Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Enzymes and Chemical Reactions
Caricato da
api-261905259Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Enzymes and Chemical Reactions
Caricato da
api-261905259Copyright:
Formati disponibili
Chemical Reactions
and
Enzymes
Chemical Reactions
A process that changes one set of
chemicals into another set of chemicals
Your Turn!
Determine the difference between
reactants and products
Reactants Product
Chemical Reactions
REACTANTS
The elements or compounds that enter into a
chemical reaction
PRODUCTS
The elements or compounds produced by a
chemical reaction
ALWAYS involve the breaking of bonds in
reactants and the formation of new bonds
in products
Chemical Reactions:
CO
2
+ H
2
0 H
2
CO
3
H
2
CO
3
CO
2
+ H
2
O
Reactant(s) Product(s)
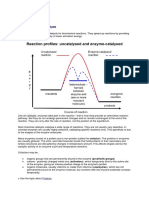
Energy in Reactions
In order to stay alive, organisms need to
carry out reactions that require energy.
Energy in Reactions
Activation Energy
The energy that is needed to get a reaction
started
Determines whether the overall chemical
reaction releases energy or absorbs energy
Your Turn!
Looking at the graph, explain what an
enzyme does to activation energy
Enzyme Reactions
Enzymes lower the activation energy!
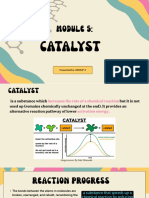
What is a catalyst?
Catalysts are substances that speed up
the rate of a chemical reaction.
Catalysts lower a reactions activation
energy.
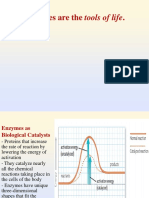
What is an enzyme?
proteins that act as biological catalysts.
allow essential chemical reactions that are
otherwise too slow to occur
very specific, generally catalyzing only one
chemical reaction
How do enzyme reactions work?
Enzymes provide a site where reactants
can be brought together to react.
Enzyme reactions depend on a physical
AND chemical fit between the enzyme
molecule and its substrate(s).
Whats a substrate???
A substrate is the reactant(s).
Your Turn!
Explain why enzyme reactions are often
referred to as lock and key models
An Enzyme-Substrate Reaction is
like a
Lock-and-Key Model
Substrate
ENZYME
Enzymes in Action
Substrate(s)
Enzyme
Active Site = the site on
the enzyme where
the substrate binds with the
enzyme
Enzyme-Substrate
Complex = when the
enzyme and substrate(s) are
bonded together for the
reaction to occur
The bonds in the
substrate are
weakened and
converted into
Product(s)
Enzyme
1.
2.
3.
Enzymes in Action
At the end of the reaction, the products are
released and the enzyme is free to start
the process again.
The enzyme is not changed in the
reaction.
What can denature an enzyme?
Define the term denature.
Denature means to change the shape of the
enzyme so that the reaction cannot occur.
What can cause an enzyme to denature?
High Temperature
pH
the addition of an alcohol
Your Turn!
