Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Chapter 7 Questions
Caricato da
daniday1977Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Chapter 7 Questions
Caricato da
daniday1977Copyright:
Formati disponibili
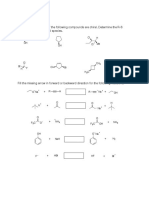
3. Hydrogenation of alkynes (Section 7.
15):
General Reaction
R-C=C-R'
H
2
I Ni
2
B (P-2)
(syn addition)
R R'
" / C=C
. / "
H H
(Z)Aikene
R H
Li or Na "c=C/
NH
3
or RNH
2
/ "-
(anti addition) H R'
(E)-Alkene
Problems
subsequent chapters we shall see a number of other methods for alkene synthesis.
Key Terms and Concepts
he key terms and concepts that are highlighted in bold, blue text within the chapter are
efined in the glossary (at the back of the book) and have hyperlinked definitions in the
accompanying WileyPLUS course (www.wileyplus.com) .
. <Problems
"'] 323
Note to Instructors: Many of the homework problems are available for assignment via WileyPLUS, an online
teaching and learning solution.
1
STRUCTURE AND NOMENCLATURE
.25 Each of the following names is incorrect. Give the correct name and explain your reasoning.
(a) trans-3-Pentene (c) 2-Methylcyclohexene (e) (Z)-3-Chloro-2-butene
(b) 1,1-Dimethylethene (d) 4-Methylcyclobutene (f) 5,6-Dichlorocyclohexene
.26 Write a structural formula for each of the following:
(a) 3-Methylcyclobutene (e) (E)-2-Pentene
(b) 1-Methylcyclopentene (f) 3,3,3-Tribromopropene
(c) 2,3-Dimethyl-2-pentene (g) (Z,4R)-4-Methyl-2-hexene
(d) (Z)-3-Hexene (h) (E,4S)-4-Chloro-2-pentene
(i) (Z)-1-Cyclopropyl-1-pentene
(j) 5-Cyclobutyl-1-pentene
(k) (R)-4-Chloro-2-pentyne
(1) (E)-4-Methylhex-4-en-1-yne
,27 Write three-dimensional formulas for and give names using (R)-(S) and (E)-(Z) designations for the isomers of:
(a) 4-Bromo-2-hexene (c) 2,4-Dichloro-2-pentene
(b) 3-Chloro-1,4-hexadiene (d) 2-Bromo-4-chlorohex-2-en-5-yne
28 Give the IUPAC names for each of the following:
(b)q-
CI
(e) \
Cl
I
324
7.29
7.30
7.31
7.32
Chapter 7 Alkenes and Alkynes I
Without consulting tables, arrange the following compounds in order of decreasing acidity:
Pentane 1-Pentene 1-Pentyne 1-Pentanol
SYNTHESIS
Outline a synthesis of propene from each of the following:
(a) Propyl chloride (c) Propyl alcohol
(b) Isopropyl chloride (d) Isopropyl alcohol
Outline a synthesis of cyclopentene from each of the following:
(a) Bromocyclopentane (b) 1,2-Dichlorocyclopentane
(e) 1,2-Dibromopropane
(f) Propyne
(c) Cyclopentanol
Starting with ethyne, outline syntheses of each of the following. You may use any other ntieded reagents, and you
need not show the synthesis of compounds prepared in earlier parts of this problem. .
(a) Propyne (f) 1-Pentyne ( ~ ) CH3GH2C=CD
(b) 1-Butyne (g) 2-Hexyne (I) H. C CH
(c) 2-Butyne (h) (Z)-2-Hexene K
3
"c=C/
3
(d) cis-2-Butene (i) (E)-2-Hexene \ 0/ ';-D
1.
(e) trans-2-Butene U) 3-Hexyne
7.33 Starting with 1-methylcyclohexene and using any other needed reagents, outline a synthesis of the following
deuterium-labeled compound:
D
c::focH,
H
7.34 Outline a synthesis of phenylethyne from each of the following:
(a)
ox
( b ) ~ B <
(c)U
(d)
0
I # Br
I#
cY'
DEHYDROHALOGENATION AND DEHYDRATION
7.35 Write a three-dimensional representation for the transition state structure leading to formation of 2-methyl-2-butene
from reaction of 2-bromo-2-methylbutane with sodium ethoxide.
