Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Electrolysis Sssss Sssssssss
Caricato da
AnitaYusrinaKulsum0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
9 visualizzazioni1 paginaThis document summarizes an experiment to determine Avogadro's number by measuring the amount of charge required to reduce 1 mole of hydrogen ions. The experiment uses electrolysis and measures the charge in Coulombs required to produce hydrogen gas from water. It defines key terms like the Faraday, Coulomb, Ampere, and relates them to determining Avogadro's number experimentally. The document outlines the introduction, results and discussion, conclusion, methodology, and references sections of a report on this experiment.
Descrizione originale:
elektro
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoThis document summarizes an experiment to determine Avogadro's number by measuring the amount of charge required to reduce 1 mole of hydrogen ions. The experiment uses electrolysis and measures the charge in Coulombs required to produce hydrogen gas from water. It defines key terms like the Faraday, Coulomb, Ampere, and relates them to determining Avogadro's number experimentally. The document outlines the introduction, results and discussion, conclusion, methodology, and references sections of a report on this experiment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
9 visualizzazioni1 paginaElectrolysis Sssss Sssssssss
Caricato da
AnitaYusrinaKulsumThis document summarizes an experiment to determine Avogadro's number by measuring the amount of charge required to reduce 1 mole of hydrogen ions. The experiment uses electrolysis and measures the charge in Coulombs required to produce hydrogen gas from water. It defines key terms like the Faraday, Coulomb, Ampere, and relates them to determining Avogadro's number experimentally. The document outlines the introduction, results and discussion, conclusion, methodology, and references sections of a report on this experiment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 1
Electrolysis, the Faraday, and Avogadros Number
Anita Yusrina Kulsum,
Departement of Chemistry, Universitas Padjadjaran, Bandung, yusrinaanita@gmail.com
Abstrack
....................................................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................
Keywords :
I. Introduction
Ampere flows for one second. Therefore,
The passage of an electric current
a Coulomb is an Ampere-Second. The
through a solution is accompanied by
elementary charge on a single electron was
chemical reactions at the electrodes.
discovered by Robert Millikan and is equal
Oxidation occurs at the anode; reduction
to 1.6 x 10-19 C.
occurs at the cathode. The amount of
reaction that occurs at the electrodes is II. Results and discussion
directly proportional to the number of III. Conclusion
electrons transferred. Thus, a Faraday is IV. Methodology
defined as the total charge carried by
Avogadros number of electrons, or 1 mole
of electrons.
In this experiment you will determine
the value of the Faraday number F by
measuring the amount of charge required
to reduce 1 mole of H+ ions according to
the reaction
2H+(aq) + 2e- H2(g)
+ 1e- 2H2(g)
(aq)
or
H+
Electric charge (q) is conveniently V. Acknowledgment
measured in Coulombs. A coulomb (C) is VI. References
the amount of electrical charge that passes
Chang,
R.2003.General
a point in a circuit when a current (I) of 1
Ed.Maidenhead UK.
Cheistry.3th
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Teachers EditionDocumento374 pagineTeachers EditionKrish Kotecha67% (3)
- Environmental Electrochemistry: Fundamentals and Applications in Pollution Sensors and AbatementDa EverandEnvironmental Electrochemistry: Fundamentals and Applications in Pollution Sensors and AbatementNessuna valutazione finora
- UDSM UG Programmes Synopsis New Version 1Documento72 pagineUDSM UG Programmes Synopsis New Version 1Juma MpangaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cognitive Reliability and Error Analysis Method (CREAM)Da EverandCognitive Reliability and Error Analysis Method (CREAM)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (2)
- Grade 7Documento1 paginaGrade 7chanuka469Nessuna valutazione finora
- Karty Pracy Ucznia Odpowiedzi ChemiaDocumento68 pagineKarty Pracy Ucznia Odpowiedzi ChemiaannaNessuna valutazione finora
- Princeton Problems in Physics with SolutionsDa EverandPrinceton Problems in Physics with SolutionsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5)
- tmpF69A TMPDocumento21 paginetmpF69A TMPFrontiersNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical School Interview QuestionsDocumento112 pagineMedical School Interview QuestionsPanasheNessuna valutazione finora
- Careers: Exploring The PossibilitiesDocumento98 pagineCareers: Exploring The Possibilitiesnmnwse100% (4)
- 20170328115124wizard of Science (Chemistry) 2 PDFDocumento37 pagine20170328115124wizard of Science (Chemistry) 2 PDFSubashiniNessuna valutazione finora
