Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
TELECOM 2G, 3G, 4G, RF, IPv6 Study Materials - GSM Interview Question - Answer
Caricato da
Sarsij MishraTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
TELECOM 2G, 3G, 4G, RF, IPv6 Study Materials - GSM Interview Question - Answer
Caricato da
Sarsij MishraCopyright:
Formati disponibili
5/18/2014 TELECOM 2G,3G,4G,RF,IPv6 Study Materials: GSM Interview Question -Answer
http://rftelecomm.blogspot.in/2013/01/gsm-interview-question-answer.html 1/8
Mobile Communication,Question related to GSM,CDMA,WCDMA & LTE,Short description about
RF Deive Test,RF Planning,RF Optimization,IPv4 & IPv6
TELECOM 2G,3G,4G,RF,IPv6 Study
Materials
Friday, January 18, 2013
GSM Interview Question -Answer
1. What is the function of SDCCH & SACCH?
Ans. (a) SDCCH---- Slow Dedicated Control Channel.
Function----
a) Location updates
b) SMS
c) Ciphering Initiation
d) Equipment Validation
e) Subscriber authentation
f) Call set up signaling
(b) SACCH---Slow Associated Control Channel.
Function:
(a) Timing advance data
(b) Transmit power control
(c) transmission of signaling data
(d) radio link supervision measurements
2. What are the reasons for Hand Overs?
(Ans) . (a) Signal Strength (RX LEVEL)
(b) Signal Quality (RX Qual)
(c) Power Budget
(d)Timing Advance.
(e) Interference
2. What are the shortcomings in handovers?
a) Call Dropping.
b) Ping- Pong handover
c) Far- Away cell effect
4. What is intelligent hand over?
Ans)Fuzzy logic
a) Neutral networks
5. What are internal & external hand over?
Ans
(1)INTERNAL HANDOVER
a) ( INTER BTS) ---- Transfer between two
channels (time slot) in same cell.
b) ( INTRA BSC ( BTS BTS)-----1 . transfer between BTS under
control of same Bsc
2 Measuring the quality of radio connection
3 Power levels
2. EXTERNAL HANDOVER.
( a) INTER BSC (BSC_ BSC)---- 1. Transfer between BTS under
the control of diff
BSC
2. BSC TO BSC
3 . NSS to attends the hand over
4. MSC controls.
Dharmendra singh
Follow
118
Presently 2G / 3G / WCDMA
RF/Telecom Consultant in
United Telecom Limited since
July 2012 to Till Date.Extensive
knowledge of TEMS, NEMO,
PROBE, MAPINFO
PROFESSIONAL, MCOM, ACTIX
& SCANNER (PCTEL, R&S TSMO).
View my complete profile
About Me
Join this site
with Google Friend Connect
Members (36) More
Already a member? Sign in
Followers
ARTS
12 have us
in circles
View
all
Follow
Google+
Followers
2014 (6)
2013 (53)
10/20 -
10/27 (2)
10/13 -
10/20 (1)
10/06 -
10/13 (1)
08/25 -
09/01 (2)
07/07 -
07/14 (1)
05/26 -
06/02 (3)
05/19 -
05/26 (1)
05/12 -
05/19 (1)
04/21 -
04/28 (6)
04/14 -
POST
Share
2
More
Next Blog Create Blog
Sign In
5/18/2014 TELECOM 2G,3G,4G,RF,IPv6 Study Materials: GSM Interview Question -Answer
http://rftelecomm.blogspot.in/2013/01/gsm-interview-question-answer.html 2/8
( b) INTER MSC ( MSC- MSC) ----1. transfer between cell under
the control of diff MSC
.What is the frequency Hopping its imp?
(Ans)
It is defined as sequential change of carrier frequency on
the radio link between mobile & base station.
Two types of freq hopping----- 1. Base band freq hopping.
2. synthesized frequency hopping.
7. Explain the major diff between BBH & SFH?
Ans
In BBH the no of hopping freq is same as no of TRX.
In SFH the no of Hoping freq can be in the range of 1to 63.
8. what are the advantages of Frequency Hopping?
1. Frequency Diversity
2. Interference Averaging
3. capacity
9. How in frequency hopping there is enhancement of network capacity?
Freq hopping implement will enable more aggressive freq
reuse pattern, that leads to better spectrum efficiency.
It can add more transceiver in the existing sites , while
maintaing the net work quality/
Freq hopping compressing the available spectrum to
make room for extra capacity
.
10. Define the freq. hopping parameters?
Frequency Hopping Parameters
GSM defines the following set of parameters:
Mobile Allocation (MA): Set of frequencies the mobile is allowed to hop over.
Maximum of 63 frequencies can be defined in the MA list.
Hopping Sequence Number (HSN): Determines the hopping order used in the
cell. It is possible to assign 64 different HSNs. Setting HSN = 0 provides cyclic hopping
sequence and HSN = 1 to 63 provide various pseudo-random hopping sequences.
