Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
1 Civil Disputes
Caricato da
api-2415052580 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
729 visualizzazioni8 pagineTitolo originale
1 civil disputes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
729 visualizzazioni8 pagine1 Civil Disputes
Caricato da
api-241505258Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 8
Civil Disputes
Civil Law is known as Private Law.
It regulates disputes between individuals;
between parties; and between individuals
and parties.
The main purpose of Civil Law is to
compensate victims.
Civil Actions include but are not
limited to the following:
Claims arising from
accidents;
Injuries done by one
person to anothers
body, property, or
reputation;
Divorces, child
custody, and support
claims;
Adoptions;
Failure to pay for
work done;
Non-payment of rent;
Unpaid debts.
The victim may bring
an action against the
person who
committed the civil
wrong for damages,
or some other civil
remedy.
Tort Law
Tort Law is a major division of Civil Law.
Tort means a wrong that is negligent.
A person who is found guilty of the
criminal offence of assault may have a civil
action (the tort of battery) filed against
him/her in order to compensate the
victim.
Some examples of an action
resulting in a crime and a tort:
If a person It may be a
crime of
And also the
tort of
Hits another
person
Assault Battery
Breaks into
someones
property
Break and Enter Trespass to
Land
Takes
someones
belongings
Theft Trespass to
Goods
Compensation usually translates to money
It is the responsibility of the injured party to bring the
action.
The action will be heard in a civil court; and if
satisfied, the court will award damages which it deems
suitable.
Criminal courts and Civil courts proceed separately
from one another.
It is up to the person who files the action to prove
that significant damages have occurred. (Reverse
Onus)
Homework
Read pg. 311+314, Answer Question #1-
4, pg. 314
Read pg. 314-315, Answer Question #1-4,
pg. 316
Read the Issue on pg. 312-313, Answer
Questions #1-5, pg. 313.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Handout 2 1 1Documento4 pagineHandout 2 1 1api-241505258Nessuna valutazione finora
- Theories of CrimeDocumento34 pagineTheories of Crimeapi-24150525892% (13)
- Torts Lecture 1 A-1Documento31 pagineTorts Lecture 1 A-1Sajad HussainNessuna valutazione finora
- Meaning of Trot Tort Law Is The Part of Law For Most Harms That Are Not Either Criminal or Based On A ContractDocumento11 pagineMeaning of Trot Tort Law Is The Part of Law For Most Harms That Are Not Either Criminal or Based On A ContractjulieNessuna valutazione finora
- Meaning of Trot Tort Law Is The Part of Law For Most Harms That Are Not Either Criminal or Based On A ContractDocumento11 pagineMeaning of Trot Tort Law Is The Part of Law For Most Harms That Are Not Either Criminal or Based On A ContractjulieNessuna valutazione finora
- Differences Between Civil Law and Criminal LawDocumento5 pagineDifferences Between Civil Law and Criminal LawAmita SinwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Law of TortsDocumento28 pagineLaw of TortsSam KariukiNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Tort LawDocumento3 pagineWhat Is Tort LawFaisal AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Madurai Kamraj BB4Documento16 pagineMadurai Kamraj BB4lovleshrubyNessuna valutazione finora
- Tort LawDocumento13 pagineTort LawAlisha Shabbir100% (1)
- Tort Law:: Intentional Torts, Such As A Claim For BatteryDocumento5 pagineTort Law:: Intentional Torts, Such As A Claim For BatteryIbadullah RashdiNessuna valutazione finora
- Torts PresentationDocumento6 pagineTorts PresentationShrida SupunyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Law of TortDocumento58 pagineLaw of TortStyle & FashionNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Law of TortsDocumento8 pagineIntroduction To Law of Tortstej chopraNessuna valutazione finora
- LAW OF TORT NotesDocumento33 pagineLAW OF TORT NotesGaurav Firodiya50% (2)
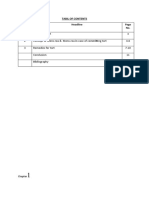
