Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Dna Synthesis: Aplastic Anemia Iron Deficiency Anemia
Caricato da
Broc Il SerbatoioTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Dna Synthesis: Aplastic Anemia Iron Deficiency Anemia
Caricato da
Broc Il SerbatoioCopyright:
Formati disponibili
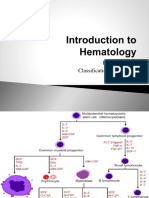
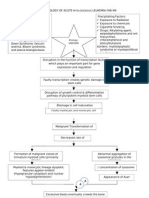
APLASTIC ANEMIA
reduction in stem cells in bone marrow Result: depressed or ineffective hematopoietic cells not just RBC (platelets, leukocytes) pancytopenia Clinical Signs: suddenly or insidious manner. Anemia, infection, hemorrhage Dx: Pancytopenia (rbc, leukocyte, platelet counts) Etiology: toxic agents 40-50% secondary to infections (hepatitis, HIV, TB) 50% idiopathic hydro soluble vit imp role in DNA SYNTHESIS Result: affects proliferation of cells rapid mitosis including bone marrow cells involved in hematopoiesis MEGALOBLASTIC ANEMIA delayed maturation of nuclei with norm cytoplasm, norm Hb content but mitotic activity defective DNA synthesismegaloblasts in marrow macrocytic anemia Mean Cell Vol >100fl Signs: anemia Symptoms: dyspnea on excretion, muscle weakness Neuro disorders: demyelination of spinal nerves (numb hands/feet-paresthesia) - Glossitis- inflamed tongue -Intestinal disorders Dx: Macrocytic normochromic anemia (MCV , NORMAL MCHC) Reticulocyte count norm or low Megaloblastosis checked by bone marrow count Tx: Vit B12 injection
IRON DEFICIENCY ANEMIA
iron deficiency most common frequent blood disorder in CHILDREN causes: menstruation, blood loss from pregnancy that were never replaced, Excessive blood loss, inadequate intake and malabsorption Consequences: mainly related to erythrocyte production Iron participates in ++ metabolic reactionscytochromes Dx: microcytic hypochromic anemia Hematocrit normal/decreased but smaller than Hb Serum iron with increase in desaturated transferrin (TIBC)
COBALAMIN/FOLATE DEFICIENCY both lead to anemia
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Aplastic and Hypoplastic Anemias Including Mylodysplastic SyndromeDocumento47 pagineAplastic and Hypoplastic Anemias Including Mylodysplastic SyndromeRahul Kumar VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- DR Vishu P Bhasin DCP Resident, Santosh Medical CollegeDocumento30 pagineDR Vishu P Bhasin DCP Resident, Santosh Medical CollegeDabogski FranceNessuna valutazione finora
- DR Vishu P Bhasin DCP Resident, Santosh Medical CollegeDocumento30 pagineDR Vishu P Bhasin DCP Resident, Santosh Medical CollegeDabogski FranceNessuna valutazione finora
- Kuliah AnemiaaDocumento44 pagineKuliah AnemiaaAhmad Umar AfNessuna valutazione finora
- SBRC HematologyOncology 1Documento80 pagineSBRC HematologyOncology 1dalia khamoNessuna valutazione finora
- ANEMIIDocumento34 pagineANEMIIAlin DragosNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Lab InvestigationsDocumento121 pagineBasic Lab InvestigationsTheop Ayodele100% (1)
- Red Cell Disorders: Excellent in Quality, Competitiveness, and CareDocumento43 pagineRed Cell Disorders: Excellent in Quality, Competitiveness, and CareDeriven Teweng0% (1)
- Microcytic Hypochromic Macrocytic Normochromic Normocytic: Anemia HematocritDocumento7 pagineMicrocytic Hypochromic Macrocytic Normochromic Normocytic: Anemia Hematocritjjjj31Nessuna valutazione finora
- SBRC HematologyOncology 2Documento80 pagineSBRC HematologyOncology 2dalia khamoNessuna valutazione finora
- Anemia Nursing Care Plan: Presented by Edi Purwanto School of Nursing University of Muhammadiyah MalangDocumento26 pagineAnemia Nursing Care Plan: Presented by Edi Purwanto School of Nursing University of Muhammadiyah MalangSevina Eka ChannelNessuna valutazione finora
- 8.23.11 Hemolytic AnemiaDocumento6 pagine8.23.11 Hemolytic Anemiatony pham baloney and hamNessuna valutazione finora
- C B C I: Omplete Lood Ount NterpretationsDocumento44 pagineC B C I: Omplete Lood Ount NterpretationsridhoniNessuna valutazione finora
- Peripheral Smear Examination PDFDocumento91 paginePeripheral Smear Examination PDFtufis02Nessuna valutazione finora
- Decreased Hemoglobin Available For Erythrocytes Microcytic, Hypochromic Anemia More Hemoglobin Available For Erythrocytes Macrocytic AnemiaDocumento2 pagineDecreased Hemoglobin Available For Erythrocytes Microcytic, Hypochromic Anemia More Hemoglobin Available For Erythrocytes Macrocytic AnemiaIB leaksNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To HematologyDocumento23 pagineIntroduction To HematologyReba PhiliposeNessuna valutazione finora