Mobile Allocation Index Offset (MAIO): Determines inside the hopping
sequence, which frequency the mobile starts do transmit on. The value of MAIO ranges
between 0 to (N-1) where N is the number of frequencies defined in the MA list.
Presently MAIO is set on per carrier basis.
Motorola has defined an additional parameter, FHI.
Hopping Indicator (FHI): Defines a hopping system, made up by an associated
set of frequencies (MA) to hop over and sequence of hopping (HSN). The value of FHI
varies between 0 to 3. It is possible to define all 4 FHIs in a single cell.
Motorola system allows to define the hopping system on a per timeslot basis. So
different hopping configurations are allowed for different timeslots. This is very useful
for interference averaging and to randomize the distribution of errors.
11. What are the effects of freq hopping?
(Ans)
1 Handovers:
2 Call setup:
3 Frame Erasure Rate (FER):
12 .Explain in brief what is FER.
Ans FER= Number of erased blocks\ total no of blocks *100
It is the right measure of voice quality.
FER is performed on speech& signaling frames
04/21 (4)
04/07 -
04/14 (2)
03/24 -
03/31 (1)
03/17 -
03/24 (3)
03/10 -
03/17 (4)
03/03 -
03/10 (2)
02/24 -
03/03 (2)
02/03 -
02/10 (2)
01/20 -
01/27 (3)
01/13 -
01/20 (5)
2G
Spectru
m SCAM
in India
INTERNS
HIP
PROGRA
MME
FOR
FOREIG
N
CANDID
ATES IN
IND...
WCDMA/3
G
Question
s &
Answers
GSM
Intervie
w
Question
-Answer
RF
Optimiza
tion and
Log File
Analysis
in GSM
01/06 -
01/13 (7)
2012 (7)
GSM Interview Question -Answer
1. What is the function of
SDCCH & SACCH ? Ans. (a) SDCCH--
-- Slow Dedicated Control Channel.
...
Telecom Basic Questions
1. The OSI model was developed
by ISO in the year___________
a. 1985 b. 1988 c. 1965 d.
1984 2. ...
LTE DRIVE TEST PARAMETERS
RSRP :- Reference signal receive
power. RSRP (dBm) = RSSI
(dBm) -10*log (12*N) where RSSI =
Received Signal Strength Indicator
...
Resume Format for RF Engineer
Dharmendra Kumar Singh
Email
id:hidharmendrasingh@gmail.com
Mobile No: ***...
Popular Posts
5/18/2014 TELECOM 2G,3G,4G,RF,IPv6 Study Materials: GSM Interview Question -Answer
http://rftelecomm.blogspot.in/2013/01/gsm-interview-question-answer.html 3/8
FER------- 0 to 4%, GOOD.
4 to 15% , slightly degraded
Greater than 15%, useless
13. What happens when speech frames discarded in FER?
System will interpolate.
14. What happens when signaling frames discarded in FER?
MS is instructed to resend.
15. What is TCH_ TCH Interference? How it is measured.
When TCH carries are reused that leads to co-channel
interference.
When TCH carrier have call activity.
This is measured by delta measurement. --- 1. BCCH carries are
diff
2. TCH carriers in both cell 1& cell2 are same AFRCN TCH
16. Define the terms?
BER--- The number of erroneous bits received
Total no of bits received.
RBER---1 Residual bit error rate
2 It is performed on demodulated speech frames that
are not mark corrupt
.BFI -- Bad frame indication.
17. Explain the parameters in TEMS POCKET mobile.
1.
2. Llcell BCCH ARFCN
3.
4.
5.
L1. Logical channel.----- BCCH
L2. Logical channel ----- TCH
BC-- serving cell BCCH AFRCN.
BS-- base station identity code.
RXLEV- recieved signal strength
TC-- traffic channel
TS - time slot number.
TX - transmit power
C/I -- Carrier to interference ratio in db
RQ -- Receive bit error rate
WCDMA/3G Questions & Answers
General 1. What is the
experience and involvement in your
current and previous UMTS design
projects? Talk about your curr...
GSM,WCDMA,RF ,RF Optimization
Interview Objective Question
Level 2-3 NPO Questions (RF
Planning & Optimisation Engg) In the
following questions, please select one
alternative wh...
Drive Test Engineer/RF Engineer
Means collecting data on vehicle
movement. Its variation has also
intuitive: Walk Test, i.e., collect data
by walking areas of interes...
Basic Parameter of WCDMA
Basic Parameters of WCDMA
Frequency
Band : 2100
MHz ...
Protocol Testing/Protocol Testing
Tools
Testing Tools Used for Protocol
Testing 1 Glomosim simulator To
Test 100 nodes on single ...
Interview question of GSM
1) Which channel is used to transmit
random access signals? BCCH CCCH
Correct! SDCCH TCH 2) Which one
of the following is the combinat...
