Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
The Introduction of Online Content Curation To C21 Case-Based Learning
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
The Introduction of Online Content Curation To C21 Case-Based Learning
Copyright:
Formati disponibili
The introduction of online content curation to C21 case-based learning
Duncan Cole1 and Anne Marie Cunningham2
1
Institute of Molecular and Experimental Medicine, Cardiff University 2 Institute of Primary Care and Public Health, Cardiff University
Objectives
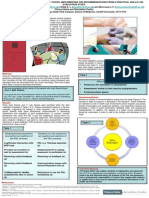
Cardiff University School of Medicine is currently undergoing a major curriculum change to case-based learning (CBL) in small groups.
A key principle of the course is that learning is active and collaborative. The internet is now a major source of healthcare information, and using this effectively is an increasingly important skill. Figure 2: Example of a CBL group Scoop.it web-page.
Our aims were therefore to: 1. support students with e-learning technologies that reflect the principles of the course 2. develop student digital literacies.
Outcome
Initial engagement has been encouraging, with 25/30 groups making some use of curation to support their learning, and 8 groups posting more than 30 Scoops by the end of Case 3. Summary so far: Scoops
Total (all groups) Min (group) Max (group)
Innovation
We have introduced the online digital curation tool Scoop.it into CBL. The process of online content curation is outlined in Figure 1. Students have the option of using the website during and between CBL sessions. The website is public, and its use is voluntary. An example is shown in figure 2.
Curators 87 0 9 3
Views 1990 7 294 66
526 0 70 18
Figure 1: The process of online content curation.
Online content is reviewed and selected by the student,(who here is the curator), and a commentary is added. This is shared on the Scoop.it website (where other users can follow the topic); students can also link to social media, and may review the material in CBL sessions. Online discussion may follow on the topic, and other users can suggest other websites, or re-scoop on to their own topic pages. FOAMed: Free Open Access Medical Education.
Mean (per group)
A number of posts have revealed good critical commentary on the curated resources.
Conclusion
We have introduced a new digital practice into our undergraduate medicine curriculum, which is in keeping with the collaborative and active learning principles of the course. We plan to explore the impact on student digital literacies in future work.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Media and Information Literacy Las 2nd Quarter EditedDocumento44 pagineMedia and Information Literacy Las 2nd Quarter EditedR-yan gorospeNessuna valutazione finora
- Models of Curriculum Change and InnovationDocumento12 pagineModels of Curriculum Change and InnovationAngelica BautistaNessuna valutazione finora
- Igcse GP Teacher Notes - Introduction ModuleDocumento6 pagineIgcse GP Teacher Notes - Introduction ModuleMacjoyle Jonnes Antonio Barretto100% (1)
- Media and Information Literacy: QUARTER 2 - Module 2Documento13 pagineMedia and Information Literacy: QUARTER 2 - Module 2Karen de los ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Media and Information Literacy Las 2nd Quarter EditedDocumento44 pagineMedia and Information Literacy Las 2nd Quarter EditedR-yan gorospe0% (1)
- Online Learning and its Users: Lessons for Higher EducationDa EverandOnline Learning and its Users: Lessons for Higher EducationNessuna valutazione finora
- Simulation Based Learning For Final Year Medical Students at Cardiff UniversityDocumento1 paginaSimulation Based Learning For Final Year Medical Students at Cardiff UniversityCardiff University School of Medicine C21 Curriculum ShowcaseNessuna valutazione finora
