Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Switch Mode Power Conversion Fundamentals
Caricato da
Roberto Castillo MirandaDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Switch Mode Power Conversion Fundamentals
Caricato da
Roberto Castillo MirandaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Switch Mode Power Conversion
Fundamentals
Slxlfo lalcones
!"#$%#&'()
CraduaLlon Course:
Power Converters for Photovoltaic Generation Systems
Agenda
ower LlecLronlcs lnLroducLlon
ldeal SwlLch
ulse WldLh ModulaLlon (WM)
8aslc uC-uC ConverLer
SwlLchlng & Average Models
SlmulaLlon w/ LLCS
ldeal SwlLch [1]
ConcepLual absLracLlon for convenlence ln Lhe sLudy of a
clrculL conflguraLlon (Lopology). noL real.
SwlLchlng luncLlon
q(L) = 0 q(L) = 1
ldeal SwlLch: CharacLerlsLlc Curve
1he ldeal swlLch can wlLhsLand lnflnlLy volLage when open and
conducL an lnflnlLe currenL when closed.
ldeal SwlLch: ower ConsumpLlon
1he ldeal swlLch has zero lmpedance and Loggles beLween Cn
and Cll sLaLes ln no Llme. 1herefore, lL uCLS nC1 consume
power.
Ideal Switch & Kirchhoffs Laws
When ldeal swlLches are used ln a clrculL conflguraLlon, lL ls
critical not to violate Kirchhoffs Current Law (KCL) or Kirchhoffs
volLage Law (kvL).
Solld SLaLe SwlLches
(ower LlecLronlc uevlces)
unconLrolled (commuLaLed by llne)
ulode
Palf-conLrolled (conLrolled Lurn-on, Lurned off by llne)
SC8 (Slllcon ConLrolled 8ecLlfler)
18lAC (1rlode AC SwlLch)
lully-conLrolled (conLrolled Lurn-on and Lurn-off)
8!1 (8lpolar !uncLlon 1ranslsLor)
MCSlL1 (MeLaloxldesemlconducLor lleld-effecL
1ranslsLor)
lC81 (lnsulaLed CaLe 8lpolar 1ranslsLor)
C1C (CaLe 1urn-off 1hyrlsLor)
MC1 (MCS ConLrolled 1hyrlsLor)
lCC1 (lnLegraLed CaLe-commuLaLed 1hyrlsLor)
Solld SLaLe SwlLches (conL.)
Diode Thyristor
Triac SCS GTO
BJT MOSFET IGBT MCT
IGCT
Solld SLaLe SwlLches (conL.)
Solld SLaLe SwlLches (conL.)
ulode CharacLerlsLlcs [1]
8!1 CharacLerlsLlcs [1]
8ldlrecLlonal-currenL SwlLch [1]
8ldlrecLlonal-volLage SwlLch [1]
lour-quadranL SwlLch [1]
ower LlecLronlcs lnLerface [1]
1he power elecLronlcs lnLerface faclllLaLes Lhe Lransfer
of power from Lhe source Lo Lhe load by converLlng
volLages and currenLs from one form Lo anoLher, ln
whlch lL ls posslble for Lhe source and load Lo reverse
roles.
