Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Dna Summary Sheet
Caricato da
api-228041573Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Dna Summary Sheet
Caricato da
api-228041573Copyright:
Formati disponibili
DNA SUMMARY SHEET: #104
o DNA provides all of the genetic information for an organisms
characteristics and functioning.
o Since DNA cannot copy itself, RNA is necessary to copy the DNA to
proteins
o The sugar in DNA is deoxyribose
o The sugar in RNA is ribose
o DNA is a double helix RNA is a single helix
o The 3 components of DNA are phosphate, a deoxyribose sugar and a
nitrogenous base
o Each segment is called a nucleotide
o The 4 nitrogenous bases are Adenine Thymine , Guanine Cystosine
o In RNA, the Thymine is replaces with Uracil, so Adenine base pairs with Uracil
o The shape of the DNA molecule was discovered by Watson & Crick with the
help of Rosalind Franklin in 1959.
o It was this picture taken by chromatography by Rosalind Franklin that helped
solve the mystery of DNAs shape
o DNA must be transcribed to RNA to produce the proteins that direct the cells
functions
o This transcription occurs in the nucleus of each cell
o Translation from mRNA (messenger RNA-transferRNA) to proteins occurs in
the Ribosomes in the cells cytoplasm.
o Proteins are made up of amino acids
o The order of the amino acids determines the shape and type of protein
produced
o 20 amino acids create the 60 amino acids that make up all of the proteins in
our bodies
o The 3-base code for the proteins is called a codon
o There are 3 special codons that code for starting and stopping
translation
o Errors in the nitrogenous base sequence can cause mutations
o A single base error can cause the wrong protein to be produced
o This can cause serious health issues (i.e., sickle cell, hemophilia, breast
cancer, Tay Sachs, etc)
o Since each amino acid has multiple codons, sometimes, an error in the
nitrogenous base sequence still codes the correct amino acid
o DNA can be used to identify related species, family relationships because
the base sequences, and therefore amino acid sequences are more similar
between close relatives than distant strangers.
DNA BASE PAIRING
___________________________________
A C G T T C G AG
T G C A A G C TC
TRANSCRIPTION TO RNA:
A C G
Thr
U U C
/ Phe /
G A G
Glu
TRANSLATION TO AMINO ACIDS:
Acids
Transcription and Translation
DNA to RNA RNA to Amino
DNA Double Helix - Sugar/phosphate backbone
Nitrogenous bases paired in the middle
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- How Genes Work GENE - Biological Unit of HeredityDocumento5 pagineHow Genes Work GENE - Biological Unit of HeredityAdonis Besa100% (1)
- Unit 5 Dna: Discuss The Chemistry of The Genetic Information CarrierDocumento5 pagineUnit 5 Dna: Discuss The Chemistry of The Genetic Information CarrierMariz Althea Jem BrionesNessuna valutazione finora
- RNA and Protein SynthesisDocumento51 pagineRNA and Protein SynthesisCanonizado ShenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Dna Transparency TeacherDocumento12 pagineDna Transparency Teacherapi-445198464100% (1)
- I. DNA, Chromosomes, Chromatin, and GenesDocumento12 pagineI. DNA, Chromosomes, Chromatin, and GeneshanzNessuna valutazione finora
- 230 GeneticCodeRNAandProteinSynthesis PDFDocumento22 pagine230 GeneticCodeRNAandProteinSynthesis PDFSubhecchha BaidyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetics Auto Saved)Documento7 pagineGenetics Auto Saved)natseeaNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA StructureDocumento50 pagineDNA StructureAngelo LucindoNessuna valutazione finora
- Proteins 123Documento43 pagineProteins 123agnasvynlutaoNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA Rep and RNA StructureDocumento30 pagineDNA Rep and RNA Structurekoromamoses235Nessuna valutazione finora