- Atlas of Forensic PathologyDocumento12 pagineAtlas of Forensic PathologyDante RamírezNessuna valutazione finora
- Casebook 2.2 Semi FinalDocumento1.015 pagineCasebook 2.2 Semi FinalCarol AnnNessuna valutazione finora
- Krishnamurthy Smitha 200908 MSDocumento100 pagineKrishnamurthy Smitha 200908 MSShashi KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- 2010 A ReviewofconductionphenomenainLi-IonbatteriesDocumento26 pagine2010 A ReviewofconductionphenomenainLi-IonbatteriesBruce LiNessuna valutazione finora
- Graduate Student Handbook 9.9.22 v.4.2Documento66 pagineGraduate Student Handbook 9.9.22 v.4.2TWangmoNessuna valutazione finora
- SECTION 1: General ConsiderationsDocumento2 pagineSECTION 1: General ConsiderationsSELLULARNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 s2.0 S1364032115004839 Main PDFDocumento14 pagine1 s2.0 S1364032115004839 Main PDFEng MohammedNessuna valutazione finora
- S1 2022 432329 TableofcontentDocumento3 pagineS1 2022 432329 TableofcontentLuana AraújoNessuna valutazione finora
- Manua (Nuc. Physics)Documento175 pagineManua (Nuc. Physics)Ujjwal RastogiNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Notes2016v15 PDFDocumento291 paginePhysics Notes2016v15 PDFCurtis Patterson100% (1)
- Paper ThermofluidDocumento16 paginePaper ThermofluidAkmal Irfan MajidNessuna valutazione finora
- 2020 Garbino Et Al Systematics ChirodermaDocumento93 pagine2020 Garbino Et Al Systematics ChirodermaNatalus StramineusNessuna valutazione finora
- The Effect of Artificial Lighting On Bats in Britain: Mres ThesisDocumento98 pagineThe Effect of Artificial Lighting On Bats in Britain: Mres Thesisgayatri parkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Bulletin 2017-18 MedicineDocumento391 pagineBulletin 2017-18 MedicineElias ElasiaNessuna valutazione finora
- BonitaDocumento257 pagineBonitaCardio Family of July 2018 Universitas Indonesia100% (1)
- Biomechanical and Neural Factors Associated With Gait DysfunctionDocumento161 pagineBiomechanical and Neural Factors Associated With Gait DysfunctionAbderrahmane HaouassiNessuna valutazione finora
- Raptor ManualDocumento75 pagineRaptor ManualCarlos Juan Martínez Pámanes100% (1)
- Deocument - 458full Download Book Methods and Applications in Petroleum and Mineral Exploration and Engineering Geology PDFDocumento41 pagineDeocument - 458full Download Book Methods and Applications in Petroleum and Mineral Exploration and Engineering Geology PDFjulie.torres496100% (13)
- International Journal of Scientific and Research PublicationsDocumento689 pagineInternational Journal of Scientific and Research PublicationsJUAN CARLOS AHUACTZIN DIAZNessuna valutazione finora
- 0 Introduccion HouseDocumento16 pagine0 Introduccion Housejorge alvarezNessuna valutazione finora
- Musanze District School: G.S Nyakinama I: Nsabimana ThadeeDocumento85 pagineMusanze District School: G.S Nyakinama I: Nsabimana ThadeeSekste MaludaNessuna valutazione finora
- In Your Answer, You Should Make Clear How Your Explanation Links With The EvidenceDocumento20 pagineIn Your Answer, You Should Make Clear How Your Explanation Links With The EvidenceAdam El TohamyNessuna valutazione finora
- Textbook of Veterinary Parasitology Introduction To Parasitology. ProtozoologyDocumento205 pagineTextbook of Veterinary Parasitology Introduction To Parasitology. Protozoologyioana_alexandra_tomaNessuna valutazione finora
- PrereqchartDocumento15 paginePrereqchartapi-345280866Nessuna valutazione finora
- India School of Solar: Introduction To The Design & Installation of Photovoltaic (PV) SystemsDocumento14 pagineIndia School of Solar: Introduction To The Design & Installation of Photovoltaic (PV) SystemsYusuf xlNessuna valutazione finora
- Obat TradisionalDocumento11 pagineObat TradisionalOktavia Catur XenografNessuna valutazione finora
- Analogue Electronics 1, DEE 1 Notes - 075733Documento137 pagineAnalogue Electronics 1, DEE 1 Notes - 075733Kirimi DanNessuna valutazione finora
- Directory of Japanese Studies in Australia and New ZealandDocumento517 pagineDirectory of Japanese Studies in Australia and New Zealandscribbler49971Nessuna valutazione finora
- Research Scholarships PDFDocumento42 pagineResearch Scholarships PDFRhyanda JonesNessuna valutazione finora
- Patterns of Mountain Vegetation Dynamics and Their Responses To Environmental Changes in The South Ecuadorian AndesDocumento243 paginePatterns of Mountain Vegetation Dynamics and Their Responses To Environmental Changes in The South Ecuadorian AndesdcontreNessuna valutazione finora
- Iscn Report 2018 International Sustainable Campus NetworkDocumento96 pagineIscn Report 2018 International Sustainable Campus NetworkguachiguachiNessuna valutazione finora
- Causes of Dropout in Primary SchoolsDocumento97 pagineCauses of Dropout in Primary SchoolsMariettaPinky De Leon TipayNessuna valutazione finora
- Male Homosexuality and PedophileDocumento195 pagineMale Homosexuality and Pedophilelinchi0% (4)