ower LlecLronlcs ConverLer [2]
Ceneral ClasslflcaLlon of ower
ConverLers
uC-uC converLers
AC-uC converLers +,-./010-,23
uC-AC converLers +045-,/-,23
AC-AC converLers +.6.78%.845-,/-,29 :;/,0< .845-,/-,23
DC: different magnitudes
AC: different magnitudes, frequency, phase
CommuLaLlon 1ype
Llne commuLaLed converLers
unconLrolled (dlode) 8ecLlflers
ConLrolled (LhyrlsLor-based) 8ecLlflers
lorced commuLaLed converLers
SwlLch Mode ConverLers
SwlLch Mode uC-uC ConverLer [1]
Current Port Voltage Port
SPST Implementation of a SPDT
SPSTs must be complementary
(Elevador)
(Reductor)
SwlLchlng ole [2]
ulse WldLh ModulaLlon (WM) [2]
A
=
n
A
=
1
ON
1
S
S
=
1
]
S
Duty Ratio
Switching Period
Average Converter Voltage
WM CaLe ulses
c(t) saw tooth for DC
c(t) triangular for AC
q(t)
q(t)
q(t)
uC-uC ConverLer Average Model
Switching Model
(Modelo de Conmutacin)
Average Model
(Modelo Promedio)
L
V
Low
I
Low
R
V
a
=dV
High
I
High
=dI
Low
V
High
V
a
L
V
Low
I
Low
R
V
High
d
(1-d)
I
High
LLCS SlmulaLlon CuLpuL
Parameters:
L=20e-6
R=0.1
Vhi=20
Vlo=10
fs=100e3
d=0.5, 0.55
LLCS: SLeady SLaLe Slgnals
!"# %&"'()*+ ,-.,- -"#/*0)*0 1234 153
Bi-directional
Converter
Buck (Step-down) Converter Boost (Step-up) Converter
*
D* =1-D
!"#$ &'()*+,*+ -./
!"#$ &'()#*(+, &(,+-./ 012
!"#$% '()*( (+,-./0./
R
o
Switching
Pole
a V
DC
C
f
L
f
V
a
V
o
Low-Pass
Filter
R
o
Switching
Pole
a
C
f
L
f
V
a
V
o
Low-Pass
Filter
V
DC
/2
V
DC
/2
DC-DC Converter Half-Bridge DC-AC Converter
Single-phase Inverter
a
b
V
DC
Split-phase Inverter
a
b
n
V
DC
/2
V
DC
/2
Full-bridge Single-phase Inverter Split-phase Inverter
Bipolar Modulation Unipolar Modulation
!"#$ &'()*+,-'.
!"# %&'()*+, -)*./*. 012
34/ 5'/67/*,8 9)(&+* &*&:8;+; )55/'; ()'/ +*;+<4. .) .4/
=/'5)'(&*,/ )5 !"#>
? .8=+,&: ;=/,.'7( )5 !"# ,)*;+;.; )5 57*9&(/*.&:
frequency that is far away from the harmonic components
,:);/ .) .4/ ;@+.,4+*< 5'/67/*,8>
Bipolar Modulation
Unipolar Modulation
!"# %&'()*+, -)*./*. 010
Cver-modulaLlon
Cccurs when Lhe modulaLlon lndex ls greaLer Lhan 1.
1hls causes dlsLorLlon of 60Pz volLage and currenLs ln Lhe
sysLem.
!"#$%&$%' ))* +,-&./$0
) (
2 2
u e + + = t Sin
V
m
V
V
DC
A
DC
a
) (
2 2
t u e + + + = t Sin
V
m
V
V
DC
A
DC
b
DC DC A b a ab
mV t Sin V m V V V = + = = ) ( u e
DC A AC conv ab
V m V V V = = =
Inverter
a
b
V
DC
DC DC a
V t Sin d dV V
|
.
|
\
|
+ + = = ) (
2
1
2
1
u e
Modulation of a DC-DC converter using a variable duty cycle
0
0
0 360
PWM DC
PWM
V V
PWM
V
grid PWM
grid
V V
I
j L
C
H
L
i
Grid
7.2 kV
11.4kV
HV DClink
Rectifier
!"#$" "&'()*+)*, -).+/0/)*
grid
V
PWM
V
0
_
0
0 360
grid rated
I grid
I I
grid
I
grid
V
Funcionamiento similar al
inversor. La potencia activa
fluye hacia el lado DC.
