Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Nursing Care Plan - Pneumothorax PDF
Caricato da
Janine Joy OrpillaDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Nursing Care Plan - Pneumothorax PDF
Caricato da
Janine Joy OrpillaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
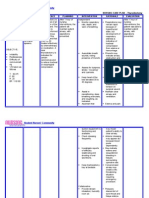
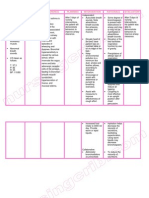
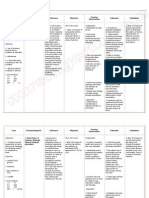
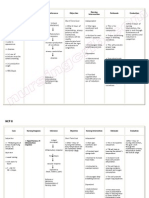
Patient B is a 67 years old male and has been diagnosed with Pneumothorax secondary to Vehicular Accident.
With CTT connected to water seal drainage. ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS Subjective Data: Nahihirapan ako huminga Tumusok kasi yung sarili kong buto sa baga ko, kaya eto inaalis nila yung namuong dugo sa baga ko As manifested by the patient. Objective Data: With chest thoracostomy connected to water seal chamber at Right, Bradypnea Temp: 36.7C RR: 14 bpm BP: 130/90 mm/Hg PR: 79 cpm Ineffective breathing pattern related to airway obstruction secondary to Pneumothorax. PLANNING After 8 hours of shift: Independent Intervention: 1. Monitor rate, Goal: rhythm, and depth The patient of respiration. Note will be able breathing to establish a irregularities, for normal, example, apneustic, effective ataxic, or cluster respiratory breathing. pattern as 2. Note competence evidenced by of gag and swallow increase reflexes and respiratory clients ability to rate. The protect own patient will airway. verbalize the understanding 3. Elevate head of of smoking free lifestyle. bed as permitted and position on Objective: sides, as indicated. The patient will be able 4. Encourage deep breathing if client to demonstrate is conscious 5. Auscultate breath breathing sounds, noting exercises to promote lung areas of hypoventilation and expansion. presence of adventitious sounds. 6. Monitor use of respiratory depressant drugs, such as sedatives. 7. Instruct the patient to avoid over-eating and gas forming foods. 8. Maintain calm attitude while
INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION >Changes may indicate onset of pulmonary complications. >Ability to mobilize or clear secretions is important to airway maintenance. Loss of swallow or cough reflex may indicate need for artificial airway or intubation. > Facilitates lung expansion and ventilation, and reduces risk of airway obstruction by tongue. > Prevents or reduces atelectasis. >Identifies pulmonary problems such as atelectasis, congestion, and airway obstruction, which may jeopardize Goal met: The patients respiratory rate is increased (RR: 18 bpm) The patient is able to demonstrate breathing exercises. And the patient is able to verbalize his understanding of smoking free lifestyle.
dealing with the patient
cerebral oxygenation. >Can increase Dependent respiratory Intervention: embarrassment Administer pain and killer/sedative/anti- complications. pyretic as prescribed by the >To avoid doctor. abdominal distension Collaborative intervention: >To limit Assist in level of Reclogging of the anxiety CTT Assist the patient in >To Follow developing plan of patients smoking cessation therapeutic (Inform the patient regimen to about the adverse stabilize her and side effects of wellness of smoking. health. >To promote maximum inspiration. >To promote faster healing and to promote patients optimal health.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Case Study Nursing Diagnosis of PneumothoraxDocumento8 pagineCase Study Nursing Diagnosis of PneumothoraxJansen Arquilita RiveraNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento10 pagineNursing Care PlanElijah S GomezNessuna valutazione finora
- NCPDocumento9 pagineNCPEjie Boy Isaga67% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural EffusionDocumento4 pagineNursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural EffusionTrixie Anne GamotinNessuna valutazione finora
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocumento2 pagineImpaired Gas ExchangeHanya Bint PotawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento22 pagineNursing Care PlanjamNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP PneumothoraxDocumento3 pagineNCP Pneumothorax'Harold Mark Borja100% (2)
