Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Present Simple Vs Present Continuous
Caricato da
api-236095657Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Present Simple Vs Present Continuous
Caricato da
api-236095657Copyright:
Formati disponibili
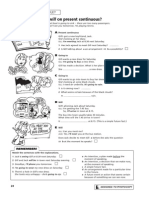
PRESENT SIMPLE VS PRESENT CONTINUOUS
Simple Present Present Progressive
infinitive (3rd person singular: infinitive + 's') I speak you speak he / she / it speaks we speak they speak
form of 'be' and verb + ing
I am speaking you are speaking he / she / it is speaking we are speaking they are speaking Exceptions
Exceptions when adding 's' : For can, may, might, must, do not add s. Example: he can, she may, it must After o, ch, sh or s, add es. Example: do - he does, wash - she washes After a consonant, the final consonant ybecomes ie. (but: not after a vowel) Example: worry - he worries but: play - he plays
Exceptions when adding 'ing' : Silent e is dropped. (but: does not apply for -ee) Example: come - coming but: agree - agreeing After a short, stressed vowel, the final consonant is doubled. Example: sit - sitting After a vowel, the final consonant l is doubled in British English (but not in American English). Example: travel - travelling (British English) but: traveling (American English) Final ie becomes y. Example: lie lying
Use
In general or right now?
Do you want to express that something happens in general or that something is happening right now?
Simple Present
Present Progressive
in general (regularly, often, never)
right now
Colin plays football every Tuesday. present actions happening one after another First Colin plays football, then he watches TV.
Look! Colin is playing football now. also for several actions happening at the same time Colin is playing football and Anne is watching. Signal words
always every ... often normally usually sometimes seldom never first then
at the moment at this moment today now right now Listen! Look!
Note: The following verbs are usually only used in Simple Present: be, have, hear, know, like, love, see, smell, think, want
Timetable / Schedule or arrangement?
Do you want to express that something is arranged for the near future? Or do you refer to a time set by a timetable or schedule?
Simple Present
Present Progressive
arrangement for the near future
action set by a timetable or schedule I am going to the cinema tonight. The film starts at 8 pm.
Daily routine or just for a limited period of time?
Do you want to talk about a daily routine? Or do you want to emphasis that something is only going on for a limited (rather short) period of time?
Simple Present
Present Progressive
only for a limited period of time (does not have to happen directly at the moment of speaking)
daily routine
Bob works in a restaurant.
Jenny is working in a restaurant this week.
Certain Verbs
The following verbs are usually only used in Simple Present (not in the progressive form). state: be, cost, fit, mean, suit Example: We are on holiday. possession: belong, have Example: Sam has a cat. senses: feel, hear, see, smell, taste, touch Example: He feels the cold. feelings: hate, hope, like, love, prefer, regret, want, wish Example: Jane loves pizza. brain work: believe, know, think, understand Example: I believe you. Introductory clauses for direct speech: answer, ask, reply, say Example: I am watching TV, he says
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Present Simple Vs Present Continuous 1. Complete The Following Sentences With Present SimpleDocumento3 paginePresent Simple Vs Present Continuous 1. Complete The Following Sentences With Present SimpleAurelia - Simona Papa - DiaconuNessuna valutazione finora
- Fair Play (Great Stories: High Beginner): Wayzgoose Graded ReadersDa EverandFair Play (Great Stories: High Beginner): Wayzgoose Graded ReadersNessuna valutazione finora