L BC BS RXLEV
L TC TS TX
C/I RQ FE
TA DSC CHM
RH CiMd
MCC MNC LAC
RA CI
5/18/2014 TELECOM 2G,3G,4G,RF,IPv6 Study Materials: GSM Interview Question -Answer
http://rftelecomm.blogspot.in/2013/01/gsm-interview-question-answer.html 4/8
FE frame erasure rate.
TA -- Timing advance
CHM --C hannel Mode
RH -- cell reselction Hystresis
CiMdCiphering mode
RAC Routing area code.
LACLocation area code.
18. Explain the analysis behind RX Qual.?
RX Qual is the basic measure. It reflects the average BER over
the certain period of time(0.5s)
RX QUAL done over 104 TDMA frames.
Limitation of RXQUAL---- 1. The distributions of bit error over
time.
2. Frame erasure
3. Hand over.
19. What are type of interference occur?
1. Co- channel interference.
2. Adj-channel interference.
3. Near end- Far end interference.
20. What is ERLANG?
Unit of telephone traffic intensity is called Erlang.
One ERLANG is one channel occupied continuously for one
hour.
1E = 64Kbps.
21. what do you mean by GOS?
It is the probabity of having a call blocked during busiest hour.
Ex GOS=0.05 means one call in 20 will be blocked call during
busiest hour because of insufficient capacity.
22. What are the technique GSM offers which combat Multipath fading?
Equalization
Diversity
Freq Hopping
Interleaving
Channel coding
23. What are control &traffic channels?
CONTROL CHANNEL.----1 BCH
2. CCCH
3. DCCH.
TRAFFIC CHANNEL-- Half rate
Full rate
EFR == Enhanced full
rate.
24. What are BCH, CCH, DCCH channels?
BCH-- 1. BCCH
5/18/2014 TELECOM 2G,3G,4G,RF,IPv6 Study Materials: GSM Interview Question -Answer
http://rftelecomm.blogspot.in/2013/01/gsm-interview-question-answer.html 5/8
2 .FCCH
3. SCH
CCCH. --- 1.PCH
2. AGCH
3. RACH
DCCH---- 1.SDCCH.
2. SACCH
3. FACCH
25. What are types of bursts?
Normal Burst
Frequency Correction Burst
Synchronization Burst.
Dummy Burst
Access Burst.
26. What is adjacent channel separation in GSM?
Urban Environment-------- 200khz
Sub Urban Environment ---- 400khz
Open environment ----- 800khz
27. What is the watt to dBm conversions?
Power in dBm = 10 log( watts *100)
0 dBm= 1mili watt
1watt = 30dbm
28. What are the optimizations you have done during Drive
Test?
What are samples in gsm?
Which modulation take place in GSM
In one TRU how many frames are there?
What is the value RXLEV of neighboring cell?
What do you mean by VAD?
What is BFI, where it is use?
2929. Define the hopping parameters in detail?
The MA is a list of hopping frequencies transmitted to a mobile every time it is
assigned to a hopping physical channel. The MA-list is a subset of the CA list. The MA-
list is automatically generated if the baseband hopping is used. If the network utilises
the RF hopping, the MA-lists have to be generated for each cell by the network planner.
The MA-list is able to point to 64 of the frequencies defined in the CA list. However, the
BCCH frequency is also included in the CA list, so the practical maximum number of
frequencies in the MA-list is 63. The frequencies in the MA-list are required to be in
increasing order because of the type of signaling used to transfer the MA-list.
The Hopping Sequence Number (HSN) indicates which hopping sequence of the
64 available is selected. The hopping sequence determines the order in which the
frequencies in the MA-list are to be used. The HSNs 1 - 63 are pseudo random sequences
used in the random hopping while the HSN 0 is reserved for a sequential sequence used
in the cyclic hopping. The hopping sequence algorithm takes HSN and FN as an input
and the output of the hopping sequence generation is a Mobile Allocation Index (MAI)
which is a number ranging from 0 to the number of frequencies in the MA-list
subtracted by one. The HSN is a cell specific parameter. For the baseband hopping two
HSNs exists. The zero time slots in a BB hopping cell use the HSN1 and the rest of the
time slots follow the HSN2 as presented in Error! Reference source not found.. All the
time slots in RF hopping cell follow the HSN1 as presented in Error! Reference source
not found..
When there is more than one TRX in the BTS using the same MA-list the Mobile
Allocation Index Offset (MAIO) is used to ensure that each TRX uses always an unique
frequency. Each hopping TRX is allocated a different MAIO. MAIO is added to MAI when
the frequency to be used is determined from the MA-list. Example of the hopping
sequence generation is presented in Error! Reference source not found.. MAIO and HSN
are transmitted to a mobile together with the MA-list. In Nokia solution the MAIO
offset
is a cell specific parameter defining the MAIO
TRX
for the first hopping TRX in a cell.