- 1 Meaning of Trot 3 2 Concept of Mens-Rea & Mens-Rea in Case of Committing Tort 4-6 3 Remedies For Tort 7-10 Conclusion 11 Bibliography 12Documento12 pagine1 Meaning of Trot 3 2 Concept of Mens-Rea & Mens-Rea in Case of Committing Tort 4-6 3 Remedies For Tort 7-10 Conclusion 11 Bibliography 12julieNessuna valutazione finora
- Law of TortDocumento17 pagineLaw of TortStyle & FashionNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Law of TortsDocumento16 pagineIntroduction To Law of TortsAyush KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To The Law of TortsDocumento15 pagineIntroduction To The Law of TortssrinivasaNessuna valutazione finora
- Short Note On TORT, Negligence & Consumer Protection & Motor ActDocumento17 pagineShort Note On TORT, Negligence & Consumer Protection & Motor ActNitin P. DholeNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is An Intentional Tort?: Negligence vs. IntentDocumento3 pagineWhat Is An Intentional Tort?: Negligence vs. IntentRhen Retoriano BarriosNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of LawDocumento5 pagineTypes of LawLaura NietoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cavendish Unversity Zambia: School of LawDocumento14 pagineCavendish Unversity Zambia: School of LawIsaac Museka LupupaNessuna valutazione finora
- Development of Torts in IndiaDocumento15 pagineDevelopment of Torts in IndiaArkaprava Bhowmik40% (5)
- Presentation ON THE LAW OF TORTS BY SMITA MOHANTY, LAWYER, ODISHA HIGH COURTDocumento59 paginePresentation ON THE LAW OF TORTS BY SMITA MOHANTY, LAWYER, ODISHA HIGH COURTSmita MohantyNessuna valutazione finora
- Law of TortsDocumento19 pagineLaw of TortsGitika TiwariNessuna valutazione finora
- Law of Torts New Syllabus 2020Documento27 pagineLaw of Torts New Syllabus 2020arjun0505Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lawoftorts-Notes-160317081339 (TORT NOTES) PDFDocumento17 pagineLawoftorts-Notes-160317081339 (TORT NOTES) PDFramu50% (2)
- Law of Tort Presentation Indore Institute of LawDocumento34 pagineLaw of Tort Presentation Indore Institute of Lawsharmamonika.123401Nessuna valutazione finora
- Legal LanguageDocumento15 pagineLegal LanguagealfiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Law of TortDocumento5 pagineThe Law of TortjoshuakalehmwalakhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Law of Tort - Project and FileDocumento16 pagineLaw of Tort - Project and Fileshubham tiwariNessuna valutazione finora
- NOTESDocumento3 pagineNOTESVed TutorialsNessuna valutazione finora
- Law of TortDocumento20 pagineLaw of Tortkuldeep gargNessuna valutazione finora
- Definition, Nature & Development of Tort Law-1Documento40 pagineDefinition, Nature & Development of Tort Law-1Dhinesh Vijayaraj100% (1)
- Nature and Scope of TortDocumento5 pagineNature and Scope of TortNayak Prem KiranNessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching Week 4 - Torts 2 (Other Torts)Documento31 pagineTeaching Week 4 - Torts 2 (Other Torts)Click HereNessuna valutazione finora
- Torts 1 FinalDocumento38 pagineTorts 1 Finaloiajwoa dgeaNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is A TortDocumento46 pagineWhat Is A Tortoiajwoa dgeaNessuna valutazione finora
- Law of Torts LAW1020 - Lecture Notes: Week 1Documento5 pagineLaw of Torts LAW1020 - Lecture Notes: Week 1Shajana ShahulNessuna valutazione finora
- Law of Torts: Presented By: Ajay Kumar Ayush Jain Chander Prakash Pratik Raj Pravin Singh Siddhartha RaghuwansiDocumento11 pagineLaw of Torts: Presented By: Ajay Kumar Ayush Jain Chander Prakash Pratik Raj Pravin Singh Siddhartha RaghuwansiShanil MallNessuna valutazione finora
- Law of Torts PDFDocumento3 pagineLaw of Torts PDFKalen TapakNessuna valutazione finora
- Law of TrotsDocumento4 pagineLaw of TrotsCharan Tej RudralaNessuna valutazione finora
- Civil LawDocumento6 pagineCivil LawCC OoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Law of TortsDocumento16 pagineIntroduction To Law of TortsSatakshi AnandNessuna valutazione finora
- TORTDocumento17 pagineTORTSabarNessuna valutazione finora