Explain what effect temperature and pH
have on enzymes
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- 1FFF11B1BD16627EE05400144FEB5F70.pptDocumento63 pagine1FFF11B1BD16627EE05400144FEB5F70.pptNur AishaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 Lesson 2 Chemical Reactions G9Documento18 pagineUnit 1 Lesson 2 Chemical Reactions G9ftamyblooNessuna valutazione finora
- EnzymesDocumento5 pagineEnzymeseyosiyas tekleweyinNessuna valutazione finora
- Slide EnzymeDocumento27 pagineSlide EnzymeReni Fatmawati100% (1)
- Grade 10 Biology Sec.2.4Documento33 pagineGrade 10 Biology Sec.2.4zakaria AlshurmanNessuna valutazione finora
- CA Lesson 02 Chemical+ReactionsDocumento21 pagineCA Lesson 02 Chemical+ReactionsI Dont think you should knowNessuna valutazione finora
- Enzyme Kinetics and Applications (Part 1a: Kinetics of Enzyme Catalyzed Reactions)Documento26 pagineEnzyme Kinetics and Applications (Part 1a: Kinetics of Enzyme Catalyzed Reactions)Nur AishaNessuna valutazione finora
- Materi 2Documento34 pagineMateri 2siti purnamaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.2 Energy: Chapter 2: Chemistry of LifeDocumento13 pagine2.2 Energy: Chapter 2: Chemistry of Lifeapi-520057338Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Enzyme Regulation in Biochemical PathwaysDocumento29 pagine1 Enzyme Regulation in Biochemical PathwayshadeelNessuna valutazione finora
- Pure Biology CHP 5 Enzymes 1Documento35 paginePure Biology CHP 5 Enzymes 1rabiayub21Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 1 - The Kinetics of Enzyme Catalyzed ReactionsDocumento18 pagineLecture 1 - The Kinetics of Enzyme Catalyzed ReactionsGenevive S. de VeraNessuna valutazione finora
- CatalysisDocumento50 pagineCatalysisnagendra_rdNessuna valutazione finora
- Enzyme and Enzyme KineticsDocumento61 pagineEnzyme and Enzyme KineticsNaiomiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical ReactionsDocumento26 pagineChemical ReactionsJerome CameroNessuna valutazione finora
- "Helper" Protein Molecules: EnzymesDocumento7 pagine"Helper" Protein Molecules: EnzymesMuhammad Junaid IqbalNessuna valutazione finora
- Simple Collision TheoryDocumento30 pagineSimple Collision TheoryJona FranciscoNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.0 CHPT 4 - Enzymes and The Regulation of Biochemical PathwaysDocumento41 pagine4.0 CHPT 4 - Enzymes and The Regulation of Biochemical PathwaysshinymaterialsNessuna valutazione finora
- Biomolecules and Cells:: Mr. Derrick Banda MSC, BSCDocumento69 pagineBiomolecules and Cells:: Mr. Derrick Banda MSC, BSCAmon Sangulube100% (1)
- Biochemistry: By: Angela Marie Ferrer BSN 2BDocumento13 pagineBiochemistry: By: Angela Marie Ferrer BSN 2BNoemi Martinez FerrerNessuna valutazione finora
- ENZYMESDocumento31 pagineENZYMESjuunisai6Nessuna valutazione finora
- Enzymes PDFDocumento50 pagineEnzymes PDFMuhammad Luqman NisaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochemistry 1: - Biochemistry of Amino Acids - Biochemistry of Proteins - Portrait of Allosteric ProteinDocumento55 pagineBiochemistry 1: - Biochemistry of Amino Acids - Biochemistry of Proteins - Portrait of Allosteric ProteinHiba N IkhmyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Title: Lecture (9) Enzymes Present By: Associate Prof - Ingy BadawyDocumento58 pagineTitle: Lecture (9) Enzymes Present By: Associate Prof - Ingy BadawyAbdo ElsaidNessuna valutazione finora
- Sameer Ahmed Group: GM-01: Function and StructureDocumento5 pagineSameer Ahmed Group: GM-01: Function and StructureSameer ButtNessuna valutazione finora
- 06 Enz 1 AMODocumento22 pagine06 Enz 1 AMOYUAN PROVIDONessuna valutazione finora
- Enzymes - Part IIDocumento71 pagineEnzymes - Part IIBarış KaplanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lasaca Report (Enzymes)Documento43 pagineLasaca Report (Enzymes)MaryAnn LasacaNessuna valutazione finora
- EnzymesDocumento205 pagineEnzymes464464naifNessuna valutazione finora