1.1 Hopping Sequence Number
1.2 Mobile Allocation Index Offset
5/18/2014 TELECOM 2G,3G,4G,RF,IPv6 Study Materials: GSM Interview Question -Answer
http://rftelecomm.blogspot.in/2013/01/gsm-interview-question-answer.html 6/8
The MAIOs for the other hopping TRXs are automatically allocated according to the
MAIO
step
-parameter introduced in the following section.
30. What is the effect of frequency hopping in RXQual?
Frequency hopping causes some changes in the RXQUAL distribution. Also,
there are some differences in a way the RXQUAL distribution should be interpreted.
The Frame Erasure Ratio (FER) is a ratio of discarded speech frames compared to
all the received speech frames. A speech frame is generally discarded if after the
decoding and error correction process any of the category 1a bits is found to be changed
based on the three parity bits following them in a speech frame.
FER is a measure of how successfully the speech frame was received after the
error correction process and it is thus a better indication of the subjective speech
quality compared to the RXQUAL which gives an estimate of the link quality in terms
of BER. The RXQUAL doesnt indicate how the bit errors were distributed in a speech
frame. The bit error distribution affects the ability of the channel decoding to correct
the errors.
The following table gives an idea of the correlation between RXQUAL and FER
and between subjective speech quality and different FER classes.
31. What is the relation link between RXQUAL& FER?
Table 1. RXQUAL vs. FER comparison according to the laboratory tests.
The relation of downlink FER and RXQUAL was measured during a FH trial. The
relation is clearly different in the hopping case compared to the non-hopping case. The
distributions of FER in each RXQUAL class are presented in Error! Reference source not
found. and Error! Reference source not found.. One clear observation can be made; in
the non-hopping case there are significant amount of samples indicating deteriorated
quality (FER>10%) in RXQUAL class 5 while in the hopping case the significant quality
deterioration (FER>10%) happens in RXQUAL class 6. Thus, it may be concluded that in
the frequency hopping networks significant quality deterioration starts at RXQUAL
class 6 while in non-hopping network this happens at RXQUAL class 5.
This improvement of FER means that the higher RXQUAL values may be
allowed in a frequency hopping network. RXQUAL thresholds are used in the handover
and power control decisions. Because of the improvement in the relative reception
performance on the RXQUAL classes 4-6, the RXQUAL thresholds affecting handover
and power control decisions should be set higher in a network using frequency hopping
network. In a frequency hopping network RXQUAL classes 0-5 are indicating good
quality.
Typically, the share of the RXQUAL classes 6 and 7 may increase after FH is
switched on, even if no other changes have been made. This may seem to be surprising
since it is expected that frequency hopping improves the network quality. However, in
most cases the quality is actually improved, but the improvement is more visible in
the call success ratio. The improved tolerance against interference and low field
strength in FH network means that it is less likely that the decoding of SACCH frames
fails causing increment in the radio link timeout counter. Thus, it is less likely that a
call is dropped because of the radio link timeout. Instead, the calls generating high
RXQUAL samples tend to stay on. This may lead to increase in the share of RXQUAL 6-
7. However, at the same time the call success rate is significantly improved.
In the Error! Reference source not found., there are presented some trial results
of a DL RXQUAL distribution with different frequency allocation reuse patterns. As can
be seen from the figures, the tighter the reuse becomes, the less samples fall in quality
class 0 and more samples fall in quality classes 1-6. Theres bigger difference in
downlink than in uplink direction.
This difference is a consequence of interference and frequency diversities that
5/18/2014 TELECOM 2G,3G,4G,RF,IPv6 Study Materials: GSM Interview Question -Answer
http://rftelecomm.blogspot.in/2013/01/gsm-interview-question-answer.html 7/8
affect the frequency hopping network. Because of these effects, the interference or low
signal strength tend to occur randomly, while in a non-hopping network it is probable
that interference or low field strength will affect several consecutive bursts making it
harder for the error correction to actually correct errors. The successful error
correction leads to less erased frames and thus improves the FER.
32. What do you understand by idle channel measurement?
When a new call is established or a handover is performed, the
BSC selects the TRX and the time slot for the traffic channel based on the idle
channel interference measurements. The frequency hopping has a significant
effect on the idle channel interference measurement results.
When the frequency hopping is used, the frequency of a hopping logical channel
is changed about 217 times in a second. The frequency of the idle time slots changes
according to the same sequence.
In a case of the random hopping, this means that the measured idle channel
interference is likely to be the same for all the TRXs that use the same MA-list. If the
interference is averaged over more than one SACCH frame, the averaging effect is even
stronger. However, normally the interferers are mobiles located in interfering cells. In
this case, there are probably differences in the measured idle channel interferences
between different time slots in the cell. This happens, because the interfering mobiles
are only transmitting during the time slot that has been allocated to them. This is
illustrated in Figure Error! No text of specified style in document.-1.
If the cyclic hopping sequence is used, there might occur differences on the
measured idle channel interference levels between the TRXs on the same time slot as
explained in the following section.
