Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Notes - Transpiration
Caricato da
api-238421605Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Notes - Transpiration
Caricato da
api-238421605Copyright:
Formati disponibili
Transpiration Transpiration explains how water moves up the plant against gravity in tubes made of dead xylem cells
without the use of a pump. Water on the surface of spongy and palisade cells (inside the leaf) evaporate and then diffuses out of the leaf through the stomata in the lower epidermis of the leaf. This is called transpiration. More water is drawn out of the xylem cells inside the leaf to replace what's lost. As the xylem cells make a continuous tube from the leaf, down the stem to the roots, this acts like a drinking straw, producing a flow of water and dissolved minerals from roots to leaves.
Factors that affect transpiration rate Factor Light Description In bright light transpiration increases Explanation The stomata (openings in the leaf) open wider to allow more carbon dioxide into the leaf for photosynthesis Evaporation and diffusion are faster at higher temperatures Water vapour is removed quickly by air movement, speeding up diffusion of more water vapour out of the leaf Diffusion of water vapour out of the leaf slows down if the leaf is already surrounded by
Temperature Transpiration is faster in higher temperatures Wind Transpiration is faster in windy conditions Transpiration is slower in humid conditions
Humidity
Factor
Description
Explanation moist air
Factors that affect transpiration rate Factor Light Description In bright light transpiration increases Explanation The stomata (openings in the leaf) open wider to allow more carbon dioxide into the leaf for photosynthesis Evaporation and diffusion are faster at higher temperatures Water vapour is removed quickly by air movement, speeding up diffusion of more water vapour out of the leaf Diffusion of water vapour out of the leaf slows down if the leaf is already surrounded by moist air
Temperature Transpiration is faster in higher temperatures Wind Transpiration is faster in windy conditions Transpiration is slower in humid conditions
Humidity
Factors that affect transpiration rate Factor Light Description In bright light transpiration increases Explanation The stomata (openings in the leaf) open wider to allow more carbon dioxide into the leaf for photosynthesis Evaporation and diffusion are faster at higher temperatures Water vapour is removed quickly by air movement, speeding up diffusion of more water vapour out of the leaf Diffusion of water vapour out of the leaf slows down if the leaf is already surrounded by moist air
Temperature Transpiration is faster in higher temperatures Wind Transpiration is faster in windy conditions Transpiration is slower in humid conditions
Humidity
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Mla - Title Page Set OutDocumento1 paginaMla - Title Page Set Outapi-238421605Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Isotope and Relative Atomic MassDocumento14 pagineIsotope and Relative Atomic Massapi-238421605100% (2)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Mla Styles - Name and Page NoDocumento2 pagineMla Styles - Name and Page Noapi-238421605Nessuna valutazione finora
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Gems Astronomy Information BrochureDocumento10 pagineGems Astronomy Information Brochureapi-238421605Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The Mole ConceptDocumento8 pagineThe Mole Conceptapi-238421605Nessuna valutazione finora
- Essay Sentence StartersDocumento2 pagineEssay Sentence Startersapi-238421605100% (1)
- One World FactorsDocumento7 pagineOne World Factorsapi-238421605Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- Plane Mirror and ImagesDocumento26 paginePlane Mirror and Imagesapi-238421605100% (3)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Owl Purdue MlaDocumento36 pagineOwl Purdue Mlaapi-238421605Nessuna valutazione finora
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- How To Cite A Website in Mla - Easybib BlogDocumento7 pagineHow To Cite A Website in Mla - Easybib Blogapi-238421605Nessuna valutazione finora
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Mole and Avogadros NumberDocumento63 pagineThe Mole and Avogadros Numberapi-238421605Nessuna valutazione finora
