Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Tissues Organizer With Blanks
Caricato da
api-2422214860 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
54 visualizzazioni5 pagineTitolo originale
tissues organizer with blanks
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
54 visualizzazioni5 pagineTissues Organizer With Blanks
Caricato da
api-242221486Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 5
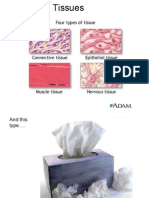
Tissues- groups of similar cells with the
same ___________and ___________
Epithelial
Found in:
Body ___________________________
Body____________________________
_________________________ular tissue
Functions:
Protection
Absorption
Filtration
Secretion
Cells fit closely together
Tissue layer always has one ______________
The lower surface is bound by a
__________________________membrane (at
attached surface)
Avascular (have ___________________supply)
____________________easily if well nourished
Simple ________________ layer
Stratified ______________ than one layer
Squamous flattened
Cuboidal cube-shaped
Columnar column-like
Connective
Found everywhere in the body
Includes the most abundant and widely
distributed tissues
Functions:
__________________ body tissues together
__________________________ the body
Provides __________________________
Variations in blood supply
Some tissue types are well vascularized
Some have poor blood supply or are avascular
Extracellular _____________________
__________________________ substance
mostly water along with adhesion proteins and
polysaccharide molecules
____________________________:
Produced by the cells
Three types:
Collagen fibers
Elastic fibers
Reticular fibers
Non-living material that surrounds living cells
Muscular
Function is to
produce
movement
____________
Three types:
Skeletal muscle
Cardiac muscle
Smooth muscle
Do not
regenerate well
Good blood
supply
Nervous
Neurons and
nerve support
cells
Function is to
send impulses to
other areas of the
body
______________
______________
Do not regenerate
well
Good blood
supply
Epithelial- one free, one attached surface, avascular
Simple-one cell layer
Stratified-more than one cell layer
Squamous
Single layer
of ________
cells
Usually
forms
membranes
Lines body
cavities-
secretion of
lubricants
Lines lungs
and
capillaries-
diffusion and
filtration
Cuboidal
Single layer
of _______-
like cells
Common in
glands and
their ducts
Forms walls
of kidney
tubules
Covers the
ovaries
Secretion
and
absorption
Columnar
Single layer of
_______ cells
Often includes
goblet cells,
which produce
mucus
Lines digestive
tract, uterine
tubes and
some parts of
uterus
May have cilia
or microvilli
Secretion,
absorption
Pseudostratified
Single layer,
but some cells
are shorter than
others
Often looks like
a double cell
layer
Sometimes
ciliated, such
as in the upper
respiratory tract
May have
goblet cells
May function in
absorption or
secretion
Cuboidal
Two layers
of cuboidal
cells
Rare in
human body
Found
mainly in
_________o
f large
glands
(mammary
glands)
Protection,
secretion
Columnar
Surface cells
are columnar,
cells
underneath
vary in size
and shape
Rare in
human body
Found mainly
in _______of
large glands
(urethra)
Protection,
secretion
Transitional
Shape of
cells
depends
upon the
amount of
________
Lines
organs of
the urinary
system
Stretching
to distend
areas with
urine
Squamous
Cells at the free
edge are
_____________,
those towards
the basement
membrane are
more cuboidal
Found as a
protective
covering where
friction is
common
Outer layer of
skin, mouth,
esophagus,
vagina
Highly
regenerative-
protection
Connective- matrix
Dense
fibrous
Fibers __________
packed
Main matrix element
is collagen fibers
Cells are fibroblasts
_____________
attach muscle to
bone
______________
attach bone to bone
Loose fibrous- fibers not tightly packed Blood
Blood cells surrounded
by fluid matrix
(_________________)
Contains red blood
cells, white blood cells,
and platelets (cell
fragments)
Fibers are visible
during clotting
Functions as the
transport vehicle for
materials
Contained inside blood
vessels
Areolar
Most widely
distributed
connective tissue
Soft, pliable tissue
Contains all fiber
types
Fibers
___________
packed
Can soak up
excess fluid
Cushion
Adipose
Matrix is an areolar
tissue in
which_____________
globules predominate
Many cells contain
large lipid deposits,
Nuclei of cells pushed
off to the side by fat
vacuole
_________________
the body
_________________
some organs, Fuel
storage,
Around kidneys and
eyeballs, in abdomen and
breasts
Reticular
Delicate network of
interwoven fibers
(treelike reticular
fibers that trap
cells)
