Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
506 Learning Plan Rubric
Caricato da
api-253792172Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
506 Learning Plan Rubric
Caricato da
api-253792172Copyright:
Formati disponibili
EDUC506: New Media Literacies in High Needs Schools
1
1
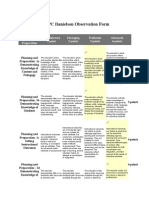
FINAL LEARNING PLAN RUBRIC
Component Beginning (0-11 points) Developing (12-15 points) Proficient (16-18 points) Accomplished (19-20 points) Comments
Supporting
Student
Learning
Evidence: The instructional design
does not support the stated
objective(s), nor is it stated how
students engage in meaningful
learning that fosters content area
skills. Developmentally appropriate
materials and resources are not
identified. Learning tasks have no
central focus or a one-dimensional
focus, may not be developmentally
appropriate and do not connect to the
larger subject matter curricular
framework.
Evidence: The instructional design
marginally supports the stated
objective(s) and somewhat engages
students in meaningful learning that
foster content area skills.
Developmentally appropriate
resources and materials are selected,
but not utilized effectively. Standards,
objectives and learning tasks are
primarily one- dimensional,
developmentally appropriate, and
have some connection to the larger
subject matter curricular framework.
Evidence: The instructional design
clearly supports the stated objective(s)
and is differentiated to address the needs
of most students and fosters content area
skills. Developmentally appropriate
resources and materials are utilized
effectively. Learning Tasks are multi-
dimensional, developmentally
appropriate and integrated into the
larger subject matter curricular
framework.
Evidence: The instructional design
clearly supports the stated objective(s)
and is differentiated to address the needs
of all students and fosters content area
skills. Students participate in its
development and in the selection of
resources, where appropriate. Learning
Tasks are multi-dimensional,
developmentally appropriate, integrated
into the larger subject matter curriculum
framework
Score: /20
Making
Curriculum
Content
Accessible
Evidence: Student characteristics,
experiences or prior learning have
little or no relationship to the learning
standards or objectives. Learning plan
does not incorporate accommodations
for a classroom with low tech, mid
tech, and high tech resources.
Evidence: Knowledge of student
characteristics, use of prior learning
or experiential backgrounds, and
support to help students who often
struggle with the content. Learning
plan marginally incorporates
accommodations for a classroom with
low tech, mid tech, and high
tech resources.
Evidence: Knowledge of student
characteristics, use of prior learning and
experiential backgrounds, and
scaffolding or other structured support
to provide access to grade level
curriculum. Learning plan incorporates
accommodations for a classroom with
low tech, mid tech, and high tech
resources, with some limitations.
Evidence: Knowledge of student
characteristics, use of prior learning and
experiential backgrounds and well-
integrated instructional strategies that
support students who struggle to access
grade level curriculum. Learning plan
incorporates detailed and appropriate
accommodations for a classroom with
low tech, mid tech, and high tech
resources.
Score: /20
Demonstrating
Knowledge of
Content and
Pedagogy
Evidence: Teacher demonstrates
minimal understanding of the subject,
the structure of the discipline, or the
content-related pedagogy as
evidenced by content misconceptions
and uncorrected errors within
submitted documentation. Theory or
research is not referenced or is
significantly misapplied. Content-
based literacy skills and New Media
Literacy skills are not introduced or
addressed in the learning plan design.
Evidence: Teacher demonstrates a
marginal understanding of the
subject, the structure of the discipline,
or the content-related pedagogy as
evidenced by the submitted
documentation. Knowledge
consistent with key principles of
theory and research. Content-based
literacy skills and New Media
Literacy skills are marginally
introduced or addressed in the
learning plan design.
Evidence: Teacher demonstrates solid
understanding of the subject, the
structure of the discipline, and the
content-related pedagogy as evidenced
by submitted documentation. Teachers
planning practices reflect sound
pedagogical knowledge. Sound
knowledge of research and theory linked
to knowledge of students in the class.
Content-based literacy skills and New
Media Literacy skills are introduced and
addressed in the learning plan design,
with limitations.
Evidence: Teacher demonstrates an
extensive understanding of the subject,
the structure of the discipline, and the
content-related pedagogy as evidenced
by submitted documentation. Teachers
planning anticipates student needs and
demonstrates a continuing search for
improved practice. Sound knowledge of
research and theory integrated with
knowledge about content and students.
