Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Government Structure Powerpoint
Caricato da
api-247406019Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Government Structure Powerpoint
Caricato da
api-247406019Copyright:
Formati disponibili
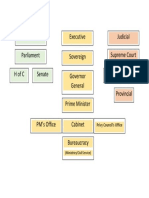
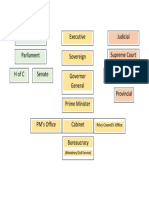
Government Structure
Legislative Branch
Parliament
Parliament = House of
Commons + Senate
House of Commons
Replica of British House of Commons
Contains 308 elected politicians (one from every riding
in Canada)
House of Commons
House of Commons
A fundamental distinction between MPs in the House is
whether they are members of the governing party or
one of the opposition parties
The largest of the opposition parties, currently the NDP,
are called the Official Opposition
Within the House of Commons there is also someone
deemed the Speaker.
This is essentially the individual who is responsible for
ensuring the MPs follow the rules when they are
questioning and debating within the House of
Commons (regular MP elected by the House)
House of Commons
In theory, it is the entire House of Commons who must
hold the executive accountable
This is done by supporting or withholding support on
votes with respect to major policy issues
Day to day, it is the job of these Members of Parliament
(MPs) to debate the bills proposed by the cabinet and
vote yes or no
Members of Parliament
Why is Party Solidarity so strong?
- 1. Responsible Government
- 2. Shared Ideologies
- 3. Generally agree with leader
- 4. Prospects of promotion
- 5. Prospects of other perks
- 6. Job security
Members of Parliament
QUESTION: If honest and meaningful
debate is not really the role of the House of
Commons in contemporary Canadian
politics, what is its role?
The Primary Purpose of the modern
parliament is to make the cabinet
accountable for its actions to the public
Members of Parliament
Holding the government to Account:
Question Period:
A daily 45-minute period in which the
opposition is allowed to ask questions of the
cabinet ministers and the Prime Minister and
they must provide an answer
Backbenchers
Definition: Since the front benches are reserved
for Cabinet members the other MPs are
considered the backbenchers. Their job is to vote
when and how their leaders tell them to.
Ways for Backbenchers to influence Parliament:
1.Membership on legislative Committees
2. Weekly Caucus Meeting
3. Private Members Bill
The Legitimation Phase
Defining Government:
A complex web of independent but inter-related
institutions:
The Crown
The Prime Minister
The Cabinet
The Civil Service
The Formal Executive
Canada is a Constitutional Monarchy:
Authority of the state is embodied in the British
Monarch, the King or Queen of Britain, who is also the
King or Queen of Canada
However, the power of the Crown is restrained by the
Constitution
The Queens Representative in Canada:
The Governor General: David Johnston
Two Central Roles:
1. Head of State:
Ceremonial
2. Guardian of Responsible Government
Ensuring the Executive Branch maintains confidence of
Legislative Branch
Three Reserve Powers:
1. Power to Appoint the Prime Minister
Selecting the person most likely to attain
confidence of the House of Commons
Election Results
- Conservative leader is current PM
Liberals: 78
Conservatives: 78
NDP: 78
Bloc: 74
Confidence requires support of 155 MPs
Who becomes Prime Minister?
