Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
Caricato da
Mat RootDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
Caricato da
Mat RootCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Some Basic concepts of chemistry
1 mole = 6.02 1023 particles = 1g. atom or 1 g molecule NA = 6.02 1023 1 a.m.u = Equivalent mass = Average atomic mass = g
Molarity (M) =
Molarity (m) =
Normality (N) =
Mole fraction Atomic mass = Equivalent mass Valency Dilution formula : M1V1 = M2V2
Atomic Structure E = h = h = h0 + K.E (Photoelectric effect) (a0 = 52.9 m)
deBroglie equation
Equilibrium Heisenberg uncertainity principle : Number of orbitals in a shell = n2 Number of electrons in a shell = 2n2 Number of radial nodes = (n l 1) (H = number of Hybrid orbitals) Bond order = States of matter Boyles law : P1V1 = P2V2 Charles law : Ideal gas equation : PV = nRT Daltons law : PTotal = P1 + P2 + P3 + ...... Density = g/cm3 KP = KC(RT)n Kw = [H+] [OH] pH = log [H+] pKw = pH + pOH Ka = C2 Kw = Ka Kb Ksp = [Ar+]x [Bx]y
Chemical Bonding
Solid State
Packing fraction : Simple cubic = Braggs equation d = nsin
, FCC =
, BCC =
Solution Henrys law X(g) = KH.P Raoults law : v.p. of solution = xAPA0 + XBPB0 Relative lowering of V.P. : Tb = i kbm Tf = i kfm = CRT
dgas =
Grahams Law
Vander waals equation : CP CV = nRT Kinetic gas equation :
Chemical Thermodynamics U = qv, H = qp H = U + ngRT C = (C = Heat capacity)
Electrochemistry G =
U = q + w (First law) H = G = H TS G = RT ln K
Aluminium Chloride :
Berrilium Chloride : BeCl2 : CO : , CO2 : O = C = O
W = ZIt
Chemical Kinetics Rate = K[A]x [B]y SiO2 :
K = Linear Silicone :
k = Ae Ea/RT
Temperature coefficient =
Yellow P :
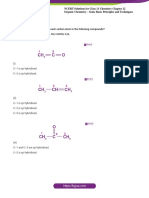
Important Structureal formula
Hydrogen peroxide : H2O2 : Water :
P4O10 :
NO2 :
N2O5 :
Orthoboric acid (H3BO3) :
HNO3 :
Diborane (B2H6) :
H4P2O7 :
Boron triflouride (BF3) :
SO2 :
H2SO4 :
BrF3 :
HClO4 :
MnO4 :
Cr2O72 :
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Inorganic ChemistryDocumento10 pagineInorganic Chemistrydebraj sethi100% (1)
- 01 Some Basic Concept of Chemistry Formula Sheets Quizrr PDFDocumento7 pagine01 Some Basic Concept of Chemistry Formula Sheets Quizrr PDFKalyana ChakravarthiNessuna valutazione finora
- Quick Revision CapsuleDocumento18 pagineQuick Revision CapsuleRacsGamer100% (1)
- Revision Capsule - Chemistry PDFDocumento8 pagineRevision Capsule - Chemistry PDFpytr100% (1)
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids NotesDocumento74 pagineAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Notessamay gujratiNessuna valutazione finora
- Trends in Inorganic ChemistryDocumento3 pagineTrends in Inorganic Chemistryrkstudyc_gmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Kcet 2021Documento9 pagineChemistry Kcet 2021Kirti Vinodkumar JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocumento37 pagineAldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acidsssheeladevi84100% (1)
- Modern Physics Formula SheetDocumento4 pagineModern Physics Formula SheetIntrovert xyzNessuna valutazione finora
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocumento26 pagineHaloalkanes and Haloarenesrajputrishi1982Nessuna valutazione finora
- Organic Chemistry - Class 12th - Practice MCQsDocumento22 pagineOrganic Chemistry - Class 12th - Practice MCQsLiza DahiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE Class-12 Chemistry Quick Revision Notes Chapter-12: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acid AldehydesDocumento11 pagineCBSE Class-12 Chemistry Quick Revision Notes Chapter-12: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acid AldehydesManoj PrakashNessuna valutazione finora