- Barriers and Solutions To Online Learning in MedicDocumento12 pagineBarriers and Solutions To Online Learning in MedicAnggoro OctaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bitacora PaperDocumento14 pagineBitacora PaperEliana ScheihingNessuna valutazione finora
- Group3 - Project BRMDocumento21 pagineGroup3 - Project BRMakashNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparing Computer-Assisted Learning Activities For Learning Clinical Neuroscience: A Randomized Control TrialDocumento12 pagineComparing Computer-Assisted Learning Activities For Learning Clinical Neuroscience: A Randomized Control Trialdavid chungNessuna valutazione finora
- Tech 3100 BbptlessonideatempDocumento2 pagineTech 3100 Bbptlessonideatempapi-391478213Nessuna valutazione finora
- Word Processing SoftwareDocumento10 pagineWord Processing SoftwareADRIANNA AISYA ZAINURINNessuna valutazione finora
- The Emerging Web 2.0 Social Software: An Enabling Suite of Sociable Technologies in Health and Health Care EducationDocumento22 pagineThe Emerging Web 2.0 Social Software: An Enabling Suite of Sociable Technologies in Health and Health Care EducationIsabel VásquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study: Scenario 3 - University of Cambridge Moves To Online TeachingDocumento28 pagineCase Study: Scenario 3 - University of Cambridge Moves To Online TeachingElparth OfficialNessuna valutazione finora
- Mil - Q2 - Module 2Documento9 pagineMil - Q2 - Module 2isipMath TutorialNessuna valutazione finora
- The Unmoocing Process: Extending The Impact of Mooc Educational Resources As OersDocumento17 pagineThe Unmoocing Process: Extending The Impact of Mooc Educational Resources As OersAland MediaNessuna valutazione finora
- How To MOOC? - A Pedagogical Guideline For PractitionersDocumento8 pagineHow To MOOC? - A Pedagogical Guideline For PractitionersMartinNessuna valutazione finora
- A Paradigm Shift in Process of TeachingDocumento7 pagineA Paradigm Shift in Process of TeachingKagyera KatakaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Learning Designs in Physiotherapy Education: A Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisDocumento18 pagineDigital Learning Designs in Physiotherapy Education: A Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisLaura Paola Corredor NietoNessuna valutazione finora
- Naskah Bing4208 tmk1 1Documento4 pagineNaskah Bing4208 tmk1 1Ryu Ko KozawaNessuna valutazione finora
- Reportweb2 0Documento21 pagineReportweb2 0api-266097473Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2021 Aasec - 2021 - 05Documento9 pagine2021 Aasec - 2021 - 05dikakilangitNessuna valutazione finora
- Bbs Learningexplosion ChiDocumento9 pagineBbs Learningexplosion ChiErick Dimas Cirilo BerazainNessuna valutazione finora
- Health Sciences and Practice Subject CentreDocumento59 pagineHealth Sciences and Practice Subject CentresubipuruNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 5 Project ImplementationDocumento11 pagineModule 5 Project ImplementationMichaela ParalejasNessuna valutazione finora
- Quarter 2 - Module 9: Power, Impact, and Implications of Media and InformationDocumento14 pagineQuarter 2 - Module 9: Power, Impact, and Implications of Media and InformationErika LayogNessuna valutazione finora
- Week-3 Community EngagementDocumento1 paginaWeek-3 Community EngagementSamlall RabindranauthNessuna valutazione finora
- PBL Essential Elements Checklist: Does The Project ?Documento3 paginePBL Essential Elements Checklist: Does The Project ?api-206431001Nessuna valutazione finora
- Large-Scale Educational CampaignsDocumento25 pagineLarge-Scale Educational CampaignsIvone G. LuizNessuna valutazione finora
- BMC Medical EducationDocumento11 pagineBMC Medical EducationLarasati Duta PratiwiNessuna valutazione finora
