Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
OPNET-Chapter 3token Ring
Caricato da
navidabedpoorDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
OPNET-Chapter 3token Ring
Caricato da
navidabedpoorCopyright:
Formati disponibili
OPNET IT Guru Academic Edition Chapter 3 Token Ring
N. Abedpoor International Imam Reza University of Mashhad
N. Abedpoor International Imam Reza University of Mashhad Dec. 2013
Chapter 3 Lab2- Token Ring
Token Ring Model Description
Model Scope and Limitations
Process Models Model Interfaces
Packet Formats
ICI Formats Token Ring Addressing and Ring Identifiers
Lab 2 Token Ring
N. Abedpoor International Imam Reza University of Mashhad Dec. 2013
Token Ring Description
The Token Ring Access Method (TR) provides general purpose networking at 4 or 16 Mbits/sec transmission rates for small or large numbers of communicating stations configured in a ring or hub topology.
Detailed information on the Token Ring protocol can be found in the following documentation:
IEEE Standard 802.5, 1985 Specification Token Ring Access Method.
N. Abedpoor International Imam Reza University of Mashhad
Dec. 2013
Model Scope and Limitations
The first important restriction is that the ring initialization and recovery processes are not modeled explicitly. While the model could be extended to address these areas (it is provided in source code form), its primary usefulness is in obtaining measurements of steady state performance. A second restriction has to do with the modeling of error conditions and in general, the role of the NMT entity. In its current form, the model makes no attempt to implement the mechanisms related to the detection of damaged frames, or the reporting of errors to NMT. The interface between MAC and NMT is, in fact, not presently incorporated into the implementation of MAC. The effects of station latency and propagation delay are also incorporated into the model. The restack operation and the THT are also explicitly modeled.
N. Abedpoor International Imam Reza University of Mashhad Dec. 2013
Model Scope and Limitations
The parameters that may be easily controlled by the user, without having to modify the internals of the provided models include: The number of stations attached to the ring The address of the station that launches the token as the simulation begins, the active monitor The delay incurred by frames and tokens as they traverse a stations ring interface The propagation delay separating stations on the ring The number of bits per second transmitted by the medium The duration of the THT, the amount of time a station may transmit on the ring The amount of time it takes a station to modify its priority stacks in a restack operation
N. Abedpoor International Imam Reza University of Mashhad Dec. 2013
Model Scope and Limitations
Model features include: 24-bit assured minimum latency Token acceleration Modularitythere can be more than one ring in a network model Token Ring link models allow you to simulate point-to-point trunk links; a single trunk link can carry traffic for multiple VLANs as specified by IEEE 802.1q.
N. Abedpoor International Imam Reza University of Mashhad
Dec. 2013
Model Scope and Limitations
Model features include: You can configure port-based VLANs on all generic bridge and switch models, and on any vendor-specific models that support this technology. To configure a VLAN, set the VLAN scheme attribute to Port-based VLAN on the bridge or switch supporting the VLAN. You can assign VLAN identifiers to specific port numbers in the VLAN Port Configuration Table. (To find a links port numbers, use Link Interfaces on the Edit Attributes (Advanced) dialog box.) Note that you can assign only one VLAN identifier to a specific port.
N. Abedpoor International Imam Reza University of Mashhad Dec. 2013
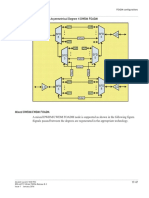
Process Models
N. Abedpoor International Imam Reza University of Mashhad
Dec. 2013
Process Models
N. Abedpoor International Imam Reza University of Mashhad
Dec. 2013
Model Interfaces
Packet Formats The following table enumerates the packet formats used in the Token Ring model suite.
N. Abedpoor International Imam Reza University of Mashhad
Dec. 2013
10
Model Interfaces
ICI Formats (Interface Control Information) The following table enumerates the interface control information (ICI) formats used in the Token Ring model suite.
N. Abedpoor International Imam Reza University of Mashhad
Dec. 2013
11
Model Interfaces
Token Ring Addressing and Ring Identifiers Each ring has a unique identifier, specified by the ring_id attribute of the tr_mac_op_v2 process model. All Token Ring MAC entities on the same ring must agree on the value of this identifier. The ring IDs can be specified to be automatically assigned to meet these requirements.