Content-based literacy skills and New
Media Literacy skills are adequately
introduced and appropriately addressed
in the learning plan design.
Score: /20
Developing Evidence: The candidate gives little Evidence: The candidate uses Evidence: The candidates use of Evidence: The candidates use of Score: /20
EDUC506: New Media Literacies in High Needs Schools
2
2
Academic
Language
or sporadic support to students to
meet the language demands of the
learning tasks.
Language and/or content is
oversimplified to the point of limiting
student access to the core content
1
of
the curriculum.
scaffolding or other support
2
to
address identified gaps between
students current language abilities
and the language demands of the
learning tasks and assessments,
including selected genres and key
linguistic features.
Candidate articulates why
instructional strategies chosen are
likely to support aspects of students
language development.
scaffolding or other support provides
access to core content while also
providing explicit models, opportunities
for practice, and feedback for students
to develop further language proficiency
for selected genres and key linguistic
features.
Candidate articulates why the
instructional strategies chosen are likely
to support specific aspects of students
language development for different
levels of language proficiency.
scaffolding or other support provides
access to core content while also
providing explicit models, opportunities
for practice, and feedback for students
to develop further language proficiency
for selected genres and key linguistic
features.
Candidate articulates why the
instructional strategies chosen are likely
to support specific aspects of students
language development for the full range
of language proficiency and projects
ways in which the scaffolds can be
removed as proficiency increases.
Assessments
and Reflective
Analysis that
allow for Depth
of
Understanding
Evidence: Teachers plan to assess
and reflective analysis of learning
plan does not contain clear criteria or
standards, and does not measure the
learning outcomes described in the
instructional objectives. Teacher has
no plans to use assessment results in
designing future instruction.
Reflections are erroneously supported
through a significant misapplication
of theory or research principles.
Candidate does not identify areas of
instruction with which s/he is
challenged or desires improvement.
Evidence: Teachers plan for student
assessment and reflective analysis of
learning plan includes criteria and
standards that are not entirely clear
and/or understood by students, but
partially measure the learning
outcomes described in the
instructional objective(s). Teacher
uses the assessment to plan for future
instruction for the class as a whole
and uses productive and receptive
modalities. Reflections are consistent
with principles from theory and
research. Candidate identifies some
areas of instruction with which s/he is
challenged or desires improvement,
with limitations.
Evidence: Teachers plan for student
assessment and reflective analysis of
learning plan includes clear assessment
criteria and standards that have been
communicated to the students, and
effectively measure the learning
outcomes described in the instructional
objective(s). Teacher uses the
assessment to plan for groups of
students and individuals and uses
productive and receptive modalities.
Reflections are based on sound
knowledge of research and theory linked
to knowledge of students in the class.
Candidate identifies areas of instruction
with which s/he is challenged or desires
improvement.
Evidence: Teachers plan for student
assessment and reflective analysis of
learning plan includes clear assessment
criteria and standards that are not only
understood by the students, but also
shows evidence of student participation
in their development. Students use the
assessment to monitor their own
progress in achieving the learning
outcomes and uses productive and
receptive modalities. Reflections are
multi-dimensional and integrate sound
knowledge of research and theory about
teaching practice, knowledge of students
in the class, and knowledge of content.
Candidate identifies specific areas of
instruction with which s/he is
challenged or desires improvement.
Score: /20
Descriptive Feedback: Total Points: / 100
1
Core content is the set of facts, concepts, skills, and abilities that are absolutely necessary to participate at least minimally in the learning/assessment tasks in the learning segment.