- Ananas Comosus Var. Comosus: The Biology of (Pineapple)Documento42 pagineAnanas Comosus Var. Comosus: The Biology of (Pineapple)Rya AgustienNessuna valutazione finora
- Section One-Basic Sciences: Radhika Aggarwal MK Dey TK Datta G UshaDocumento2 pagineSection One-Basic Sciences: Radhika Aggarwal MK Dey TK Datta G UshaIshfaq LoneNessuna valutazione finora
- Immunosensors For Detection of Pesticide ResiduesDocumento11 pagineImmunosensors For Detection of Pesticide Residuescatherine_henry-de-villeneuveNessuna valutazione finora
- Behavioral and Cognitive Effects of Microwave ExposureDocumento24 pagineBehavioral and Cognitive Effects of Microwave ExposuremwhitakerNessuna valutazione finora
- Agamben KDocumento114 pagineAgamben KPee JayNessuna valutazione finora
- Holiday Package Year 10 BiologyDocumento7 pagineHoliday Package Year 10 Biologyemmanuelkasumba50Nessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Unit 2 Question PaperDocumento16 paginePhysics Unit 2 Question PaperqeoobyogNessuna valutazione finora
- Bruce McCune-James B. GraceDocumento307 pagineBruce McCune-James B. GraceAndrea Mendoza100% (1)
- Capsulitis Adhesiva - RevDocumento6 pagineCapsulitis Adhesiva - RevLizeth ArceNessuna valutazione finora
- Methods and Applications in Petroleum and Mineral Exploration and Engineering Geology Said Gaci Full ChapterDocumento67 pagineMethods and Applications in Petroleum and Mineral Exploration and Engineering Geology Said Gaci Full Chapterjimmy.fagundes610100% (4)
- 2016 ATC AU List Updated 6717Documento40 pagine2016 ATC AU List Updated 6717Varinder AnandNessuna valutazione finora
- Summer Internship Experience 2022 PDFDocumento247 pagineSummer Internship Experience 2022 PDFMazharul IslamNessuna valutazione finora
- Life Science Honors For Middle School B v5 Zf8 s1Documento809 pagineLife Science Honors For Middle School B v5 Zf8 s1TheReaderLu100% (2)
- The Exact Time of Death and Birth Time CorrectionDocumento360 pagineThe Exact Time of Death and Birth Time Correctionlinchi100% (4)
- Appendix For RecrystllizationDocumento1 paginaAppendix For RecrystllizationAnitaYusrinaKulsumNessuna valutazione finora
- ResultDocumento1 paginaResultAnitaYusrinaKulsumNessuna valutazione finora
- Freezing Point DepressionDocumento16 pagineFreezing Point DepressionAnitaYusrinaKulsum100% (1)
- Massa MolarDocumento12 pagineMassa MolarAnitaYusrinaKulsumNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Quest HW 3aDocumento5 paginePhysics Quest HW 3aFuriFuriNessuna valutazione finora
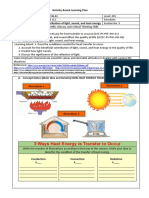
- Chapter 03 - Solar Energy and Earth-Sun Relationships True / FalseDocumento15 pagineChapter 03 - Solar Energy and Earth-Sun Relationships True / FalseAhmoosiNessuna valutazione finora
- XT1C 160 TMD 25-450 4p F F: General InformationDocumento3 pagineXT1C 160 TMD 25-450 4p F F: General InformationHenrics MayoresNessuna valutazione finora
- WEEK 1 Base and Derived UnitsDocumento6 pagineWEEK 1 Base and Derived UnitsannmarieNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics SPM ModificationsDocumento7 paginePhysics SPM ModificationsMuhammad Jaziem100% (1)
- Light WavesDocumento19 pagineLight WavesDejaunae LawsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Building Electrical Systems Design & DraftingDocumento103 pagineBuilding Electrical Systems Design & DraftingEisa Ibrahim Eisa93% (73)
- LS2 How Lights Sound and Heat Travels Week 5Documento9 pagineLS2 How Lights Sound and Heat Travels Week 5Thrisha BagalanonNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap IDocumento56 pagineChap ICybertron BadeeNessuna valutazione finora
- KCET 2022 PhysicsDocumento8 pagineKCET 2022 PhysicsSuhas Renu85Nessuna valutazione finora
- Petrus Peregrinus': EpistoDocumento8 paginePetrus Peregrinus': EpistoDeborah ValandroNessuna valutazione finora
- Instrument-Transformer-Testing-Brochure-ENU 2Documento1 paginaInstrument-Transformer-Testing-Brochure-ENU 2balbeloanna7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Dipesh PDFDocumento19 paginePhysics Dipesh PDFKripesh BaralNessuna valutazione finora
- LECTURE NOTES - 3rd ETC - EMI - A PradhanDocumento74 pagineLECTURE NOTES - 3rd ETC - EMI - A PradhanAjit PatraNessuna valutazione finora
- Crankshaft Position Sensor Inductive, Referenced, Voltage During CrankingDocumento7 pagineCrankshaft Position Sensor Inductive, Referenced, Voltage During Crankingdanieldario33Nessuna valutazione finora
- Washer Installation 50TS8 - EN PDFDocumento102 pagineWasher Installation 50TS8 - EN PDFComfort KanjiNessuna valutazione finora
- CXC Electrical ExamDocumento7 pagineCXC Electrical Examkesna100% (2)
- Electrical Substation: Quotation ForDocumento15 pagineElectrical Substation: Quotation ForMohammad MohiuddinNessuna valutazione finora
- AC Servo Motor&DriverDocumento3 pagineAC Servo Motor&DriverJose Antonio Siñani VilteNessuna valutazione finora
- Inven Alkes Unit KPW Dan Penunjang2010Documento181 pagineInven Alkes Unit KPW Dan Penunjang2010aben kolingNessuna valutazione finora
