Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Goodman 1
Caricato da
Manoj BallaDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Goodman 1
Caricato da
Manoj BallaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
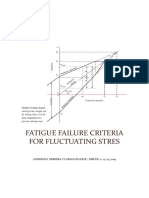
Goodman and Soderberg Failure Criteria a Sy Yield Line Sf
Goodman Failure Line Soderberg Failure Line m Sy
Soderberg m m + b = a m( 0) + b = S f m( S y ) + b = 0 b = Sf m= Sf Sy Sf Sy Goodman m m + b = a m( 0) + b = S f m( S ut ) + b = 0 b = Sf m= Sf S ut Sf S ut m + S f = a
Sut
m + S f = a
m Sf 1 S =a y
S f 1 m = a S ut
What happens if the alternating stress is low and constant, but the mean stress continues to increase ?
Sy
Sf
a Load Line m
Failure
Goodman Failure Line m Sy Sut
The ratio of
m + S y = 'a (equation of yield line) m = ' a + S y n= m 'm
to
is the factor of safety
Vary alternating stress and hold mean stress constant
a Sy Yield Line Sf
a m
Goodman Failure Line m Sy Sut
' S f 1 m = a S ut n= a 'a
ratio of
to
is the factor of safety
maintain load line ratio, increase alternating and mean stresses
a Sy Yield Line Sf
Goodman Failure Line m Sy Sut
'a m = S f 1 m 'm S ut Sf ' m a + = Sf ' m S ut m = Sf 'a S f + ' m S ut
n=
m 'm
Given the following information, construct a Goodman Failure Diagram and determine factors of safety considering constant alternating stress and increasing mean stress, constant mean stress and increasing alternating stress, and increasing mean and alternating stress with a constant load line slope. a = 8.72 ksi m = 10.5 ksi Sut = 80 ksi Sy = 60 ksi Sf = 21.8 ksi
Potrebbero piacerti anche
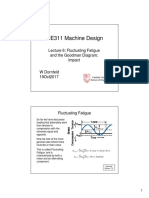
- ME311 Machine Design: Lecture 6: Fluctuating Fatigue and The Goodman Diagram ImpactDocumento24 pagineME311 Machine Design: Lecture 6: Fluctuating Fatigue and The Goodman Diagram Impactamalendu_biswas_1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Non-Symmetrical Cyclic Stress: Time - TDocumento2 pagineNon-Symmetrical Cyclic Stress: Time - TrevandifitroNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson No. 8 in Machine Design 1Documento7 pagineLesson No. 8 in Machine Design 1Carl JavierNessuna valutazione finora
- Fatigue Failure Criteria For Fluctuating StressDocumento5 pagineFatigue Failure Criteria For Fluctuating Stressaura lucia benavidesNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson No. 8 in Machine Design 1Documento7 pagineLesson No. 8 in Machine Design 1Carl JavierNessuna valutazione finora
- Prof. Zongjin Li Department of Civil Engineering: CIVL 111 Construction MaterialsDocumento61 pagineProf. Zongjin Li Department of Civil Engineering: CIVL 111 Construction MaterialsniroNessuna valutazione finora
- Fatigue ANalysis SN CurveDocumento11 pagineFatigue ANalysis SN CurveM Rafiq RajaNessuna valutazione finora
- UntitledDocumento13 pagineUntitledZulfiqar AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 09Documento119 pagineChapter 09vschein333Nessuna valutazione finora
- Me 311 Machine Design Notes 06Documento12 pagineMe 311 Machine Design Notes 06AdiKurdiNessuna valutazione finora
- FFT 5Documento13 pagineFFT 5Avinash Kumar Jha 4-Year B.Tech. Mechanical EngineeringNessuna valutazione finora
- Design For Variable Loading 2 2012Documento43 pagineDesign For Variable Loading 2 2012tianshuguoNessuna valutazione finora
