Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Math Ss Program
Caricato da
api-2819875730 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
45 visualizzazioni2 pagineCOMMON CORE STANDARDS Module Lesson Title Grade 2 Program Content March 2012 Lesson Title Comparing Two-Digit Numbers on a Number Line Comparing and Ordering two-digit numbers.
Descrizione originale:
Titolo originale
math ss program
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCOMMON CORE STANDARDS Module Lesson Title Grade 2 Program Content March 2012 Lesson Title Comparing Two-Digit Numbers on a Number Line Comparing and Ordering two-digit numbers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
45 visualizzazioni2 pagineMath Ss Program
Caricato da
api-281987573COMMON CORE STANDARDS Module Lesson Title Grade 2 Program Content March 2012 Lesson Title Comparing Two-Digit Numbers on a Number Line Comparing and Ordering two-digit numbers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 2
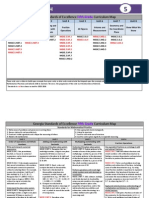
COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS
Module
ORIGO Education.
Lesson
Title
Grade 2 Program Content
March 2012
Lesson
Title
Writing Tens and Ones, and Number Names
Comparing Two-Digit Numbers on a Number Line
Writing Two-Digit Numbers
Comparing and Ordering Two-Digit Numbers
Reading and Writing Two-Digit Numbers
Exploring the Properties of Odd and Even Numbers
10
Working with Two-Digit Numbers on a Hundred Chart
Exploring the Relative Position of Two-Digit Numbers
(Number Track)
Exploring the Relative Position of Two-Digit Numbers
(Number Line)
11
Sorting Data in Different Ways
Working with Two-Digit Numbers on a Number Line
12
Interpreting and Constructing One-to-One Picture Graphs
Working with Addition
Using Place Value (Number Line) to Add Two-Digit Numbers
Using the Commutative Property of Addition
with Count-On Facts
Reading and Writing Time on the Hour and Half
Past the Hour
Relating Addition and Subtraction Facts Count-On Facts
Working with Duration Hours
Working with Count-On Fact Families
10
Identifying Five-Minute Intervals
Extending the Count-On Addition Strategy to
Two-Digit Numbers
11
Working with Five-Minute Intervals
Using Place Value (Number Board) to Add Two-Digit Numbers
12
Working with Duration Hours and Minutes
Working with Hundreds
Measuring Length with Uniform Non-Standard Units
Writing Three-Digit Numbers
Introducing the Inch
Reading and Representing Three-Digit Numbers
Working with Inches
Writing Three-Digit Number Names
10
Introducing Feet
Writing Three-Digit Numerals
11
Working with Feet and Inches
Identifying Three-Digit Numbers on a Number Line
12
Introducing Yards
Exploring the Comparing Model of Subtraction
Working with Use-Doubles Fact Families
Extending the Count-Back Strategy to Two-Digit Numbers
Extending the Use-Doubles Addition Strategy Beyond the
Facts
Working with Time Quarter Past the Hour
Using Place Value (Number Board) to Subtract
Two-Digit Numbers
Using Place Value (Number Line) to Subtract
Two-Digit Numbers
10
Identifying and Recording Time Using a.m. and p.m.
Working with the Use-Doubles Addition Strategy
11
Working with Timetables and Duration
Relating Addition and Subtraction Use-Doubles Facts
12
Working with the Calendar
Representing Three-Digit Numbers With Zeros
Marking the Direction of Turn
Representing Three-Digit Numbers With Teens and Zeros
Describing Amounts of Turn
Writing Three-Digit Numbers in Numerals and Words
Identifying Polygons
Working with Three-Digit Numbers to One Thousand
10
Identifying Quadrilaterals
Comparing Three-Digit Numbers
11
Working with Polygons
Ordering Three-Digit Numbers
12
Drawing 2D Shapes
Using the Make-Ten Addition Strategy
Using Place Value to Add Two-Digit Numbers
With Bridging
Working with Make-Ten Fact Families
Introducing Centimeters
Extending the Make-Ten Addition Strategy Beyond the Facts
Measuring in Centimeters
Analyzing Addition Patterns With Bridging
10
Introducing Meters
Extending the Use-Doubles Addition Strategy
11
Working with Meters
Using Place Value to Add Two-Digit Numbers
12
Using Line Plots to Record Length
Module
10
ORIGO Education.
