abdel BakiNessuna valutazione finora
- Flat Cables: 1.0mm High Density FLEXDocumento2 pagineFlat Cables: 1.0mm High Density FLEXNairo FilhoNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculate No of Plate-Pipe Earthing & Size of Earthing Strip (10.6.13)Documento36 pagineCalculate No of Plate-Pipe Earthing & Size of Earthing Strip (10.6.13)jiguparmar1516Nessuna valutazione finora
- Front Elevation Section A-A: Tower FoundationDocumento1 paginaFront Elevation Section A-A: Tower FoundationkoklenderNessuna valutazione finora
- Solid Circular SystemDocumento6 pagineSolid Circular SystemSanjay LohodasanNessuna valutazione finora
- 05 Foundation DesignsDocumento137 pagine05 Foundation DesignsSudan ShresthaNessuna valutazione finora
- Steel Fabric PropertiesDocumento2 pagineSteel Fabric PropertiesDennis Tan100% (1)
- Metals For Bus BarsDocumento19 pagineMetals For Bus BarsYuttapong SupattaravongNessuna valutazione finora
- Water Tank & Pump House CalcDocumento102 pagineWater Tank & Pump House CalcDenishmakvanaNessuna valutazione finora
- NYSYDocumento5 pagineNYSYsaturasatuNessuna valutazione finora
- Catalogue PoralDocumento10 pagineCatalogue Poralashish2783Nessuna valutazione finora
- Furse Conductors FlyerDocumento8 pagineFurse Conductors FlyerBibin JoyNessuna valutazione finora
- N2XBYDocumento5 pagineN2XBYcyuenkNessuna valutazione finora
- Katalog KmiDocumento4 pagineKatalog Kmisheila fitriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Upload 4-M4Documento23 pagineUpload 4-M4Amal ZakirNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 SteelDocumento39 pagine3 Steelyassoo-ir-221Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Engineers Toolbox 4Documento1 paginaThe Engineers Toolbox 4kmmansafNessuna valutazione finora
- Thump RuleDocumento9 pagineThump RulefarhanyazdaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Tunnel PortalDocumento7 pagineTunnel PortaldsanandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Dimensionare Bare CupruDocumento5 pagineDimensionare Bare CupruAnne KelleyNessuna valutazione finora
- Fibran ECODocumento7 pagineFibran ECOulton1237624Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 (Concrete Work)Documento25 pagineChapter 4 (Concrete Work)nurulselangorNessuna valutazione finora
- Solutions Manual to accompany Engineering Materials ScienceDa EverandSolutions Manual to accompany Engineering Materials ScienceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Lecture Notes on Reinforced Concrete DesignDa EverandLecture Notes on Reinforced Concrete DesignNessuna valutazione finora
- The Value of Science in the Smithy and ForgeDa EverandThe Value of Science in the Smithy and ForgeNessuna valutazione finora
- Copper Flashings And Weatherings - A Practical HandbookDa EverandCopper Flashings And Weatherings - A Practical HandbookNessuna valutazione finora
- A Practical Workshop Companion for Tin, Sheet Iron, and Copper Plate Workers: Containing Rules for Describing Various Kinds of Patterns used by Tin, Sheet Iron, and Copper Plate Workers, Practical Geometry, Mensuration of Surfaces and Solids, Tables of the Weights of Metals, Lead Pipe, Tables of Areas and CircumferencesDa EverandA Practical Workshop Companion for Tin, Sheet Iron, and Copper Plate Workers: Containing Rules for Describing Various Kinds of Patterns used by Tin, Sheet Iron, and Copper Plate Workers, Practical Geometry, Mensuration of Surfaces and Solids, Tables of the Weights of Metals, Lead Pipe, Tables of Areas and CircumferencesNessuna valutazione finora
- XXth Century Sheet Metal Worker - A Modern Treatise on Modern Sheet Metal WorkDa EverandXXth Century Sheet Metal Worker - A Modern Treatise on Modern Sheet Metal WorkNessuna valutazione finora
