Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
18 4 Questions
Caricato da
api-236187225Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
18 4 Questions
Caricato da
api-236187225Copyright:
Formati disponibili
18.
4 ACID-BASE TITRATIONS
PG 227
1. 2. 3. 4. a. b. 0.15 mol dm
-3
A: this is because it is a sudden change that will only occur and change the pH to 7 when it is exactly 100% neutralized. Therefor it will remain only slightly higher pH than the initial concentration of the acid. B: This is because at the half-neutralization point the half oft eh weak acid will have been converted to its conjugate base, and therefore their concentrations and pH are equal. C: This is because a weak acid has a pH relatively close to 7 whilst a strong base has a substantially higher value than 7 (closer to 14).
c. d. e.
i. 11.24 ii. 9.3: This is because at 7.5 it is the mid-point of the equivalence point. Therefore the + number of OH ions is equal to H ions. Therefore the pOH is 4.7 as well as the pKb value. Therefore pOH + pH = 14. (14-4.7=9.3) iii. 5.06 (sketched) The section of that is around a pH of 9.0, this is because the adding of a small amount of base or acid is resisted upon the pH and therefore there is no great change of the pH. The pH would remain at 13 until just before the equivalence point. However twice the amount of acid would need to be used to get to the equivalence point.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Intro To Methyl Chloride Plant 1Documento57 pagineIntro To Methyl Chloride Plant 1Kimberly ConleyNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparative Study On Direct Shear Behavior of Manufactured and Recycled Shredded Tyre Steel Fiber Reinforced Self-Consolidating ConcreteDocumento9 pagineComparative Study On Direct Shear Behavior of Manufactured and Recycled Shredded Tyre Steel Fiber Reinforced Self-Consolidating ConcreteDiego SukNessuna valutazione finora
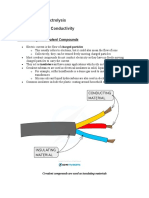
- Key Concept Chapter 10 ElectrolysisDocumento20 pagineKey Concept Chapter 10 ElectrolysisKim KatNessuna valutazione finora
- Sae J122-2017Documento12 pagineSae J122-2017phan hoai nam PhanNessuna valutazione finora
- A Review On Reference StandardsDocumento12 pagineA Review On Reference StandardsjyothiNessuna valutazione finora
- PFM920I-6U-U Datasheet 20221020Documento2 paginePFM920I-6U-U Datasheet 20221020GgopNessuna valutazione finora
- Design and Analysis of Machine Components: Dr. Sharnappa JoladarashiDocumento20 pagineDesign and Analysis of Machine Components: Dr. Sharnappa JoladarashiMAHESHWARNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual For Water Filter SystemDocumento2 pagineManual For Water Filter Systemgjnxjbm8pbNessuna valutazione finora
- Oxidizing Alcohols LabDocumento4 pagineOxidizing Alcohols LabAaron LauNessuna valutazione finora
- Buckling Commentary E-Mar18 PDFDocumento132 pagineBuckling Commentary E-Mar18 PDFthomas1313Nessuna valutazione finora
- 9th Chemistry 4 ChapDocumento3 pagine9th Chemistry 4 ChapJaveria ZaidiNessuna valutazione finora
- MANDA-TOWNHOUSE - Technical SpecificationsDocumento10 pagineMANDA-TOWNHOUSE - Technical SpecificationsMark Nathan Sta. MonicaNessuna valutazione finora
- Methods and Techiniques in PathologyDocumento15 pagineMethods and Techiniques in PathologyKiran100% (1)
- v91 247 PDFDocumento6 paginev91 247 PDFbariah al-bashirahNessuna valutazione finora
- BERKLEY - Catalogo Caà As 2011Documento8 pagineBERKLEY - Catalogo Caà As 2011dondepescasNessuna valutazione finora
- Bill of Material: 103PW2 - PL5/16"X4" - 1'-3" - 2 REQ'DDocumento1 paginaBill of Material: 103PW2 - PL5/16"X4" - 1'-3" - 2 REQ'Dai ambaraNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 s2.0 S0950061820318560 MainDocumento7 pagine1 s2.0 S0950061820318560 MainElias SoaresNessuna valutazione finora
- Marvets Eric PaulDocumento44 pagineMarvets Eric PaulEugenu DragoescuNessuna valutazione finora
- Binary Phase DiagramsDocumento60 pagineBinary Phase DiagramsmaryzeenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physical and Mechanical Properties of ConcreteDocumento5 paginePhysical and Mechanical Properties of ConcreteInternational Journal of Research in Engineering and TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- The Passivated Emitter and Rear Cell (PERC) PDFDocumento8 pagineThe Passivated Emitter and Rear Cell (PERC) PDFShadab AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Rubio Monocoat Furniture DataDocumento1 paginaRubio Monocoat Furniture DataJosh PiersmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Avt 200 #1 Aircarft StructureDocumento99 pagineAvt 200 #1 Aircarft StructureStrause Vince Jansen RetuyaNessuna valutazione finora
- 3003 Polyether Polyol TDSDocumento1 pagina3003 Polyether Polyol TDSbkandemirpolexNessuna valutazione finora
- Project One - Ecr Epcm Services Contract: Level Instruments DatasheetsDocumento105 pagineProject One - Ecr Epcm Services Contract: Level Instruments DatasheetsKhan Akhtar HusainNessuna valutazione finora
- Actvated Sludge Process SSWMDocumento28 pagineActvated Sludge Process SSWMGREENLAB ECL TECHNessuna valutazione finora
- Science ExperimentDocumento9 pagineScience ExperimentAnil KarnawatNessuna valutazione finora
- Maaping With 3D DataDocumento5 pagineMaaping With 3D Datanasir.hdip8468Nessuna valutazione finora
- Twistlock TestingDocumento44 pagineTwistlock Testingkandahar_specNessuna valutazione finora
- Copper-Brazed Steel Tubing: Standard Specification ForDocumento4 pagineCopper-Brazed Steel Tubing: Standard Specification ForSofiaJabadanEspulgar100% (1)