- EnzymesDocumento14 pagineEnzymesCarl Agape DavisNessuna valutazione finora
- ENVS 532: DR Assad Al-Thukair Associate ProfessorDocumento20 pagineENVS 532: DR Assad Al-Thukair Associate ProfessorAbu Muhsin Al NgapakyNessuna valutazione finora
- EnzymesDocumento7 pagineEnzymesSheena Grace B. LobatonNessuna valutazione finora
- What Are Enzymes?Documento11 pagineWhat Are Enzymes?krishnarajagopal2011Nessuna valutazione finora
- Enzymes: Function and StructureDocumento5 pagineEnzymes: Function and Structuretiyf mojaleedNessuna valutazione finora
- Enzymes: Biological CatalystsDocumento34 pagineEnzymes: Biological CatalystsLeondreNessuna valutazione finora
- ERT211 CHP 1-2 PDFDocumento27 pagineERT211 CHP 1-2 PDFsobiyamaragathavelNessuna valutazione finora
- Enzymes Are The Tools of LifeDocumento31 pagineEnzymes Are The Tools of LifedrhydrogenNessuna valutazione finora
- Enzyme Worksheet Answer KeyDocumento3 pagineEnzyme Worksheet Answer KeyEnessa Yurkin100% (1)
- Cells Use Energy To Grow, Make New Parts, and ReproduceDocumento33 pagineCells Use Energy To Grow, Make New Parts, and ReproduceMuhammad Kholifh ArdlillahNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 - EnzymesDocumento84 pagineChapter 1 - EnzymesNorsuzianaNessuna valutazione finora
- Enzymes PresDocumento34 pagineEnzymes PresRasmia SalamNessuna valutazione finora
- Enzymes PresDocumento57 pagineEnzymes Pres4tqpxmts7zNessuna valutazione finora
- Che41102 Reactor Engineering I: Dr. Mustafa Abbas MustafaDocumento42 pagineChe41102 Reactor Engineering I: Dr. Mustafa Abbas Mustafaibtihal esamNessuna valutazione finora
- Enzymes: by Nura Malahayati THP-FP UnsriDocumento71 pagineEnzymes: by Nura Malahayati THP-FP UnsriIkhsan muttaqinNessuna valutazione finora
- Enzymes and The Active SiteDocumento23 pagineEnzymes and The Active SiteLaura GambaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem 3Documento103 pagineChem 3César ArenasNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson #8 - EnzymesDocumento29 pagineLesson #8 - EnzymesMaya AwadNessuna valutazione finora
- Enzymes Their Significance and AppliocationDocumento14 pagineEnzymes Their Significance and AppliocationArslan AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical ReactionDocumento92 pagineChemical ReactionDionisio BrinosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical ReactionsDocumento11 pagineChemical Reactionsapi-272822216Nessuna valutazione finora
- EnzymesDocumento17 pagineEnzymesMartyn PereiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Reactions and Enzymes 2Documento26 pagineChemical Reactions and Enzymes 2api-240096234100% (1)
- EnzymesDocumento41 pagineEnzymesaa9140697874Nessuna valutazione finora
- Physci Catalyst 101Documento34 paginePhysci Catalyst 101Kyuptonite KimNessuna valutazione finora
- Bachelor of Science in Medical Laboratory Science: Biochemistry LectureDocumento16 pagineBachelor of Science in Medical Laboratory Science: Biochemistry LectureDCRUZNessuna valutazione finora
- ENZYMESDocumento12 pagineENZYMESmarianne.gugulan07Nessuna valutazione finora
- Enzymes & Energetics - CTPWDocumento42 pagineEnzymes & Energetics - CTPWjessicatieuuNessuna valutazione finora
- Enzyme Reactions PresentationDocumento23 pagineEnzyme Reactions PresentationscarlettNessuna valutazione finora
- EnzymesDocumento3 pagineEnzymesDavid PetalcurinNessuna valutazione finora
- Training Session 5: Gas Turbine Repair: by Scott Hastie / Liburdi Turbine ServicesDocumento42 pagineTraining Session 5: Gas Turbine Repair: by Scott Hastie / Liburdi Turbine Serviceskp pkNessuna valutazione finora
- Airconditioning Feb 2018 Rev 4 Presentation-7Documento59 pagineAirconditioning Feb 2018 Rev 4 Presentation-7darius james del mar86% (7)
- PolyolsDocumento12 paginePolyolsA MahmoodNessuna valutazione finora
- MSDS Colamate SS40Documento3 pagineMSDS Colamate SS40mndmatt100% (2)