Figure Error! No text of specified style in document.-1. Idle channel interference
in a case of the random RF hopping
33 .what are types of handover?
There are four different types of handover in the GSM system, which involve
transferring a call between:
Channels (time slots) in the same cell
Cells (Base Transceiver Stations) under the control of the same
Base Station Controller (BSC),
Cells under the control of different BSCs, but belonging to the
same Mobile services Switching Center (MSC), and
Cells under the control of different MSCs.
34. what are important parameter of power saving in GSM
Discontinuous transmission
Minimizing co-channel interference is a goal in any cellular system, since it
allows better service for a given cell size, or the use of smaller cells, thus increasing the
overall capacity of the system. Discontinuous transmission (DTX) is a method that
takes advantage of the fact that a person speaks less that 40 percent of the time in
normal conversation [22], by turning the transmitter off during silence periods. An
added benefit of DTX is that power is conserved at the mobile unit.
The most important component of DTX is, of course, Voice Activity Detection. It
must distinguish between voice and noise inputs, a task that is not as trivial as it
appears, considering background noise. If a voice signal is misinterpreted as noise, the
transmitter is turned off and a very annoying effect called clipping is heard at the
receiving end. If, on the other hand, noise is misinterpreted as a voice signal too often,
the efficiency of DTX is dramatically decreased. Another factor to consider is that when
the transmitter is turned off, there is total silence heard at the receiving end, due to
the digital nature of GSM. To assure the receiver that the connection is not dead,
comfort noise is created at the receiving end by trying to match the characteristics of
the transmitting end's background noise.
Discontinuous reception
Another method used to conserve power at the mobile station is discontinuous
reception. The paging channel, used by the base station to signal an incoming call, is
structured into sub-channels. Each mobile station needs to listen only to its own sub-
channel. In the time between successive paging sub-channels, the mobile can go into
sleep mode, when almost no power is used.
All of this increases battery life considerably when compared to analog
: What is Tri-band and Dual-band?
A: A tri-band phone operates at three supported frequencies, such as 900/1800/1900 MHz or 850/1800/1900
5/18/2014 TELECOM 2G,3G,4G,RF,IPv6 Study Materials: GSM Interview Question -Answer
http://rftelecomm.blogspot.in/2013/01/gsm-interview-question-answer.html 8/8
Newer Post Older Post Home
Subscribe to: Post Comments (Atom)
Posted by Dharmendra singh at Friday, January 18, 2013
MHz. A dual-band phone operates at two frequencies, such as 850/1900 MHz or 900/1800
+2 Recommend this on Google
Post a Comment
Create a Link
3 comments:
swetank aginhotri said...
these are very helpful.
thanks
May 9, 2014 at 1:37 PM
swetank aginhotri said...
these are very helpful.
thanks
May 9, 2014 at 1:38 PM
swetank aginhotri said...
these are very helpful.
thanks
May 9, 2014 at 1:39 PM
Links to this post
Simple template. Template images by luoman. Powered by Blogger.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Cross-Layer Resource Allocation in Wireless Communications: Techniques and Models from PHY and MAC Layer InteractionDa EverandCross-Layer Resource Allocation in Wireless Communications: Techniques and Models from PHY and MAC Layer InteractionNessuna valutazione finora
- Mobile Network Optimization: A Guide for 2G and 3G Mobile Network OptimizationDa EverandMobile Network Optimization: A Guide for 2G and 3G Mobile Network OptimizationValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (3)
- GSM RF Interview Questions and AnswersDocumento21 pagineGSM RF Interview Questions and AnswersWA Khan100% (1)
- 2G 3G Interview QuestionsDocumento10 pagine2G 3G Interview Questionsmohnish1999Nessuna valutazione finora
- GSM Optimization InterviewDocumento43 pagineGSM Optimization InterviewAhmed GamalNessuna valutazione finora
- LTE RF Design and Optimization Interview QuestionsDocumento3 pagineLTE RF Design and Optimization Interview QuestionsJaved AminNessuna valutazione finora
- Interview QADocumento19 pagineInterview QAsatya vara prasad ballaNessuna valutazione finora
- LTE Questions and AnswersDocumento11 pagineLTE Questions and Answersdutta.somnath100% (5)
- Rach ProcedureDocumento20 pagineRach ProcedureMadhu ValluriNessuna valutazione finora
