Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
8 1 Questions
Caricato da
api-236187225Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
8 1 Questions
Caricato da
api-236187225Copyright:
Formati disponibili
8.
1 THEORIES OF ACIDS AND BASES
PG 211
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. C: An acid will cause for a solution with a pH less than 7 + C: A di(two)protic acid will dissociate into two H ions and consequently H2SO4 is the acid that will dissociate into two hydrogen ions. -2 + B: CO3 is acting as base as it is accepting the H ion -2 + C: is the conjugate base as the product (SO3 ) is the compound which will accept the H ion for the reverse equilibrium reaction. D: I would expect this to add as a base as it has the ability to accept a positive ion as it is a negative ion. a. b. c. d. e. 7. a. i. An acid is a proton donor. Consequently the substance will give a proton (H ion which contains no shells nor electrons) to a base. + ii. A base is a proton accepter. Consequently the substance will accept a proton (H ion) which was extracted from the acid. + HNO3 + HzSO4 H2NO3 + HSO4 + + HNO3 acts as an acid as it accepts the H ion whilst the HzSO4 acts as a base as it gives an H ion. + HNO3 + HzSO4 H2NO3 + HSO4 Conjugate means that for the reverse reaction in the equilibrium reaction which product from the forward reaction acts as the acid or base and consequently forms the acid (from the conjugate base) or base (from the conjugate acid).
+
Cl
HCl PO4
-3
HPO4 C5H5N
-2
C5H5NH + NH4NH2 +2 H3N NH3 OOCCOO OOCCOOH
+
b. c. d.
8. a. b. Diprotic means that when the compound (acid) dissociates it will have two H ions form each compound and therefore donate these ions. Amphiprotic means that it has both acidic and basic properties, and therefore depending on the theory or situation it will act as a base in the reaction (in this case the reverse reaction) or an acid. Consequently it will either donate or accept a proton(s). Therefore if a proton is gained it -2 will become an acid (H2CO3) or if a proton is donated it will become a base (CO3 ). + H2SO4 + H2CO3 HCO3 + H3SO4
+
c.
Water is also Amphiprotic. H2O it can either dissociate into a H ion (acid) or OH ion (base). + + Water can be a base and accept a H ion to form (H3O ) + H2O OH + H + + H2O + H H3O Lewis acid is a substance that can accept an electron pair regardless of it is a H ion.
+
9. a. b.
c. d.
It is dative bond. The electrons shared are obtained from the chloride ion. i. Trigonal planar ii. Tetrahedral
10. a. b. c. d. e. Lewis Base Phosphorous has a lone pair in which it can donate. Lewis Acid Boron has an incomplete shell and therefore accept a lone pair. Lewis Base Sulfur has a lone pair in which it can donate. Lewis Base Sulfur has a lone pair in which it can donate. Lewis Acid +2 Copper (Cu ) has incomplete orbital shells (P and D) and can consequently accept a lone pair.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5795)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- USP-NF Atorvastatin CalciumDocumento8 pagineUSP-NF Atorvastatin CalciumPhạm Đức LộcNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch62 Written AssignmentDocumento4 pagineCh62 Written AssignmentHau Hei, Matthew LinNessuna valutazione finora
- Pamphlet 164 Edition2 August2007 Rev 1Documento35 paginePamphlet 164 Edition2 August2007 Rev 1Noman Abu-FarhaNessuna valutazione finora
- MSDS Listing AlphabeticalDocumento9 pagineMSDS Listing AlphabeticalAdrian RodriguezNessuna valutazione finora
- Nomenclature of Electron-Transfer Proteins: Nomenclature Committee of The International Union of Biochemistry (NC-IUB)Documento13 pagineNomenclature of Electron-Transfer Proteins: Nomenclature Committee of The International Union of Biochemistry (NC-IUB)gustaboo3584Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 3 - Titration of Soda - Citric AcidDocumento9 pagineLab 3 - Titration of Soda - Citric AcidAndrea Satira100% (1)