11
12
Lesson
Title
Lesson
Title
Skip Counting by Two or Five
Using the Turnaround Idea with Arrays
Adding Equal Jumps of Two or Five
Identifying and Comparing Amounts of Money
Describing Equal Groups
Relating Amounts of Money
Adding Equal Groups
10
Working with Cents
Describing Arrays
11
Working with Dollars
Adding Equal Rows
12
Working with Dollars and Cents
Composing and Decomposing Two-Digit Numbers
Using Place Value (Number Line) to Solve
Subtraction Problems
Using Place Value to Subtract One-Digit Numbers from
Two-Digit Numbers
Introducing the Pound
Calculating Difference Between Two-Digit Numbers
Working with Pounds
Consolidating Subtraction with Two-Digit Numbers
10
Introducing the Kilogram
Relating Addition and Subtraction Beyond the Facts
11
Working with Kilograms
Using a Place-Value Strategy to Subtract Two-Digit Numbers
12
Comparing Customary and Metric Units
Exploring the Relative Position of Three-Digit Numbers
Identifying One-Half, One-Fourth, and One-Third of a Collection
Estimating Answers Adding Within 100
Identifying One-Half, One-Fourth, and One-Third of a Region
Estimating Answers Subtracting Within 100
Exploring Fractions
10
Analyzing Fractions
Using the Associative Property of Addition with Three
One- and Two-Digit Numbers
Using the Associative Property of Addition with Four
One- and Two-Digit Numbers
11
Working with Parts of a Whole (Equal Size)
Solving Word Problems
12
Exploring Area
Extending the Count-On Strategy to Three-Digit Numbers
Using Place Value to Add Three-Digit Numbers
With Bridging
Using Place Value to Add Two- and Three-Digit Numbers
Consolidating Addition with Three-Digit Numbers
Using Place Value to Add Three-Digit Numbers
Identifying Polyhedrons
Composing Three-Digit Numbers
10
Identifying Pyramids
11
Investigating 3D Objects
Using Place Value to Add One- and Three-Digit Numbers
With Bridging
Using Place Value to Add Two- and Three-Digit Numbers
With Bridging
12
Drawing 3D Objects
Extending the Count-Back Strategy to Three-Digit Numbers
Introducing the Multiplication Symbol ()
Using Place Value to Subtract Two-Digit Numbers from
Three-Digit Numbers
Using Multiplication Equal Groups
Using Place Value to Subtract Three-Digit Numbers
Using Division Language Sharing
Consolidating Subtraction of Two- and Three-Digit Numbers
10
Relating Multiplication and Division (Sharing)
Using a Place-Value Strategy to Subtract Three-Digit Numbers
11
Using Division Language Grouping
Using a Place-Value Strategy to Solve Subtraction Problems
12
Relating Multiplication and Division (Grouping)
Decomposing Three-Digit Numbers
Using Place Value to Subtract One-Digit Numbers from
Three-Digit Numbers With Bridging
Consolidating Subtraction of One-Digit Numbers
With Bridging
Using Place Value to Subtract Two-Digit Numbers from
Three-Digit Numbers With Bridging
Consolidating Subtraction of Two-Digit Numbers
With Bridging
Using Place Value to Subtract Three-Digit Numbers
With Bridging
Consolidating Subtraction of Three-Digit Numbers
With Bridging
Consolidating Subtraction of Two- and Three-Digit Numbers
With Bridging
Introducing Cups, Pints, and Quarts
10
Working with Cups, Pints, and Quarts
11
Introducing Liters
12
Working with a Liter
3
4
5
6
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Origo Math Practice Book 1Documento53 pagineOrigo Math Practice Book 1avanidave0% (2)
- Yearly Plan Mathematic Special Remedial Programme 1-6: Pre-NumberDocumento22 pagineYearly Plan Mathematic Special Remedial Programme 1-6: Pre-NumberIdris Abdul RahimNessuna valutazione finora
- Tnready Blueprint g4 MathDocumento10 pagineTnready Blueprint g4 Mathapi-282869532Nessuna valutazione finora
- Place ValueDocumento13 paginePlace Valueapi-316762611Nessuna valutazione finora
- BUDGET OF WORK Math 5 & 6Documento8 pagineBUDGET OF WORK Math 5 & 6Kyzer Calix LaguitNessuna valutazione finora