- Kidnap by John EscottDocumento25 pagineKidnap by John EscottMarina El-SuleimanNessuna valutazione finora
- Grandad's Eleven (Great Stories: High Beginner): Wayzgoose Graded ReadersDa EverandGrandad's Eleven (Great Stories: High Beginner): Wayzgoose Graded ReadersValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Young Stars 4 Unit 8Documento12 pagineYoung Stars 4 Unit 8RETOS CONSULTING SACNessuna valutazione finora
- Channel Runner (Great Stories: Low Intermediate): Wayzgoose Graded ReadersDa EverandChannel Runner (Great Stories: Low Intermediate): Wayzgoose Graded ReadersNessuna valutazione finora
- Amazon Rally: Eduardo Amos and Elisabeth PrescherDocumento25 pagineAmazon Rally: Eduardo Amos and Elisabeth PrescherIn a Rush EnglishNessuna valutazione finora
- Sherlock Holmes in Simple English: The Speckled BandDa EverandSherlock Holmes in Simple English: The Speckled BandNessuna valutazione finora
- The Fifteenth Character by Rosemary BorderDocumento9 pagineThe Fifteenth Character by Rosemary BorderMaryori Vidales RubioNessuna valutazione finora
- Folktales (Big Ideas: High Beginner): Wayzgoose Graded ReadersDa EverandFolktales (Big Ideas: High Beginner): Wayzgoose Graded ReadersNessuna valutazione finora
- The Thirty Nine Steps-Glossary PDFDocumento1 paginaThe Thirty Nine Steps-Glossary PDFSalmen AllouchNessuna valutazione finora
- Eyes Open 1-Unit 8 HolidaysDocumento6 pagineEyes Open 1-Unit 8 HolidaysNgoc Anh LuuNessuna valutazione finora
- Classroom Dynamics in Japanese ClassroomsDocumento341 pagineClassroom Dynamics in Japanese ClassroomsKevin WeirNessuna valutazione finora
- 英语语音 (2007) 屠蓓Documento29 pagine英语语音 (2007) 屠蓓carlzhangNessuna valutazione finora
- Australia and New Zeland BookDocumento18 pagineAustralia and New Zeland BookŪla PetrauskienėNessuna valutazione finora
- The Adventures of Pinocchio (ESL/EFL Version with Audioo)Da EverandThe Adventures of Pinocchio (ESL/EFL Version with Audioo)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Solutions Pre Intermediate Unit 5 Reading GuidesDocumento12 pagineSolutions Pre Intermediate Unit 5 Reading GuidespabloNessuna valutazione finora
- The Black PearlsDocumento18 pagineThe Black PearlsSyed Tahseen100% (1)
- O HenryDocumento2 pagineO Henrymail2winagNessuna valutazione finora
- Everybody Up Correlation v2Documento9 pagineEverybody Up Correlation v2progmetallerNessuna valutazione finora
- Northanger Abbey Jane Austin SampleDocumento25 pagineNorthanger Abbey Jane Austin SampleOlivera Petrovic0% (1)
- A Wedding at Christmas by Chrissie ManbyDocumento11 pagineA Wedding at Christmas by Chrissie ManbyHodder StoughtonNessuna valutazione finora
- Joey War HorseDocumento9 pagineJoey War HorseVivaVillaMty0% (1)
- Netty Sargent and The House-Jennifer BassettDocumento6 pagineNetty Sargent and The House-Jennifer Bassettjwon070428Nessuna valutazione finora
- b2 Listening 2020 enDocumento1 paginab2 Listening 2020 enKiss GézaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tom Sowyer (Beginners)Documento31 pagineTom Sowyer (Beginners)Oscar GutierrezNessuna valutazione finora
- Gulliver PDFDocumento3 pagineGulliver PDFChristopherBustosNessuna valutazione finora
- Solutions Upper-Intermediate. Workbook. Keys - 2017, 3rd - 36p PDF - PDF - News - CelebrityDocumento1 paginaSolutions Upper-Intermediate. Workbook. Keys - 2017, 3rd - 36p PDF - PDF - News - Celebritykajuskapitonovaslmao8Nessuna valutazione finora
- NewEnt A2Documento13 pagineNewEnt A2Angie BustosNessuna valutazione finora
- A Murder Is Announced: Teacher's NotesDocumento5 pagineA Murder Is Announced: Teacher's NotesИлона СергеевнаNessuna valutazione finora
- Wordlist: File 1Documento17 pagineWordlist: File 1David Peñaranda MorenoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Canterville Ghost: by Oscar WildeDocumento8 pagineThe Canterville Ghost: by Oscar WildeIrloaNessuna valutazione finora