Each MAC entity has a physical address, specified by the station_address attribute of the tr_mac_op_v2 process model. Token Ring addresses must be consecutive (no gaps in numbering) and increase in the direction of the point-to-point links along a ring. In addition, when using these models in conjunction with the Spanning Tree Bridge models, the addresses must be unique across the entire OPNET network to support correct bridge address learning. The addresses can be specified to be automatically assigned to meet these requirements.
N. Abedpoor International Imam Reza University of Mashhad
Dec. 2013
12
Lab 2 Token Ring
A Shared-Media Network with Media Access Control
A token ring network consists of a set of nodes connected in a ring. The ring is a single shared medium. The token ring technology involves a distributed algorithm that controls when each node is allowed to transmit. With a ring topology, any link or node failure would render the whole network useless. This problem can be solved by using a star topology where nodes are connected to a token ring hub. The hub acts as a relay, known as a multi station access unit (MSAU)
N. Abedpoor International Imam Reza University of Mashhad
Dec. 2013
13
The token, which is just a special sequence of bits, circulates around the ring; each node receives and then forwards the token. When a node that has a frame to transmit sees the token, it takes the token off the ring and instead inserts its frame into the ring. When the frame makes its way back around to the sender, this node strips its frame off the ring and reinserts the token. The token holding time (THT) is the time a given node is allowed to hold the token. The THT has an effect on the utilization and fairness of the network, where utilization is the measure of the bandwidth used versus that available on the given ring.
N. Abedpoor International Imam Reza University of Mashhad
Dec. 2013
14
In this lab, you will set up a token ring network with 14 nodes connected in a star topology. The links you will use operate at a data rate of 4 Mbps. You will study how the utilization and delay of the network are affected by the network load as well as the THT.
Pay Attention and Then Start
N. Abedpoor International Imam Reza University of Mashhad
Dec. 2013
15
NOTES:
Create Project:
Name the project <your initials>_Token Name the scenario Balanced make sure that Create Empty Scenario
Choose Office for Network Scale
N. Abedpoor International Imam Reza University of Mashhad
Dec. 2013
16
NOTES:
Create the Network:
Use Rapid Configuration. Star Topology Choose Token_ring from Model List
N. Abedpoor International Imam Reza University of Mashhad
Dec. 2013
17
Save Project
N. Abedpoor International Imam Reza University of Mashhad
Dec. 2013
18
NOTES: Configure Network Nodes configure the THT of the nodes Select Similar Nodes Edit Attributes. Set Value Shown in figure.
N. Abedpoor International Imam Reza University of Mashhad
Dec. 2013
19
NOTES: Configure the Simulation
N. Abedpoor International Imam Reza University of Mashhad
Dec. 2013
20
NOTES: Configure the Simulation
Object Attributes Tab
Office Network.*.Token Ring Parameters[0].THT Duration
N. Abedpoor International Imam Reza University of Mashhad
Dec. 2013
21
NOTES: Configure the Simulation
Advanced Tab
Set Scalar File Name to <your initials>_Token_Balanced
N. Abedpoor International Imam Reza University of Mashhad
Dec. 2013
22
NOTES: Choose the Statistics
Choose Individual Statistics - Expand the Global Statistics hierarchy a) Traffic Sink check the Traffic Received (packets/sec) box b) Traffic Source - check the Traffic Sent (packets/sec) box Expand the Node Statistics hierarchy a) Utilization
N. Abedpoor International Imam Reza University of Mashhad
Dec. 2013
23
NOTES: to collect the average of the above statistics as a scalar value by the end of each simulation run: Simulation menu - Statistics (Advanced)
N. Abedpoor International Imam Reza University of Mashhad
Dec. 2013
24
NOTES: be sure Traffic Sent and Traffic Received appeared under the Global Statistics Probes and Utilization appeared under Node Statistics Probes Set the Values for both Traffic Sent and traffic Rec
N. Abedpoor International Imam Reza University of Mashhad
Dec. 2013
25
we need to analyze the effect of THT on the network performance: Objects menu Create Attribute Probe Right Click on new Attribute Probe Choose Attributed Object expand Office Network select Node_0 Right Click on new Attribute Probe Edit Attributes Save from File Menu
N. Abedpoor International Imam Reza University of Mashhad
Dec. 2013
26
NOTES: Duplicate Scenario The token ring network scenario we just implemented is balanced: the distribution of the generated traffic in all nodes is the same. To compare performance, you will create an unbalanced scenario as follows: 1- Scenarios menu Duplicate Scenario name Unbalanced OK 2- select Nod_0 and Nod_7 by shift-Clicking Right click Edit Attributes Set the Interarrival time Value show in this figure. 3- select all nodes except Nod_0 and Nod_7 Right click Edit Attributes Set the Interarrival time Value show in this figure. 4- click anywhere in the workspace to unselect objects.
