Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Formula Sheet - Engineering Physics II - Electricity and Magnetism - PHY 303L UT Austin
Caricato da
Jeremy PriestDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Formula Sheet - Engineering Physics II - Electricity and Magnetism - PHY 303L UT Austin
Caricato da
Jeremy PriestCopyright:
Formati disponibili
E & M - Basic Physical Concepts
Electric force and electric eld
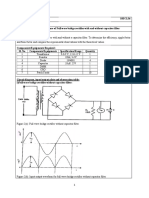
Electric force between 2 point charges: |F | = k 1r2 2 k = 8.987551787 109 N m2 /C2 1 = 8.854187817 1012 C2 /N m2 0 = 4 k qp = qe = 1.60217733 (49) 1019 C mp = 1.672623 (10) 1027 kg me = 9.1093897 (54) 1031 kg ~ ~ =F Electric eld: E
q |Q| Point charge: |E | = k r2 , |q | |q |
Q Current: I = d dt = n q vd A Ohms law: V = I R, E = J ` I E=V ` , J = A, R = A
2
Current and resistance
2 Power: P = I V = V R =I R Thermal coecient of : = 0 T Motion of free electrons in an ideal conductor: E J = m a = vd qm =n q n q2
Direct current circuits
V =IR
~ =E ~1 + E ~2 + E Field patterns: point charge, dipole, k plates, rod, spheres, cylinders,. . . Charge distributions: Q Linear charge density: = x
Q Area charge density: A = A Q Surface charge density: surf = surf A Q Volume charge density: = V
Electric ux and Gauss law
~ n Flux: = E A = E A Gauss law: Outgoing Flux from S, S = Qenclosed 0 Steps: to obtain electric eld ~ pattern and construct S Inspect E H ~ dA ~ = Qencl , solve for E ~ Find s = surf ace E
0
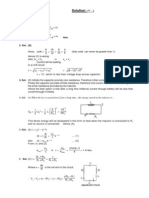
dq di i di Charging: E Vc R i = 0, 1 c dt + R dt = c + R dt = 0 dq i di Discharge: 0 = Vc R i = q c + R dt , c + R dt = 0
Series: V = I Req = I R1 + I R2 + I R3 + , I = Ii V = V + V + V + , V = V Parallel: I = R i R1 R2 R3 eq Steps: in application of Kirchho s Rules Label currents: i1 , i2 , i3 , . . . P P Node equations: iin = iout P P Loop equations: (E ) + (iR)=0 Natural: + for loop-arrow entering terminal for loop-arrow-parallel to current ow y 1 t RC circuit: if d dt + R C y = 0, y = y0 exp( R C )
Magnetic eld and magnetic force
i
Spherical: s = 4 r2 E Cylindrical: s = 2 r ` E Pill box: s = E A, 1 side; = 2 E A, 2 sides k ~ = 0, Esurf Conductor: E = 0, E = surf
in
Potential
surf
0 0 Wire: B = 2 Axis of loop: B = r 2 (a2 +x2 )3/2 ~ = i~ ~ q~ ~ Magnetic force: F `B vB M ~B ~, Loop-magnet ID: ~ = iA ~ = iAn 2 m v 1 = 2r Circular motion: F = r = q v B , T = f v ~ = qE ~ + q~ ~ Lorentz force: F vB ~ Hall eect: V = FM d , U = ~ B
0 = 4 107 T m/A
a2 i
Potential energy: U = q V 1 eV 1.6 1019 J Positive charge moves from high V to low V Q Point charge: V = kr V = V 1 + V2 = . . .