- IGCSE Cie The Nuclear Atom P1Documento10 pagineIGCSE Cie The Nuclear Atom P1Payail Parineeta PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Cem AssDocumento13 pagineCem AssHarshdeep SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Ogun State Ministry of Education, Science and Technology Unified Scheme of Work Physics First Term Ss1 S/N Topic Sub Topic ContentDocumento14 pagineOgun State Ministry of Education, Science and Technology Unified Scheme of Work Physics First Term Ss1 S/N Topic Sub Topic ContentOluwatobi Peter AdemosuNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Emi-And-Ac 501138Documento41 pagine1 Emi-And-Ac 501138EdumaaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Many Uses of Transmission Line ArrestersDocumento8 pagineThe Many Uses of Transmission Line ArrestersVK DharmikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Elektrisola Datasheet AlDocumento4 pagineElektrisola Datasheet AlCarlos CaraballoNessuna valutazione finora
- Master of Science (M.SC.) Semester-IV (CBCS) Physics Examination Nuclear and Particle Physics Compulsory Paper-1Documento2 pagineMaster of Science (M.SC.) Semester-IV (CBCS) Physics Examination Nuclear and Particle Physics Compulsory Paper-1Sanyam KumariNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus Content 2020-2021 (Term3) : Learning OutcomesDocumento6 pagineSyllabus Content 2020-2021 (Term3) : Learning OutcomesЕлнур ИкимбаевNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Absorption SpectrosDocumento4 pagineAtomic Absorption SpectrosAye Ei MonNessuna valutazione finora
- Question Paper: Biology - 100 Chemistry - 50 Physics - 50Documento24 pagineQuestion Paper: Biology - 100 Chemistry - 50 Physics - 50harita shindeNessuna valutazione finora
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideDa EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideNessuna valutazione finora
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincDa EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (137)
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactDa EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (5)
- Formulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsDa EverandFormulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsNessuna valutazione finora
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeDa EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (4)
- AP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeDa EverandAP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- The Periodic Table of Elements - Alkali Metals, Alkaline Earth Metals and Transition Metals | Children's Chemistry BookDa EverandThe Periodic Table of Elements - Alkali Metals, Alkaline Earth Metals and Transition Metals | Children's Chemistry BookNessuna valutazione finora
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsDa EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (146)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeDa EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolDa EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeDa EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (90)
- The Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionDa EverandThe Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- AP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeDa EverandAP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeNessuna valutazione finora
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsDa EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (3)
- Tribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering MaterialsDa EverandTribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering MaterialsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Water-Based Paint Formulations, Vol. 3Da EverandWater-Based Paint Formulations, Vol. 3Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (6)
- Taste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodDa EverandTaste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (20)
- Ingredients: A Visual Exploration of 75 Additives & 25 Food ProductsDa EverandIngredients: A Visual Exploration of 75 Additives & 25 Food ProductsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeDa EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (14)
- Bioplastics: A Home Inventors HandbookDa EverandBioplastics: A Home Inventors HandbookValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (2)
- The Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableDa EverandThe Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (22)
- High School Chemistry: Comprehensive Content for High School ChemistryDa EverandHigh School Chemistry: Comprehensive Content for High School ChemistryNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Chemistry: A Modern IntroductionDa EverandFundamentals of Chemistry: A Modern IntroductionValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactDa EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)