- Medical Genetic II Dna RnaDocumento49 pagineMedical Genetic II Dna RnaHarry ManuhutuNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit C Chap 18 Cell DivisionDocumento9 pagineUnit C Chap 18 Cell DivisionJane XuNessuna valutazione finora
- Nucleic Acids Store, Transmit and Help Express Hereditary InformationDocumento6 pagineNucleic Acids Store, Transmit and Help Express Hereditary InformationDanielle GuerraNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein SynthesisDocumento6 pagineProtein SynthesisRashFlygon ZNessuna valutazione finora
- CH17Documento5 pagineCH17Raziya NgNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec 014 Gene To ProteinDocumento6 pagineLec 014 Gene To ProteinQusizleNessuna valutazione finora
- BCH 305 (Chemistry & Metabolism of Nucleic Acids)Documento30 pagineBCH 305 (Chemistry & Metabolism of Nucleic Acids)ihebunnaogochukwu24Nessuna valutazione finora
- Protein Synthesis and MutationsDocumento41 pagineProtein Synthesis and MutationsAdrian D. MasinadingNessuna valutazione finora
- Molecular Structure of DNA, RNA, and Proteins DNA Replication and Protein Synthesis (Cenabre, Fortun, Ibal)Documento2 pagineMolecular Structure of DNA, RNA, and Proteins DNA Replication and Protein Synthesis (Cenabre, Fortun, Ibal)Jessa Mae IbalNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA Notes PDFDocumento12 pagineDNA Notes PDFRamling PatrakarNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure of DNA Science Presentation in Light Blue Green Lined StyleDocumento44 pagineStructure of DNA Science Presentation in Light Blue Green Lined StyleGxmini playsNessuna valutazione finora
- 3rd Quarter W4 LECTURE On Protein Synthesis in DNA and MutationDocumento53 pagine3rd Quarter W4 LECTURE On Protein Synthesis in DNA and MutationMorante GeraldineNessuna valutazione finora
- Heredity - How A Protein Is Made Using DNA InformationDocumento45 pagineHeredity - How A Protein Is Made Using DNA Informationkath chandriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Differences Between DNA and RNADocumento6 pagineDifferences Between DNA and RNAGevo GegantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Rna PDFDocumento49 pagineRna PDFbangbro93_30900715Nessuna valutazione finora
- CH 13 RNA and Protein SynthesisDocumento12 pagineCH 13 RNA and Protein SynthesisHannah50% (2)
- Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis PDFDocumento55 pagineNucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis PDFAleine Leilanie Oro0% (1)
- Sean's DNA Review SheetDocumento6 pagineSean's DNA Review Sheetsean2013Nessuna valutazione finora
- DNA Replication and Protein SynthesisDocumento34 pagineDNA Replication and Protein SynthesisJessa Mae Infante PadillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio 102 Assign 5Documento4 pagineBio 102 Assign 5arica foxNessuna valutazione finora
- In-Depth Steps Towards Nucleic Acid and Protein SynthesisDocumento21 pagineIn-Depth Steps Towards Nucleic Acid and Protein SynthesisGbenga AjaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Nucleic AcidDocumento30 pagineNucleic AcidMerrylFranciscoNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA Replication and Protein SynthesisDocumento53 pagineDNA Replication and Protein SynthesisDeborah Chloe EnriquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Dna and Rna StructureDocumento26 pagineDna and Rna StructureVince Lenzer BeliganioNessuna valutazione finora
- Nucleotides, Nucleic Acids, and HeredityDocumento42 pagineNucleotides, Nucleic Acids, and HeredityLyssaMarieKathryneEgeNessuna valutazione finora
- The Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocumento28 pagineThe Central Dogma of Molecular BiologysannsannNessuna valutazione finora
- F1 - Genetic ControlDocumento91 pagineF1 - Genetic Controlchoon lee minNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Today and Tomorrow Without Physiology 5th Edition Starr Solutions Manual 1Documento14 pagineBiology Today and Tomorrow Without Physiology 5th Edition Starr Solutions Manual 1janesilvapwoikcfjgb100% (26)