Three Reserve Powers:
1. Power to Appoint the Prime Minister
Selecting the person most likely to attain confidence of
the House of Commons
GG would use his or her discretion
This is a substantial bit of political power
Three Reserve Powers:
2. The Power to dismiss a Prime Minister who attempts
to govern without the confidence of the House of
Commons
Three Reserve Powers:
3. The power to dissolve parliament and call an election
Govenor General will generally heed the advice of the
PMbut not always
The Political Executive
Centre of the policy-making process
In reality, it is the Cabinet that exercises executive
power
It also largely controls the legislative process
Fusion of Powers
In theory, this body is comprised on Members of
Parliament appointed by Governor General
In practice, these choices are made by the Prime
Minister
Prime Minister determines the size of cabinet
Generally between 25 and 40 members
Currently there are 37 members
To be appointed to Cabinet is basically the central goal
of all federal politicians
Responsibilities:
Every member is put in charge of a particular ministry
or department
The member becomes the top politician responsible for
public policy in his or her particular department or
jurisdiction
Prime or First minister is first minister of cabinet
Prime Ministers Power:
1. Advise the Governor General on the make-up of
cabinet
Control over character of Cabinet
Control over his or her Party
Prime Ministers Power:
2. Chair of Cabinet
Can essentially guide Cabinet decision-making
Central Agenda Setter in Canadian Politics
Prime Ministers Power:
3. Power to advise the Governor General with respect
to dissolution of parliament and holding of elections
Significant Partisan Advantage over other Parties
Prime Ministers Power:
4. Power to appoint top bureaucrats, judges, senators,
and even the Governor General
5. Canadas Chief Diplomat
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (890)
- Fast Cash LoansDocumento4 pagineFast Cash LoansFletcher GorisNessuna valutazione finora
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- Barangay Tax Code Sample PDFDocumento14 pagineBarangay Tax Code Sample PDFSusan Carbajal100% (2)
- Nelson Mandela's Leadership and Anti-Apartheid StruggleDocumento34 pagineNelson Mandela's Leadership and Anti-Apartheid StruggleAmmara Khalid100% (1)
- DGF - (S) Epiroc Rock Drills Ab Dc1 (C) Epiroc Argentina S.A. - v435551 - Commercial InvoiceDocumento18 pagineDGF - (S) Epiroc Rock Drills Ab Dc1 (C) Epiroc Argentina S.A. - v435551 - Commercial InvoiceElvio MNessuna valutazione finora
- Counter-Affidavit Denies Charges of Coercion and ThreatsDocumento3 pagineCounter-Affidavit Denies Charges of Coercion and ThreatsRio LorraineNessuna valutazione finora
- CoTeSCUP Vs Secretary of EducationDocumento12 pagineCoTeSCUP Vs Secretary of EducationsundaeicecreamNessuna valutazione finora
- Day 1 Photography Scavenger Hunt 1Documento1 paginaDay 1 Photography Scavenger Hunt 1api-247406019Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Shot Skills 1Documento28 pagine1 Shot Skills 1api-247406019Nessuna valutazione finora
- TV Poster Photoshop SkillsDocumento1 paginaTV Poster Photoshop Skillsapi-247406019Nessuna valutazione finora
- Media Arts Course OutlineDocumento1 paginaMedia Arts Course Outlineapi-247406019Nessuna valutazione finora
- 7 Shots Assignment Rubric 1Documento1 pagina7 Shots Assignment Rubric 1api-247406019Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1920s Student Study GuideDocumento2 pagine1920s Student Study Guideapi-247406019Nessuna valutazione finora
- Extra Features AssignmentDocumento1 paginaExtra Features Assignmentapi-247406019Nessuna valutazione finora
- Autodesk Fusion 360 3d Printing Unit RubricsDocumento1 paginaAutodesk Fusion 360 3d Printing Unit Rubricsapi-247406019Nessuna valutazione finora
- Socials 10 Government Structure PowerpointDocumento31 pagineSocials 10 Government Structure Powerpointapi-247406019Nessuna valutazione finora
- Plug It in Plug It in Inspirational AssignmentDocumento1 paginaPlug It in Plug It in Inspirational Assignmentapi-247406019Nessuna valutazione finora
- Video Notes 1920sDocumento2 pagineVideo Notes 1920sapi-247406019Nessuna valutazione finora
- Inspirational Mug AssignmentDocumento2 pagineInspirational Mug Assignmentapi-247406019Nessuna valutazione finora
- Analyzing CreditDocumento3 pagineAnalyzing Creditapi-247406019Nessuna valutazione finora
- Events That Took Place From 1915Documento3 pagineEvents That Took Place From 1915api-247406019Nessuna valutazione finora
- Filing Income Tax Tips To Help You Understand Things BetterDocumento2 pagineFiling Income Tax Tips To Help You Understand Things Betterapi-247406019Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1920s Lets Talk About MoneyDocumento2 pagine1920s Lets Talk About Moneyapi-247406019Nessuna valutazione finora