N. Abedpoor International Imam Reza University of Mashhad Dec. 2013
27
NOTES: 5- Click Configure/Run Simulation button:
Name the scalar file <your initials>_Token_Unbalanced
N. Abedpoor International Imam Reza University of Mashhad
Dec. 2013
28
NOTES: Run the Simulation
Scenarios menu Manage Scenario. Value under Results column to <collect> OK (to run Simulation) After simulation completes, click close Save your Project
N. Abedpoor International Imam Reza University of Mashhad
Dec. 2013
29
NOTES: View the Results Flow Steps in your source document to get the flowing results.
N. Abedpoor International Imam Reza University of Mashhad
Dec. 2013
30
NOTES: View the Results Flow Steps in your source document to get the results.
test your self in OPNET simulation now.
Start as professionals
N. Abedpoor International Imam Reza University of Mashhad Dec. 2013
31
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- OPNET-Chapter 4 - Switched LANs NetworksDocumento44 pagineOPNET-Chapter 4 - Switched LANs Networksnavidabedpoor0% (1)
- OPNET Chapter 1-IntroductionDocumento83 pagineOPNET Chapter 1-IntroductionnavidabedpoorNessuna valutazione finora
- Plan If 2000Documento5 paginePlan If 2000kajfahmNessuna valutazione finora
- Introducing Network Design Concepts: Designing and Supporting Computer Networks - Chapter 1Documento32 pagineIntroducing Network Design Concepts: Designing and Supporting Computer Networks - Chapter 1Desalegn KodosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Performance Evaluation of LEACH Protocol For Wireless Sensor NetworkDocumento5 paginePerformance Evaluation of LEACH Protocol For Wireless Sensor NetworkIJIRAE- International Journal of Innovative Research in Advanced EngineeringNessuna valutazione finora
- Mimo and OFDM in Wireless CommunicationDocumento5 pagineMimo and OFDM in Wireless CommunicationEditor IJRITCCNessuna valutazione finora
- Applying Time-Division Multiplexing in Star-Based Optical NetworksDocumento4 pagineApplying Time-Division Multiplexing in Star-Based Optical NetworksJuliana CantilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Project DocumentsDocumento6 pagineProject DocumentsSyed Shah KhalidNessuna valutazione finora
- A Survey of Network Simulation Tools: Current Status and Future DevelopmentsDocumento6 pagineA Survey of Network Simulation Tools: Current Status and Future DevelopmentsSebastián Ignacio Lorca DelgadoNessuna valutazione finora
- CN Lab FinalDocumento59 pagineCN Lab Finalreddy aditya456Nessuna valutazione finora
- Optical Add DropDocumento15 pagineOptical Add DropAnonimastacio de la FuenteNessuna valutazione finora
- CCN Completed1Documento46 pagineCCN Completed1Deepa JerinNessuna valutazione finora
- KhushiDocumento15 pagineKhushiparwatenishikantNessuna valutazione finora
- The Comparison of Routers by Firms Cisco, Juniper and HuaweiDocumento8 pagineThe Comparison of Routers by Firms Cisco, Juniper and HuaweiJosue CaceresNessuna valutazione finora
- Multistage Interconnection Network For Mpsoc: Performances Study and Prototyping On FpgaDocumento6 pagineMultistage Interconnection Network For Mpsoc: Performances Study and Prototyping On Fpgagk_gbuNessuna valutazione finora
- Greater Noida Institute of Technology: SESSION-2020-2021Documento39 pagineGreater Noida Institute of Technology: SESSION-2020-2021Abhishek ChauhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Computer Network Lab Mannual (18ECL76)Documento99 pagineFinal Computer Network Lab Mannual (18ECL76)Ankushh RNessuna valutazione finora