- The COVID-19 Pandemic Is Affectation Countless Challenges To Our Health Care System and To Say Nothing of Our Society As A Whole WorldDocumento2 pagineThe COVID-19 Pandemic Is Affectation Countless Challenges To Our Health Care System and To Say Nothing of Our Society As A Whole WorldHema BalasubramaniamNessuna valutazione finora
- Review of Global Education NetworksDocumento14 pagineReview of Global Education NetworksMicheleGrayBodineNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer - Assisted Learning: Dr.G.Sidhartha KiranDocumento20 pagineComputer - Assisted Learning: Dr.G.Sidhartha KiranIrfan ChaudharyNessuna valutazione finora
- To Media Studies GcseDocumento34 pagineTo Media Studies GcseStephhouseNessuna valutazione finora
- Repurposing Project Report FinalDocumento9 pagineRepurposing Project Report Finalapi-295585111Nessuna valutazione finora
- Quarter 2 - Module 11: Introduction To Media and Information LiteracyDocumento15 pagineQuarter 2 - Module 11: Introduction To Media and Information LiteracyAngelica DacapioNessuna valutazione finora
- Research Namin 1Documento15 pagineResearch Namin 1Alih NasilNessuna valutazione finora
- 281207.JO System Development For E-Learning 3Documento20 pagine281207.JO System Development For E-Learning 3arjNessuna valutazione finora
- The Development of Multimedia EvaluationDocumento10 pagineThe Development of Multimedia EvaluationSameerchand PudaruthNessuna valutazione finora
- Faure-Carvallo-Redes Sociales y Educación SuperiorDocumento14 pagineFaure-Carvallo-Redes Sociales y Educación SuperiorJosé William Pérez JiménezNessuna valutazione finora
- Regmi-Jones2020 Article ASystematicReviewOfTheFactorsEDocumento18 pagineRegmi-Jones2020 Article ASystematicReviewOfTheFactorsEVuyolwethu MafangaNessuna valutazione finora
- Canadian Nursing Students' Use of Social Media in Their LearningDocumento32 pagineCanadian Nursing Students' Use of Social Media in Their LearningShaddi Sophia LeraNessuna valutazione finora
- Innovating Pedagogy Report 2013Documento42 pagineInnovating Pedagogy Report 2013glacyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Concept Paper WritingDocumento4 pagineConcept Paper WritingJerimee derf CalustreNessuna valutazione finora
- A Novel Integration of Online and Flipped Classroom Instructional Models in Public Health Higher EducationDocumento9 pagineA Novel Integration of Online and Flipped Classroom Instructional Models in Public Health Higher EducationRafa GorgoryNessuna valutazione finora
- Directions: Please Supply The Information by Filling in The Blanks or Checking inDocumento18 pagineDirections: Please Supply The Information by Filling in The Blanks or Checking inNova CabigNessuna valutazione finora
- Ali 2018Documento15 pagineAli 2018arif candrautamaNessuna valutazione finora
- Research Proposal UpdatedDocumento7 pagineResearch Proposal Updatedshella brananolaNessuna valutazione finora
- 04 Beyond The Basic Prductivity Tools Lesson Idea Template 1Documento2 pagine04 Beyond The Basic Prductivity Tools Lesson Idea Template 1api-424570014Nessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis of Dynamic Resource Access Patterns in A Blended Learning CourseDocumento10 pagineAnalysis of Dynamic Resource Access Patterns in A Blended Learning CourseThumbCakesNessuna valutazione finora
- Resources 2Documento9 pagineResources 2Shukura ShuaibNessuna valutazione finora
- Pfacol Final Report Sep 2014Documento28 paginePfacol Final Report Sep 2014api-264552622Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biomimicry Design Tooling: Stevens, Laura (1,2,3) de Vries, Marc (2) Van Den Broek, Jos (3) Rijken, DickDocumento8 pagineBiomimicry Design Tooling: Stevens, Laura (1,2,3) de Vries, Marc (2) Van Den Broek, Jos (3) Rijken, DickKalyani sonekarNessuna valutazione finora
- 2022 - A Qualitative Multiple Case Study in Quebec and Nova ScotiaDocumento18 pagine2022 - A Qualitative Multiple Case Study in Quebec and Nova ScotiaFernanda Gusmão LouredoNessuna valutazione finora