- GP208 Spring 2020 Homework 1 Edx SolutionsDocumento6 pagineGP208 Spring 2020 Homework 1 Edx Solutionsdeivy ardila100% (1)
- Advanced Mechanical Design: by Dr. Syed IsmailDocumento16 pagineAdvanced Mechanical Design: by Dr. Syed IsmailvijayNessuna valutazione finora
- Fatigue and Fracture MechanicsDocumento77 pagineFatigue and Fracture MechanicsrunondiveshNessuna valutazione finora
- Fatigue DesignDocumento83 pagineFatigue DesignPrathamNessuna valutazione finora
- Fatigue AnalysisDocumento8 pagineFatigue Analysisaap1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chap06 Fatigue PDFDocumento30 pagineChap06 Fatigue PDFAlex IskandarNessuna valutazione finora
- Tresca - Von MisiesDocumento5 pagineTresca - Von MisiesNIr HillerNessuna valutazione finora
- 4-1 Low Cycle Fatigue - High Cycle Fatigue - BDocumento9 pagine4-1 Low Cycle Fatigue - High Cycle Fatigue - BkandeabigaelNessuna valutazione finora
- Task 5 (Matmod)Documento3 pagineTask 5 (Matmod)Zharif SangkulaNessuna valutazione finora
- Smith-Waterman Algorithm: AMPP 0708-Q1 Eduard Ayguade Juan J. Navarro Dani Jimenez-GonzalezDocumento18 pagineSmith-Waterman Algorithm: AMPP 0708-Q1 Eduard Ayguade Juan J. Navarro Dani Jimenez-GonzalezquyetthNessuna valutazione finora
- 2:5 Design For Cyclic Loading: 1. Completely Reversing Cyclic Stress and Endurance StrengthDocumento8 pagine2:5 Design For Cyclic Loading: 1. Completely Reversing Cyclic Stress and Endurance StrengthasmauzumNessuna valutazione finora
- Mohr Circle1 PDFDocumento5 pagineMohr Circle1 PDFFatima KhalidNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic1 StaticstaticDocumento25 pagineTopic1 StaticstaticعلاءإدريسNessuna valutazione finora
- Fatigue Failure Theories:: Soderberg Line, Goodman Line and Gerber's ParabolaDocumento5 pagineFatigue Failure Theories:: Soderberg Line, Goodman Line and Gerber's ParabolaHanan ShayiboNessuna valutazione finora
- Stability Analysis Procedures - Theory and LimitationsDocumento41 pagineStability Analysis Procedures - Theory and LimitationsAndyra Jaiz BadduNessuna valutazione finora
- EN380 Naval Materials Science and Engineering Course Notes, U.S. Naval AcademyDocumento13 pagineEN380 Naval Materials Science and Engineering Course Notes, U.S. Naval AcademyMahmoudNessuna valutazione finora
- سفاري - 11 - 10 - 2023، 12:55 مDocumento1 paginaسفاري - 11 - 10 - 2023، 12:55 مMaryam ʚiïɞNessuna valutazione finora
- Dynamic Behavior of Jack-Up ISOPE10Documento36 pagineDynamic Behavior of Jack-Up ISOPE10Imran Siddiqui100% (1)
- Chapter Six: Sections 6.1 - 6.3Documento22 pagineChapter Six: Sections 6.1 - 6.3Çhêrê Løýãl ÇhêrêNessuna valutazione finora
- Cover+lampiran Perhitungan+lampiran Foto Go 8Documento6 pagineCover+lampiran Perhitungan+lampiran Foto Go 8yosefinmargaretta3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sucesiones Tipo PolinomioDocumento1 paginaSucesiones Tipo PolinomiomichingonNessuna valutazione finora
- Yield CriterionDocumento36 pagineYield CriterionravindrababugNessuna valutazione finora
- FATIGUE Analysis NotesDocumento52 pagineFATIGUE Analysis NotesNITESH BORKARNessuna valutazione finora
- Failure Theory in MetalsDocumento16 pagineFailure Theory in MetalsManoj SainiNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic2 FatigueDocumento36 pagineTopic2 Fatigue777894292Nessuna valutazione finora