- Goodbye, MR HollywoodDocumento20 pagineGoodbye, MR HollywoodnoetheslayerNessuna valutazione finora
- ThumbelinaDocumento14 pagineThumbelinaМАРИЯ ПетковаNessuna valutazione finora
- Space: Preview The ReaderDocumento13 pagineSpace: Preview The Readerbeatriz mancaNessuna valutazione finora
- Room 13 and Other Ghost Stories Elementary MacmiDocumento2 pagineRoom 13 and Other Ghost Stories Elementary MacmiBilal Ahmed Bhatti100% (1)
- 3RD AD IR - The Last Juror Level 2Documento76 pagine3RD AD IR - The Last Juror Level 2florencia scarpetta100% (1)
- Stephen Rabley - Between Two Worlds (EnglishOnlineClub - Com)Documento15 pagineStephen Rabley - Between Two Worlds (EnglishOnlineClub - Com)Luli AcostaNessuna valutazione finora
- Adrian Mole SummaryDocumento9 pagineAdrian Mole SummarySofia SmjNessuna valutazione finora
- Owl Hall Episode 7Documento4 pagineOwl Hall Episode 7Mike KeagNessuna valutazione finora
- Extreme Sports Readings PenguinDocumento19 pagineExtreme Sports Readings PenguinVLADIMIR HUARICALLONessuna valutazione finora
- Speak Now 1 WB Answer KeyDocumento36 pagineSpeak Now 1 WB Answer KeyShirin MehboodiNessuna valutazione finora
- Three Men in A Boat AnswersDocumento3 pagineThree Men in A Boat Answersmuneersn100% (3)
- A Type of Text: A Narrative: Iin Hermiyanto, S.PDDocumento44 pagineA Type of Text: A Narrative: Iin Hermiyanto, S.PDAfitt100% (1)
- Ted 2011 Wa Less Stuff More Happiness Graham Hill 6 MinDocumento3 pagineTed 2011 Wa Less Stuff More Happiness Graham Hill 6 MinPeetaceNessuna valutazione finora
- What A LotteryDocumento18 pagineWhat A LotteryVladimir MartínezNessuna valutazione finora
- Word Picture Sentence: This Is An ExampleDocumento2 pagineWord Picture Sentence: This Is An ExampleChristian Alberto Jalon GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Oxford Bookworms Stage 4 A Morbid Taste For Bone 0194791793 PDFDocumento3 pagineOxford Bookworms Stage 4 A Morbid Taste For Bone 0194791793 PDFCanberk Akgul50% (2)
- DEATH IN THE FREEZER ActivitiesDocumento5 pagineDEATH IN THE FREEZER ActivitiesLaura Alicia TerragnoNessuna valutazione finora
- BOOKWORMS Engage PDFDocumento3 pagineBOOKWORMS Engage PDFLeonardoNessuna valutazione finora
- 20the First DateDocumento4 pagine20the First DateSebastian CamachoNessuna valutazione finora
- Tinker's FarmDocumento2 pagineTinker's FarmKyungsoo EkaaNessuna valutazione finora
- t1 Stage 2 MR StinkDocumento4 paginet1 Stage 2 MR Stinkapi-1999980920% (2)
- Black Beauty: by Anna SewellDocumento12 pagineBlack Beauty: by Anna SewellfyfcnfcbzNessuna valutazione finora
- 0 AnneofGreenGables TNDocumento3 pagine0 AnneofGreenGables TNGraciela AhumadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Writing A Story HomeworkDocumento2 pagineWriting A Story Homeworkapi-236095657Nessuna valutazione finora
- Transitions ExerciseDocumento1 paginaTransitions Exerciseapi-236095657Nessuna valutazione finora
- Irregularverbsingroups 1Documento2 pagineIrregularverbsingroups 1api-236095657Nessuna valutazione finora
- Common Irregular Verbs GroupedDocumento3 pagineCommon Irregular Verbs Groupedapi-236095657Nessuna valutazione finora
- Robbie Williams Angel EnglishDocumento6 pagineRobbie Williams Angel Englishapi-236095657Nessuna valutazione finora
- Future FormasDocumento4 pagineFuture Formasapi-236095657100% (2)
- World War Z WorkshopDocumento6 pagineWorld War Z Workshopapi-236095657Nessuna valutazione finora
- Simple Past Past PerfectDocumento2 pagineSimple Past Past Perfectapi-236095657Nessuna valutazione finora
- Irregular Plurals ListDocumento1 paginaIrregular Plurals Listapi-236095657Nessuna valutazione finora