2
Such support might include one or more of the following: modeling of strategies for comprehending or constructing texts such as a sonnet; explicit communication of the expected features of oral or written texts (e.g., using rubrics,
models, and frames); use of strategies that provide visual representations of content while promoting literacy development (e.g., graphic organizers); vocabulary development techniques (context cues, categorization, analysis of word parts,
etc.); opportunities to work together with students with different kinds of language and literacy skills, etc.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- CST Students with Disabilities: New York State Teacher CertificationDa EverandCST Students with Disabilities: New York State Teacher CertificationNessuna valutazione finora
- SDLC Instructional Performance Rating Rubric Fy13Documento9 pagineSDLC Instructional Performance Rating Rubric Fy13api-184947815Nessuna valutazione finora
- Otes Rubric and MapDocumento5 pagineOtes Rubric and Mapapi-237658564Nessuna valutazione finora
- Final Evaluation - Janet WellmanDocumento13 pagineFinal Evaluation - Janet Wellmanapi-384686461Nessuna valutazione finora
- Finaleval Ug TrevantDocumento13 pagineFinaleval Ug Trevantapi-395319636Nessuna valutazione finora
- Finaleval Ug TrevantDocumento13 pagineFinaleval Ug Trevantapi-395319636Nessuna valutazione finora
- Framework For EvaluationDocumento7 pagineFramework For Evaluationapi-236831571Nessuna valutazione finora
- Domain 1 Teacher Self-ReflectionDocumento3 pagineDomain 1 Teacher Self-ReflectionleezenarosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Domain 1Documento1 paginaDomain 1api-325413961Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan 2Documento6 pagineLesson Plan 2api-299978111Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lisa EvalDocumento5 pagineLisa Evalapi-203365948Nessuna valutazione finora
- Joel ObservationDocumento8 pagineJoel Observationapi-258404762Nessuna valutazione finora
- Final Evaluation JohnDocumento4 pagineFinal Evaluation Johnapi-246211386Nessuna valutazione finora
- Module e pt27s2013-1428129Documento25 pagineModule e pt27s2013-1428129api-235755026Nessuna valutazione finora
- Program of Studies and Instructional Procedures ANDREDocumento13 pagineProgram of Studies and Instructional Procedures ANDREMichael CalesajrNessuna valutazione finora
- Intended vs. Implemented vs. Achieved CurriculumDocumento36 pagineIntended vs. Implemented vs. Achieved Curriculumdangkusay94% (63)
- Teaching Standards Performance Criteria Rubric - Adapted From Charlotte DanielsonDocumento5 pagineTeaching Standards Performance Criteria Rubric - Adapted From Charlotte Danielsonapi-250421371Nessuna valutazione finora
- Va Teacher Standards Look Fors CombinedDocumento28 pagineVa Teacher Standards Look Fors CombinedMary McDonnell100% (1)
- Media Specialist ObservationDocumento8 pagineMedia Specialist Observationapi-362532338Nessuna valutazione finora
- Se JJ 1Documento13 pagineSe JJ 1api-403227537Nessuna valutazione finora
- Kentuckyteacherstandards 2Documento11 pagineKentuckyteacherstandards 2api-320207927Nessuna valutazione finora
- Final Evaluation AdeliDocumento13 pagineFinal Evaluation Adeliapi-301715328Nessuna valutazione finora
- MAT Conceptual FrameworkDocumento29 pagineMAT Conceptual FrameworkNewboy45Nessuna valutazione finora
- TEAL Lesson PlanningDocumento3 pagineTEAL Lesson PlanningLee Siu FongNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan Rubric: ElementDocumento4 pagineLesson Plan Rubric: Elementapi-317463324Nessuna valutazione finora
- T-TESS Rubric & Documentation: Domain 1.1: Standards and AlignmentDocumento17 pagineT-TESS Rubric & Documentation: Domain 1.1: Standards and AlignmentSofia Violeta100% (1)
- CT Observation Lesson 2Documento5 pagineCT Observation Lesson 2api-219913113Nessuna valutazione finora
- Gs-Assessing The CurriculumDocumento36 pagineGs-Assessing The CurriculumRon Joseph Eugenio CortezNessuna valutazione finora
- ENGLISH I Secondary Education Curriculum 2010Documento39 pagineENGLISH I Secondary Education Curriculum 2010Ludger KresnikNessuna valutazione finora