- Energy Efficient Minimum Broadcast Routing in ASNDocumento5 pagineEnergy Efficient Minimum Broadcast Routing in ASNEditor IJRITCCNessuna valutazione finora
- Aodv ThesisDocumento4 pagineAodv ThesisBrittany Brown100% (1)
- Analysis of Routing Protocols Based On Network Parameters in WANETDocumento7 pagineAnalysis of Routing Protocols Based On Network Parameters in WANETTayyab RafiqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter5 Network Layers RoutingDocumento63 pagineChapter5 Network Layers Routingforallofus435Nessuna valutazione finora
- Module 3Documento109 pagineModule 3geles73631Nessuna valutazione finora
- CS549 MiniProj Aug20Documento3 pagineCS549 MiniProj Aug20Jhonny SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Report On Dynamic Routing Using Acl: Camellia Institute of TechnologyDocumento56 pagineProject Report On Dynamic Routing Using Acl: Camellia Institute of TechnologyRitanjan DawnNessuna valutazione finora
- Medi-Caps University 2020-2021Documento11 pagineMedi-Caps University 2020-2021Krati ChhabraNessuna valutazione finora
- Progress ReportDocumento8 pagineProgress ReportTonmoyNessuna valutazione finora
- ReportDocumento18 pagineReportMohd Mujtaba AkhtarNessuna valutazione finora
- CN Lab File-1Documento51 pagineCN Lab File-1Shreya VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- TCP Concurrent Echo Program Using Fork and ThreadDocumento5 pagineTCP Concurrent Echo Program Using Fork and ThreadEditor IJRITCCNessuna valutazione finora
- College of Arbaminch Institute of Technology (AMIT)Documento15 pagineCollege of Arbaminch Institute of Technology (AMIT)TekletsadikNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment No:13: Name Tarun Shetty Class Be Extc B Batch B2 Roll No. 54Documento4 pagineExperiment No:13: Name Tarun Shetty Class Be Extc B Batch B2 Roll No. 54Dikshit ShettyNessuna valutazione finora
- Enterprise Network Using CiscoDocumento22 pagineEnterprise Network Using CiscoBHARATH DNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Communications Lab FileDocumento53 pagineComputer Communications Lab Fileyageshpandey88Nessuna valutazione finora
- University of Engineering & Technology (UET) Taxila Computer Communication Networks LABDocumento4 pagineUniversity of Engineering & Technology (UET) Taxila Computer Communication Networks LABAreeba NoorNessuna valutazione finora
- Simulation Based Performance Analyses On Ripv2, Eigrp, and Ospf Using OpnetDocumento24 pagineSimulation Based Performance Analyses On Ripv2, Eigrp, and Ospf Using OpnetAadan CaddeNessuna valutazione finora
- A Unique Design Based Processing Layer For Modular Architecture in Wireless Sensor Networks and Its ApplicationsDocumento5 pagineA Unique Design Based Processing Layer For Modular Architecture in Wireless Sensor Networks and Its ApplicationsseventhsensegroupNessuna valutazione finora
- Performance Study of Dymo On Demand Protocol Using Qualnet 5.0 SimulatorDocumento5 paginePerformance Study of Dymo On Demand Protocol Using Qualnet 5.0 SimulatorIOSRJEN : hard copy, certificates, Call for Papers 2013, publishing of journalNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Engineering Department: CertificateDocumento19 pagineComputer Engineering Department: Certificatehenee patelNessuna valutazione finora
- FGM Dam 2016 04 15Documento41 pagineFGM Dam 2016 04 15NICOLAS ANDRES RAMOS LEIVANessuna valutazione finora
- Thesis On Manet Routing ProtocolsDocumento7 pagineThesis On Manet Routing Protocolsjosephineromeroalbuquerque100% (2)
- Ijaiem 2013 07 09 022Documento8 pagineIjaiem 2013 07 09 022International Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNessuna valutazione finora