- Coordination Compounds Board 1 Shot PDFDocumento25 pagineCoordination Compounds Board 1 Shot PDFGaurav67% (6)
- Chemistry: CheatDocumento22 pagineChemistry: CheatKashish UpadhyayNessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE Class 12 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Study NotesDocumento355 pagineCBSE Class 12 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Study NotesDharaneesh S.k.100% (1)
- Alkene DPPDocumento20 pagineAlkene DPPKalyan ReddtNessuna valutazione finora
- Pre-Medical: Chemistry Allen: Carbonyl Compounds, Acids and It'S Derivatives Carbonyl CompoundsDocumento18 paginePre-Medical: Chemistry Allen: Carbonyl Compounds, Acids and It'S Derivatives Carbonyl CompoundsJK JHANessuna valutazione finora
- Metal ClustersDocumento23 pagineMetal ClustersSyed Safi AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Model Question Grade XI Chemistry (Theory) F.M: 75 Attempt All Questions Group "A"Documento4 pagineModel Question Grade XI Chemistry (Theory) F.M: 75 Attempt All Questions Group "A"Supriya Rai0% (1)
- Ncert Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Jan11 Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles and TechniquesDocumento32 pagineNcert Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Jan11 Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles and TechniquesSachit GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Coordination Chemistry Jeemain - GuruDocumento30 pagineCoordination Chemistry Jeemain - GuruJp PatidarNessuna valutazione finora
- 11 Alcohols Phenols and EthersDocumento2 pagine11 Alcohols Phenols and EthersVarun Sankpal100% (1)
- SHM Formula Sheet @cbseinfiniteDocumento6 pagineSHM Formula Sheet @cbseinfiniteRekha JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic Chemistry - General Organic ChemistryDocumento79 pagineOrganic Chemistry - General Organic ChemistryTetakali SandeepNessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE Class 12 Alcohol Phenol and Ether Study NotesDocumento378 pagineCBSE Class 12 Alcohol Phenol and Ether Study NotesV T PRIYANKANessuna valutazione finora
- CHEM20024 Lecture Notes 11 - Free Energy and EquilibriumDocumento27 pagineCHEM20024 Lecture Notes 11 - Free Energy and EquilibriumEzriel QuantumNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment - (P-Block) Halogen and Noble Gases - JH Sir PDFDocumento33 pagineAssignment - (P-Block) Halogen and Noble Gases - JH Sir PDFKohli Kiran100% (1)
- Co Ordination Compounds MHT CET Synopsis PDFDocumento11 pagineCo Ordination Compounds MHT CET Synopsis PDFAbhishek MandlikNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Reactions NotesDocumento141 pagineChemical Reactions Notesapi-182809945Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Paper For ChemistryDocumento23 pagineSample Paper For ChemistryAmit joshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Amines: Pre-Medical: Chemistry Allen 3.1 AnilineDocumento10 pagineAmines: Pre-Medical: Chemistry Allen 3.1 AnilineJK JHANessuna valutazione finora
- Common Name: Organic ChemistryDocumento10 pagineCommon Name: Organic ChemistryLakshya wardhan singh ShekhawatNessuna valutazione finora
- Name ReactionsDocumento10 pagineName ReactionsParam SoniNessuna valutazione finora
- NCERT Notes For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2: Solutions: Solute and SolventDocumento11 pagineNCERT Notes For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2: Solutions: Solute and Solventshradha bittuNessuna valutazione finora