- Myp 4 Bio TabooDocumento11 pagineMyp 4 Bio Tabooapi-238421605Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Ws Static Electricity 1Documento4 pagineWs Static Electricity 1api-238421605Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rules For Drawing Electrical CircuitsDocumento2 pagineRules For Drawing Electrical Circuitsapi-238421605100% (1)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- ElectricityDocumento54 pagineElectricityapi-238421605Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- Ws - Power and ResistanceDocumento4 pagineWs - Power and Resistanceapi-238421605Nessuna valutazione finora
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- ID Kajian Sistem Usahatani Buah Kesemek Dio PDFDocumento17 pagineID Kajian Sistem Usahatani Buah Kesemek Dio PDFReva SundariNessuna valutazione finora
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- Tube India 2018 Exhibitor List 25 11 2018Documento2 pagineTube India 2018 Exhibitor List 25 11 2018Rohit KadamNessuna valutazione finora
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Fof Act 1 Forest Health Indicator CompleteDocumento14 pagineFof Act 1 Forest Health Indicator Completepress_jakeNessuna valutazione finora
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Unit 6 IrrigationDocumento20 pagineUnit 6 IrrigationHRIDYA MGNessuna valutazione finora
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
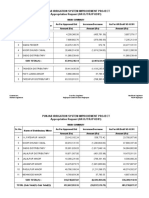
- Punjab Irrigation System Improvement Project Appropriation Request (AR-DJT/RJP-02/01)Documento205 paginePunjab Irrigation System Improvement Project Appropriation Request (AR-DJT/RJP-02/01)muhammad iqbalNessuna valutazione finora
- 3M Protocol Rc222Documento1 pagina3M Protocol Rc222Rommel SacramentoNessuna valutazione finora
- 13a. Road Construction MethodsDocumento18 pagine13a. Road Construction MethodsSheeraz AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Jatropha Curcas LDocumento3 pagineJatropha Curcas LChin Suk MeiNessuna valutazione finora
- Phyllosticta Leaf SpotDocumento3 paginePhyllosticta Leaf Spotapi-233056161Nessuna valutazione finora
- CG - 2017 PDFDocumento292 pagineCG - 2017 PDFkimsioNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab BH 02Documento7 pagineLab BH 02Pembangunan Kantilever Medan - BerastagiNessuna valutazione finora
- The Book of Pears: Chapter 1 - The PearDocumento20 pagineThe Book of Pears: Chapter 1 - The PearChelsea Green PublishingNessuna valutazione finora
- BC, BM, WMM & DBM & GSBDocumento5 pagineBC, BM, WMM & DBM & GSBikreddy68% (38)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- During Compaction: Void SpacesDocumento21 pagineDuring Compaction: Void SpacesMinilik Tikur SewNessuna valutazione finora
- Radish Seed ProductionDocumento14 pagineRadish Seed ProductionVerra Myza AratNessuna valutazione finora
- Coriander PerennialDocumento1 paginaCoriander Perennialios007Nessuna valutazione finora
- All Kinds of PlantsDocumento8 pagineAll Kinds of PlantsAna Bahamondes Dinamarca100% (1)
- ASSIGNMENT2Documento4 pagineASSIGNMENT2Laurence Allyson Montejo Siason100% (2)
- Silico Fix BrochureDocumento2 pagineSilico Fix Brochuresachinkarape4844Nessuna valutazione finora
- MES Assets Estimate-R1Documento25 pagineMES Assets Estimate-R1Jayashri MallickNessuna valutazione finora
- Faarfield: FAARFIELD V 1.42 - Airport Pavement DesignDocumento2 pagineFaarfield: FAARFIELD V 1.42 - Airport Pavement Designpoiuji jinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sangare Sall SafiatouDocumento116 pagineSangare Sall Safiatoushiksha torooNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Botany Handbook 3.11 WebDocumento31 pagineBasic Botany Handbook 3.11 WebAudrygodwyn100% (2)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- 01 Soils of India KPupsc 20 20Documento6 pagine01 Soils of India KPupsc 20 20Swati SrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis of M15 ConcreteDocumento2 pagineAnalysis of M15 ConcreteChau Suktana EnlingNessuna valutazione finora
- South America IV PDFDocumento1 paginaSouth America IV PDFDeymer Nicson RUiz TiradoNessuna valutazione finora
- Susdrain Going With The Flow InfographicDocumento1 paginaSusdrain Going With The Flow InfographicAsyraf DzahiriNessuna valutazione finora
- J6 J 2 Ar ERINM62 ZSa 27 Wa Yq LK TC EDocumento116 pagineJ6 J 2 Ar ERINM62 ZSa 27 Wa Yq LK TC EJelena Savicevic100% (1)
- BRE Digest Guide10Documento22 pagineBRE Digest Guide10LikhinNessuna valutazione finora
- Arthropod Management in Vineyards - Pests, Approaches, and Future DirectionsDocumento510 pagineArthropod Management in Vineyards - Pests, Approaches, and Future Directionsdachaustrasse100% (1)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincDa EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (137)