- Stage 3 Mathematics Teaching CycleDocumento4 pagineStage 3 Mathematics Teaching Cycleapi-232861709Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sukatan Matapelajaran Matematik Sekolah RendahDocumento1 paginaSukatan Matapelajaran Matematik Sekolah RendahNoorLiza Hj AkuanNessuna valutazione finora
- Cls6 Math ch1 Day2 Module2Documento4 pagineCls6 Math ch1 Day2 Module2shuvanNessuna valutazione finora
- Panel Latihan Unit Pendidikan Khas Sektor Pendidikan Swasta dan Pendidikan Khas Jabatan Pelajaran Negeri JohorDocumento61 paginePanel Latihan Unit Pendidikan Khas Sektor Pendidikan Swasta dan Pendidikan Khas Jabatan Pelajaran Negeri JohorAzimin ZulkifliNessuna valutazione finora
- I Can Add Three 1-Digit NumbersDocumento6 pagineI Can Add Three 1-Digit NumbersAvo LutionNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics Scope and Sequence: Foundation to Year 10Documento8 pagineMathematics Scope and Sequence: Foundation to Year 10lvminhtrietNessuna valutazione finora
- 0 K-N, Math PresentationDocumento18 pagine0 K-N, Math PresentationAYU IMTYAS RUSDIANSYAHNessuna valutazione finora
- Placement TestDocumento12 paginePlacement TesthokeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Brigantine North Middle School CurriculumDocumento47 pagineBrigantine North Middle School Curriculumapi-340154826Nessuna valutazione finora
- ESF Number: K2 Year 2 Year 4 Year 6Documento6 pagineESF Number: K2 Year 2 Year 4 Year 6Stu LoweNessuna valutazione finora
- Math Makes Sense Grade 6 Unit 9Documento3 pagineMath Makes Sense Grade 6 Unit 9AnthonyNessuna valutazione finora
- Teacher Unit Name Unit Description: Primary SecondaryDocumento3 pagineTeacher Unit Name Unit Description: Primary SecondaryMichelle YoungNessuna valutazione finora
- K-10 Mathematics continuum for curriculum developmentDocumento1 paginaK-10 Mathematics continuum for curriculum developmentJedda Decker100% (1)
- Ujian Diagnostik MatematikDocumento60 pagineUjian Diagnostik MatematikNur Syafiqah Lamaris AbdullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Ujian Diagnostik Matematik Baru (Ikamr) 2Documento61 pagineUjian Diagnostik Matematik Baru (Ikamr) 2ashhwinnyNessuna valutazione finora
- Ujian Diagnostik: Instrumen Kemahiran Asas Matematik Sekolah Rendah Program Pemulihan KhasDocumento61 pagineUjian Diagnostik: Instrumen Kemahiran Asas Matematik Sekolah Rendah Program Pemulihan KhasAnonymous qggx2VNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 4 Math MapDocumento1 paginaGrade 4 Math Mapapi-294862378Nessuna valutazione finora
- Y1-6 Maths Statements - Number - Multiplication & DivisionDocumento3 pagineY1-6 Maths Statements - Number - Multiplication & DivisionAndy BrookeNessuna valutazione finora
- 4th Math Curriculum MapDocumento6 pagine4th Math Curriculum Mapapi-266473918Nessuna valutazione finora
- Budget of Work in Mathematics 4Documento6 pagineBudget of Work in Mathematics 4Rowena Casonete Dela TorreNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Topic Covered PrintDocumento2 pagineMaths Topic Covered PrintAmy ParsonsNessuna valutazione finora
- Ujian Diagnostik Matematik: Nama: Kelas: Sekolah: TarikhDocumento60 pagineUjian Diagnostik Matematik: Nama: Kelas: Sekolah: TarikhHema LatthaNessuna valutazione finora
- Egyptian CurriculumDocumento24 pagineEgyptian CurriculumAsri DwitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Math 4 Summary List of Lessons 1st Grading - MontellanoDocumento4 pagineMath 4 Summary List of Lessons 1st Grading - MontellanoJhon Ray Cagampang0% (1)
- Ramsbury Calculation PolicyDocumento5 pagineRamsbury Calculation Policyapi-294851656Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pupil Level DescriptorsDocumento7 paginePupil Level DescriptorsPritpal SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- I Nstrumen Penentu Kemahiran Asas Numerasi Pra Sekolah 2012Documento61 pagineI Nstrumen Penentu Kemahiran Asas Numerasi Pra Sekolah 2012adieeNessuna valutazione finora