Forms stroma
(internal
supporting
network) of
_______________
organs such as:
Lymph nodes
Spleen
Bone marrow
Connective(cont)
Bone
Bone cells in _____________
(cavities)
Hard matrix of calcium salts
(lamella) in a circular pattern
around a central Haversian
Canal
Large numbers of
__________________fibers
Used to _______________and
____________________the
body
Skeleton
Cartilage- semi-solid matrix
Hyaline
Most common cartilage
Composed of:
Abundant collagen fibers
_______________ matrix
Chondrocytes- cartilage
cells
Fibers not really visible-
appears ______________
Entire fetal skeleton is
hyaline cartilage
At ends of bones, rings of
trachea, larynx, where ribs
attach to sternum
Elastic
Provides __________
Contains visible elastic
fibers
Chondrocytes-
cartilage cells
Example: supports the
external ear, tip of the
nose
Fibrocartilage
Highly compressible-
absorbs ___________
Chondrocytes-
cartilage cells
Visible parallel fibers
Example: forms
cushion-like discs
between vertebrae, in
meniscus of knee, in
pubic symphysis
Muscle- contractile tissue Nervous- irritable, conductive
Skeletal
Can be controlled
_______________
Cells attach to
connective tissue
Cells are striated
Cells have more than
one nucleus
Cells are long fibers,
usually parallel to one
another
For locomotion of the
body
Attached to________
or skin
Cardiac
Found only in the
________________
Function is to pump
blood (involuntary)
Cells attached to
other cardiac muscle
cells at intercalated
disks
Cells are striated
One nucleus per cell
(most of time)
Branched fibers
Smooth
_________________
muscle
Surrounds hollow
_________________
(digestive, bladder)
Attached to other
smooth muscle cells
No visible striations
One nucleus per cell
Cells are spindle
shaped- wider in the
middle and narrower
at the ends
Neuron
Function is to send
__________________
to other areas of the
body
Irritability
Conductivity
Long projections come
from a cell body
Found in brain, spinal
cord, and nerves
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Game Rules PDFDocumento12 pagineGame Rules PDFEric WaddellNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissue Anatomy and Physiology: The Four Main Tissue TypesDocumento35 pagineTissue Anatomy and Physiology: The Four Main Tissue Typessnp88100% (1)
- Photographing Shadow and Light by Joey L. - ExcerptDocumento9 paginePhotographing Shadow and Light by Joey L. - ExcerptCrown Publishing Group75% (4)
- Yy Yyy Y Yy Y YYYDocumento64 pagineYy Yyy Y Yy Y YYYsreedam100% (1)
- Anatomy - TissuesDocumento43 pagineAnatomy - TissuesGleceree Filomeno100% (1)
- Interpretation of Arterial Blood Gases (ABGs)Documento6 pagineInterpretation of Arterial Blood Gases (ABGs)afalfitraNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissues: Types, Functions & ClassificationDocumento18 pagineTissues: Types, Functions & ClassificationZainab AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissue Structure & FunctionDocumento74 pagineTissue Structure & FunctionTaufiqurrahman Sidqi100% (1)
- Oracle Learning ManagementDocumento168 pagineOracle Learning ManagementAbhishek Singh TomarNessuna valutazione finora
- Connective Tissue TypesDocumento34 pagineConnective Tissue TypesLizette Joy Cuilan-CamiloNessuna valutazione finora
- Structures and Functions of Animal Tissues and Cell ModificationDocumento105 pagineStructures and Functions of Animal Tissues and Cell ModificationArvie Jay Castillo100% (1)
- Animal Tissue: Chapter - 10 Std. XIDocumento110 pagineAnimal Tissue: Chapter - 10 Std. XIYash Soneji100% (2)
- SCA ALKO Case Study ReportDocumento4 pagineSCA ALKO Case Study ReportRavidas KRNessuna valutazione finora
- TissuesDocumento91 pagineTissuesSon Ezekiel Gabriel I. BenitezNessuna valutazione finora
- S5-42 DatasheetDocumento2 pagineS5-42 Datasheetchillin_in_bots100% (1)
- Plant and Animal Organ Systems FunctionsDocumento18 paginePlant and Animal Organ Systems FunctionsHannah CastroNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal Tissues: Types, Structure & FunctionsDocumento6 pagineAnimal Tissues: Types, Structure & FunctionsbasheerskNessuna valutazione finora