- Strength of Material and Machine DesigneDocumento668 pagineStrength of Material and Machine DesigneMunir AlaqiliNessuna valutazione finora
- Appendix E Ramberg-Osgood Stress-Strain Curve For Base MaterialDocumento4 pagineAppendix E Ramberg-Osgood Stress-Strain Curve For Base Materialanno_xNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanics of MaterialsDocumento34 pagineMechanics of MaterialsCharn69% (16)
- Yield CriteriaDocumento23 pagineYield CriteriaJuan MNessuna valutazione finora
- AERO 404-Sp22-Fatigue-1Documento25 pagineAERO 404-Sp22-Fatigue-1Shanmukha SrinivasNessuna valutazione finora
- Portfolio MGMT - Marathon - With FormulaeDocumento159 paginePortfolio MGMT - Marathon - With FormulaeHariKrishna ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Failure CriteriaDocumento11 pagineFailure Criteriavickyflyer1Nessuna valutazione finora
- V e V e: V V Voltage reflection coefficient - Complex = + − ΓDocumento13 pagineV e V e: V V Voltage reflection coefficient - Complex = + − ΓTomáš ShejbalNessuna valutazione finora
- Z-Value Calculation: August 18, 1999Documento9 pagineZ-Value Calculation: August 18, 1999atul110045Nessuna valutazione finora
- GP208 HW1 State of Stress Solutions PDFDocumento6 pagineGP208 HW1 State of Stress Solutions PDFSofiaNessuna valutazione finora
- GP208 HW1 State of Stress SolutionsDocumento6 pagineGP208 HW1 State of Stress SolutionsIsaac Muñoz100% (1)
- ML2 MohrCircleDocumento5 pagineML2 MohrCircleAnonymous ep7LE5ZdP5Nessuna valutazione finora
- ENTC 376 Chapter 9 Lecture Notes-III-Stress TransformationDocumento27 pagineENTC 376 Chapter 9 Lecture Notes-III-Stress TransformationYahia Raad Al-AniNessuna valutazione finora
- Report Fatigue PDFDocumento21 pagineReport Fatigue PDFHassan Aero100% (1)
- Mat 124 TheoryDocumento1 paginaMat 124 Theorymustafa sertNessuna valutazione finora
- Geardesign Team 1 3EM2Documento11 pagineGeardesign Team 1 3EM2Dries CaersNessuna valutazione finora
- PoM-4.6-Spearman Rank Correlation and RegressionDocumento33 paginePoM-4.6-Spearman Rank Correlation and RegressionDhiraj SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- International StandardDocumento10 pagineInternational StandardManoj BallaNessuna valutazione finora
- WeldingDocumento34 pagineWeldingManoj BallaNessuna valutazione finora
- Rail Track Material Catalogue Nov17Documento44 pagineRail Track Material Catalogue Nov17Manoj BallaNessuna valutazione finora
- AsmeDocumento11 pagineAsmeManoj BallaNessuna valutazione finora
- API 510 Exam - 5C - Answer - KeyDocumento1 paginaAPI 510 Exam - 5C - Answer - KeyManoj BallaNessuna valutazione finora
- Radiographic Interpretation: Radiographs of WeldsDocumento22 pagineRadiographic Interpretation: Radiographs of WeldsManoj BallaNessuna valutazione finora
- 3rd Party-NDT-CCS-Post Weld Heat Treatement Procedure For SAPID Approval PDFDocumento11 pagine3rd Party-NDT-CCS-Post Weld Heat Treatement Procedure For SAPID Approval PDFManoj Balla100% (1)
- UT Thickness ProcedureDocumento8 pagineUT Thickness ProcedureManoj Balla100% (3)
- ASNT Level III MT Questions and Answers PDFDocumento20 pagineASNT Level III MT Questions and Answers PDFManoj Balla100% (5)
- CSWIP Welding Inspection Plate Section PracticalDocumento31 pagineCSWIP Welding Inspection Plate Section PracticalManoj Balla100% (3)
- Pipe Chart PDFDocumento2 paginePipe Chart PDFCarlos Rivera0% (1)