!"#$%& ()#*+$,$
conv
V
grid
V
L
V
L
I
conv
V
grid
V
L
V
L
I
conv
V
grid
V
L
V
L
I
grid R L conv
V V V V
conv
V
grid
V
L
V
L
I
L L
I L j V
0
R
V
L I
L
R
V
conv
=m*V
DC Grid
Unity Power Factor
C
H
L
i
Grid
7.2 kV
11.4kV
HV DClink
Rectifier
-5
0
5
Input current (A), Grid Voltage (kV)
0 0.002 0.004 0.006 0.008 0.01 0.012 0.014 0.016
-4000
-3000
-2000
-1000
0
1000
2000
3000
4000
Time (sec)
Vpwm and CCA(Vpwm)
I
in
(A)
v
in
(kV)
v
pwm
(V)
CCA(v
pwm
)
grid
V
i
L
V
grid
I
PWM
V
PWM
v
grid
i
i
L
V
!"# %&'()*)&+ ,)(- ./)(0 !1
C
H
L
i
Grid
7.2 kV
11.4kV
HV DClink
Rectifier
-5
0
5
Input current (A), Grid Voltage (kV)
0 0.002 0.004 0.006 0.008 0.01 0.012 0.014 0.016
-4000
-3000
-2000
-1000
0
1000
2000
3000
4000
Time (sec)
Vpwm and CCA(Vpwm)
I
in
(A)
v
in
(kV)
v
pwm
(V)
CCA(v
pwm
)
45 deg leading current
grid
V
i
L
V
grid
I
PWM
V
i
L
V
!"# %&'()*)&+ ,)(- .&/0)12 !3
!"#$%&"'()* ,-.*/%*/
C
f
L
f
DClink
Double-Phase Inverter LC Filter
L
f
C
f
Load
DC b a ab
mV V V V
2
) (
2
DC DC
A n a an
V
m t Sin
V
m V V V
) (
2 2
t Sin
V
m
V
V
DC
A
DC
a
0
2
DC
n
V
V
Inverter
a
b
n
V
DC
/2
V
DC
/2
!"#$%&'"()* ,(- .$&%/01&*2 3)42-'2-
C
f
L
f
C
L
LV DClink
Double-Phase Inverter LC Filter
L
f
C
f
Load 400 V
-100
-50
0
50
100
Io(A)
0.01 0.012 0.014 0.016 0.018 0.02 0.022 0.024
-20
0
20
40
60
80
100
Time (sec)
Ii(A)
-400
-200
0
200
400
Vpwm(V)
0.01 0.012 0.014 0.016 0.018 0.02 0.022 0.024
-200
-100
0
100
200
Time (sec)
Vo(V)
0.0119 0.012 0.012 0.0121 0.0121 0.0122
-1
-0.5
0
0.5
1
Time (sec)
Vtri(V), Vc(V)
1 o
V
2 o
V
i
I
1 PWM
V
!"#$$%&"'($ *+,-$#.$#
) (
2 2
t Sin
V
m
V
V
DC
A
DC
a
)
3
2
(
2 2
t Sin
V
m
V
V
DC
A
DC
b
)
6
(
2
3
t Sin V m V V V
DC A b a ab
DC A ab
V m V 866 . 0
)
3
2
(
2 2
t Sin
V
m
V
V
DC
A
DC
c
Three-Phase Converter
V
DC
a
c
b
!"#$$%&"'($ *+,-$#.$# /0 1$2.#'3
V
DC
/2
V
DC
/2
Three-Phase Converter
a
c
b
n
Four-Leg Three-Phase Converter
a
c
b
n
) (
2
t Sin
V
m V V V
DC
A n a an
) (
2 2
t Sin
V
m
V
V
DC
A
DC
a
0
2
DC
n
V
V
)
6
(
2
3
t Sin V m V V V
DC A b a ab
an
V
bn
V
cn
V
ab
V
8eferences
[1] Binseng Wang, Lecture Power Conversion, Topological
Fundamental EEE 598 Renewable Energy Systems, ASU.
[2] Dr. Raja Ayyanar, Lecture Introduction EEE 572 Advanced
ower LlecLronlcs, ASu.
CuesLlons?
1hanks!