- Class 6-Second Assessment Block Test Syllabus - 03-08-2019-1 PDFDocumento5 pagineClass 6-Second Assessment Block Test Syllabus - 03-08-2019-1 PDFBappy Dutta GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Present Continuous. Theory and ExercisesDocumento3 paginePresent Continuous. Theory and ExercisesCinthia ZapataNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 - Bands and Fans: Gold First New EditionDocumento48 pagineUnit 1 - Bands and Fans: Gold First New EditionРоман ФедишинNessuna valutazione finora
- Bcpp6e TB Ch06Documento31 pagineBcpp6e TB Ch06jennyayumi100% (1)
- Active and Passive VoiceDocumento10 pagineActive and Passive VoiceNia ApriLiaNessuna valutazione finora
- GR 2 PT 2 Portion and BlueprintDocumento3 pagineGR 2 PT 2 Portion and BlueprintAbhishek SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Exam Technique - Editing & Short-Answer Questions (LC & RC)Documento1 paginaExam Technique - Editing & Short-Answer Questions (LC & RC)Katrin DoszpodNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported Speech Indirect SpeechDocumento8 pagineReported Speech Indirect SpeechAndie OteroNessuna valutazione finora
- Possessive Adjectives and Subject Pronouns (I/my, You/your, Etc.)Documento6 paginePossessive Adjectives and Subject Pronouns (I/my, You/your, Etc.)Libarra12Nessuna valutazione finora
- Juan Carlos UribeDocumento2 pagineJuan Carlos Uribemaribel varelasNessuna valutazione finora
- The ConjunctionDocumento7 pagineThe ConjunctionGunay Eliyeva100% (1)
- Past Vs Present PerfDocumento9 paginePast Vs Present PerfZaya HuzzNessuna valutazione finora
- A City Break British English Student Ver2Documento4 pagineA City Break British English Student Ver2KatyNessuna valutazione finora
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2012: International GCSE English (4EBO/01) English Language ADocumento16 pagineMark Scheme (Results) January 2012: International GCSE English (4EBO/01) English Language AJohn HopkinsNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparatives and Superlatives PracticeDocumento5 pagineComparatives and Superlatives PracticeValentina RamirezNessuna valutazione finora
- SiopaoDocumento3 pagineSiopaoRizza Mae AngelesNessuna valutazione finora
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use: Simple PresentDocumento6 pagineTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use: Simple PresentAprilia Putri CahyaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Using Functional Grammar An Explorer S Guide PDFDocumento178 pagineUsing Functional Grammar An Explorer S Guide PDFAdriana Hikawczuk100% (1)
- Simple Present Questions and FrequencyDocumento26 pagineSimple Present Questions and Frequencyandersonorellana114Nessuna valutazione finora
- Aslib 2007 DanielssonDocumento11 pagineAslib 2007 DanielssonAndrei Militaru0% (1)
- Understanding-Semantics-Sebastian-Lobner Second EditionDocumento35 pagineUnderstanding-Semantics-Sebastian-Lobner Second EditionAli Ali100% (2)
- Relative Clauses 3º Eso E IES Isaac PeralDocumento21 pagineRelative Clauses 3º Eso E IES Isaac PeralMaría Jiménez MijánNessuna valutazione finora
- Common Characteristics of The Germanic LanguagesDocumento6 pagineCommon Characteristics of The Germanic LanguagesaniNessuna valutazione finora
- M1 Language Systems GrammarDocumento16 pagineM1 Language Systems GrammarMahgoub AlarabiNessuna valutazione finora
- On The Syntax of Reflexives in Yoruba Atoyebi UtrechtDocumento24 pagineOn The Syntax of Reflexives in Yoruba Atoyebi UtrechtTunde KarimuNessuna valutazione finora
- Indefinite PronounsDocumento2 pagineIndefinite PronounsIsabel Sigue AquíNessuna valutazione finora
- Kuliah 6 Prosedur Terjemahan Newmark AAWDocumento24 pagineKuliah 6 Prosedur Terjemahan Newmark AAWUMI NUR HIDAYAH ABD AZIZNessuna valutazione finora
- Module VDocumento5 pagineModule VJohn Christian CorderoNessuna valutazione finora
- MS2 MS3 MS4 Levels Official Yearly Planning & Omitted LessonsDocumento15 pagineMS2 MS3 MS4 Levels Official Yearly Planning & Omitted LessonsSamir Bounab87% (15)
- CinderellaDocumento3 pagineCinderellaJhonathan JustinoNessuna valutazione finora