- My Homework Lesson 6 Subtract Four Digit NumbersDocumento4 pagineMy Homework Lesson 6 Subtract Four Digit Numbersisvgmchkf100% (1)
- I-Ready Vertical Alignment 3rd Marking Period k-2Documento6 pagineI-Ready Vertical Alignment 3rd Marking Period k-2api-265244540Nessuna valutazione finora
- Australian Curriculum - Maths RubricDocumento8 pagineAustralian Curriculum - Maths Rubricapi-264721797Nessuna valutazione finora
- MATH103 Math For Todays WorldDocumento425 pagineMATH103 Math For Todays Worldalfredomedardo100% (2)
- Classroom-Ready Number Talks for Third, Fourth and Fifth Grade Teachers: 1,000 Interactive Math Activities that Promote Conceptual Understanding and Computational FluencyDa EverandClassroom-Ready Number Talks for Third, Fourth and Fifth Grade Teachers: 1,000 Interactive Math Activities that Promote Conceptual Understanding and Computational FluencyNessuna valutazione finora
- UJIAN DIAGNOSTIK MATEMATIK (BM) PSPNDocumento61 pagineUJIAN DIAGNOSTIK MATEMATIK (BM) PSPNALIF KHAIRUDDINNessuna valutazione finora
- $R12SETIDocumento28 pagine$R12SETIbirrajNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathlathon SyllabusDocumento3 pagineMathlathon SyllabusvivekgeethaNessuna valutazione finora
- Learn Numbers 1-9 with Addition and SubtractionDocumento123 pagineLearn Numbers 1-9 with Addition and SubtractionGeorge AlenNessuna valutazione finora
- New Maths Calculation PolicyDocumento11 pagineNew Maths Calculation PolicyMr DownesNessuna valutazione finora
- Addition Made Easy (Making Math Easy)Documento50 pagineAddition Made Easy (Making Math Easy)timlawson100100% (17)
- Mathematics: (Philippine Elementary Learning Competencies) Basic Education CurriculumDocumento34 pagineMathematics: (Philippine Elementary Learning Competencies) Basic Education CurriculumNel ManjaresNessuna valutazione finora
- Scheme of Work Maths Stage 7Documento18 pagineScheme of Work Maths Stage 7Sue Adames de Velasco100% (7)
- Term 3 Mathematics OverviewDocumento8 pagineTerm 3 Mathematics Overviewapi-208000806Nessuna valutazione finora
- CCSSI Math Standards 1Documento4 pagineCCSSI Math Standards 1establoid1169Nessuna valutazione finora
- Open Term 3Documento57 pagineOpen Term 3ernsteinsNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics RevisedCurriculum 2021-2022Documento9 pagineMathematics RevisedCurriculum 2021-2022iqra darNessuna valutazione finora
- Math Fluency Activities for K–2 Teachers: Fun Classroom Games That Teach Basic Math Facts, Promote Number Sense, and Create Engaging and Meaningful PracticeDa EverandMath Fluency Activities for K–2 Teachers: Fun Classroom Games That Teach Basic Math Facts, Promote Number Sense, and Create Engaging and Meaningful PracticeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Open Term 1 - North CoastDocumento61 pagineOpen Term 1 - North CoasternsteinsNessuna valutazione finora
- Kindergarten Unit 6 Outline Overview 2017Documento33 pagineKindergarten Unit 6 Outline Overview 2017api-401628488Nessuna valutazione finora
- New Syllabus Key IdeasDocumento5 pagineNew Syllabus Key Ideasapi-198803582100% (1)
- GRADE 7:8 MATH StrandsDocumento3 pagineGRADE 7:8 MATH StrandspuneetNessuna valutazione finora
- Gwinnett County Public Schools Mathematics: Grade 4 - Instructional Calendar 2020-2021Documento3 pagineGwinnett County Public Schools Mathematics: Grade 4 - Instructional Calendar 2020-2021api-519622916Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2015-16 Aps Fifth Grade Curriculum MapDocumento6 pagine2015-16 Aps Fifth Grade Curriculum Mapapi-291816007Nessuna valutazione finora
- Continuum 2014Documento2 pagineContinuum 2014api-198803582100% (1)
- Ujian Diagnostik Matematik Baru (Ikamr) 2Documento61 pagineUjian Diagnostik Matematik Baru (Ikamr) 2Dhanish SivalingamNessuna valutazione finora
- Stress-Free Math: A Visual Guide to Acing Math in Grades 4-9Da EverandStress-Free Math: A Visual Guide to Acing Math in Grades 4-9Nessuna valutazione finora