- K - 103 Law of TortDocumento34 pagineK - 103 Law of TortPravin Sinha100% (1)
- The Word Tort OriginatesDocumento8 pagineThe Word Tort OriginatesMkNessuna valutazione finora
- CIVIL LAWdd AND CRIMINAL LAWDocumento6 pagineCIVIL LAWdd AND CRIMINAL LAWaryanNessuna valutazione finora
- Q & A - Law of Torts - Very ImportantDocumento24 pagineQ & A - Law of Torts - Very Importantvijay.s12usNessuna valutazione finora
- Law of TortsDocumento51 pagineLaw of TortsBharathi S VNessuna valutazione finora
- Law of Torts 2020Documento84 pagineLaw of Torts 2020Gargi PandeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Legal Remedies Available For Mailicious Prosecution VictimsDocumento17 pagineLegal Remedies Available For Mailicious Prosecution VictimsUjjwal SabooNessuna valutazione finora
- Torts AssingmentDocumento2 pagineTorts Assingmentsmart prabhuNessuna valutazione finora
- TortsDocumento5 pagineTortsȘova AngelicaNessuna valutazione finora
- Law of Torts WithDocumento103 pagineLaw of Torts Withhassanbhaiff4546Nessuna valutazione finora
- Law of Tort FinalDocumento23 pagineLaw of Tort FinalIsha Goel67% (3)
- Law of TortsDocumento5 pagineLaw of TortsPrishita SaraiwalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Civil LawDocumento3 pagineCivil Lawfaisal awaisNessuna valutazione finora
- Diapositivas Primero y SeegundoDocumento70 pagineDiapositivas Primero y SeegundoRuben Antonio Hernández FloresNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Intro. To TortDocumento21 pagine1 Intro. To TorttumeloNessuna valutazione finora
- Adr Presentation 2018Documento6 pagineAdr Presentation 2018api-241505258Nessuna valutazione finora
- Criminal Code Treasure Hunt 2018Documento4 pagineCriminal Code Treasure Hunt 2018api-241505258100% (1)
- Mock Trial Roles 2019Documento4 pagineMock Trial Roles 2019api-241505258Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fids Presentation Worksheet Charter Cases 2017Documento4 pagineFids Presentation Worksheet Charter Cases 2017api-241505258Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ycja Note SheetDocumento8 pagineYcja Note Sheetapi-241505258Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ontario Human Rights Code Slide 2017Documento22 pagineOntario Human Rights Code Slide 2017api-241505258100% (1)
- Chapter 5Documento25 pagineChapter 5api-241505258Nessuna valutazione finora
- Termination: Filing An Employment Standards ClaimDocumento12 pagineTermination: Filing An Employment Standards Claimapi-241505258Nessuna valutazione finora
- Clu3m Fids Matheson V Lewis 2014Documento2 pagineClu3m Fids Matheson V Lewis 2014api-241505258Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cln4u SentencingDocumento17 pagineCln4u Sentencingapi-241505258Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Courts of Ontario FlowchartDocumento1 paginaThe Courts of Ontario Flowchartapi-241505258Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Sources of LawDocumento23 pagine1 Sources of Lawapi-2415052580% (1)
- Exam 11 LawreviewDocumento1 paginaExam 11 Lawreviewapi-241505258Nessuna valutazione finora
- Wsia 1Documento2 pagineWsia 1api-241505258Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Legal TheoryDocumento26 pagine2 Legal Theoryapi-24150525850% (2)
- Jurisdiction of Ontario CourtsDocumento3 pagineJurisdiction of Ontario Courtsapi-241505258Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mocktrialroles 2016Documento4 pagineMocktrialroles 2016api-241505258Nessuna valutazione finora
- LabourlawintroquizDocumento2 pagineLabourlawintroquizapi-241505258Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter1 TextDocumento27 pagineChapter1 Textapi-241505258Nessuna valutazione finora
- Clu3m Ontario Human Rights Code 2016 PPTX 1Documento31 pagineClu3m Ontario Human Rights Code 2016 PPTX 1api-241505258100% (1)
- LabourhistoryDocumento8 pagineLabourhistoryapi-241505258Nessuna valutazione finora
- Labourlawunitproject 2016Documento2 pagineLabourlawunitproject 2016api-241505258Nessuna valutazione finora
- LabourhistoryincanadaDocumento8 pagineLabourhistoryincanadaapi-241505258Nessuna valutazione finora