- Action Research Assignment and Rubric Spring 2016Documento4 pagineAction Research Assignment and Rubric Spring 2016api-209955250Nessuna valutazione finora
- Site Teacher EvaluationDocumento5 pagineSite Teacher Evaluationapi-210610643Nessuna valutazione finora
- Final Student Teacher EvaluationDocumento5 pagineFinal Student Teacher Evaluationapi-315681675Nessuna valutazione finora
- Student Teaching Final Evaluation 2013Documento5 pagineStudent Teaching Final Evaluation 2013api-213638088Nessuna valutazione finora
- Final Evaluation JaniceDocumento4 pagineFinal Evaluation Janiceapi-246211386Nessuna valutazione finora
- Learning Outcomes and Learning Experiences For Technically Developed Curriculum Projects in TESL Dr. Azadeh AsgariDocumento28 pagineLearning Outcomes and Learning Experiences For Technically Developed Curriculum Projects in TESL Dr. Azadeh AsgariDr. Azadeh AsgariNessuna valutazione finora
- MIDTERM EXAM IN CURRICULUM PLANNINGDocumento3 pagineMIDTERM EXAM IN CURRICULUM PLANNINGmbberaldeNessuna valutazione finora
- Instructional PlanningDocumento6 pagineInstructional PlanningMarienel Ilagan100% (1)
- OTES Rubric 2016-17 Accomplished Only Cheat SheetDocumento8 pagineOTES Rubric 2016-17 Accomplished Only Cheat SheetsaxbillNessuna valutazione finora
- Performance Appraisal Rubric 1Documento8 paginePerformance Appraisal Rubric 1api-250808296Nessuna valutazione finora
- Learning OutcomesDocumento13 pagineLearning Outcomesnegmatovabarno67Nessuna valutazione finora
- Curriculum Development and Evaluation With Emphasis On TrainerDocumento9 pagineCurriculum Development and Evaluation With Emphasis On TrainerRoxanne MaghuyopNessuna valutazione finora
- Professional Learning PlanDocumento13 pagineProfessional Learning Planapi-319867689Nessuna valutazione finora
- Teacher Candidate Observation Instrument Spring 2014 Field Experience OnlyDocumento10 pagineTeacher Candidate Observation Instrument Spring 2014 Field Experience Onlyapi-409593396Nessuna valutazione finora
- Intended VsDocumento14 pagineIntended VsRyan Morales67% (3)
- Leon Final 2015 SpringDocumento5 pagineLeon Final 2015 Springapi-280368887Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dip Ed Booklet Updated December 2014Documento23 pagineDip Ed Booklet Updated December 2014Rosana HerreroNessuna valutazione finora
- Providing District Support - AARPE 1 and 2 Combined STD 1 Teacher Look ForsDocumento7 pagineProviding District Support - AARPE 1 and 2 Combined STD 1 Teacher Look ForsjenNessuna valutazione finora
- Jackie Wedick Final Evaluation Spring 2015Documento5 pagineJackie Wedick Final Evaluation Spring 2015api-279117953Nessuna valutazione finora
- First Year - Summative Evaluation - April 2016Documento16 pagineFirst Year - Summative Evaluation - April 2016api-264963856Nessuna valutazione finora
- Us Observation Feedback Form 2 - Darius WimbyDocumento4 pagineUs Observation Feedback Form 2 - Darius Wimbyapi-291004299Nessuna valutazione finora
- Final Evaluation From GingerDocumento5 pagineFinal Evaluation From Gingerapi-282581952Nessuna valutazione finora
- Us Observation Lesson 3Documento5 pagineUs Observation Lesson 3api-219913113Nessuna valutazione finora
- Monika Obs 1Documento9 pagineMonika Obs 1api-311130965Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cus3701 - MQC Assignment 1Documento5 pagineCus3701 - MQC Assignment 1Shanté MichealsNessuna valutazione finora
- Important Factors While Developing Text BooksDocumento7 pagineImportant Factors While Developing Text Booksmaila amjadNessuna valutazione finora
- 0311 CG2 EnglishDocumento115 pagine0311 CG2 EnglishstellmendzNessuna valutazione finora
- Curriculum Compacting: An Easy Start to Differentiating for High Potential StudentsDa EverandCurriculum Compacting: An Easy Start to Differentiating for High Potential StudentsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- The Structured Method of Pedagogy: Effective Teaching in the Era of the New Mission for Public Education in the United StatesDa EverandThe Structured Method of Pedagogy: Effective Teaching in the Era of the New Mission for Public Education in the United StatesNessuna valutazione finora