- Red Blood Cells PathologyDocumento47 pagineRed Blood Cells PathologyRodriguez Vivanco Kevin DanielNessuna valutazione finora
- Interferences With Diffusion: AnemiaDocumento49 pagineInterferences With Diffusion: AnemiaMaryAnn ElizabethNessuna valutazione finora
- Anemia Workshop1Documento80 pagineAnemia Workshop1api-3762917Nessuna valutazione finora
- Red Cell DisorderDocumento43 pagineRed Cell DisorderYuliusDenisChrismaajiNessuna valutazione finora
- Red Blood Cell DisordersDocumento56 pagineRed Blood Cell DisordersMunawar Adhar100% (4)
- Polycythemia Vera: Sarit Levinsky GROUP M1656Documento12 paginePolycythemia Vera: Sarit Levinsky GROUP M1656Sarit LevinskyNessuna valutazione finora
- DR Bambang - Anemia OverviewDocumento263 pagineDR Bambang - Anemia OverviewOkta Dwi Kusuma AyuNessuna valutazione finora
- Hematology HematopoiesisDocumento69 pagineHematology HematopoiesisSharmin Nahar NabilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Approach To AnemiaDocumento33 pagineApproach To AnemiaVaibhav KrishnaNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Interpret HEMATOLOGY Test ResultsDocumento36 pagineHow To Interpret HEMATOLOGY Test Resultssylvia haryantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Aematology: Col Kamran AfzalDocumento32 pagineAematology: Col Kamran AfzalZaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Haemoglobinopathies 2Documento53 pagineHaemoglobinopathies 2Igwe SolomonNessuna valutazione finora
- Interpretive Summary: Nucleated RBCDocumento2 pagineInterpretive Summary: Nucleated RBCWael SafwatNessuna valutazione finora
- PejowebApproach To Anemia by Dr. Joel Solorzani RomeroDocumento57 paginePejowebApproach To Anemia by Dr. Joel Solorzani RomeroAshraf FaragNessuna valutazione finora
- Anemia OsamaDocumento57 pagineAnemia Osamaosamafoud7710Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tutori - Anemia MhsDocumento38 pagineTutori - Anemia Mhszaky ariandyNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Acute Myelogenous Leukemia Fab m4Documento3 paginePathophysiology of Acute Myelogenous Leukemia Fab m4KristaMaeC.Lazo100% (2)
- 19 Intro To AnemiaDocumento3 pagine19 Intro To AnemiaPeter JosephNessuna valutazione finora
- HematologieDocumento74 pagineHematologieAndrew Sig100% (1)
- Anaemia: by Swaathi R Final Year MbbsDocumento33 pagineAnaemia: by Swaathi R Final Year MbbsGopi NathNessuna valutazione finora
- 21 Anaemia and PancytopeniaDocumento42 pagine21 Anaemia and PancytopeniaLeon Hui MingNessuna valutazione finora
- Anaemia: Dr. Mahmudul Huque. Mbbs (DMC), MD (Em)Documento32 pagineAnaemia: Dr. Mahmudul Huque. Mbbs (DMC), MD (Em)Junayed Safar MahmudNessuna valutazione finora
- อ - ชลลดา - Approach to AnemiaDocumento44 pagineอ - ชลลดา - Approach to AnemiaSOPHIASTIA KUSBIANTI MHS 2017Nessuna valutazione finora
- Anemia & Leukemia NotesDocumento6 pagineAnemia & Leukemia NotesJennNessuna valutazione finora
- Leukocytic Disorders: Non-Neoplastic AlterationsDocumento36 pagineLeukocytic Disorders: Non-Neoplastic AlterationsIseth ISethNessuna valutazione finora
- Anemia Aplastik: Presentan: Tika Adilistya Pembimbing: Prof. Dr. Riadi Wirawan, SPPK (K)Documento36 pagineAnemia Aplastik: Presentan: Tika Adilistya Pembimbing: Prof. Dr. Riadi Wirawan, SPPK (K)Tika AdilistyaNessuna valutazione finora
- PANCYTOPENIADocumento51 paginePANCYTOPENIAResmyNessuna valutazione finora
- Hemolytic AnemiaDocumento99 pagineHemolytic AnemiaSagar Chandrakant Mhetre100% (3)
- Systematic Plan For The Diagnosis of AnaemiaDocumento31 pagineSystematic Plan For The Diagnosis of AnaemiaAriyike OmoobaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hafizuddin Mohamed Fauzi P-UM0037/10Documento54 pagineHafizuddin Mohamed Fauzi P-UM0037/10Hafizuddin Mohamed FauziNessuna valutazione finora
- Robbins Pathology Chapter 14 - RBCsDocumento7 pagineRobbins Pathology Chapter 14 - RBCsscorpiosphinx79100% (10)
- Anemi Aplastik Dan MielodisplasiaDocumento34 pagineAnemi Aplastik Dan MielodisplasiaRoby KieranNessuna valutazione finora