- Federal Govt StructureDocumento1 paginaFederal Govt Structureapi-247406019Nessuna valutazione finora
- Income Tax Reflection WorksheetDocumento1 paginaIncome Tax Reflection Worksheetapi-247406019Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Causes of WwiDocumento3 pagineThe Causes of Wwiapi-247406019Nessuna valutazione finora
- Wwi Video NotesDocumento4 pagineWwi Video Notesapi-247406019Nessuna valutazione finora
- Beginning of The War WorksheetDocumento4 pagineBeginning of The War Worksheetapi-247406019Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Canadian Senate Worksheet 1Documento1 paginaThe Canadian Senate Worksheet 1api-247406019Nessuna valutazione finora
- Absolute Monarchy To Constitutional Monarchy Flow Chart 1Documento2 pagineAbsolute Monarchy To Constitutional Monarchy Flow Chart 1api-247406019Nessuna valutazione finora
- Trench Gas WarfareDocumento2 pagineTrench Gas Warfareapi-247406019Nessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Democracy Movie AssignmentDocumento1 paginaWhat Is Democracy Movie Assignmentapi-247406019Nessuna valutazione finora
- Elections Worksheet 1Documento2 pagineElections Worksheet 1api-247406019Nessuna valutazione finora
- Elections Worksheet 2Documento2 pagineElections Worksheet 2api-247406019Nessuna valutazione finora
- Social Studies 10 Course Outline 2021-22Documento2 pagineSocial Studies 10 Course Outline 2021-22api-247406019Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cwlit10 Course OutlineDocumento1 paginaCwlit10 Course Outlineapi-247406019Nessuna valutazione finora
- Federal Govt StructureDocumento1 paginaFederal Govt Structureapi-247406019Nessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of Cost Accounting 16th Edition Vanderbeck Solution ManualDocumento47 paginePrinciples of Cost Accounting 16th Edition Vanderbeck Solution Manualcorey100% (30)
- RemLaw Transcript - Justice Laguilles Pt. 2Documento25 pagineRemLaw Transcript - Justice Laguilles Pt. 2Mark MagnoNessuna valutazione finora
- Tally TestDocumento6 pagineTally TestRia MakkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Chinese in The PHDocumento15 pagineChinese in The PHMandalihan GepersonNessuna valutazione finora
- Kotak Mahindra Bank Limited FY 2020 21Documento148 pagineKotak Mahindra Bank Limited FY 2020 21Harshvardhan PatilNessuna valutazione finora
- G.R. No. 173227Documento6 pagineG.R. No. 173227Maria Lourdes Nacorda GelicameNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 04Documento14 pagineLecture 04Parvaiz Ali Naat OfficialNessuna valutazione finora
- Performance Evaluation and Ratio Analysis of Apple IncDocumento18 paginePerformance Evaluation and Ratio Analysis of Apple IncSayed Abu SufyanNessuna valutazione finora
- LG Eva MSDSDocumento8 pagineLG Eva MSDSpbNessuna valutazione finora
- Elements Air France Vs CarascosoDocumento10 pagineElements Air France Vs Carascosomaria lourdes lopenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Disclosure To Promote The Right To Information: IS 5290 (1993) : Specification For Landing Valves (CED 22: Fire Fighting)Documento20 pagineDisclosure To Promote The Right To Information: IS 5290 (1993) : Specification For Landing Valves (CED 22: Fire Fighting)Tanmoy Dutta100% (1)
- Tenancy Request FormDocumento2 pagineTenancy Request Formofficebackup allmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Chiavi Quaderno Degli EserciziDocumento2 pagineChiavi Quaderno Degli EsercizimoisesNessuna valutazione finora
- Recognition and Moral Obligation (Makale, Honneth)Documento21 pagineRecognition and Moral Obligation (Makale, Honneth)Berk Özcangiller100% (1)
- Aarti Brochure 2009Documento4 pagineAarti Brochure 2009Sabari MarketingNessuna valutazione finora
- E-Ticket: Travel InformationDocumento2 pagineE-Ticket: Travel InformationAli BajwaNessuna valutazione finora
- Inventory Transactions in OracleDocumento3 pagineInventory Transactions in OracleSiddiqa AyeshaNessuna valutazione finora
- Indian Ethos & Business Ethics End Term PaperDocumento12 pagineIndian Ethos & Business Ethics End Term Paperkuntal bajpayeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Rosit vs. Davao DoctorsDocumento12 pagineRosit vs. Davao DoctorsWilfredNessuna valutazione finora
- Barry Keen Micra InterviewDocumento304 pagineBarry Keen Micra Interviewjuly1962Nessuna valutazione finora
- Jagna Municipal Development Council Meeting MinutesDocumento3 pagineJagna Municipal Development Council Meeting MinutesAubrey Marie VillamorNessuna valutazione finora
- NCLAT OrderDocumento32 pagineNCLAT OrderShiva Rama Krishna BeharaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ajay LaishettyDocumento2 pagineAjay LaishettyTimothy BrownNessuna valutazione finora
- ORDINANCE 2011-732: Code Providing For AnDocumento89 pagineORDINANCE 2011-732: Code Providing For AnThe Florida Times-UnionNessuna valutazione finora