- Becoming a Better Science Teacher: 8 Steps to High Quality Instruction and Student AchievementDa EverandBecoming a Better Science Teacher: 8 Steps to High Quality Instruction and Student AchievementNessuna valutazione finora
- Challenges of MultilingualismDocumento5 pagineChallenges of MultilingualismSakshi SadhanaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Impact of Technology On EducationDocumento8 pagineThe Impact of Technology On EducationAnalyn LaridaNessuna valutazione finora
- Development of ESP Materials For AccountingDocumento7 pagineDevelopment of ESP Materials For AccountingI Gde Rama Putra YudaNessuna valutazione finora
- Listening SkillsDocumento9 pagineListening SkillsMohd Shabir100% (1)
- Math 8 ADocumento4 pagineMath 8 Aapi-280517032Nessuna valutazione finora
- Measurement and EvaluationDocumento18 pagineMeasurement and Evaluationaparna100% (3)
- Bon Air Close Reading WorksheetDocumento4 pagineBon Air Close Reading Worksheetapi-280058935Nessuna valutazione finora
- Background of Curriculum DevelopmentDocumento44 pagineBackground of Curriculum DevelopmentKL PablicoNessuna valutazione finora
- Wilmington Head Start IncDocumento10 pagineWilmington Head Start Incapi-355318161Nessuna valutazione finora
- 01.what Is Floppy S Phonics Sounds and LettersDocumento1 pagina01.what Is Floppy S Phonics Sounds and LettersClaudiaCGNessuna valutazione finora
- Critical Period HypothesisDocumento17 pagineCritical Period HypothesisYaoJia100% (2)
- Reading and Writing q1 w3 Mod3Documento12 pagineReading and Writing q1 w3 Mod3Renz Ian T. Dacoron100% (1)
- 2016 ProgramBook PDFDocumento360 pagine2016 ProgramBook PDFeugeniu222Nessuna valutazione finora
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocumento2 pagineDepartment of Education: Republic of The Philippinesami mendiolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Annex 2 FOrm For HGPDocumento2 pagineAnnex 2 FOrm For HGPDaisy Timajo ValledorNessuna valutazione finora
- Delasa, Afric John Arkoncel, KouchiDocumento4 pagineDelasa, Afric John Arkoncel, KouchiGa MusaNessuna valutazione finora
- Strong Interest Inventory Manual 2012 SupplementDocumento129 pagineStrong Interest Inventory Manual 2012 SupplementBobby Antonio0% (1)
- KARL BÜHLER'S AND ERNST CASSIRER'S - Verbum - XXXI - 1-2 - 1 - 4 - HalawaDocumento24 pagineKARL BÜHLER'S AND ERNST CASSIRER'S - Verbum - XXXI - 1-2 - 1 - 4 - HalawaMeti MallikarjunNessuna valutazione finora
- Lee (2006) Humor in Academic DiscourseDocumento20 pagineLee (2006) Humor in Academic Discoursefaze2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Model Form NotesDocumento7 pagineModel Form NotesDianita PachecoNessuna valutazione finora
- Instrument Flying Handbook PDFDocumento371 pagineInstrument Flying Handbook PDFAshmi ShajiNessuna valutazione finora
- PPSTDocumento2 paginePPSTHasanor MatanogNessuna valutazione finora
- Application FormDocumento5 pagineApplication Formrenzenzo92Nessuna valutazione finora
- Edu 214 Midterm Part 1Documento4 pagineEdu 214 Midterm Part 1api-309089718Nessuna valutazione finora
- Form 1. School Learning Outcomes Assessment and Intervention ReportDocumento2 pagineForm 1. School Learning Outcomes Assessment and Intervention ReportCedrick PerenaNessuna valutazione finora
- 7 The Dition Standards and IndicatorsDocumento25 pagine7 The Dition Standards and IndicatorslionelremediosNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategies To Teach SpeakingDocumento14 pagineStrategies To Teach SpeakingDías Académicos Sharing SessionsNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding Unemployment in IndiaDocumento16 pagineUnderstanding Unemployment in IndiaSanthosh Kumar0% (1)
- Critical Reasoning Strategy Guide - by Veera KarthikDocumento52 pagineCritical Reasoning Strategy Guide - by Veera KarthikVeera karthik100% (2)
- Curriculum Vitae: Name E-Mail ID MobileDocumento2 pagineCurriculum Vitae: Name E-Mail ID MobileAvik KunduNessuna valutazione finora