- Wrought Ironwork - A Manual of Instruction for Rural CraftsmenDa EverandWrought Ironwork - A Manual of Instruction for Rural CraftsmenValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Sexton's Pocket-Book for Boiler-Makers and Steam Users: Comprising a Variety of Useful Information for Employer and Workmen, Government Inspectors, Board of Trade Surveyors, Engineers in Charge of Works and Ships, Foreman of Manufactories, and the General Steam-Using PublicDa EverandSexton's Pocket-Book for Boiler-Makers and Steam Users: Comprising a Variety of Useful Information for Employer and Workmen, Government Inspectors, Board of Trade Surveyors, Engineers in Charge of Works and Ships, Foreman of Manufactories, and the General Steam-Using PublicNessuna valutazione finora
- Fig. 1.3 Fine Tuning An EstimateDocumento2 pagineFig. 1.3 Fine Tuning An EstimatekmmansafNessuna valutazione finora
- The Engineers Toolbox 6Documento1 paginaThe Engineers Toolbox 6kmmansafNessuna valutazione finora
- Collection of Construction Cost Data Workbook Modified Bills of Quantity FormatDocumento2 pagineCollection of Construction Cost Data Workbook Modified Bills of Quantity FormatkmmansafNessuna valutazione finora
- Plumbing Estimation 1Documento2 paginePlumbing Estimation 1kmmansafNessuna valutazione finora
- The Engineers Toolbox 4Documento1 paginaThe Engineers Toolbox 4kmmansafNessuna valutazione finora
- Cost Model: Value Engineering StudyDocumento1 paginaCost Model: Value Engineering StudykmmansafNessuna valutazione finora
- The Engineers Toolbox 3Documento1 paginaThe Engineers Toolbox 3kmmansafNessuna valutazione finora
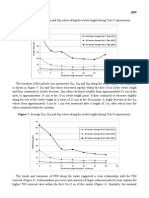
- Water 2014, 6: 1896 Figure 2. Conceptual Swale Testing SetupDocumento1 paginaWater 2014, 6: 1896 Figure 2. Conceptual Swale Testing SetupkmmansafNessuna valutazione finora
- The Engineers Toolbox 5Documento1 paginaThe Engineers Toolbox 5kmmansafNessuna valutazione finora
- Swales Paper - 06-01887 17Documento1 paginaSwales Paper - 06-01887 17kmmansafNessuna valutazione finora
- Water 2014, 6: 1902 6. ConclusionsDocumento1 paginaWater 2014, 6: 1902 6. ConclusionskmmansafNessuna valutazione finora
- Water 2014, 6: 12.0 All Swales-TD-TP Data All Swales-TC-TP Data All Swales-TB-TP Data All Swales-TA-TP DataDocumento1 paginaWater 2014, 6: 12.0 All Swales-TD-TP Data All Swales-TC-TP Data All Swales-TB-TP Data All Swales-TA-TP DatakmmansafNessuna valutazione finora
- Swales Paper - 06-01887 14Documento1 paginaSwales Paper - 06-01887 14kmmansafNessuna valutazione finora
- Swales Paper - 06-01887 13Documento1 paginaSwales Paper - 06-01887 13kmmansafNessuna valutazione finora
- Water 2014, 6: Particle Size ( M)Documento1 paginaWater 2014, 6: Particle Size ( M)kmmansafNessuna valutazione finora
- Water 2014, 6: 900 All Swales-TD-TSS Data All Swales-TC-TSS Data All Swales-TB-TSS Data All Swales-TA-TSS DataDocumento1 paginaWater 2014, 6: 900 All Swales-TD-TSS Data All Swales-TC-TSS Data All Swales-TB-TSS Data All Swales-TA-TSS DatakmmansafNessuna valutazione finora
- Water 2014, 6: Test Name Swale Name Experiment Inflow Ivmc (%) Outflow (%) WQ TestsDocumento1 paginaWater 2014, 6: Test Name Swale Name Experiment Inflow Ivmc (%) Outflow (%) WQ TestskmmansafNessuna valutazione finora
- Swales Paper - 06-01887 5Documento1 paginaSwales Paper - 06-01887 5kmmansafNessuna valutazione finora
- Swales Paper - 06-01887 1Documento1 paginaSwales Paper - 06-01887 1kmmansafNessuna valutazione finora
- Water 2014, 6: 1892 3. Study ObjectivesDocumento1 paginaWater 2014, 6: 1892 3. Study ObjectiveskmmansafNessuna valutazione finora
- Superstructure EstimationDocumento68 pagineSuperstructure Estimationkmmansaf100% (2)
- Road Estimation 1Documento11 pagineRoad Estimation 1kmmansafNessuna valutazione finora
- BOQ in GeneralDocumento9 pagineBOQ in Generalkmmansaf100% (1)
- Swales Paper - 06-01887 4Documento1 paginaSwales Paper - 06-01887 4kmmansafNessuna valutazione finora
- Swales Paper - 06-01887 3Documento1 paginaSwales Paper - 06-01887 3kmmansafNessuna valutazione finora
- Protection Work EstimationDocumento24 pagineProtection Work EstimationkmmansafNessuna valutazione finora
- Substructure EstimationDocumento44 pagineSubstructure Estimationkmmansaf100% (1)