7.36 When trans-2-methylcyclohexanol (see the following reaction) is subjected to acid-catalyzed dehydration, the major
product is 1-methylcyclohexene:
CH
3
6,0H
HA
~
heat
0
"
However, when trans-1-bromo-2-methylcyclohexane is subjected to dehydrohalogenation, the major product is
3-methylcyclohexene:
x,.,B.
u ~ < c5
EtONa
EtOH, heat
H
Account for the different products of these two reactions.
7
7
7.
I 7.40
7.41
7.42
7.43
Problems
'G!..P
325
7.37 Write stfuctutai formulas for alL the products that would be obtained when each of the following alkyl halides is
heated with sodium ethoxi.de in ethanol. When more than one product results, you should indicate which would be
the major product and which wduld be the minor product(s). You may neglect cis-trans isomerism of the products
when answering this question.
(a) )y
Br
(d) (fsr
/""-Br
(e)C(_
<ocx.s_r
7.38 Write structural formulas for all the products that would be obtained when each of the following alkyl halides is
heated with potassium tert-butoxide in tert-butyi alcohol. When more than one product results, you should indi-
cate which would be the major product and which would be the minor product(s). You may neglect cis-trans iso-
merism of the products when question.
Br
JX
/""-Br
(e) (fsr
7.39 Starting with ai1.fippropriate alkyl halide and base, outline syntheses that would yield each ofthe following alkenes
as the major (or only) product:
(c) )y (d) D
(e)o-
7.40 Arrange the following alcohols in order of their reactivity toward acid-catalyzed dehydration (with the most reac-
tive first):
1-Pentanol 2-Methyl-2-butanol 3-Methyl-2-butanol
7.41 Give the products that would be formed when each of the following alcohols is subjected to acid-catalyzed dehy-
dration. If more than one product would be formed, designate the alkene that would be the major product. (Neglect
cis-trans isomerism.)
(a) XH
(b)
)y
OH
/""-oH
(d)
(e) ('r(
7.42 l -Bromobicyclo[2.2.1]heptane does not undergo elimination (below) when heated with a base. Explain this fail-
ure to react. (Construction of molecular models may help.)
7.43
When the deuterium-labeled compound shown at right is subjected to dehydrohalo-
genation using sodium ethoxide in ethanol, the only alkene product is 3-methylcy-
clohexene. (The product contains no deuterium.) Provide an explanation for this
result.
:X
\
326 Chapter 7 Alkenes and Alkynes I
7.44 Provide a mechanistic explanation for each of the following reactions:
7.45
acid (cat.)
(b) CrOH
acid (cat.)
t.
t.
(major product)
(y
(major product)
(c) 'l
(d) PhXH;-Ph
.-- f''H
Br
INDEX OF HYDROGEN DEFICIENCY
AgN0
3
EtOH
>=<
(major product).
EtONa
EtOH, t.
/ -\Ph
(E only)
Caryophyllene, a compound found in oil of cloves, has the molecular formula C
15
H
24
and has no triple bonds.
Reaction of caryophyllene with an excess of hydrogen in the presence of a platinum catalyst produces a
compound with the formula C
15
H
28
. How many (a) double bonds and (b) rings does a molecule of caryophyl-
lene have?
7.46 Squalene, an important intermediate in the biosynthesis of steroids, has the molecular formula C
30
H
50
and has no
triple bonds.
(a) What is the index of hydrogen deficiency of squalene?
(b) Squalene undergoes catalytic hydrogenation to yield a compound with the molecular formula C
30
H
62
. How many
double bonds does a molecule of squalene have?
(c) How many rings?
STRUCTURE ELUCIDATION
7.47 Compounds I and J both have the molecular formula C
7
H
14
. Compounds I and J are both optically active and both
rotate plane-polarized light in the same direction. On catalytic hydrogenation I and J yield the same compound K
(C
7
H
16
) . Compound K is optically active. Propose possible structures for I, J, and K.