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- ZVS-ZCS Bidirectional Full-Bridge DC-DC ConverterDocumento6 pagineZVS-ZCS Bidirectional Full-Bridge DC-DC ConverterPradhapndk100% (1)
- DC-DC Converter Using LM2576Documento50 pagineDC-DC Converter Using LM2576unmesh shirodkarNessuna valutazione finora
- SKEM 3742 Electro Pneumatic Labsheet PDFDocumento7 pagineSKEM 3742 Electro Pneumatic Labsheet PDFWalter VermehrenNessuna valutazione finora
- ABB DC Power - Supplies - Catalog PDFDocumento118 pagineABB DC Power - Supplies - Catalog PDFAdnan Naeem MalikNessuna valutazione finora
- Uc 3845Documento23 pagineUc 3845Bahram RN100% (1)
- Switch-Mode DC-AC Inverters: Converters For Ac Motor Drives and Uninterruptible Power SuppliesDocumento19 pagineSwitch-Mode DC-AC Inverters: Converters For Ac Motor Drives and Uninterruptible Power SuppliesHartoyo MpNessuna valutazione finora
- Fa Dps 119apDocumento2 pagineFa Dps 119appedroNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Signal Processing Systems: Implementation Techniques: Advances in Theory and ApplicationsDa EverandDigital Signal Processing Systems: Implementation Techniques: Advances in Theory and ApplicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- IQMath Fixed Vs Floating PDFDocumento30 pagineIQMath Fixed Vs Floating PDFGautam KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Release Notice: PCB Outline DrawingDocumento5 pagineRelease Notice: PCB Outline DrawingsunilbeedasseeNessuna valutazione finora
- How An SMPS WorksDocumento7 pagineHow An SMPS WorksĐorđe PopovićNessuna valutazione finora
- Control Valve DataDocumento10 pagineControl Valve DatasachinrmishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Supply Module1 To PLCDocumento6 paginePower Supply Module1 To PLCchiranjeeviNessuna valutazione finora
- Operating Instructions PS-AMS Series PSQDocumento24 pagineOperating Instructions PS-AMS Series PSQNishanth KallingentavidaNessuna valutazione finora
- Operating Manual PS-AMS 11 Series PSL: Translation Into English LanguageDocumento28 pagineOperating Manual PS-AMS 11 Series PSL: Translation Into English LanguagezeljkoradaNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Supply Trainer Using Lm723 IcDocumento8 paginePower Supply Trainer Using Lm723 IcDinesh Kumar MehraNessuna valutazione finora
- DC TO DC Buck Book ConvertorDocumento20 pagineDC TO DC Buck Book ConvertorAmit KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Two-Stage H-Bridge Transformer Coupled DC-DC Converter With Zero Voltage SwitchingDocumento8 pagineTwo-Stage H-Bridge Transformer Coupled DC-DC Converter With Zero Voltage SwitchingRakeshconclaveNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Supplies Module 03Documento20 paginePower Supplies Module 03LeonardoXanMNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Supply Theory of OperationDocumento6 paginePower Supply Theory of OperationsaeidraminaNessuna valutazione finora
- Optical and Microwave Technologies for Telecommunication NetworksDa EverandOptical and Microwave Technologies for Telecommunication NetworksNessuna valutazione finora
- Optimization Techniques and Applications with ExamplesDa EverandOptimization Techniques and Applications with ExamplesNessuna valutazione finora
- Fs 9001Documento16 pagineFs 9001Mauricio GuanellaNessuna valutazione finora
- Switch Mode Multi Level Power AmplifierDocumento56 pagineSwitch Mode Multi Level Power AmplifierLuiz Clemente PimentaNessuna valutazione finora
- DC-DC Power ConvertersDocumento14 pagineDC-DC Power ConvertersArmando PontesNessuna valutazione finora
- LG 50ps60 Training ManualDocumento142 pagineLG 50ps60 Training ManualjesusNessuna valutazione finora
- British Special Quality Valves and Electron Tube Devices Data Annual 1964–65Da EverandBritish Special Quality Valves and Electron Tube Devices Data Annual 1964–65Nessuna valutazione finora
- EMT 369 Wk2 Power Semiconductor Devices (GC)Documento53 pagineEMT 369 Wk2 Power Semiconductor Devices (GC)Ashraf YusofNessuna valutazione finora