- Biology Today and Tomorrow Without Physiology 5th Edition Starr Solutions Manual 1Documento10 pagineBiology Today and Tomorrow Without Physiology 5th Edition Starr Solutions Manual 1sook100% (33)
- Research Paper On Central DogmaDocumento4 pagineResearch Paper On Central Dogmaefjk5y50100% (1)
- Quarter 3-DNA SCIENCE 10Documento29 pagineQuarter 3-DNA SCIENCE 10Rubeliza LawengNessuna valutazione finora
- Nucleic Acid ChemistryDocumento47 pagineNucleic Acid Chemistryjohn2001royNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochemistry - Biosynthesis of Protein & Protein ChemistryDocumento113 pagineBiochemistry - Biosynthesis of Protein & Protein ChemistryAdella AnggrainiNessuna valutazione finora
- DR Linda Molecular BiosDocumento73 pagineDR Linda Molecular BiosValency BathoNessuna valutazione finora
- Basics of Molecular BiologyDocumento10 pagineBasics of Molecular BiologyOday MadiNessuna valutazione finora
- AG-DNA & RNA StructuresDocumento41 pagineAG-DNA & RNA StructuresMohan bhargavNessuna valutazione finora
- Nucleic Acid ProjectDocumento18 pagineNucleic Acid ProjectPramod Etarvi100% (7)
- Rotein Ynthesis: Big PictureDocumento3 pagineRotein Ynthesis: Big PicturehomamunfatNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 4 KKKDocumento32 pagineModule 4 KKKbhrayancachero100% (1)
- Dna, Rna and Protein SynthesisDocumento26 pagineDna, Rna and Protein SynthesisB R YNessuna valutazione finora
- Dna StructureDocumento42 pagineDna StructureCedric BaldozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Dianne D. Mariano BSN 101Documento9 pagineDianne D. Mariano BSN 101Dianne MarianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Science-10 Q3 Module-4 Week-5Documento5 pagineScience-10 Q3 Module-4 Week-5Marl Rina EsperanzaNessuna valutazione finora
- How Cells Work CompilationDocumento18 pagineHow Cells Work CompilationJocelyn Diaz AbangNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Genetic Inheritance LabDocumento5 pagineHuman Genetic Inheritance LabAntonov MikalisNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetic CodeDocumento3 pagineGenetic CodeAngelica PagaduanNessuna valutazione finora
- Sintesis Protein TA 2023-2024Documento111 pagineSintesis Protein TA 2023-2024fdla rhmahNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 1 - A1.2 Nucleic AcidsDocumento63 pagineTopic 1 - A1.2 Nucleic AcidsOlatundeNessuna valutazione finora
- Nucleic Acid and Protein Synthesis 2017-18Documento18 pagineNucleic Acid and Protein Synthesis 2017-18ADEEL AHMADNessuna valutazione finora
- EnzymesDocumento7 pagineEnzymesapi-228041573Nessuna valutazione finora
- Emerald Necklace MapDocumento1 paginaEmerald Necklace Mapapi-228041573Nessuna valutazione finora
- Respiratory Diagram CompletedDocumento2 pagineRespiratory Diagram Completedapi-228041573Nessuna valutazione finora
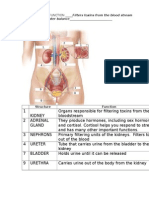
- Urinary Diagram CompletedDocumento1 paginaUrinary Diagram Completedapi-228041573Nessuna valutazione finora
- Circulatory System CompletedDocumento2 pagineCirculatory System Completedapi-228041573Nessuna valutazione finora
- GeneticsDocumento3 pagineGeneticsapi-228041573Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cells Summary SheetDocumento2 pagineCells Summary Sheetapi-228041573Nessuna valutazione finora
- Classification Cheat SheetDocumento2 pagineClassification Cheat Sheetapi-228041573Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biomolecules Review SheetDocumento2 pagineBiomolecules Review Sheetapi-228041573Nessuna valutazione finora
- All About CupcakesDocumento4 pagineAll About CupcakesRevtech RevalbosNessuna valutazione finora
- G 10 ICT WorkSheetc 2.2 English MDocumento8 pagineG 10 ICT WorkSheetc 2.2 English MMohamaad SihatthNessuna valutazione finora
- Tillotson HD & HR Service ManualDocumento11 pagineTillotson HD & HR Service ManualBeckyNessuna valutazione finora