- CCNA 1 v7 Modules 4 - 7 - Ethernet Concepts Exam AnswersDocumento15 pagineCCNA 1 v7 Modules 4 - 7 - Ethernet Concepts Exam Answersmieczyslawaklocko14Nessuna valutazione finora
- RTL Compiler PDFDocumento49 pagineRTL Compiler PDFStudent100% (1)
- IEC2020063 PWC NetsimDocumento15 pagineIEC2020063 PWC NetsimMedha TiwariNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Network No1 Introduction From APCOMS (UandiStar)Documento36 pagineComputer Network No1 Introduction From APCOMS (UandiStar)UdayKumar JayavaramNessuna valutazione finora
- Formal Design and Verification of On Chip Networking: Al Sammane, J. Schmaltz and BorrioneDocumento2 pagineFormal Design and Verification of On Chip Networking: Al Sammane, J. Schmaltz and BorrioneMichael ZimmermanNessuna valutazione finora
- Specialization Sap Id Name: Minor-1 ProjectDocumento19 pagineSpecialization Sap Id Name: Minor-1 ProjectMohd Mujtaba AkhtarNessuna valutazione finora
- Con RamDocumento12 pagineCon RamRAJKUMARNessuna valutazione finora
- Hallenges and Romising Esults in O Rototyping Sing S: C P R N CP U FpgaDocumento10 pagineHallenges and Romising Esults in O Rototyping Sing S: C P R N CP U FpgaMark NeishaburiNessuna valutazione finora
- L N Computer Network: B Ivth SDocumento15 pagineL N Computer Network: B Ivth SWilliam MoseleyNessuna valutazione finora
- ThesisDocumento18 pagineThesisSourav MahatoNessuna valutazione finora
- (IJCST-V4I5P9) : Molli Srinivasa Rao, Dr. S. Pallam ShettyDocumento5 pagine(IJCST-V4I5P9) : Molli Srinivasa Rao, Dr. S. Pallam ShettyEighthSenseGroupNessuna valutazione finora
- Assign1 CNSDocumento11 pagineAssign1 CNSKaruna PardhiNessuna valutazione finora
- CN Practical FileDocumento26 pagineCN Practical Filearshpoddar4Nessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Networks Lab ManualDocumento34 pagineComputer Networks Lab ManualRamesh VarathanNessuna valutazione finora
- Internet WorkingDocumento18 pagineInternet WorkingUrja DhabardeNessuna valutazione finora
- Increasing Network Lifetime by Energy-Efficient Routing Scheme For OLSR ProtocolDocumento5 pagineIncreasing Network Lifetime by Energy-Efficient Routing Scheme For OLSR ProtocolManju ManjuNessuna valutazione finora
- CCN OelDocumento7 pagineCCN OelAbdul ShakoorNessuna valutazione finora
- Cisco Packet Tracer Implementation: Building and Configuring Networks: 1, #1Da EverandCisco Packet Tracer Implementation: Building and Configuring Networks: 1, #1Nessuna valutazione finora
- An Approach To Routing in A Clos: Randy Bush Randy IIJ Lab & Arrcus With Keyur Patel, Arrcus and A Cast of DozensDocumento63 pagineAn Approach To Routing in A Clos: Randy Bush Randy IIJ Lab & Arrcus With Keyur Patel, Arrcus and A Cast of Dozensa3172741Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2021 IC SEFET Ieee Kavitha LalithaDocumento7 pagine2021 IC SEFET Ieee Kavitha LalithaR.V.S.LALITHANessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Networks Prev Papers-LazysrmiteDocumento4 pagineComputer Networks Prev Papers-LazysrmiteChalla RohitNessuna valutazione finora
- M852 1 6-SERIAL A4 E ScreenDocumento29 pagineM852 1 6-SERIAL A4 E ScreenRiky FitriadiNessuna valutazione finora
- ETherCAT CommunicationDocumento218 pagineETherCAT CommunicationNguyen Van TrungNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 Network TypesDocumento79 pagineChapter 3 Network TypesFikaduNessuna valutazione finora
- Combricks Rs 485 Scope Repeater Type 1 ManualDocumento217 pagineCombricks Rs 485 Scope Repeater Type 1 ManualCarlos CarlosNessuna valutazione finora