- UntitledDocumento164 pagineUntitledAlexander CalimlimNessuna valutazione finora
- Is 3018-E Learning Course Evaluation Report-Group eDocumento16 pagineIs 3018-E Learning Course Evaluation Report-Group eapi-291874016Nessuna valutazione finora
- 04 1stQ TLE10 Lesson 4 Current Multimedia TrendsDocumento13 pagine04 1stQ TLE10 Lesson 4 Current Multimedia TrendsJoev Quezon IINessuna valutazione finora
- Cope Kalantzis FiveThesesontheFutureofLearning09Oct20Documento22 pagineCope Kalantzis FiveThesesontheFutureofLearning09Oct20Thembisile ButheleziNessuna valutazione finora
- The Impact of The COVID-19 Pandemic On User Experience With Online Education Platforms in ChinaDocumento31 pagineThe Impact of The COVID-19 Pandemic On User Experience With Online Education Platforms in ChinaKayli is addicted to anime and comicsNessuna valutazione finora
- Moodle Innovation Learning TechnologyDocumento16 pagineMoodle Innovation Learning TechnologyNatalia LobachNessuna valutazione finora
- Helping Medical Students To Develop Their Digital Presence.Documento1 paginaHelping Medical Students To Develop Their Digital Presence.amcunninghamNessuna valutazione finora
- Developing Standards For Dental EducatorsDocumento1 paginaDeveloping Standards For Dental EducatorsCardiff University School of Medicine C21 Curriculum ShowcaseNessuna valutazione finora
- As Me 09 AbstractDocumento2 pagineAs Me 09 AbstractCardiff University School of Medicine C21 Curriculum ShowcaseNessuna valutazione finora
- Delivering Inclusive Healthcare Curricula: Addressing The Needs of Lesbian, Gay and Bisexual (LGB) Staff, Students and Patients.Documento1 paginaDelivering Inclusive Healthcare Curricula: Addressing The Needs of Lesbian, Gay and Bisexual (LGB) Staff, Students and Patients.Cardiff University School of Medicine C21 Curriculum ShowcaseNessuna valutazione finora
- Listening and Acting On Participant Voices: Implementing The Recommendations From A Practical Skills Log Evaluation Study.Documento1 paginaListening and Acting On Participant Voices: Implementing The Recommendations From A Practical Skills Log Evaluation Study.Cardiff University School of Medicine C21 Curriculum ShowcaseNessuna valutazione finora
- Student Evaluation For C21Documento1 paginaStudent Evaluation For C21Cardiff University School of Medicine C21 Curriculum ShowcaseNessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching The Humanities in Medical EducationDocumento1 paginaTeaching The Humanities in Medical EducationCardiff University School of Medicine C21 Curriculum ShowcaseNessuna valutazione finora
- Drama and Public HealthDocumento1 paginaDrama and Public HealthCardiff University School of Medicine C21 Curriculum ShowcaseNessuna valutazione finora
- What Medical Students Are Frightened of and Why? Secondary Analysis of Medical Student Focus Group DataDocumento1 paginaWhat Medical Students Are Frightened of and Why? Secondary Analysis of Medical Student Focus Group DataCardiff University School of Medicine C21 Curriculum ShowcaseNessuna valutazione finora
- Equality and Diversity - How Do We Embed This Unsexy Topic in The Framework of Medical Education?Documento1 paginaEquality and Diversity - How Do We Embed This Unsexy Topic in The Framework of Medical Education?Cardiff University School of Medicine C21 Curriculum ShowcaseNessuna valutazione finora
- Modelling Cohen's Method For Standard Setting Progress Tests in The Cardiff Medical SchoolDocumento1 paginaModelling Cohen's Method For Standard Setting Progress Tests in The Cardiff Medical SchoolCardiff University School of Medicine C21 Curriculum ShowcaseNessuna valutazione finora
- Students' Evaluation of The OSCE Experience in Cardiff Medical SchoolDocumento1 paginaStudents' Evaluation of The OSCE Experience in Cardiff Medical SchoolCardiff University School of Medicine C21 Curriculum Showcase100% (1)