q 1 q2 Energy of a charge-pair: U = k r 12 Potential dierence: |V | = |E sk |, RB ~ ~ ~ s V = E s, VB VA = A E d~ d V V V E = dr , Ex = x = x , etc. f ix y,z
~ and magnetism of matter Sources of B
~
v r r 0 q~ ~ = 0 i ` Biot-Savart Law: B 4 r2 , B = 4 r2 2 0 i y B = 4 sin , sin = a , y = r a r r2 H ~ d~ Amperes law: M = B s= I
Q Q Q Q Series: V = C =C +C +C + , Q = Q i eq 1 2 3 Parallel: Q = Ceq V = C1 V + C2 V + , V = Vi 0 A Q Q Parallel plate-capacitor: C = V =E d = d 2 RQ Q 1 2 Energy: U = 0 V dq = 1 2 C , u = 2 0 E 2 1 2 Dielectrics: C = C0 , U = 21 Q C0 , u = 2 0 E Q Spherical capacitor: V = 4 Q 0 r1 4 0 r2
Capacitances
Q=CV
E = Displ. current: Id = 0 d dt 0 dt Magnetism in atom: Orbital motion: = i A = 2 e mL
Steps: to obtain magnetic eld ~ pattern and construct loop L Inspect B ~. Find M and Iencl , and solve for B
d (E A)
encircled
QA = d dt
~ Potential energy: U = p ~E
eh 24 J/T orbit = n B , B = 2 m = 9.27 10 h Spin: S = 2 , spin = B Magnetism in matter: 0 B = B0 + BM = (1 + ) B0 = (1 + ) 0 B 0 = m H Ferromagnetic: 1 Diamagnetic: 1 < 0 Paramagnetic: 0 < 1, M = C TB
34 J s L = mvr = n h, h = 2h = 1.06 10
Maxwell equations: H H ~ dA ~ = Q, ~ dA ~ = 0, E B 0 H H B E ~ d~ ~ d~ E s = ddt , B s = 0 [I + 0 ddt ]
A = d (A cos t) Rotating loop: d dt dt Cutting B lines change B Eind Eind
~ opposes change of Lenz law: Induced B B d (B A ) d B d B A + B d A = = dt dt dt dt A = ` v, d A = d 1 R R Moving rods: d dt dt dt 2
B E = N ddt , R ~ d~ E= E s,
Faradays law
B =
~M ~ =F E q
~ dA ~, B
U , P = 2S Complete reection: P = 2c c
Reection and Refraction
v2 2 1 Index of refraction: n n2 = v1 = 1 Snells law: n1 sin 1 = n2 sin 2 Critical angle: n2 > n1 , n2 sin c = n1 sin 90 Total reection: > c
Mirrors and lenses
1 1 1 p+q = f
A Long solenoid: L = N B i , B = 0 n i 1 2 Energies: UL = 2 L i2 , uB = 2 1 B
0
N2 21 i1 Mutual: E2 = M21 d i1 dt , M21 = M12 = i, L = N , V = L di Self: E = L d L i dt dt
Inductance
1 2 2 UC = 21 C q , uE = 2 0 E q i L C: VL + VC = 0 L d dt = C q = q0 cos( t + ), q = L1 C , UC + UL = UC max = UL max = U0 y Decay Equations: d dt = a y , y = y0 exp(a t) VL + R VL = 0, L R: E = VL + R i, ddt Lh i E 1 exp R t VL = E exp Rt , i = L R L L R C: r 2 R R Q Q0 e 2 L t cos d t, d = L1 C 2L
Ray tracing rules: Mirror: At symm pt S , reected symmetrically through center of sphere, undeected. Parallel to axis, converges toward F (or diverges away from F ), f = R 2 . Lens: Through center of lens, undeected. Parallel to axis, converges toward F (or diverges away from F ) Image: q > 0 (real), q < 0 (virtual) Focal point F : at p = , q = f f = |f |, + convergent, divergent 0 q Magnication: M = h h = p
n2 n2 n1 1 Refraction at spherical surface: n p + q = R R is coordinate of center with origin at S , with S the symmetry surface on the axis point of n 1 1 1 2 Lens maker: f = n1 1 R R
0 q n1 Two media: M = h h = p n2 1 2
Huygens principles: Points in wave front are sources of next wavelets Forward tangent surface is next wave front
Underdamped, critically damped & overdamped Impedance: [Ohm ] Z
Interference
Maxima = 0, 2 , 4 , ; Minima = , 3 , 5 , Double slits: Iaverage = I0 cos2 2 , = k.