7.48
(+)-I (CyH14) H2, Pt
K (CyH1
6
)
(+)-J (C7H14) (Optically active)
Compounds Land M have the molecular formula C
7
H
14
. Compounds Land Mare optically inactive, are non-
resolvable, and are diastereomers of each other. Catalytic hydrogenation of either Lor M yields N. Compound
N is optically inactive but can be resolved into separate enantiomers. Propose possible structures for L, M,
and N.
l (CyH14) H2, Pt
(Optically inactive)
N
M (CyH14)
(Optically inactive)
;'((Optically inactive,
resolvable)
(L and M are diastereomers)
7
7
7.521
7.53
7.54
1.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Organic Ps Chapter 7Documento33 pagineOrganic Ps Chapter 7Mond DamascoNessuna valutazione finora
- JEE (Main + Adv.) Chemistry IUPAC Title ProblemsDocumento28 pagineJEE (Main + Adv.) Chemistry IUPAC Title ProblemsAvijeet kumar Mishra100% (1)
- KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA (Ahmedabad Region) CLASS XII CHEMISTRY SAMPLE PAPER FOR COORDINATION COMPOUNDSDocumento8 pagineKENDRIYA VIDYALAYA (Ahmedabad Region) CLASS XII CHEMISTRY SAMPLE PAPER FOR COORDINATION COMPOUNDSGunjan BisenNessuna valutazione finora
- Question Bank - Sem - III - TYBSC Chemistry Paper - II (Inorganic Chemistry)Documento8 pagineQuestion Bank - Sem - III - TYBSC Chemistry Paper - II (Inorganic Chemistry)Nirmal PatilNessuna valutazione finora
- Bridge Course Material - 1Documento11 pagineBridge Course Material - 1Priya SonuNessuna valutazione finora
- Synthesis of Potassium Tris(oxalato)ferrate(III) TrihydrateDocumento4 pagineSynthesis of Potassium Tris(oxalato)ferrate(III) Trihydratenathirahjaini0% (1)
- Amine PDFDocumento19 pagineAmine PDFJohn Jerald VillamancaNessuna valutazione finora
- Test Transition Elements 3rd SecondaryDocumento1 paginaTest Transition Elements 3rd SecondaryAboahmed AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Coordination CompoundsDocumento5 pagineCoordination CompoundsKehkasha BanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Preib Enrichment Quantum Numbers Edit3Documento2 paginePreib Enrichment Quantum Numbers Edit3api-270154205Nessuna valutazione finora
- 12B Alcohol 2Documento11 pagine12B Alcohol 2Kasun RatnayakeNessuna valutazione finora
- Homework 3Documento13 pagineHomework 3polypeptideNessuna valutazione finora
- VB and MO Theories Explain ColourDocumento52 pagineVB and MO Theories Explain ColourShrutiNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Chapter Experimental Techniques in Chemistry Short Questions With Answers PDFDocumento11 pagine2 Chapter Experimental Techniques in Chemistry Short Questions With Answers PDFAnonymous JAJWp33w2100% (2)
- Electronic Structure and Chemical KineticsDocumento30 pagineElectronic Structure and Chemical KineticsMike PatenaudeNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 6: Base Extraction of Benzoic Acid From Acetanilide Followed by Recrystallization and MP DeterminationDocumento9 pagineLab 6: Base Extraction of Benzoic Acid From Acetanilide Followed by Recrystallization and MP Determinationbebo4gpaNessuna valutazione finora
- Predicting Redox Reactions (No MS)Documento1 paginaPredicting Redox Reactions (No MS)AsadNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercise 2Documento23 pagineExercise 2Tushar RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Dms 111 Manual by Michael K. Chirchir and Githii WainainaDocumento173 pagineDms 111 Manual by Michael K. Chirchir and Githii WainainaAdventist NaturopathyNessuna valutazione finora
- CHEM1280 2012 13 Midterm Exam Solution PDFDocumento5 pagineCHEM1280 2012 13 Midterm Exam Solution PDFLouisNessuna valutazione finora
- Document 1Documento9 pagineDocument 1Nishi tomarNessuna valutazione finora
- 11-IUPAC Nomenclature (Assignment)Documento8 pagine11-IUPAC Nomenclature (Assignment)dharmesh kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Moving Charges and Magnetism Practice QuestionsDocumento13 pagineCBSE Class 12 Physics Moving Charges and Magnetism Practice QuestionsSmitha ThomasNessuna valutazione finora
- Critical Reasoning: Drill 1: SolutionsDocumento17 pagineCritical Reasoning: Drill 1: SolutionslognNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic Chemistry Detection MethodsDocumento4 pagineOrganic Chemistry Detection MethodsNagendra BharadwazNessuna valutazione finora