- LTE Tutorials (TELCOM HUB) : LTE Basics and OverviewDocumento55 pagineLTE Tutorials (TELCOM HUB) : LTE Basics and OverviewBromand TurkmaniNessuna valutazione finora
- 4g-Lte BasicsDocumento12 pagine4g-Lte Basicsdavis tukwaNessuna valutazione finora
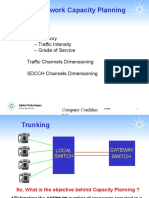
- GSM Network Capacity Planning: Traffic Channels DimensioningDocumento41 pagineGSM Network Capacity Planning: Traffic Channels DimensioningSushil OjhaNessuna valutazione finora
- LTE RF Interview QuestionsDocumento2 pagineLTE RF Interview QuestionsriteshmceNessuna valutazione finora
- LTE Interview QuestionsDocumento6 pagineLTE Interview QuestionsFarrukh Saleem67% (3)
- TOP 250+ LTE RF Planning Optimization For 4g Interview Questions and Answers 17 December 2019 - LTE RF Planning Optimization For 4g Interview Questions - Wisdom Jobs India PDFDocumento17 pagineTOP 250+ LTE RF Planning Optimization For 4g Interview Questions and Answers 17 December 2019 - LTE RF Planning Optimization For 4g Interview Questions - Wisdom Jobs India PDFyogesh pantNessuna valutazione finora
- LTEDocumento57 pagineLTEarvindsarvesh207645Nessuna valutazione finora
- Interviewquestionofgsm 141012233825 Conversion Gate01Documento94 pagineInterviewquestionofgsm 141012233825 Conversion Gate01Alex UmeakuNessuna valutazione finora
- Telecom Protocol TestingDocumento4 pagineTelecom Protocol TestingMukul RaghuvanshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Drive Test Interview QuestionsDocumento14 pagineDrive Test Interview QuestionsArun Kumar Sharma94% (31)
- UMTS Interview Questions and AnswerDocumento24 pagineUMTS Interview Questions and AnswervikydilseNessuna valutazione finora
- Radio Parameters ExplainedDocumento3 pagineRadio Parameters ExplainedZaryab Nisar100% (1)
- Interview QuestionDocumento8 pagineInterview QuestionVikas MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- 05 GSM BSS Network KPI (TCH Congestion Rate) Optimization ManualDocumento35 pagine05 GSM BSS Network KPI (TCH Congestion Rate) Optimization ManualMistero_H100% (3)
- 12 LTE Interview Questions and AnswersDocumento19 pagine12 LTE Interview Questions and AnswersAlex Umeaku100% (1)
- Narrowband Interference Suppression (RAN15.0 - 01) PDFDocumento21 pagineNarrowband Interference Suppression (RAN15.0 - 01) PDFSam FicherNessuna valutazione finora
- RF QuestionsDocumento31 pagineRF QuestionsShashank PrajapatiNessuna valutazione finora
- LTE Bit Rate CalculationDocumento36 pagineLTE Bit Rate Calculationaidenpark100% (1)
- LTE Network Planning - Huawei TechnologiesDocumento54 pagineLTE Network Planning - Huawei Technologiessparksss123Nessuna valutazione finora
- LTE FDD network optimization techniques under 40 charactersDocumento14 pagineLTE FDD network optimization techniques under 40 charactersJagannath ChoudhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- GSM TCH Call DropDocumento21 pagineGSM TCH Call DropPakcik Kamal100% (1)
- eRAN7.0 MIMO Feature: Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. HUAWEI ConfidentialDocumento31 pagineeRAN7.0 MIMO Feature: Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. HUAWEI ConfidentialAdil NaseerNessuna valutazione finora
- LTE in Ten MinutesDocumento15 pagineLTE in Ten MinutesYao Julien Koffi100% (2)
- Lte Interview QuestionsDocumento15 pagineLte Interview QuestionsĐinh Nhâm100% (1)
- Optimize XCAL user guide for SEO with concise titleDocumento22 pagineOptimize XCAL user guide for SEO with concise titleRF Optimization100% (2)
- 2G KPI TrainingDocumento14 pagine2G KPI Trainingcurtiskamoto100% (1)
- GSM Basic QuestionsDocumento11 pagineGSM Basic QuestionsAqęēļ ShèrGįļļNessuna valutazione finora
- RNPO Tutorial Engr SystemsDocumento161 pagineRNPO Tutorial Engr SystemsOmokuru NicholasNessuna valutazione finora
- LTE Interview1Documento5 pagineLTE Interview1Uzair SiddiquiNessuna valutazione finora
- LTE Signaling: Troubleshooting and OptimizationDa EverandLTE Signaling: Troubleshooting and OptimizationValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2)
- Mobile Terminal Receiver Design: LTE and LTE-AdvancedDa EverandMobile Terminal Receiver Design: LTE and LTE-AdvancedNessuna valutazione finora
- LTE Self-Organising Networks (SON): Network Management Automation for Operational EfficiencyDa EverandLTE Self-Organising Networks (SON): Network Management Automation for Operational EfficiencySeppo HämäläinenNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding UMTS Radio Network Modelling, Planning and Automated Optimisation: Theory and PracticeDa EverandUnderstanding UMTS Radio Network Modelling, Planning and Automated Optimisation: Theory and PracticeMaciej NawrockiNessuna valutazione finora