- Allegheny Power Planning CriteriaDocumento19 pagineAllegheny Power Planning Criteriaksdp1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sri Vidya College of Engineering & Technology Virudhunagar: Department: Semester: Vi SUBJECT CODE / Name: CE 6602Documento34 pagineSri Vidya College of Engineering & Technology Virudhunagar: Department: Semester: Vi SUBJECT CODE / Name: CE 6602JEYA KUMARNessuna valutazione finora
- MantrasDocumento45 pagineMantrasharibhakta100% (1)
- Experiments: Mouthpiece, Which Is A Short Tube of Length About Equal To The Radius of The Orifice That Projects Into TheDocumento4 pagineExperiments: Mouthpiece, Which Is A Short Tube of Length About Equal To The Radius of The Orifice That Projects Into Thefrancis dimakilingNessuna valutazione finora
- At Home Activities Mathlink Cubes Big BuildersDocumento7 pagineAt Home Activities Mathlink Cubes Big BuildersdrchiNessuna valutazione finora
- Oscillations NotesDocumento48 pagineOscillations Notesabdulrehman881122Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ancient CivilizationsDocumento9 pagineAncient CivilizationsMarienne LaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Rider's Manual: BMW MotorradDocumento136 pagineRider's Manual: BMW MotorradAlex Quintana100% (1)
- Technical Datasheet: ENGUARD™ BP 75 ARF Multi Purpose Bonding Paste With FibresDocumento2 pagineTechnical Datasheet: ENGUARD™ BP 75 ARF Multi Purpose Bonding Paste With FibresFernando Cesar PérezNessuna valutazione finora
- Metal-Tek Electric Contact Cleaner Spray - TDS (2021)Documento1 paginaMetal-Tek Electric Contact Cleaner Spray - TDS (2021)metal-tek asteNessuna valutazione finora
- Volume 15, Number 2 February 2011Documento154 pagineVolume 15, Number 2 February 2011Nicolai BabaliciNessuna valutazione finora
- 4864.21 - Optics System 2Documento39 pagine4864.21 - Optics System 2Edgar Jose Aponte MartinezNessuna valutazione finora
- Airborne Doppler Radar Navigation of Jet Transport Aircraft-EftDocumento10 pagineAirborne Doppler Radar Navigation of Jet Transport Aircraft-Eftjulio perezNessuna valutazione finora
- Patel, Anita - Super Indian Snack and Street Food Recipes PDFDocumento117 paginePatel, Anita - Super Indian Snack and Street Food Recipes PDFBella ImèneNessuna valutazione finora
- Boiler Sizing Guide PDFDocumento1 paginaBoiler Sizing Guide PDFfmkhan21100% (1)
- English: Third Quarter - Module 3Documento12 pagineEnglish: Third Quarter - Module 3Anna Agravante-SulitNessuna valutazione finora
- Ao+ WDM12 R40DDocumento8 pagineAo+ WDM12 R40DPedro Igor Oliveira CarvalhoNessuna valutazione finora
- Design & Fabrication of Low Cost Small-Scale Fatigue Testing MachineDocumento12 pagineDesign & Fabrication of Low Cost Small-Scale Fatigue Testing MachinekshitijNessuna valutazione finora
- Festivals of IndiaDocumento51 pagineFestivals of IndiaDhatchayani RamkumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Systems of Linear Equations With Two VariablesDocumento34 pagineSystems of Linear Equations With Two VariablesFatima KausarNessuna valutazione finora
- Marine Upholstery SpecsDocumento1 paginaMarine Upholstery SpecsRezza KurniawanNessuna valutazione finora
- HP 300s+ Scientific Calculator: Sophisticated Design Ideal For Math and Science StudentsDocumento3 pagineHP 300s+ Scientific Calculator: Sophisticated Design Ideal For Math and Science StudentsgemaNessuna valutazione finora
- What Makes A Cup of NESCAFÉ So Special? The Best Coffee Beans andDocumento4 pagineWhat Makes A Cup of NESCAFÉ So Special? The Best Coffee Beans andYenny YanyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Colegio de San Gabriel Arcangel of Caloocan, IncDocumento7 pagineColegio de San Gabriel Arcangel of Caloocan, IncKIRITO SALINASNessuna valutazione finora
- Textile and ClothingDocumento12 pagineTextile and ClothingAstra CloeNessuna valutazione finora
- Pediatric Airway ManagementDocumento2 paginePediatric Airway ManagementSilvy AmaliaNessuna valutazione finora