Inductive XL = L, Capactive XC = 1 C R (t) = 1 T f (t) dt Mean value: f 0 T
1 1
A C Circuits q
R2 + (XL XC )2
2 2 1 [sin t]rms = [sin2 t] = [ 1 2 (1 cos 2 t)] = 2
y sin = for small , sin tan d , tan = L , ~ ~ ~2 + A ~3 + Phasor diagram: A = A1 + A Ax = A1x + A2x + A3x + , Ay = A1y + A2y + First minimum for N slits: = 2 N Thin lm: = k + |1ref lected 2ref lected |, = 2 t ref lected = (denser medium); =0 (lighter medium) a b c sin = sin = sin
Electromagnetic waves
0 0 U d z = u c Intensity: I = P = A A R z dt ~ dA ~ = dU + P Energy conservation: S R dt Complete absorption: Momentum p = U c p 1 U 1 = u = S Pressure: P = F = = c A t A c t A
~ E ~ , propagating along: E ~ B ~ B u = u E + u B , uE = u B ~ B ~ ~=E =I = Erms Brms Poynting vector: S , S
Properties of em waves: E = Em cos(k z t), B = E c z c v=d dt = k = f = T , n = v speed of light: c = 1 = 2.99792458 108 m/s
0 0
Resolution criterion: criterion = 1.22 D Grating: Principle maxima = m
raction Di 2 sin 2 Single slit: I = I0 , = k , = a sin
2
Polarization
Brewster (n1 < n2 ): n1 sin br = n2 sin( 2 br ) Polarizer: Etransmit = E0 cos , I = I0 cos2 I0 I Unpolarized light: = 2 Transmitted Intensity: I 0 = I cos2 I0 R 2 cos2 d = I0 I0 = 2 0 2
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Formula Sheet: Electricity and MagnetismDocumento3 pagineFormula Sheet: Electricity and MagnetismThivagar RajasekaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Booklet - WJEC Physics A-LevelDocumento7 pagineData Booklet - WJEC Physics A-LevelStellaNessuna valutazione finora
- Homework 04-Solutions PDFDocumento11 pagineHomework 04-Solutions PDFElizabeth DouglasNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch22 h3 Extra Solutions PDFDocumento4 pagineCh22 h3 Extra Solutions PDFld393563Nessuna valutazione finora
- 3 מטלהDocumento6 pagine3 מטלהניצן גונןNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Quest HW 3aDocumento5 paginePhysics Quest HW 3aFuriFuriNessuna valutazione finora
- HW4 SolutionsDocumento15 pagineHW4 Solutionsellie<3100% (3)
- DC Circuit Notes O LevelDocumento6 pagineDC Circuit Notes O Levelaliayanraza5Nessuna valutazione finora
- HW3 SolutionsDocumento15 pagineHW3 Solutionsellie<3100% (1)
- RLC Series and ParallelDocumento8 pagineRLC Series and ParallelFaizanAshrafNessuna valutazione finora
- Formula Sheet Physics 220 PDFDocumento6 pagineFormula Sheet Physics 220 PDFNimish RamtekeNessuna valutazione finora
- Homework 05-Solutions PDFDocumento5 pagineHomework 05-Solutions PDFld393563Nessuna valutazione finora
- Formula Sheet PhysicsDocumento26 pagineFormula Sheet Physicsmsa.0.70920Nessuna valutazione finora
- Formulas For Calculus-Based Physics 1Documento1 paginaFormulas For Calculus-Based Physics 1Steven J. Biars100% (2)
- Formula SheetDocumento2 pagineFormula SheetFrank PriceNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 11Documento20 pagineChapter 11서승찬100% (1)
- Electrical units of measurment (V,A,Ω,W,... ) PDFDocumento7 pagineElectrical units of measurment (V,A,Ω,W,... ) PDFShoaib QuraishiNessuna valutazione finora
- Ubc Math 264/elec 211 Formulas For Quiz 1 - 2016-02-01Documento2 pagineUbc Math 264/elec 211 Formulas For Quiz 1 - 2016-02-01SteveFarraNessuna valutazione finora
- Homework 03-Solutions PDFDocumento11 pagineHomework 03-Solutions PDFElizabeth DouglasNessuna valutazione finora
- Arfken MMCH 7 S 2 e 1Documento2 pagineArfken MMCH 7 S 2 e 1HassanNessuna valutazione finora
- Infy Mock Test 07a Verbal FDocumento7 pagineInfy Mock Test 07a Verbal FSaravana KarthikeyanNessuna valutazione finora
- AE LAB - Experiment No.2-1Documento4 pagineAE LAB - Experiment No.2-1Prajwal PatilNessuna valutazione finora
- Cheat Sheet Unit 4 Electric PowerDocumento1 paginaCheat Sheet Unit 4 Electric PowerkerrevNessuna valutazione finora
- 21A - Charge and PolarizationDocumento7 pagine21A - Charge and Polarizationdelano whattsNessuna valutazione finora
- Series Parallel Circuit Notes PDFDocumento6 pagineSeries Parallel Circuit Notes PDFClaireDiscipuloNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Quest HW 1bDocumento5 paginePhysics Quest HW 1bFuriFuriNessuna valutazione finora