- Mobile WiMAX: A Systems Approach to Understanding IEEE 802.16m Radio Access TechnologyDa EverandMobile WiMAX: A Systems Approach to Understanding IEEE 802.16m Radio Access TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- VoLTE and ViLTE: Voice and Conversational Video Services over the 4G Mobile NetworkDa EverandVoLTE and ViLTE: Voice and Conversational Video Services over the 4G Mobile NetworkNessuna valutazione finora
- CAMEL: Intelligent Networks for the GSM, GPRS and UMTS NetworkDa EverandCAMEL: Intelligent Networks for the GSM, GPRS and UMTS NetworkValutazione: 2 su 5 stelle2/5 (1)
- Backhauling / Fronthauling for Future Wireless SystemsDa EverandBackhauling / Fronthauling for Future Wireless SystemsKazi Mohammed Saidul HuqNessuna valutazione finora
- 5g Radio Access Networks Complete Self-Assessment GuideDa Everand5g Radio Access Networks Complete Self-Assessment GuideValutazione: 1 su 5 stelle1/5 (2)
- Essential 4G Guide: Learn 4G Wireless In One DayDa EverandEssential 4G Guide: Learn 4G Wireless In One DayValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (12)
- BERT in Machine Learning - Aman KharwalDocumento8 pagineBERT in Machine Learning - Aman KharwalSarsij MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Population changes in upstate New York counties 2010-2018Documento3 paginePopulation changes in upstate New York counties 2010-2018Sarsij MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- MB RefDocumento631 pagineMB RefJames CauchiNessuna valutazione finora
- Treglia QGIS Tutorial 2 12Documento52 pagineTreglia QGIS Tutorial 2 12Suraj_SubediNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.3 Selection of Appropriate Data Analysis TechniqueDocumento15 pagine2.3 Selection of Appropriate Data Analysis TechniqueSarsij MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- English Health Claim Form L1Documento5 pagineEnglish Health Claim Form L1Gaurav TharejaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1 Introduction To Data AnalysisDocumento8 pagine1.1 Introduction To Data AnalysisAbdul MohammadNessuna valutazione finora
- Osm Data in Gis Formats Free PDFDocumento20 pagineOsm Data in Gis Formats Free PDFSarsij MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Latency Analysis and Reduction in A 4G NetworkDocumento93 pagineLatency Analysis and Reduction in A 4G Networkfabieste100% (1)
- S Presso BrochureDocumento14 pagineS Presso BrochureMayank Sharma100% (1)
- MBA HandBook2019Documento243 pagineMBA HandBook2019Anonymous MHMqCrzgTNessuna valutazione finora
- National Immunization ScheduleDocumento1 paginaNational Immunization ScheduleSudheer100% (1)
- Python Matplotlib Cheat SheetDocumento1 paginaPython Matplotlib Cheat SheetsreedharNessuna valutazione finora
- Features/Prameters LTE OptimizationDocumento3 pagineFeatures/Prameters LTE OptimizationFuzail Khan50% (2)
- Sector MakerDocumento1 paginaSector MakerthanhbdtNessuna valutazione finora
- Deep Learning Library Guide with Free Books, Courses, Videos & MoreDocumento3 pagineDeep Learning Library Guide with Free Books, Courses, Videos & MorerakikiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Sector MakerDocumento1 paginaSector MakerthanhbdtNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding Machine Learning Theory AlgorithmsDocumento449 pagineUnderstanding Machine Learning Theory AlgorithmsHigor EduardoNessuna valutazione finora
- LTE Best Practices Ebook CO-108320-EnDocumento71 pagineLTE Best Practices Ebook CO-108320-EnashishsinghchouhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Qgis Tutorial CompiledDocumento35 pagineQgis Tutorial CompiledSarsij MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- An Analysis of The Requirements For Session Border Control in IMS NetworksDocumento33 pagineAn Analysis of The Requirements For Session Border Control in IMS NetworksSarsij MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Treglia QGIS Tutorial 3 0Documento48 pagineTreglia QGIS Tutorial 3 0anggaxkusumaNessuna valutazione finora
- Evolution in Mobile Radio Networks: Multiple Antenna Systems & Flexible NetworksDocumento29 pagineEvolution in Mobile Radio Networks: Multiple Antenna Systems & Flexible NetworksSarsij MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Qgis Tutorial Compiled PDFDocumento174 pagineQgis Tutorial Compiled PDFhazim_74Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lte Measurement EventsDocumento15 pagineLte Measurement Eventscnt2ssk100% (2)
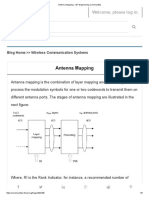