- Ee 328 Lecture 11Documento55 pagineEe 328 Lecture 11somethingfornowNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Electronics 2: Continuous-time Signals and SystemsDa EverandFundamentals of Electronics 2: Continuous-time Signals and SystemsNessuna valutazione finora
- DC-DC ChoppersDocumento24 pagineDC-DC ChoppersAbdullah NasirNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of RF and Microwave Transistor AmplifiersDa EverandFundamentals of RF and Microwave Transistor AmplifiersNessuna valutazione finora
- A Very High Frequency DC-DC Converter Based On A Class Pfi Resonant InverterDocumento10 pagineA Very High Frequency DC-DC Converter Based On A Class Pfi Resonant InvertererdemsecenNessuna valutazione finora
- Effect of Current On EDMDocumento58 pagineEffect of Current On EDMAli M. ElghawailNessuna valutazione finora
- A Fête of Topology: Papers Dedicated to Itiro TamuraDa EverandA Fête of Topology: Papers Dedicated to Itiro TamuraY. MatsumotoNessuna valutazione finora
- ATX-5400M (Microlab 350W)Documento2 pagineATX-5400M (Microlab 350W)haroutuon100% (1)
- 1.1 Introduction To Buck ConverterDocumento44 pagine1.1 Introduction To Buck Converterapi-19810277Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ec 2252 Communication Theory Lecture NotesDocumento120 pagineEc 2252 Communication Theory Lecture NotesAnonymous G4srxwO3jINessuna valutazione finora
- 21 Toma EmanoilDocumento6 pagine21 Toma EmanoilFredy Peñafiel PazNessuna valutazione finora
- ECE320 HW4 SolutionDocumento4 pagineECE320 HW4 Solutiondigital2000100% (1)
- Over Voltage, Over Current, Transient Voltage & Reverse Polarity Protection Circuit Using RT1720 Hot Swap Controller With Fault TimerDocumento10 pagineOver Voltage, Over Current, Transient Voltage & Reverse Polarity Protection Circuit Using RT1720 Hot Swap Controller With Fault TimerKoushik MaityNessuna valutazione finora
- Estimating MOSFET Parameters From The Data Sheet PDFDocumento18 pagineEstimating MOSFET Parameters From The Data Sheet PDFmbkfet100% (1)
- Servo Stabilizer Manual - 2KVADocumento5 pagineServo Stabilizer Manual - 2KVAilesh22100% (1)
- Meanwell SP 320Documento1 paginaMeanwell SP 320Wee Chuan Poon100% (1)
- Three Phase Appliance ProtectorDocumento40 pagineThree Phase Appliance ProtectorJeevan PreethuNessuna valutazione finora
- A Discussion About Maximum Power TransferDocumento8 pagineA Discussion About Maximum Power TransferRebwar Osman100% (1)
- Single Phase Inverter With Pi ControllerDocumento12 pagineSingle Phase Inverter With Pi ControllerNimish SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Instruction Manual: Smart Valve PositionerDocumento52 pagineInstruction Manual: Smart Valve Positionerabbas dehghanNessuna valutazione finora
- What Are The Advantages and Disadvantages of A Bi-Directional DC To A DC Converter?Documento14 pagineWhat Are The Advantages and Disadvantages of A Bi-Directional DC To A DC Converter?BALAJINessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 1 Nitesh Hatankar (I-48) Title: Objective: AbstractDocumento5 pagineExperiment 1 Nitesh Hatankar (I-48) Title: Objective: AbstractKkNessuna valutazione finora
- SEPIC ConverterDocumento16 pagineSEPIC ConverterDina GaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Control Cable Philosophy-RevisedDocumento2 pagineControl Cable Philosophy-RevisedRaj HussainNessuna valutazione finora
- Application Note AN-6026: Design of Power Factor Correction Circuit Using FAN7529Documento23 pagineApplication Note AN-6026: Design of Power Factor Correction Circuit Using FAN7529miloud1911Nessuna valutazione finora
- SMC Penumatic Circuit ValvesDocumento75 pagineSMC Penumatic Circuit Valvesbohoo123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Generating 50Hz PWM Using PIC16F877ADocumento2 pagineGenerating 50Hz PWM Using PIC16F877AZarko DacevicNessuna valutazione finora
- Power ElectronicsDocumento264 paginePower ElectronicsJayashree C RaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual Norac UC3 2004 446BC-MAN2dDocumento64 pagineManual Norac UC3 2004 446BC-MAN2daritmeticsNessuna valutazione finora