- Prioritized Nursing Problem For Pneumothorax Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention RationaleDocumento3 paginePrioritized Nursing Problem For Pneumothorax Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention RationaleJoshua VillarbaNessuna valutazione finora
- Subjective: Ventilation AssistanceDocumento3 pagineSubjective: Ventilation AssistanceJobelle Acena100% (2)
- NCP Impaired Gas Exhange CHEST INJURYDocumento4 pagineNCP Impaired Gas Exhange CHEST INJURYMa. Elaine Carla Tating100% (2)
- NCP For HemothoraxDocumento12 pagineNCP For Hemothoraxroseonabreeze0% (1)
- Oxygenation - NCPDocumento5 pagineOxygenation - NCPCazze SunioNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Respiratory DistressDocumento2 pagineAcute Respiratory Distressminaanne100% (3)
- 6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansDocumento7 pagine6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansShaina Fe RabaneraNessuna valutazione finora
- Ards NCPDocumento5 pagineArds NCPgopscharanNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento4 pagineNCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceKim Gabrielle Exene LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Copd4Documento15 pagineNCP Copd4Alessa Marie Crisostomo Salazar100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento9 pagineNursing Care PlanJam AbantaoNessuna valutazione finora
- 7 NCPDocumento7 pagine7 NCPVina EmpialesNessuna valutazione finora
- ThyroidectomyDocumento2 pagineThyroidectomyYenyen Legas100% (2)
- Asthma Impaired Gas ExchangeDocumento2 pagineAsthma Impaired Gas ExchangeNedeve Ozned100% (5)
- Nursing Care Plan For Pneumonia With Diagnosis InterventionsDocumento4 pagineNursing Care Plan For Pneumonia With Diagnosis InterventionsJazzmin Angel ComalingNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Presence of Secretion in Trachea-Bronchial Tree Secondary To History of CAPDocumento2 pagineNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Presence of Secretion in Trachea-Bronchial Tree Secondary To History of CAPpa3kmedina100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento4 pagineNursing Care PlanAdreanah Martin RañisesNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento3 pagineNursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceYum C88% (26)
- NCP - AnxietyDocumento1 paginaNCP - AnxietyNovie Carla100% (1)
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To BronchospasmDocumento2 pagineIneffective Airway Clearance Related To BronchospasmReylan Garcia100% (4)
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento4 pagineNursing Care PlanJoshua Pascasio100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Bronchial AsthmaDocumento2 pagineNursing Care Plan Bronchial AsthmaSummer Ilu100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento3 pagineNursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearancederic100% (13)
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Breathing Pattern Hepatic MassDocumento2 pagineNursing Care Plan Ineffective Breathing Pattern Hepatic MassRheegell Ellar-Fuertes100% (3)
- Asthma Risk For Activity IntoleranceDocumento1 paginaAsthma Risk For Activity IntoleranceWdy Tanakht Sparrow100% (4)
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocumento2 pagineIneffective Breathing PatternJoy Arizala CarasiNessuna valutazione finora
- Impaired Gas Exchange-Sample NCPDocumento1 paginaImpaired Gas Exchange-Sample NCPKaycee BinanNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP For BronchitisDocumento4 pagineNCP For BronchitisJessa Borre100% (1)
- Preoperative and Post Liver Transplant Nursing Care PlanDocumento5 paginePreoperative and Post Liver Transplant Nursing Care PlanOctoober67% (6)
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocumento5 pagineIneffective Breathing PatternruguNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP RHDDocumento7 pagineNCP RHDHenry Roque Tagalag80% (5)