- PHYS363 Formula SheetDocumento2 paginePHYS363 Formula SheetBen MacLellan100% (1)
- HW1 A SolutionsDocumento5 pagineHW1 A SolutionsAli Abbas SheriffNessuna valutazione finora
- Multivariate Random VariablesDocumento29 pagineMultivariate Random VariablesEdmond ZNessuna valutazione finora
- Anderson Bridge ExperimentDocumento5 pagineAnderson Bridge Experimentsachin singh NegiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 02Documento22 pagineChapter 02Andres A. TabuyoNessuna valutazione finora
- IntegratorDocumento38 pagineIntegratorSyed AshmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice FinalDocumento26 paginePractice Finalchaseutd123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Equations Sheet For FYS1120: Electric Fields Maxwell's EquationsDocumento3 pagineEquations Sheet For FYS1120: Electric Fields Maxwell's EquationsLeseat NocaNessuna valutazione finora
- Things To Know For The Physics GRE: Daniel Beller October 28, 2009Documento20 pagineThings To Know For The Physics GRE: Daniel Beller October 28, 2009Arif SolmazNessuna valutazione finora
- Phys 1004 - Cheat - Sheet. Electromagnetism and WavesDocumento2 paginePhys 1004 - Cheat - Sheet. Electromagnetism and WavesNadya B.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Formula Sheet PHYS 157Documento1 paginaFormula Sheet PHYS 157Carmen YangNessuna valutazione finora
- Formula Sheet-158Documento2 pagineFormula Sheet-158justinkarlpolicarpioNessuna valutazione finora
- 1202 Final Eq SheetDocumento2 pagine1202 Final Eq SheetTheodore MarghituNessuna valutazione finora
- Phys303K Dicus Exam4Solutions Spring08Documento16 paginePhys303K Dicus Exam4Solutions Spring08Kayla WorachekNessuna valutazione finora
- Bütün Fizik FormülleriDocumento13 pagineBütün Fizik Formüllerimhasan13Nessuna valutazione finora
- PhysicsDocumento4 paginePhysicstim94leeNessuna valutazione finora
- Study MaterialDocumento42 pagineStudy MaterialWhite DevilNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecse 353 Electromagnetic Fields and Waves Formulas: V) V + V V V V 0Documento6 pagineEcse 353 Electromagnetic Fields and Waves Formulas: V) V + V V V V 0Eileen FuNessuna valutazione finora
- University Physics Equation SheetDocumento2 pagineUniversity Physics Equation SheetDipesh BhandariNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Sheet PhysicsDocumento4 pagineData Sheet PhysicsBernice JohnsonNessuna valutazione finora
- GRE Physics Subject Test Cheat Sheet: by Winston Yin, 2015. Please Add Missing EquationsDocumento4 pagineGRE Physics Subject Test Cheat Sheet: by Winston Yin, 2015. Please Add Missing EquationsjaredNessuna valutazione finora
- University Physics Equation SheetDocumento2 pagineUniversity Physics Equation SheetKyle OberleNessuna valutazione finora
- Phys 122 Equation Sheet Exam 3Documento3 paginePhys 122 Equation Sheet Exam 3zxc100311Nessuna valutazione finora
- Formula SheetDocumento5 pagineFormula SheetKevin YeNessuna valutazione finora
- Solution:: DT DQ e RC C V BDocumento5 pagineSolution:: DT DQ e RC C V BAritra LahiriNessuna valutazione finora
- Part 1 - Physics: L B A G 2Documento7 paginePart 1 - Physics: L B A G 2bindaaz301Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanics Formulae For Physics Proficiency Exams: Motion, Forces, Work, Energy and MomentumDocumento4 pagineMechanics Formulae For Physics Proficiency Exams: Motion, Forces, Work, Energy and MomentumeiufjojNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 3Documento15 pagineAssignment 3Jofy GeorgeNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Formulas: R R R R R R R R R R R R TanDocumento9 paginePhysics Formulas: R R R R R R R R R R R R TanLarry ArevaloNessuna valutazione finora
- 72 ReviewerDocumento17 pagine72 ReviewerGeronimo Allan Jerome AcostaNessuna valutazione finora
- Formula Sheet For PhysicsDocumento6 pagineFormula Sheet For PhysicsAsim ButtNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics 21 SolutionsDocumento92 paginePhysics 21 SolutionsOğuzhan Odbay100% (1)