- USMLE - Heme & Lymph PathologyDocumento21 pagineUSMLE - Heme & Lymph PathologyMatt McGlothlinNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 11 - Blood VesselsDocumento6 pagineChapter 11 - Blood VesselsAgnieszka WisniewskaNessuna valutazione finora
- Leukemias Nursing ManagementDocumento20 pagineLeukemias Nursing ManagementAnusha Verghese100% (5)
- Chapter 14 Red Blood CellsDocumento37 pagineChapter 14 Red Blood CellsCatherine LiuNessuna valutazione finora
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus SLE: DefinitionDocumento19 pagineSystemic Lupus Erythematosus SLE: DefinitionShimmering MoonNessuna valutazione finora
- Anemia NotesDocumento6 pagineAnemia NotesElstella Eguavoen Ehicheoya100% (2)
- CBC 150106153749 Conversion Gate02Documento44 pagineCBC 150106153749 Conversion Gate02KhetanNessuna valutazione finora
- د رفل hematologicDocumento60 pagineد رفل hematologicmuhammad.fajr.pharmacy96Nessuna valutazione finora
- DR Nilukshi Perera Consultant HaematologistDocumento68 pagineDR Nilukshi Perera Consultant HaematologistThaveeshaLindsayWhiteNessuna valutazione finora
- Hematology Notes for Medical StudentsDa EverandHematology Notes for Medical StudentsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Nursing: Lab Values: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideDa EverandNursing: Lab Values: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideNessuna valutazione finora
- Effects of A 7-Week Practical Blood Flow Restriction Program - 2014Documento11 pagineEffects of A 7-Week Practical Blood Flow Restriction Program - 2014Broc Il SerbatoioNessuna valutazione finora
- HTN ArticleDocumento16 pagineHTN ArticleBroc Il SerbatoioNessuna valutazione finora
- Altering The Rest Interval During High-Intensity Interval. 2013Documento10 pagineAltering The Rest Interval During High-Intensity Interval. 2013Broc Il SerbatoioNessuna valutazione finora
- 2014 Fall - BSCN Year 4 Aug 8Documento4 pagine2014 Fall - BSCN Year 4 Aug 8Broc Il SerbatoioNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Effects of Caffeine On Strength and Muscle Activation of The Elbow Flexors. 2014 AHoPDocumento21 pagineAcute Effects of Caffeine On Strength and Muscle Activation of The Elbow Flexors. 2014 AHoPBroc Il SerbatoioNessuna valutazione finora
- 2014 Merged Game Schedule Rev 6.1Documento5 pagine2014 Merged Game Schedule Rev 6.1Broc Il SerbatoioNessuna valutazione finora
- The Effects of 12 Weeks of HMB Free Acid Supplementation On Muscle Mass, Strength, and Power in Resistance Trained IndividualsDocumento11 pagineThe Effects of 12 Weeks of HMB Free Acid Supplementation On Muscle Mass, Strength, and Power in Resistance Trained IndividualsBroc Il SerbatoioNessuna valutazione finora
- Game Sheet - Lemke V MadawaskaDocumento2 pagineGame Sheet - Lemke V MadawaskaBroc Il SerbatoioNessuna valutazione finora
- Canadian Journal of DiabetesDocumento7 pagineCanadian Journal of DiabetesBroc Il SerbatoioNessuna valutazione finora
- Echocardiography (Cardiac Echography, Heart Sonography)Documento2 pagineEchocardiography (Cardiac Echography, Heart Sonography)Broc Il SerbatoioNessuna valutazione finora
- High - and Low-Bar Squatting Techniques During Weight-Training.1996Documento14 pagineHigh - and Low-Bar Squatting Techniques During Weight-Training.1996Broc Il SerbatoioNessuna valutazione finora
- Laws of The Game 2013-2014Documento148 pagineLaws of The Game 2013-2014Diaitisia.grNessuna valutazione finora
- Effect of Soccer Footwear On Landing Mechanics. 2014Documento7 pagineEffect of Soccer Footwear On Landing Mechanics. 2014Broc Il SerbatoioNessuna valutazione finora
- A Time-Efficient Reduction of Fat Mass in 4 Days With Exercise and Caloric Restriction. 2014Documento11 pagineA Time-Efficient Reduction of Fat Mass in 4 Days With Exercise and Caloric Restriction. 2014Broc Il SerbatoioNessuna valutazione finora
- Egg Protein AssimilationDocumento9 pagineEgg Protein AssimilationBroc Il SerbatoioNessuna valutazione finora
- Laws of The Game 2013-2014Documento148 pagineLaws of The Game 2013-2014Diaitisia.grNessuna valutazione finora
- Altering The Rest Interval During High-Intensity Interval. 2013Documento10 pagineAltering The Rest Interval During High-Intensity Interval. 2013Broc Il SerbatoioNessuna valutazione finora
- Talent Development - FranceDocumento6 pagineTalent Development - FranceAkram HamiciNessuna valutazione finora