- Direct Download Productdesc 01 01 2017 01 07 2022 Current 26 07 2022 2 40 PMDocumento9 pagineDirect Download Productdesc 01 01 2017 01 07 2022 Current 26 07 2022 2 40 PMAli KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- MSC Sem 2 Unit 1.1Documento13 pagineMSC Sem 2 Unit 1.1almas shaikhNessuna valutazione finora
- MR-VP Medium (Glucose Phosphate Broth) : CompositionDocumento2 pagineMR-VP Medium (Glucose Phosphate Broth) : CompositionsravaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Plastic Industry Presentation POMDocumento20 paginePlastic Industry Presentation POMmalaikaarshad665Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter I - ElectrolysisDocumento41 pagineChapter I - ElectrolysisRodella ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
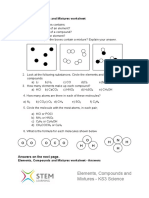
- Worksheet Elements Compounds Mixtures ks3Documento4 pagineWorksheet Elements Compounds Mixtures ks3eric sivanesh0% (1)
- Carboxylic Acid and Its DerivativeDocumento52 pagineCarboxylic Acid and Its DerivativeThe RockNessuna valutazione finora
- Natural ProductsDocumento82 pagineNatural ProductsChandra Reddy100% (1)
- Notes 5 HMR 2 Shift PDFDocumento23 pagineNotes 5 HMR 2 Shift PDFMariam IshtiaqNessuna valutazione finora
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Chemistry 9701/12Documento16 pagineCambridge International AS & A Level: Chemistry 9701/12spandan BhattaraiNessuna valutazione finora
- Solved Problems in Advanced Organic Synthesis CSIR NETDocumento20 pagineSolved Problems in Advanced Organic Synthesis CSIR NETAdiChemAdi100% (5)
- P2O5/Sio2 As An Efficient and Mild Catalyst For Trimethylsilylation of Alcohols Using HexamethyldisilazaneDocumento7 pagineP2O5/Sio2 As An Efficient and Mild Catalyst For Trimethylsilylation of Alcohols Using HexamethyldisilazaneAndra OktafianNessuna valutazione finora
- Benzyl Alcohol: 2. Physical PropertiesDocumento10 pagineBenzyl Alcohol: 2. Physical PropertiesniteshacharyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Portland Cement HydrationDocumento35 paginePortland Cement Hydrationrazvan248675% (4)
- Water's Composition and PropertiesDocumento17 pagineWater's Composition and PropertiesLinda BogdaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Basics of Resin Based Water SofteningDocumento31 pagineBasics of Resin Based Water SofteningalexNessuna valutazione finora
- SPM Percubaan 2008 SBP Chemistry AnswersDocumento19 pagineSPM Percubaan 2008 SBP Chemistry AnswersChinWynn.com94% (16)
- Phospholipid: From: Encyclopedia of Food Chemistry, 2019Documento8 paginePhospholipid: From: Encyclopedia of Food Chemistry, 2019Eiann Jasper LongcayanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Previous HSE Questions From The Chapter "Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers"Documento3 paginePrevious HSE Questions From The Chapter "Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers"Nikhil MathewNessuna valutazione finora
- Redox ReactionsDocumento8 pagineRedox Reactionsdanielphilip68Nessuna valutazione finora
- EXPT. 4: Quantitative Analysis of Soda Ash by Double-Indicator TitrationDocumento3 pagineEXPT. 4: Quantitative Analysis of Soda Ash by Double-Indicator TitrationAbiNessuna valutazione finora
- CHM413 Exp 3Documento5 pagineCHM413 Exp 3Anis NasuhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbonyl Compounds Aldehydes and KetonesDocumento7 pagineCarbonyl Compounds Aldehydes and KetonesLynde Claire Dilag100% (1)
- US9005884Documento10 pagineUS9005884Thanh Hậu TrầnNessuna valutazione finora