- Exam3 Solution Sum06Documento5 pagineExam3 Solution Sum06wenwenNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch02 - Coulomb's Law and Electric Field IntensityDocumento26 pagineCh02 - Coulomb's Law and Electric Field Intensityjp ednapilNessuna valutazione finora
- Circular Dichroism of Protein: PC3267 Updated in Jan. 2007Documento7 pagineCircular Dichroism of Protein: PC3267 Updated in Jan. 2007Chellam Gayathri SubashNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmaceutical Botany With Taxonomy Laboratory (PHBIO 1101L)Documento6 paginePharmaceutical Botany With Taxonomy Laboratory (PHBIO 1101L)Yuri DryzgaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ripple Tank Lab GuidelinesDocumento9 pagineRipple Tank Lab Guidelinesjavierdb2012Nessuna valutazione finora
- Figuras de Interferencia HiáxicasDocumento19 pagineFiguras de Interferencia HiáxicasLeo Alvarez RomeroNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Atmospheric ScatteringDocumento15 pagineAtmospheric ScatteringSid WorldNessuna valutazione finora
- NEET 2018 Aakash Solution Code DDDocumento35 pagineNEET 2018 Aakash Solution Code DDvinayNessuna valutazione finora
- 2009 2nd Exam Physics 211 Summer-SolutionDocumento7 pagine2009 2nd Exam Physics 211 Summer-Solutionpredrag dNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 13 Section 3 WebsiteDocumento10 pagineChapter 13 Section 3 Websiteapi-260037870Nessuna valutazione finora
- Author's Accepted Manuscript: Physica B: Physics of Condensed MatterDocumento29 pagineAuthor's Accepted Manuscript: Physica B: Physics of Condensed MatteryassinebouazziNessuna valutazione finora
- C&A MFL06, Microscopio Óptico Dual, Manual EnglishDocumento6 pagineC&A MFL06, Microscopio Óptico Dual, Manual EnglishTICTRONICA Ltda.Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1.3.1 Equations & Graphs of Motion MS PDFDocumento3 pagine1.3.1 Equations & Graphs of Motion MS PDFnaziya begumNessuna valutazione finora
- AOSS321 L08 020309 Centrifugal Gravity Coriolis ForceDocumento65 pagineAOSS321 L08 020309 Centrifugal Gravity Coriolis ForceErvin ArrasyidNessuna valutazione finora
- Textised! L12 Working With CCD DataDocumento6 pagineTextised! L12 Working With CCD DataVickySwiftNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 0910 Spring Set2Documento3 pagineAssignment 0910 Spring Set2Sarp Yiğit ŞirinNessuna valutazione finora
- Bartolo B.D., Collins J. (Eds.) Biophotonics.. Spectroscopy, Imaging, Sensing, and ManipulationDocumento450 pagineBartolo B.D., Collins J. (Eds.) Biophotonics.. Spectroscopy, Imaging, Sensing, and ManipulationLiviu LucaNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes of 10th Cbse Human EyeDocumento7 pagineNotes of 10th Cbse Human EyeAvichal TatuNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 23 Intro To Optical Amplifiers PDFDocumento12 pagineLecture 23 Intro To Optical Amplifiers PDF0938089460Nessuna valutazione finora
- Physics 12 Unit 4 SolnsDocumento119 paginePhysics 12 Unit 4 SolnsSRX84X0% (1)
- Bericht Mendocinomotor PDFDocumento24 pagineBericht Mendocinomotor PDFKodos666100% (1)
- ColorimeterDocumento23 pagineColorimetershalaka.agarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Sunset and Sunrise TipsDocumento4 pagineSunset and Sunrise TipsAvinash ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Sony Dsr-pd175, Pd177, Pd198 Operating ManualDocumento128 pagineSony Dsr-pd175, Pd177, Pd198 Operating ManualManojChakkambath100% (1)
- Lecture SP 015 Lesson 2 PDFDocumento23 pagineLecture SP 015 Lesson 2 PDFAnonymous hKDpglNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics General ObjectivesDocumento22 paginePhysics General ObjectivesOlamide RokeebNessuna valutazione finora
- Why Is The Sky BlueDocumento7 pagineWhy Is The Sky BlueY D Amon GanzonNessuna valutazione finora
- Losses in Optical FiberDocumento8 pagineLosses in Optical FiberthatoneJgd100% (8)
- CH 05Documento34 pagineCH 05claudio100% (1)
- Comsol Command EmwDocumento21 pagineComsol Command EmwcontactsitaNessuna valutazione finora