- The Research On The Reliability Evaluation Systems of Communication NetworksDocumento8 pagineThe Research On The Reliability Evaluation Systems of Communication NetworksKADEKODI PRAVIN BHASKARNessuna valutazione finora
- IFTAS v3 Solution Document13.02.23Documento97 pagineIFTAS v3 Solution Document13.02.23davidglitsNessuna valutazione finora
- Csi ZG582 Course HadnoutDocumento14 pagineCsi ZG582 Course Hadnoutdeepak kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Network TopologyDocumento35 pagineNetwork TopologyLekshmi NairNessuna valutazione finora
- Network Infrastructure Lesson 2Documento90 pagineNetwork Infrastructure Lesson 2Rukiah Lei DeeNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA Center For SDA Lab Guide v1.0.3 - (Final)Documento235 pagineDNA Center For SDA Lab Guide v1.0.3 - (Final)Pablo ProañoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cs 601Documento23 pagineCs 601chiNessuna valutazione finora
- Student Packet Tracer ManualDocumento27 pagineStudent Packet Tracer ManualEcaNessuna valutazione finora
- NIL CISCO SD-WAN & Security Bootcamp 20.1 - LGDocumento108 pagineNIL CISCO SD-WAN & Security Bootcamp 20.1 - LGPepito CortizonaNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Manual Do Produto 1830 PSS 16IIDocumento58 pagine4 Manual Do Produto 1830 PSS 16IIClaudia DombroskiNessuna valutazione finora
- Crsimulator: A Discrete Simulation Model For Cognitive Radio Ad Hoc Networks in Omnet ++Documento8 pagineCrsimulator: A Discrete Simulation Model For Cognitive Radio Ad Hoc Networks in Omnet ++VijayKumar LokanadamNessuna valutazione finora
- Network Design Module2 2022 2023Documento9 pagineNetwork Design Module2 2022 2023Jhe MaejanNessuna valutazione finora
- 16.5.2 Lab - Secure Network Devices - ILMDocumento11 pagine16.5.2 Lab - Secure Network Devices - ILMArun KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab - Configuring 802.1Q Trunk-Based Inter-VLAN Routing Topology (Use F0/1 Anywhere It Says G0/1) (Most Answers Appear, You Complete Last Two Questions On pp6-7)Documento17 pagineLab - Configuring 802.1Q Trunk-Based Inter-VLAN Routing Topology (Use F0/1 Anywhere It Says G0/1) (Most Answers Appear, You Complete Last Two Questions On pp6-7)Muhd SyarafuddinNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 8 Network TopologyDocumento25 pagineLecture 8 Network TopologydeepaksinghalNessuna valutazione finora
- Icnd Part 1, Vol 1Documento367 pagineIcnd Part 1, Vol 1Tin Myo Thaw100% (1)
- Network Simulator2 (NS2) Basic CommandsDocumento4 pagineNetwork Simulator2 (NS2) Basic Commandshariharanpotter100% (7)
- Assignment 2 171Documento5 pagineAssignment 2 171171-2022 Pranav MhalsekarNessuna valutazione finora
- OG For WDM ASON Network Management - (V100R006C02 - 01)Documento354 pagineOG For WDM ASON Network Management - (V100R006C02 - 01)Taha TounsiNessuna valutazione finora
- 4-1892 - PK Controller Product Update - v2Documento43 pagine4-1892 - PK Controller Product Update - v2Mayer FernandesNessuna valutazione finora
- Advance Metering Infrastructure and DLMS/COSEM Standards For Smart GridDocumento6 pagineAdvance Metering Infrastructure and DLMS/COSEM Standards For Smart GridKingkulkNessuna valutazione finora
- Performance Analysis of The Bus Topology Network For Effectual Data DistributionDocumento8 paginePerformance Analysis of The Bus Topology Network For Effectual Data DistributionIJEACS UKNessuna valutazione finora
- PBL Activity 1 M.Ali ArifDocumento4 paginePBL Activity 1 M.Ali ArifMUHAMMAD Ali ArifNessuna valutazione finora