- SimplAir EPL BrochureDocumento12 pagineSimplAir EPL BrochureHfksosnaaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ball Bearing Installation and MaintenanceDocumento12 pagineBall Bearing Installation and Maintenancecengiz kutukcuNessuna valutazione finora
- Belden CatalogDocumento6 pagineBelden Catalogeddyson_24Nessuna valutazione finora
- Receipt Printer TP31: Operator ManualDocumento71 pagineReceipt Printer TP31: Operator Manualpnkemgne100% (1)
- VT TouchDocumento8 pagineVT TouchVictorNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Team PG120 Series - CatalogDocumento1 paginaPower Team PG120 Series - CatalogTitanplyNessuna valutazione finora
- Micro Programmed ControlDocumento24 pagineMicro Programmed Controlapi-26870484100% (8)
- Ficha Tecnica FTS20.Documento14 pagineFicha Tecnica FTS20.milton cardenasNessuna valutazione finora
- Spare Parts Side Door ElevatorDocumento9 pagineSpare Parts Side Door ElevatorAnthony WaaliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Feeding Mechanisam On Sweing MachineDocumento9 pagineFeeding Mechanisam On Sweing MachineShahan AkhtarNessuna valutazione finora
- R1A4016R B12A1H1A A: Q Series PumpsDocumento40 pagineR1A4016R B12A1H1A A: Q Series Pumpseaglego00Nessuna valutazione finora
- Access Power Solutions Installation and Operation Guide: (APS3-300 Series)Documento114 pagineAccess Power Solutions Installation and Operation Guide: (APS3-300 Series)Elvis Eliud HernándezNessuna valutazione finora
- S1.2S S1.5S S1.2S IL S1.5S IL S1.2S SL S1.5S Il S1.2S S1.5S (C442)Documento192 pagineS1.2S S1.5S S1.2S IL S1.5S IL S1.2S SL S1.5S Il S1.2S S1.5S (C442)Emerson RibeiroNessuna valutazione finora
- Samsung LE-40A866 - 20081009152533312 - BN68-01701B-00Eng-0910Documento72 pagineSamsung LE-40A866 - 20081009152533312 - BN68-01701B-00Eng-0910a11615870Nessuna valutazione finora
- Troubleshooting: Micom Px4XDocumento17 pagineTroubleshooting: Micom Px4Xdian JaelaniNessuna valutazione finora
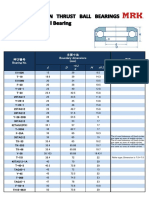
- King Pin Thrust Ball BearingsDocumento3 pagineKing Pin Thrust Ball BearingsFernando Bautista100% (2)
- MTH 2603 AwaauuvDocumento7 pagineMTH 2603 Awaauuvwilliam2001lebelNessuna valutazione finora
- DC Fan DatasheetDocumento1 paginaDC Fan DatasheetPhantom PNessuna valutazione finora
- Gree Cassette Brochure 4pp 2016 Web PDFDocumento4 pagineGree Cassette Brochure 4pp 2016 Web PDFFiroz AlamNessuna valutazione finora
- Owners ManualDocumento10 pagineOwners ManualknockcontrolNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 10 - Material Handling System (Conveyors) 2T 2021-2022Documento66 pagineWeek 10 - Material Handling System (Conveyors) 2T 2021-2022Pitt Andre LozadaNessuna valutazione finora
- HALFEN - HD - 22-EN - Kotwy Tuleje WzmocnioneDocumento48 pagineHALFEN - HD - 22-EN - Kotwy Tuleje WzmocnioneArkadiuszNessuna valutazione finora
- Interview QuesDocumento12 pagineInterview Quesvlsi_asicNessuna valutazione finora
- Minimum System Requirements For Professional Edition ... - AMAGDocumento9 pagineMinimum System Requirements For Professional Edition ... - AMAGLarry RicoNessuna valutazione finora
- HC15Documento28 pagineHC15Julian A GarzonNessuna valutazione finora
- Guia Usuario Controlador Robot YRC Series Omron PDFDocumento286 pagineGuia Usuario Controlador Robot YRC Series Omron PDFJose OrtegaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hfpt-11 Intelligent Thermal Detector: For Firefinder XLS™ and Fs-250 Fire Alarm Control PanelDocumento2 pagineHfpt-11 Intelligent Thermal Detector: For Firefinder XLS™ and Fs-250 Fire Alarm Control PanelMazenabs AbsNessuna valutazione finora
- 750to850 Retrofit-A2Documento38 pagine750to850 Retrofit-A2이성종Nessuna valutazione finora
- MC34161, MC33161, NCV33161 Universal Voltage Monitors: Marking DiagramsDocumento21 pagineMC34161, MC33161, NCV33161 Universal Voltage Monitors: Marking DiagramsВалераNessuna valutazione finora