- Sample Planning and Designing Lab For Chemistry UpdatedDocumento2 pagineSample Planning and Designing Lab For Chemistry UpdatedRangerNessuna valutazione finora
- Design Os Sewers (Blue Book)Documento388 pagineDesign Os Sewers (Blue Book)savanotrebor100% (1)
- Transformers&ReactorsDocumento56 pagineTransformers&ReactorsDilip KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinetics of Oxidation of Ammonia in Solutions Containing Ozone With or Without Hydrogen PeroxideDocumento6 pagineKinetics of Oxidation of Ammonia in Solutions Containing Ozone With or Without Hydrogen PeroxideBrent WoottonNessuna valutazione finora
- IDEALEQNDocumento2 pagineIDEALEQNNick HabibiNessuna valutazione finora
- Estimation of Glucose Concentration PDFDocumento3 pagineEstimation of Glucose Concentration PDFAmiel DionisioNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Sensors: Comprehensive Sensor Technologies, Vol. 6: Chemical Sensors ApplicationsDocumento77 pagineChemical Sensors: Comprehensive Sensor Technologies, Vol. 6: Chemical Sensors ApplicationsMomentum PressNessuna valutazione finora
- Cem Tec White PuDocumento2 pagineCem Tec White Pupravi3434Nessuna valutazione finora
- Calculation of Pipe Reinforcement ASME B31 3Documento5 pagineCalculation of Pipe Reinforcement ASME B31 3Umar Aslam0% (1)
- Reynolds-Averaged Navier-Stokes EquationsDocumento3 pagineReynolds-Averaged Navier-Stokes EquationsMirko GraneseNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Test 10Documento57 paginePractice Test 10The LightNessuna valutazione finora
- Testing of Building Stones - Rock Tests On Lab & FieldDocumento3 pagineTesting of Building Stones - Rock Tests On Lab & FieldআকাশআহসানNessuna valutazione finora
- Paper BioDocumento17 paginePaper BioI-hana D'yanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Venair - Tubo Vena (En)Documento2 pagineVenair - Tubo Vena (En)TelxinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Resistance Chart FRPDocumento36 pagineChemical Resistance Chart FRPHrishikesanNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanical Properties of Carbon Fiber Composite MaterialsDocumento2 pagineMechanical Properties of Carbon Fiber Composite MaterialsmehtabpathanNessuna valutazione finora
- Czm-On The Practical Application of The Cohesive ModelDocumento25 pagineCzm-On The Practical Application of The Cohesive ModelAldyansyah PutraNessuna valutazione finora
- Borescope Sample Report PDFDocumento14 pagineBorescope Sample Report PDFWalter TrajadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Water Budget of Inter-Cropped Maize and Cassava On Bench TerracesDocumento31 pagineWater Budget of Inter-Cropped Maize and Cassava On Bench TerracesSudharsananPRSNessuna valutazione finora
- Aiats-2022 (Cf+Oym) Test-03 Code-A&b Solutions 09.01.2022Documento40 pagineAiats-2022 (Cf+Oym) Test-03 Code-A&b Solutions 09.01.2022Yatin PrakashNessuna valutazione finora
- Nutrition of The Tamandua I. Nutrient Composition of Termites and Stomach Contents From Wild TAMANDUA BANDEIRA PDFDocumento16 pagineNutrition of The Tamandua I. Nutrient Composition of Termites and Stomach Contents From Wild TAMANDUA BANDEIRA PDFgabrielwerneckNessuna valutazione finora
- E3877 Optics FormulasDocumento6 pagineE3877 Optics FormulasKaran DoshiNessuna valutazione finora
- World Atmospheric CO2, Its 14C Specific Activity,.2Documento15 pagineWorld Atmospheric CO2, Its 14C Specific Activity,.2Anonymous yE2LIYBNessuna valutazione finora
- Climaveneta I-Accurate IaxDocumento68 pagineClimaveneta I-Accurate IaxOctavio Farid Rossi YumhaNessuna valutazione finora
- DNV 2012 Results Options Dialog in AutoPIPE - Pipe Stress and Vessel Design - Wiki - Pipe Stress and Vessel Design - Bentley CommunitiesDocumento9 pagineDNV 2012 Results Options Dialog in AutoPIPE - Pipe Stress and Vessel Design - Wiki - Pipe Stress and Vessel Design - Bentley CommunitiesLK AnhDungNessuna valutazione finora
- Act 2Documento6 pagineAct 2JHON LHOYD CORPUZNessuna valutazione finora