- Nursing Care Plan Patient EndotrachealDocumento2 pagineNursing Care Plan Patient EndotrachealCyrus De Asis67% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural EffusionDocumento5 pagineNursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural Effusionmac042250% (4)
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento4 pagineNursing Care Planapi-309251523Nessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Nursing Care Plan For Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome ARDSDocumento6 pagineNCP Nursing Care Plan For Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome ARDSTina Larsen100% (4)
- ANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationDocumento2 pagineANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationEdrianne Tui100% (2)
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento4 pagineNursing Care PlanJoy Callo100% (2)
- Risk For Infection Related To Failure To Avoid Pathogen Secondary To Exposure To COVID-19Documento2 pagineRisk For Infection Related To Failure To Avoid Pathogen Secondary To Exposure To COVID-19Yessamin Paith Roderos100% (1)
- NCP # 1 Acute PainDocumento3 pagineNCP # 1 Acute Painernst_bondoc50% (2)
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Related To Bronchospasm, Decreased Lung ExpansionDocumento2 pagineIneffective Breathing Pattern Related To Bronchospasm, Decreased Lung ExpansionReylan Garcia43% (7)
- POC Ineffective Breathing PatternDocumento1 paginaPOC Ineffective Breathing Patterncuicuita100% (1)
- Afib NCPDocumento3 pagineAfib NCPGen RodriguezNessuna valutazione finora
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Goals Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocumento3 pagineCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Goals Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationIngrid Nicolas100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance (Bronchi)Documento2 pagineNursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance (Bronchi)deric94% (17)
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento14 pagineNursing Care PlanVin Landicho100% (1)
- Oxy Act 2Documento5 pagineOxy Act 2Joshua DauzNessuna valutazione finora
- ARDSDocumento18 pagineARDSChurrizo IslamiNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP For COPD and Acute PainDocumento7 pagineNCP For COPD and Acute PainLenny SucalditoNessuna valutazione finora
- Impaired Gas Exchange PneumoniaDocumento2 pagineImpaired Gas Exchange PneumoniaAngel Cabatingan100% (4)
- Nursing Management of Patient With Mechanical VentilationDocumento77 pagineNursing Management of Patient With Mechanical Ventilationrojina poudel0% (1)
- Asthma Nursing Care Plan - NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento2 pagineAsthma Nursing Care Plan - NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceCyrus De Asis92% (24)
- Nursing DiagnosisDocumento4 pagineNursing DiagnosisKrizzia CarlosNessuna valutazione finora
- WeaningDocumento24 pagineWeaningEko YeppiNessuna valutazione finora
- Mycoplasma PneumoniaDocumento1 paginaMycoplasma PneumoniaJanine Joy OrpillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Garbage Disposal Teaching Plan PDFDocumento3 pagineGarbage Disposal Teaching Plan PDFJanine Joy Orpilla100% (1)
- Tuberculosis or TBDocumento1 paginaTuberculosis or TBJanine Joy OrpillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Clarithromycin Drug StudyDocumento1 paginaClarithromycin Drug StudyJanine Joy Orpilla100% (4)
- Clarithromycin Drug StudyDocumento1 paginaClarithromycin Drug StudyJanine Joy Orpilla100% (4)
- The Durie Salmon Staging System PDFDocumento2 pagineThe Durie Salmon Staging System PDFJanine Joy OrpillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cobalt PDFDocumento6 pagineCobalt PDFJanine Joy OrpillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 4 Organizing PDFDocumento4 pagineModule 4 Organizing PDFJanine Joy OrpillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 2 The Evolution of Management Thoughts PDFDocumento9 pagineModule 2 The Evolution of Management Thoughts PDFJanine Joy Orpilla100% (4)