- Defender 90 110 Workshop Manual 5 WiringDocumento112 pagineDefender 90 110 Workshop Manual 5 WiringChris Woodhouse50% (2)
- Description MicroscopeDocumento4 pagineDescription MicroscopeRanma SaotomeNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Use Hyper-V Snapshot Revert, Apply, and Delete OptionsDocumento15 pagineHow To Use Hyper-V Snapshot Revert, Apply, and Delete OptionsKaran MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Picco Tac 1095 N Hydrocarbon ResinDocumento2 paginePicco Tac 1095 N Hydrocarbon ResindevanandamqaNessuna valutazione finora
- Predictive Analytics: QM901.1x Prof U Dinesh Kumar, IIMBDocumento36 paginePredictive Analytics: QM901.1x Prof U Dinesh Kumar, IIMBVenkata Nelluri PmpNessuna valutazione finora
- Anti-Anginal DrugsDocumento39 pagineAnti-Anginal Drugspoonam rana100% (1)
- Math 2 Curriculum GuideDocumento19 pagineMath 2 Curriculum GuideMichelle Villanueva Jalando-onNessuna valutazione finora
- BRKSPG-2904-2904 - Cisco Live Session - v2-CL PDFDocumento182 pagineBRKSPG-2904-2904 - Cisco Live Session - v2-CL PDFMohamed SamirNessuna valutazione finora
- PLC of MaggiDocumento19 paginePLC of Maggikrati agarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- The Power of Networking for Entrepreneurs and Founding TeamsDocumento28 pagineThe Power of Networking for Entrepreneurs and Founding TeamsAngela FigueroaNessuna valutazione finora
- RISO MZ Servicemanual EnglDocumento438 pagineRISO MZ Servicemanual Englkuvalda2000_8645336367% (3)
- Pump IntakeDocumento6 paginePump IntakeAnonymous CMS3dL1T100% (1)
- UntitledDocumento21 pagineUntitledRoberto RamosNessuna valutazione finora
- ECE 4400 Performance Analysis Local Computer Networks HomeworkDocumento2 pagineECE 4400 Performance Analysis Local Computer Networks HomeworkNguyen Phi HungNessuna valutazione finora
- New Microwave Lab ManualDocumento35 pagineNew Microwave Lab ManualRadhikaNessuna valutazione finora
- James and Robson 2014 UAVDocumento8 pagineJames and Robson 2014 UAVAdriRGNessuna valutazione finora
- 4900 DatasheetDocumento2 pagine4900 DatasheetMakam Raghu100% (1)
- EVS XT2+ Tech Ref Software Manual v10.03 PDFDocumento80 pagineEVS XT2+ Tech Ref Software Manual v10.03 PDFgibonulNessuna valutazione finora
- Komposit UHMWPE Sebagai Alternatif Bantalan Rel Kereta Api: Abel Evan, Alia Kristika, Farid Mulia LatiefDocumento11 pagineKomposit UHMWPE Sebagai Alternatif Bantalan Rel Kereta Api: Abel Evan, Alia Kristika, Farid Mulia LatiefAlia KristikaNessuna valutazione finora
- ZJJ 3Documento23 pagineZJJ 3jananiwimukthiNessuna valutazione finora
- OB HandoutsDocumento16 pagineOB HandoutsericNessuna valutazione finora
- Balajit Nath Pandita-Specific Principles of Kashmir Saivism-Munshiram Manoharlal Publishers (1998) PDFDocumento228 pagineBalajit Nath Pandita-Specific Principles of Kashmir Saivism-Munshiram Manoharlal Publishers (1998) PDFvramaniitkNessuna valutazione finora
- 8483724Documento24 pagine8483724ejkiranNessuna valutazione finora
- JC Metcalfe - The Power of WeaknessDocumento3 pagineJC Metcalfe - The Power of Weaknesschopin23Nessuna valutazione finora
- SBFP Timeline 2019Documento1 paginaSBFP Timeline 2019Marlon Berjolano Ere-erNessuna valutazione finora
- SID-2AF User Manual English V3.04Documento39 pagineSID-2AF User Manual English V3.04om_zahidNessuna valutazione finora
- DelhiDocumento40 pagineDelhiRahul DharNessuna valutazione finora
- Semi Detailed Lesson Plan ElementaryDocumento3 pagineSemi Detailed Lesson Plan ElementaryJinky JunioNessuna valutazione finora
- RFID Receiver Antenna Project For 13.56 MHZ BandDocumento5 pagineRFID Receiver Antenna Project For 13.56 MHZ BandJay KhandharNessuna valutazione finora
- Analogue Lab Manual AL7212 V2.1-Panduan Praktek DSR Elektronika-DikonversiDocumento235 pagineAnalogue Lab Manual AL7212 V2.1-Panduan Praktek DSR Elektronika-DikonversiAl-FarabiNessuna valutazione finora