- Anat Ch5 OutlineDocumento4 pagineAnat Ch5 OutlinemindythompsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 5 - Body TissuesDocumento10 pagineModule 5 - Body Tissues10. Briol AlvinNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Types of Connective Tissue and Their FunctionsDocumento4 pagine4 Types of Connective Tissue and Their FunctionsJoanne GodezanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Body Tissues Power PointDocumento60 pagineHuman Body Tissues Power PointMaxwell C Jay KafwaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Histology Notes: Epithelial TissueDocumento4 pagineHistology Notes: Epithelial TissueSteph AsideNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 5 Tissues, Cell CyclesDocumento90 pagineLecture 5 Tissues, Cell Cyclesaidar.seralinNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 7 Biology Crosswords and Basic Biology FactsDocumento10 pagineGrade 7 Biology Crosswords and Basic Biology FactsMelanie AbaldeNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7 Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocumento25 pagineChapter 7 Structural Organisation in Animalsamit lakraNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 Tissues, Glands, Membranes OverviewDocumento3 pagineChapter 4 Tissues, Glands, Membranes OverviewKate MontenegroNessuna valutazione finora
- The Fascinating World of TissuesDocumento68 pagineThe Fascinating World of TissuesO.r. Cadz100% (1)
- Body TissuesDocumento10 pagineBody TissuesNaanmatha PuspanathanNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissue and HistologyDocumento28 pagineTissue and HistologymagdangalmaryfrancessNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissue Membranes GuideDocumento4 pagineTissue Membranes GuideElleNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal TissuesDocumento15 pagineAnimal TissuesLitaMeilinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Animaltissues 180604115637Documento40 pagineAnimaltissues 180604115637proud.student2023Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tissues (Notes)Documento11 pagineTissues (Notes)Rezeil CaNessuna valutazione finora
- General Biology IIDocumento6 pagineGeneral Biology IIFrederick SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Connective TissueDocumento21 pagineConnective TissueCalvin Lin Jia RongNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1-A5-Discussion On Body TissuesDocumento6 pagineModule 1-A5-Discussion On Body TissuesWilliam DC RiveraNessuna valutazione finora
- Connective Tissue - LabDocumento53 pagineConnective Tissue - LabArnold ArzobalNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal Tissues Levels of Organization: TissueDocumento15 pagineAnimal Tissues Levels of Organization: TissueDiane Fontanilla100% (1)
- Tissues 2Documento48 pagineTissues 2chikwatumilessNessuna valutazione finora
- Body Tissues: Tissue Matrix MuscleDocumento8 pagineBody Tissues: Tissue Matrix Muscle9. Hoàng Mai ChiNessuna valutazione finora
- tISSUE 11 PDFDocumento6 paginetISSUE 11 PDFJasselle OcbaNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal TissuesDocumento11 pagineAnimal TissuesEduard LaudeNessuna valutazione finora
- General-Biology-module-1-2Documento12 pagineGeneral-Biology-module-1-2cabellaNessuna valutazione finora
- L.5 Cell PartsDocumento2 pagineL.5 Cell PartsColtonNessuna valutazione finora
- CTDocumento84 pagineCTNigusu SolomonNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissues, Integumentary System and Bone TissueDocumento12 pagineTissues, Integumentary System and Bone TissueChristine BalanzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissues (Anatomy 1)Documento83 pagineTissues (Anatomy 1)nanakwame5769Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tissues, Organs and Organ SystemsDocumento17 pagineTissues, Organs and Organ SystemsDestinee Sullivan100% (1)
- Types of Tissues and Their FunctionsDocumento39 pagineTypes of Tissues and Their FunctionsSnehasish DebnathNessuna valutazione finora
- Epithelial Tissue Functions and ClassificationDocumento10 pagineEpithelial Tissue Functions and ClassificationMichael NyaongoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Four Primary Tissue Types:: Epithelial (Covering) Connective Tissue (Support) Muscle (Movement) Nervous (Control)Documento33 pagineThe Four Primary Tissue Types:: Epithelial (Covering) Connective Tissue (Support) Muscle (Movement) Nervous (Control)Maira Garcia C.100% (2)
- Tissue (Notes) (1) 6roDocumento4 pagineTissue (Notes) (1) 6romljnura3Nessuna valutazione finora
- HISTOLOGY Is The Study of Tissues.: 4 MAJOR TISSUE TYPES: Epithelial (Covering)Documento5 pagineHISTOLOGY Is The Study of Tissues.: 4 MAJOR TISSUE TYPES: Epithelial (Covering)Katie RodriguezNessuna valutazione finora
- Epithelial TissueDocumento57 pagineEpithelial TissuePreet Kaur100% (1)
- Connective TissueDocumento49 pagineConnective TissuePaapa MorrisNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 05 TissuesDocumento50 pagineCH 05 TissuesAlina Ghe100% (1)
- Epithel Connective TissuesDocumento47 pagineEpithel Connective TissuesAnonymous nErkwtXnuS100% (1)