- Module 5 - Staffing PDFDocumento15 pagineModule 5 - Staffing PDFJanine Joy OrpillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 8 Leadership Theory and Practice PDFDocumento10 pagineModule 8 Leadership Theory and Practice PDFJanine Joy OrpillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Accounting For Merchandising Business ACG 2021 Module 5Documento45 pagineAccounting For Merchandising Business ACG 2021 Module 5Janine Joy Orpilla50% (2)
- K12 Sa Pilipinas, Solusyon Ba?: Barbie Forteza Bea Binene Elmo Magalona Derick Monasterio Lexi Fernandez Kristofer MartinDocumento8 pagineK12 Sa Pilipinas, Solusyon Ba?: Barbie Forteza Bea Binene Elmo Magalona Derick Monasterio Lexi Fernandez Kristofer MartinJanine Joy OrpillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Inner Life CommentaryDocumento88 pagineInner Life CommentaryAndraž PogačnikNessuna valutazione finora
- Haruchika Noguchi - Katsugen BreathingDocumento4 pagineHaruchika Noguchi - Katsugen BreathingТом Вейцман100% (3)
- Yoga Remedies For Body and MindDocumento6 pagineYoga Remedies For Body and Mindantonio2311Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sweep-On 2000 Crew Oxygen Mask System - CMMDocumento50 pagineSweep-On 2000 Crew Oxygen Mask System - CMMreginaldo11Nessuna valutazione finora
- Soal First Aid Quiz MentorDocumento9 pagineSoal First Aid Quiz MentorAlmira PutriNessuna valutazione finora
- Equipment For SurgeryDocumento19 pagineEquipment For SurgerysanathNessuna valutazione finora
- SP 046 - SP Booster Plus - InternationalDocumento6 pagineSP 046 - SP Booster Plus - InternationalJeremiah WalkerNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade Four Consolidated Worksheeets: ScienceDocumento12 pagineGrade Four Consolidated Worksheeets: Scienceezerah nuwagabaNessuna valutazione finora
- JMDN en PDFDocumento359 pagineJMDN en PDFFebiana Rima DiputriNessuna valutazione finora
- SRM PagesDocumento21 pagineSRM PagesDagli Fnf SandipNessuna valutazione finora
- Breathwork Fundamentals GuidebookDocumento148 pagineBreathwork Fundamentals GuidebookJuliana RennerNessuna valutazione finora
- MSDS N1Documento4 pagineMSDS N1tiffyoloNessuna valutazione finora
- An Outline of Taiji Theory - Brennan TranslationDocumento21 pagineAn Outline of Taiji Theory - Brennan Translationanattā100% (4)
- Jet VentilationDocumento5 pagineJet Ventilationskumar bNessuna valutazione finora
- Kundalini Yoga Kriya-Develop Your Hidden GreatnessDocumento2 pagineKundalini Yoga Kriya-Develop Your Hidden GreatnessLut Ten100% (1)
- Transformers Accessories and Support EquipmentDocumento44 pagineTransformers Accessories and Support Equipmenthajimak100% (2)
- Detailed Guide of 26 Bikram Yoga Poses & BenefitsDocumento57 pagineDetailed Guide of 26 Bikram Yoga Poses & Benefitscbarriuso100% (1)
- Brahmavidya MeditationDocumento14 pagineBrahmavidya MeditationPranavNessuna valutazione finora
- A Ghost in The MachineDocumento7 pagineA Ghost in The MachineSicklslicerNessuna valutazione finora
- Newport HT70 - HT70 Plus BrochureDocumento9 pagineNewport HT70 - HT70 Plus BrochurethellinniNessuna valutazione finora
- Yoga and Mindfulness For KidsDocumento106 pagineYoga and Mindfulness For KidsAshvita100% (1)
- 11 Principles of The NaqshbandiaDocumento15 pagine11 Principles of The NaqshbandiaShahid Wahab NawabNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiology of LungDocumento29 pagineAnatomy and Physiology of LungKetheesaran Lingam100% (1)
- 172 Anatomy Resp SystemDocumento29 pagine172 Anatomy Resp SystemJerry ZahidNessuna valutazione finora
- NANDA Nursing Diagnosis: Ineffective Breathing Pattern Related To As Evidenced by NANDA DefinitionDocumento3 pagineNANDA Nursing Diagnosis: Ineffective Breathing Pattern Related To As Evidenced by NANDA DefinitionTrisha VergaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Lithium Polymer Battery SDSDocumento10 pagineLithium Polymer Battery SDSUpik LapeoNessuna valutazione finora
- Capnography QuickguideDocumento52 pagineCapnography QuickguideAli SaadoonNessuna valutazione finora
- Surya NamaskarDocumento6 pagineSurya NamaskarKrm ChariNessuna valutazione finora
- RESPIRATIONDocumento5 pagineRESPIRATIONShatviga VisvalingamNessuna valutazione finora
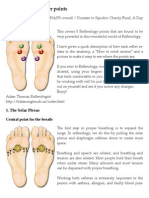
- Reflexology - 5 Power PointsDocumento6 pagineReflexology - 5 Power Pointsrickiti9100% (1)