Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Some Characteristic of The Contemporary Music
Caricato da
ngbachTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Some Characteristic of The Contemporary Music
Caricato da
ngbachCopyright:
Formati disponibili
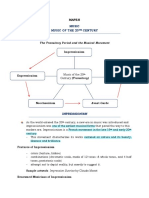
SOME CHARACTERISTIC OF THE CONTEMPORARY MUSIC
The bridge to the Contemporary period was formed during the last quarter of the
nineteenth century through a new painting movement called Impressionism. About 1870 a
group of French painters ( Monet, Renoir, Degas etc.) rejected the accepted Romanticism
in favour of a new style that sought to portray art as the artists impression of a subject.
Composers like Debussy (1862-1918) and Ravel (1875-1937) portrayed musically these
innovations in art and poetry. (Mallarme, Verlaine and The bridge to the Contemporary
period was formed during the last quarter of the nineteenth century through the new
painting movement known as others) New sonorities in orchestration and piano music
developed which often incorporated extra musical material from art and literature,
sometimes containing non-Western melodies and rhythms, introduced new scales (wholetone, modes) and chord uses. They used unresolved dissonances to portray a veiled
illusionary effect.
Twentieth century music reflects the influences of art and literature in a mechanistic,
atomic age. The emergence of pleasant sounding, pastel-coloured Impressionistic music
led to experiments with twelve-tone music. (Schoenberg) This produced cerebral, atonal,
often angular and disjointed musical effects. Other twentieth century musical experiments
are with electronic music. Influences such as electronically amplified instruments and jazz,
rock, and popular elements are associated with this period.
Within this modern era, there are great style variations from Post-Romanticism (Mahler,
Rachmaninoff) to Impressionism, to new concepts of melodic tonality-rhythm expressed in
the music of Bartok, Stravinsky, Prokofiev, Copland, Shostakovich, Barber and Gorecki.
Some general characteristics of Contemporary Music are:
(Contemporary compositions vary widely, so this is not a complete list; and not all these
characteristics are present in every composition.)
1. Fewer lyrical melodies than the music of former periods.
2. Dissonant harmonies.
3. Complex rhythms.
4. Percussiveness.
5. Greater use of woodwind, brass and percussion instruments than in music of earlier
periods.
6. The use of synthetic and electronic sounds.
-
Portray = miu t sinh ng, v chn dung = to paint or draw the likeness
Innovation = something new, and contrary to established customs, manners
Sonority = The quality or state of being sonorous / sonorous = resonant
Incorporate = kt hp cht ch - United or combined together to form in one body.
Veiled = Covered by
Illusion = An unreal image presented to the bodily or mental vision
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- 1ST Music of The 20TH 1STWKDocumento48 pagine1ST Music of The 20TH 1STWKNICOLE QUEJARRONessuna valutazione finora
- Music 10 2015Documento25 pagineMusic 10 2015Jeric MatunhayNessuna valutazione finora
- First Quarter Music10Documento63 pagineFirst Quarter Music10Ysabelle TagarumaNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation1 Q1 Music Lesson1 G10 ImpressionismDocumento84 paginePresentation1 Q1 Music Lesson1 G10 Impressionismcheeneerain banaganNessuna valutazione finora
- Mapeh Grade 10 Module 1Documento12 pagineMapeh Grade 10 Module 1Jorely Barbero Munda100% (7)
- Music Q1 - Module IIDocumento28 pagineMusic Q1 - Module IIEric CayetanoNessuna valutazione finora
- 20th-Century Classical Music - Wikipedia PDFDocumento59 pagine20th-Century Classical Music - Wikipedia PDFJerma Lyn BruaNessuna valutazione finora
- Art and Music Have Developed in Parallel With Each Other: Impressionism Century 20th Century ImpressionismDocumento15 pagineArt and Music Have Developed in Parallel With Each Other: Impressionism Century 20th Century ImpressionismJiji Carinan - TaclobNessuna valutazione finora
- 20th Century Music HistoryDocumento14 pagine20th Century Music HistoryKarl Lewis100% (2)
- MAPEHDocumento25 pagineMAPEHSam V.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 1-Music With QuizDocumento79 pagineLesson 1-Music With Quizkitcath100% (1)
- Mapeh REVIEWER MUSICDocumento6 pagineMapeh REVIEWER MUSICNicole Faye RamosNessuna valutazione finora
- Sorista EnglanniksiDocumento4 pagineSorista EnglanniksiOtto VilleNessuna valutazione finora