- Epithelium and Connective TissueDocumento32 pagineEpithelium and Connective Tissueyusufgarba2002Nessuna valutazione finora
- Animal Tissues: Structures and Functions in 40 CharactersDocumento41 pagineAnimal Tissues: Structures and Functions in 40 Charactersenkidani100% (1)
- M 1 PPT-PDF XI Bio CH 7 Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocumento39 pagineM 1 PPT-PDF XI Bio CH 7 Structural Organisation in Animalsamarendrar87Nessuna valutazione finora
- Plant Tissue TypesDocumento6 paginePlant Tissue TypesBhoomika GoyalNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch. 3 Notes - Epitheal TissuesDocumento22 pagineCh. 3 Notes - Epitheal TissuesLinda Yurani Carvajal AngaritaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology 112: Chapter 5: TissuesDocumento5 pagineBiology 112: Chapter 5: TissuesSwetha GowthamNessuna valutazione finora
- Skeletal System: The Dog Stole the Professor's NotesDa EverandSkeletal System: The Dog Stole the Professor's NotesNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissues Study GuideDocumento7 pagineTissues Study Guideapi-242221486Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit Plan For Ap 10 Day Teaching ClinicalDocumento29 pagineUnit Plan For Ap 10 Day Teaching Clinicalapi-242221486Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tissue Bingo KeyyDocumento7 pagineTissue Bingo Keyyapi-242221486Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ethical Use StatementDocumento1 paginaEthical Use Statementapi-242221486Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dana Page CVDocumento2 pagineDana Page CVapi-242221486Nessuna valutazione finora
- Zelev 1Documento2 pagineZelev 1evansparrowNessuna valutazione finora
- Sewage Pumping StationDocumento35 pagineSewage Pumping StationOrchie DavidNessuna valutazione finora
- Guiding Childrens Social Development and Learning 8th Edition Kostelnik Test BankDocumento16 pagineGuiding Childrens Social Development and Learning 8th Edition Kostelnik Test Bankoglepogy5kobgk100% (27)
- 20 Ua412s en 2.0 V1.16 EagDocumento122 pagine20 Ua412s en 2.0 V1.16 Eagxie samNessuna valutazione finora
- Brick TiesDocumento15 pagineBrick TiesengrfarhanAAANessuna valutazione finora
- Catalogoclevite PDFDocumento6 pagineCatalogoclevite PDFDomingo YañezNessuna valutazione finora
- #### # ## E232 0010 Qba - 0Documento9 pagine#### # ## E232 0010 Qba - 0MARCONessuna valutazione finora
- Mission Ac Saad Test - 01 QP FinalDocumento12 pagineMission Ac Saad Test - 01 QP FinalarunNessuna valutazione finora
- 5511Documento29 pagine5511Ckaal74Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sharp Ar5731 BrochureDocumento4 pagineSharp Ar5731 Brochureanakraja11Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dole-Oshc Tower Crane Inspection ReportDocumento6 pagineDole-Oshc Tower Crane Inspection ReportDaryl HernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Katie Tiller ResumeDocumento4 pagineKatie Tiller Resumeapi-439032471Nessuna valutazione finora
- Manual Analizador Fluoruro HachDocumento92 pagineManual Analizador Fluoruro HachAitor de IsusiNessuna valutazione finora
- Pita Cyrel R. Activity 7Documento5 paginePita Cyrel R. Activity 7Lucky Lynn AbreraNessuna valutazione finora
- GMWIN SoftwareDocumento1 paginaGMWIN SoftwareĐào Đình NamNessuna valutazione finora
- CIT 3150 Computer Systems ArchitectureDocumento3 pagineCIT 3150 Computer Systems ArchitectureMatheen TabidNessuna valutazione finora
- Inorganica Chimica Acta: Research PaperDocumento14 pagineInorganica Chimica Acta: Research PaperRuan ReisNessuna valutazione finora
- BIBLIO Eric SwyngedowDocumento34 pagineBIBLIO Eric Swyngedowadriank1975291Nessuna valutazione finora
- John Hay People's Alternative Coalition Vs Lim - 119775 - October 24, 2003 - JDocumento12 pagineJohn Hay People's Alternative Coalition Vs Lim - 119775 - October 24, 2003 - JFrances Ann TevesNessuna valutazione finora
- Energy AnalysisDocumento30 pagineEnergy Analysisca275000Nessuna valutazione finora
- DC Motor Dynamics Data Acquisition, Parameters Estimation and Implementation of Cascade ControlDocumento5 pagineDC Motor Dynamics Data Acquisition, Parameters Estimation and Implementation of Cascade ControlAlisson Magalhães Silva MagalhãesNessuna valutazione finora
- Malware Reverse Engineering Part 1 Static AnalysisDocumento27 pagineMalware Reverse Engineering Part 1 Static AnalysisBik AshNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem 102 Week 5Documento65 pagineChem 102 Week 5CAILA CACHERONessuna valutazione finora
- LM1011 Global ReverseLogDocumento4 pagineLM1011 Global ReverseLogJustinus HerdianNessuna valutazione finora