- Antenna Mapping - IET Engineering CommunitiesDocumento6 pagineAntenna Mapping - IET Engineering CommunitiesSarsij MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Big Data and The Telecom IndustryDocumento10 pagineBig Data and The Telecom IndustrySarsij MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Nokia Siemens Networks gratuity claim formDocumento2 pagineNokia Siemens Networks gratuity claim formSarsij MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Transmission Carrier-to-Noise Ratio, Signal-To PDFDocumento42 pagineDigital Transmission Carrier-to-Noise Ratio, Signal-To PDFSarsij MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Antenna Parameters Part 4 - Port To Port Isolation, Power Handling Ability and MoreDocumento5 pagineAntenna Parameters Part 4 - Port To Port Isolation, Power Handling Ability and MoreSarsij MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Nabila Shaffa Rizky Chandra: Listening Section Reading SectionDocumento1 paginaNabila Shaffa Rizky Chandra: Listening Section Reading Sectionnabila shaffaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gen Set Controller Ig NT GCDocumento222 pagineGen Set Controller Ig NT GCjun joie jr. ruizNessuna valutazione finora
- Pabx ProposalDocumento15 paginePabx ProposalAizat FaliqNessuna valutazione finora
- Copy For 3rd CotDocumento4 pagineCopy For 3rd CotJosephine RiveraNessuna valutazione finora
- EJM-08-2015-0591 Integrated Marketing Communication From An Instrumental To A CustomercentricDocumento28 pagineEJM-08-2015-0591 Integrated Marketing Communication From An Instrumental To A CustomercentricAkshay ChaudhryNessuna valutazione finora
- Hipertensi: Tekanan Darah TinggiDocumento33 pagineHipertensi: Tekanan Darah TinggiErika SetyodiharjoNessuna valutazione finora
- A Glossary of It Takes Two To Talk Strategies ForDocumento9 pagineA Glossary of It Takes Two To Talk Strategies ForMel Docampo33% (3)
- Overview of Unit:: English Year 8Documento2 pagineOverview of Unit:: English Year 8zaribugireNessuna valutazione finora
- Task 1b PlanningDocumento4 pagineTask 1b Planningapi-266573312Nessuna valutazione finora
- Marketing Budget Plan TemplateDocumento7 pagineMarketing Budget Plan Templateyat3nfk0Nessuna valutazione finora
- Internet Protocol: FunctionDocumento5 pagineInternet Protocol: FunctionSuganya AlagarNessuna valutazione finora
- Use Case Diagram Guidelines for Better Use CasesDocumento5 pagineUse Case Diagram Guidelines for Better Use CasesNguyễnTânQuýNessuna valutazione finora
- 5147 - C - CheatSheet - 2010 - BlueDocumento2 pagine5147 - C - CheatSheet - 2010 - BlueSayyad HasanNessuna valutazione finora
- Vicki Stevenson's authentic materials lesson planDocumento3 pagineVicki Stevenson's authentic materials lesson planVicki Jade Stevenson100% (1)
- Engineering Cisco Meraki Solutions 1Documento41 pagineEngineering Cisco Meraki Solutions 1Blue PitNessuna valutazione finora
- An Etymological Dictionary of Altaic LanguagesDocumento1.556 pagineAn Etymological Dictionary of Altaic LanguagesMehdi Hassani ArdabilliNessuna valutazione finora
- Niche Market DiscoveryDocumento44 pagineNiche Market DiscoveryAl SummersNessuna valutazione finora
- Collage - 5th Grade - 3Documento4 pagineCollage - 5th Grade - 3api-484991409Nessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Manifesting WorkbookDocumento8 pagineAdvanced Manifesting WorkbookJoao Na Miyuki75% (8)
- Gmail - Careers With EYDocumento5 pagineGmail - Careers With EYVasudev RNessuna valutazione finora
- Building Strong RelationshipsDocumento9 pagineBuilding Strong Relationshipsapi-547783947Nessuna valutazione finora
- Seicam 2020e PDFDocumento4 pagineSeicam 2020e PDFridwansuronoNessuna valutazione finora
- PANEL DISCUSSION TECHNIQUEDocumento29 paginePANEL DISCUSSION TECHNIQUESneha GavandeNessuna valutazione finora
- Rubric Assessment ReadingDocumento2 pagineRubric Assessment Readingsyedzaqhwan100% (8)
- Collins English For Life B1 SpeakingDocumento14 pagineCollins English For Life B1 SpeakingDoan, Thoai MD AdminNessuna valutazione finora
- The Digital Publishing Communications CircuitDocumento23 pagineThe Digital Publishing Communications CircuitobjetpetitlNessuna valutazione finora
- English ConversationDocumento3 pagineEnglish ConversationRianiNessuna valutazione finora
- College of Education: Lesson Plan in Profed06 ObjectivesDocumento3 pagineCollege of Education: Lesson Plan in Profed06 ObjectivesElmer Pajarito Belarmino100% (1)
- Media and Information Literacy: Quarter 4 - Module 1Documento28 pagineMedia and Information Literacy: Quarter 4 - Module 1Randy Reyes33% (3)
- Ijafb 2022 42 08 25Documento8 pagineIjafb 2022 42 08 25Austine Ampofo TwumasiNessuna valutazione finora