- Learning Activity Sheets in Mapeh 10Documento18 pagineLearning Activity Sheets in Mapeh 10Badeth Ablao90% (21)
- MAPEH ReviewerDocumento12 pagineMAPEH ReviewerCassandra Jeurice UyNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 1 MusicDocumento71 pagineLesson 1 MusickitcathNessuna valutazione finora
- Expressionism NOTEDocumento7 pagineExpressionism NOTEisaac afolabiNessuna valutazione finora
- 20th-Century Classical MusicDocumento7 pagine20th-Century Classical MusicLaraya OlchondraNessuna valutazione finora
- Mapeh Q1Documento10 pagineMapeh Q1Czarina D. AceNessuna valutazione finora
- Music Quarter 1Documento25 pagineMusic Quarter 1Rocelgie JimenezNessuna valutazione finora
- Music NotesDocumento4 pagineMusic NotesGirli JoseeNessuna valutazione finora
- 20th Century Music EssayDocumento3 pagine20th Century Music EssayIsaac CortvriendNessuna valutazione finora
- Music Music of The 20 Century: MapehDocumento16 pagineMusic Music of The 20 Century: MapehApril Sophie DavidNessuna valutazione finora
- Music Music of The 20 Century: MapehDocumento26 pagineMusic Music of The 20 Century: MapehApril Sophie DavidNessuna valutazione finora
- Modern Nationalism 2019 Version PresentationDocumento8 pagineModern Nationalism 2019 Version PresentationTon OpridoNessuna valutazione finora
- Music of The 20th CenturyDocumento8 pagineMusic of The 20th CenturyAlbert Ian CasugaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 1 MusicDocumento34 pagineLesson 1 MusickitcathNessuna valutazione finora
- Western Classical Overview 4 1Documento7 pagineWestern Classical Overview 4 1Joms HomelessNessuna valutazione finora
- History of 20 Century: 20th-Century Classical Music Describes Orchestral Works, Chamber Music, SoloDocumento16 pagineHistory of 20 Century: 20th-Century Classical Music Describes Orchestral Works, Chamber Music, SoloMary Rose QuimanjanNessuna valutazione finora
- GRADE 10 MUSIC Q1 Wk1Documento8 pagineGRADE 10 MUSIC Q1 Wk1Elma AlbertoNessuna valutazione finora
- Quarter 3 Mapeh Learning MaterialDocumento31 pagineQuarter 3 Mapeh Learning MaterialKem Marian MauricioNessuna valutazione finora
- Welcome!: Grade 10 MapehDocumento29 pagineWelcome!: Grade 10 MapehAnela KimNessuna valutazione finora
- 20th Century MusicDocumento95 pagine20th Century MusicMer LynNessuna valutazione finora
- Q1-MUSIC Grade 10Documento55 pagineQ1-MUSIC Grade 10Shanny Libiano75% (8)
- Modern Art MusicDocumento10 pagineModern Art MusicFisella Music CourseNessuna valutazione finora
- 1st Q MusicDocumento2 pagine1st Q MusicashNessuna valutazione finora
- 20 Century "Isms": Impressionism, Expressionism, and NeoclassicismDocumento19 pagine20 Century "Isms": Impressionism, Expressionism, and NeoclassicismKristine ApostolNessuna valutazione finora
- LAS MAPEH 10 Q1 W1 MusicDocumento6 pagineLAS MAPEH 10 Q1 W1 MusicJemalyn Hibaya LasacaNessuna valutazione finora
- Romantic PeriodDocumento47 pagineRomantic PeriodApryll SuñgaNessuna valutazione finora
- Music of The 20TH Century (Lecture)Documento6 pagineMusic of The 20TH Century (Lecture)Rome BilloteNessuna valutazione finora
- The History of Classical Music: Bach - Brandenburg Concert No.3Documento20 pagineThe History of Classical Music: Bach - Brandenburg Concert No.3paul gabotero cabulong100% (1)
- (Day 1) Music of The 20TH CenturyDocumento8 pagine(Day 1) Music of The 20TH Centuryqwer asdfNessuna valutazione finora
- Primitvism: BELA BARTOK (1881-1945)Documento6 paginePrimitvism: BELA BARTOK (1881-1945)zach catindigNessuna valutazione finora
- The History of Instrumental MusicDocumento25 pagineThe History of Instrumental MusicLoi SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- MAPEH MUSIC 10 Q1 HandoutsDocumento6 pagineMAPEH MUSIC 10 Q1 HandoutsAesha BalayonNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is 20th Century MusicDocumento37 pagineWhat Is 20th Century MusicGazelle Piyokcka Mapagmahal AquiloNessuna valutazione finora
- Music 10 Hand OutsDocumento5 pagineMusic 10 Hand OutsDiane CatapangNessuna valutazione finora
- Impressionist MusicDocumento17 pagineImpressionist MusicDolfiParthaHutagalungNessuna valutazione finora
- Pointers To Review For The Quarter 1 MAPEH 10Documento51 paginePointers To Review For The Quarter 1 MAPEH 10Gian ObongenNessuna valutazione finora
- Neo-Romanticism Neo-Classicism Nationalism: The Modern/20th Century Era (1900 - Present)Documento6 pagineNeo-Romanticism Neo-Classicism Nationalism: The Modern/20th Century Era (1900 - Present)Francis BawegNessuna valutazione finora