- ITL Public School Holiday Homework Class XII CHEMISTRYDocumento14 pagineITL Public School Holiday Homework Class XII CHEMISTRYNisith Kr DasNessuna valutazione finora
- Pre Board English 12thDocumento9 paginePre Board English 12thParth SinglaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Paper For ChemistryDocumento23 pagineSample Paper For ChemistryAmit joshiNessuna valutazione finora
- CAIE Chemistry A-Level: 24: ElectrochemistryDocumento8 pagineCAIE Chemistry A-Level: 24: ElectrochemistryahumanbeinginearthNessuna valutazione finora
- Physical Education-1 231231 200610Documento79 paginePhysical Education-1 231231 200610mehaktyagi422Nessuna valutazione finora
- Study Guide 2Documento4 pagineStudy Guide 2Orçun AtasevenNessuna valutazione finora
- Nomenclature - DPP OkDocumento12 pagineNomenclature - DPP Oknawazishmd819100% (1)
- Hybridization in Transition ElementsDocumento3 pagineHybridization in Transition ElementsAbdul QayyumNessuna valutazione finora
- HL Questions On Electrophilic Addition ReactionsDocumento1 paginaHL Questions On Electrophilic Addition ReactionsPranavaNessuna valutazione finora
- NCERT Notes For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 SolutionsDocumento11 pagineNCERT Notes For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Solutionsshradha bittuNessuna valutazione finora
- DPP GoccccDocumento10 pagineDPP GoccccMayur Khichi0% (1)
- XII - Physics - Preboard 1 - Set A 2023Documento6 pagineXII - Physics - Preboard 1 - Set A 2023Anuradha MukherjeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 1Documento4 pagineExperiment 1JasmeetSinghNessuna valutazione finora
- GOC Sheet PDFDocumento55 pagineGOC Sheet PDFAayush KharbandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Integrated TeachingDocumento3 pagineIntegrated TeachingLaiza Mira Jean AsiaNessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Coordination CompoundsDocumento2 pagineCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Coordination CompoundsDeepa PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Supplementary Exercise Acids and BasesDocumento113 pagine4 Supplementary Exercise Acids and Bases云吸仓鼠吉尼斯保持者Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry SynopsisDocumento7 pagineChemistry SynopsisDr Prashant Shihora100% (1)
- 12 - Chemistry QP (Set-Ii)Documento6 pagine12 - Chemistry QP (Set-Ii)Shravan ZoneNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbonyl Compounds 12thDocumento24 pagineCarbonyl Compounds 12thRaju SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- (HKL) - Procedure For Finding The Miller Indices of A PlaneDocumento4 pagine(HKL) - Procedure For Finding The Miller Indices of A PlaneAkshay Kumar100% (1)
- Techniques Studying Fast Chemical ReactionsDocumento15 pagineTechniques Studying Fast Chemical ReactionsWaNnur WanEe Mohd Yusof100% (1)
- Unit 10 - Week 9: Assignment 9Documento5 pagineUnit 10 - Week 9: Assignment 9UmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Note IUPAC NomenclatureDocumento29 pagineLecture Note IUPAC NomenclatureDebarghya MukherjeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7 Stereochemistry: Answers Prof. Sivaguru JayaramanDocumento18 pagineChapter 7 Stereochemistry: Answers Prof. Sivaguru JayaramanRahma AshrafNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Class 11 AssignmentDocumento5 pagineChemistry Class 11 AssignmentDON'T CRAMNessuna valutazione finora
- Important Questions For CBSE Class 12 Chemistry The P-Block ElementsDocumento41 pagineImportant Questions For CBSE Class 12 Chemistry The P-Block ElementsyndtfndtgndNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbon's Unique Bonding PropertiesDocumento11 pagineCarbon's Unique Bonding PropertiesGaurav SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Alkene DPPDocumento20 pagineAlkene DPPKalyan ReddtNessuna valutazione finora
- Umpolung reactivity: methods for interchanging carbonyl donor and acceptor reactivityDocumento28 pagineUmpolung reactivity: methods for interchanging carbonyl donor and acceptor reactivitymeauna100% (1)
- Iron-Sulfur Protein - WikipediaDocumento21 pagineIron-Sulfur Protein - Wikipediaamar hattimareNessuna valutazione finora
- Iit Jee Chemistry DPP by :pjoyDocumento3 pagineIit Jee Chemistry DPP by :pjoyPrakash Joy50% (4)
- Chapter 2 Acid and BaseDocumento8 pagineChapter 2 Acid and BaseKelsi Kyla PeraltaNessuna valutazione finora
- Alcohol Phenol & EtherDocumento13 pagineAlcohol Phenol & EtherAbir DuttaNessuna valutazione finora