- Distinguish by A Single Chemical Test: Prepared By-A.P. Singh Pgt-Chemistry - KV Aliganj LucknowDocumento1 paginaDistinguish by A Single Chemical Test: Prepared By-A.P. Singh Pgt-Chemistry - KV Aliganj LucknowChetan KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic: ChemistryDocumento8 pagineOrganic: ChemistryDhilip KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics: DPP - Daily Practice ProblemsDocumento4 paginePhysics: DPP - Daily Practice ProblemsAnkita Majumder100% (1)
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - PYQ Chemistry Class 11 PDF DownloadDocumento9 pagineChemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - PYQ Chemistry Class 11 PDF DownloadamreshNessuna valutazione finora
- Stereoisomerism VKP SirDocumento49 pagineStereoisomerism VKP SirSandeep ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Formulae For: Haloalkane & Hal OarenesDocumento9 pagineFormulae For: Haloalkane & Hal OarenesSâmïr Kumar MundariNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.mole Concept PDFDocumento35 pagine1.mole Concept PDFSubham roushan100% (1)
- Name Reactions of Organic ChemistryDocumento7 pagineName Reactions of Organic ChemistryNaynam SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- ELECTROCHEMISTRYDocumento4 pagineELECTROCHEMISTRYSAIRAJ PRABHAKAR PAWARNessuna valutazione finora
- Molecular Orbital Theory in Homonuclear and Heteronuclear Diatomic MoleculesDocumento12 pagineMolecular Orbital Theory in Homonuclear and Heteronuclear Diatomic MoleculesJeevanantham VelayuthamNessuna valutazione finora
- CH12 - GOC - Shobhit NirwanDocumento61 pagineCH12 - GOC - Shobhit NirwanRao GootleyNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 5 Coordination CompoundsDocumento53 pagineCH 5 Coordination Compoundsgerawop972Nessuna valutazione finora
- Xi Chemistry Target Paper 2021 (New)Documento3 pagineXi Chemistry Target Paper 2021 (New)Prince MtbyNessuna valutazione finora
- Sarvodaya.2puc - Mid-Term. IMPORTANT QUESTIONS IN CHEMISTRYDocumento4 pagineSarvodaya.2puc - Mid-Term. IMPORTANT QUESTIONS IN CHEMISTRYRavindar PurohitNessuna valutazione finora
- Electromeric EffectDocumento6 pagineElectromeric EffectProfKaleem AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Tricks - Formulas of Chemistry-I PDFDocumento57 pagineTricks - Formulas of Chemistry-I PDFMUHAMMAD AHMADNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic: Gaseous State: Chemistry Lecture NotesDocumento32 pagineTopic: Gaseous State: Chemistry Lecture NotesDibya Ranjan BissoyiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Class 12 Revision MaterialDocumento52 pagineChemistry Class 12 Revision Materialkrish dabhiNessuna valutazione finora
- (2099) Lecture Notes P Block 15 16 E.pdf - TMPDocumento39 pagine(2099) Lecture Notes P Block 15 16 E.pdf - TMPRamJiPandeyNessuna valutazione finora
- S BlockDocumento84 pagineS BlockPrakhar ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- Periodic Classification - Mind Maps - Arjuna JEE 2.0 2024Documento1 paginaPeriodic Classification - Mind Maps - Arjuna JEE 2.0 2024Harsh Singh RajputNessuna valutazione finora
- Equilibrium - Shobhit NirwanDocumento27 pagineEquilibrium - Shobhit Nirwanlyra caddelNessuna valutazione finora
- Coordination Chemistry JEE AdvancedDocumento44 pagineCoordination Chemistry JEE AdvancedKartikey SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- AToms Model Questions + SolutionDocumento8 pagineAToms Model Questions + SolutionKarttik SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Facts Formulae ChemistryDocumento53 pagineFacts Formulae ChemistryAbhay Vishwakarma0% (1)
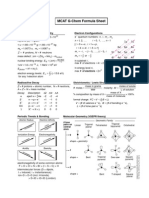
- 16 - MCAT G-Chem Formula SheetDocumento2 pagine16 - MCAT G-Chem Formula SheetNathan Korean Kim100% (7)