- Romantic MusicDocumento5 pagineRomantic MusicHades Luciferos PallonesNessuna valutazione finora
- Vocal and Instrumental Music of 20th CenturyDocumento3 pagineVocal and Instrumental Music of 20th CenturyJasmine Mae LapigNessuna valutazione finora
- Music 10 Reviewer. Quarter 1Documento5 pagineMusic 10 Reviewer. Quarter 1mitchbalonzo7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Music HandoutDocumento10 pagineMusic HandoutFaith Joy Adriano AlcalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 1 ImpressionismDocumento15 pagineLesson 1 Impressionismreyciel brazaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 1 ImpressionismDocumento15 pagineLesson 1 Impressionismreyciel brazaNessuna valutazione finora
- Music History - The Romantic Period (1825-1900)Documento5 pagineMusic History - The Romantic Period (1825-1900)mcheche12Nessuna valutazione finora
- Modern Art MusicDocumento14 pagineModern Art MusicrandadebsNessuna valutazione finora
- Romantic Music (1850-1900) : Composers of The PeriodDocumento6 pagineRomantic Music (1850-1900) : Composers of The Periodann monteNessuna valutazione finora
- Nguyen Tac Giai Sa HinhDocumento3 pagineNguyen Tac Giai Sa HinhngbachNessuna valutazione finora
- De Cuong Mon HocDocumento3 pagineDe Cuong Mon HocngbachNessuna valutazione finora
- Three Points of Failure in Present Music EducationDocumento1 paginaThree Points of Failure in Present Music EducationngbachNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinh Dang Hien (Nguyen Bach - Linh Trieu)Documento4 pagineKinh Dang Hien (Nguyen Bach - Linh Trieu)ngbachNessuna valutazione finora
- Children's Choir Information and Sign-Up Sheet: 2015-2016 Church YearDocumento2 pagineChildren's Choir Information and Sign-Up Sheet: 2015-2016 Church YearngbachNessuna valutazione finora
- A Hero of MusicDocumento2 pagineA Hero of MusicngbachNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 - Roman Numeral Analysis: Altered ChordsDocumento2 pagine2 - Roman Numeral Analysis: Altered ChordsngbachNessuna valutazione finora
- Liszt and The PianoDocumento3 pagineLiszt and The PianongbachNessuna valutazione finora
- Three Points of Failure in Present Music EducationDocumento1 paginaThree Points of Failure in Present Music EducationngbachNessuna valutazione finora
- StudioDocumento31 pagineStudiongbachNessuna valutazione finora
- Gioù Mong Manh: Country Saùng Taùc: Leâ Quaân Hoøa Aâm: Leâ Quang VuõDocumento8 pagineGioù Mong Manh: Country Saùng Taùc: Leâ Quaân Hoøa Aâm: Leâ Quang VuõngbachNessuna valutazione finora
- 39 TienDung NganLanYeuDocumento5 pagine39 TienDung NganLanYeungbachNessuna valutazione finora
- Liszt and The PianoDocumento3 pagineLiszt and The PianongbachNessuna valutazione finora
- Music TeachingDocumento10 pagineMusic TeachingngbachNessuna valutazione finora
- Caùc Maãu Daùng (Form) Caáu Truùc: Hình 27 Khuoân Ñaøn GuitarDocumento2 pagineCaùc Maãu Daùng (Form) Caáu Truùc: Hình 27 Khuoân Ñaøn GuitarngbachNessuna valutazione finora
- Music EducationDocumento2 pagineMusic EducationngbachNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical Use: Christian Friedrich Ludwig BuschmannDocumento1 paginaMedical Use: Christian Friedrich Ludwig BuschmannngbachNessuna valutazione finora
- Music EducationDocumento2 pagineMusic EducationngbachNessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching IdeasDocumento5 pagineTeaching IdeasngbachNessuna valutazione finora
- Music TerminologyDocumento66 pagineMusic TerminologyngbachNessuna valutazione finora
- Thieát Bò Caét Raõnh Vieàn (Purfling Cutter) : ShimsDocumento1 paginaThieát Bò Caét Raõnh Vieàn (Purfling Cutter) : ShimsngbachNessuna valutazione finora
- 20th Century MusicDocumento7 pagine20th Century MusicngbachNessuna valutazione finora
- Baøo Goã: Hình 32. Baøo Moät Löng Baèng Goã Caây ThíchDocumento2 pagineBaøo Goã: Hình 32. Baøo Moät Löng Baèng Goã Caây ThíchngbachNessuna valutazione finora
- Thu Chaát Lieäu Midi: CUBASE - Phaàn Meàm Thu Nhaïc Tuyeät Vôøi 93Documento11 pagineThu Chaát Lieäu Midi: CUBASE - Phaàn Meàm Thu Nhaïc Tuyeät Vôøi 93ngbachNessuna valutazione finora
- Music HistoryDocumento1 paginaMusic HistoryngbachNessuna valutazione finora
- Claude Debussy: Cuoäc Ñôøi Vaø Taùc PhaåmDocumento4 pagineClaude Debussy: Cuoäc Ñôøi Vaø Taùc PhaåmngbachNessuna valutazione finora
- Music ScoresDocumento60 pagineMusic ScoresngbachNessuna valutazione finora
- Chopin Year 2010: PartnerzyDocumento2 pagineChopin Year 2010: PartnerzyngbachNessuna valutazione finora
- Music SheetsDocumento1 paginaMusic SheetsngbachNessuna valutazione finora