- Safety Data Sheet Highlights Key Hazards and ProtectionsDocumento7 pagineSafety Data Sheet Highlights Key Hazards and ProtectionsOm Prakash RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Script - TEST 5 (1st Mid-Term)Documento2 pagineScript - TEST 5 (1st Mid-Term)Thu PhạmNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Management-Capital BudgetingDocumento39 pagineFinancial Management-Capital BudgetingParamjit Sharma100% (53)
- Cast Copper Alloy Solder Joint Pressure Fittings: ASME B16.18-2018Documento41 pagineCast Copper Alloy Solder Joint Pressure Fittings: ASME B16.18-2018crescon designNessuna valutazione finora
- Uk GeographyDocumento9 pagineUk GeographyStainbok MihaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Arraignment PleaDocumento4 pagineArraignment PleaJoh SuhNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategies in Various Speech SituationsDocumento6 pagineStrategies in Various Speech SituationsSky NayytNessuna valutazione finora
- Susan Oyama The Ontogeny of Information Developmental Systems and Evolution Science and Cultural Theory 2000Documento297 pagineSusan Oyama The Ontogeny of Information Developmental Systems and Evolution Science and Cultural Theory 2000Marelin Hernández SaNessuna valutazione finora
- Yoga Practice Guide: DR - Abhishek VermaDocumento26 pagineYoga Practice Guide: DR - Abhishek VermaAmarendra Kumar SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- AnnovaDocumento4 pagineAnnovabharticNessuna valutazione finora
- Prof 7 - Capital Market SyllabusDocumento10 pagineProf 7 - Capital Market SyllabusGo Ivanizerrckc100% (1)
- 40 Energising BreathsDocumento1 pagina40 Energising BreathsOwlbearNessuna valutazione finora
- Pashmina vs Cashmere: Which Luxury Fiber Is SofterDocumento15 paginePashmina vs Cashmere: Which Luxury Fiber Is SofterSJVN CIVIL DESIGN100% (1)
- Brochure For Graduate DIploma in Railway Signalling 2019 v1.0 PDFDocumento4 pagineBrochure For Graduate DIploma in Railway Signalling 2019 v1.0 PDFArun BabuNessuna valutazione finora
- HRM ........Documento12 pagineHRM ........Beenish AbbasNessuna valutazione finora
- A Comparative Look at Jamaican Creole and Guyanese CreoleDocumento18 pagineA Comparative Look at Jamaican Creole and Guyanese CreoleShivana Allen100% (3)
- Sikkim Public Works Liability of Government and Contractor Act 1983Documento11 pagineSikkim Public Works Liability of Government and Contractor Act 1983Latest Laws TeamNessuna valutazione finora
- 6-Modul - PTI412 - IoT-1-2020Documento17 pagine6-Modul - PTI412 - IoT-1-202020200801015 Joko SulistyoNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Write A Cover Letter For A Training ProgramDocumento4 pagineHow To Write A Cover Letter For A Training Programgyv0vipinem3100% (2)
- RPP Microteaching TaruliDocumento9 pagineRPP Microteaching TaruliTaruli Sianipar 165Nessuna valutazione finora
- PCC ConfigDocumento345 paginePCC ConfigVamsi SuriNessuna valutazione finora
- Sahar NSC FixDocumento45 pagineSahar NSC FixSahar AndhikaNessuna valutazione finora
- SubjectivityinArtHistoryandArt CriticismDocumento12 pagineSubjectivityinArtHistoryandArt CriticismMohammad SalauddinNessuna valutazione finora
- Spain Usa ExtraditionDocumento2 pagineSpain Usa ExtraditionAdrian BirdeaNessuna valutazione finora
- Segmenting, Targeting, and Positioning (STP)Documento16 pagineSegmenting, Targeting, and Positioning (STP)Rachmat PutraNessuna valutazione finora
- Recommender Systems Research GuideDocumento28 pagineRecommender Systems Research GuideSube Singh InsanNessuna valutazione finora
- BiblicalDocumento413 pagineBiblicalMichael DiazNessuna valutazione finora
- Ajaz CVDocumento1 paginaAjaz CVAjazNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 2 - BT MLH 11 - KeyDocumento2 pagineUnit 2 - BT MLH 11 - KeyttyannieNessuna valutazione finora
- RQQDocumento3 pagineRQQRazerrdooNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeDa EverandScience Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeDa EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (90)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeDa EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- It's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingDa EverandIt's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (10)
- Coating and Drying Defects: Troubleshooting Operating ProblemsDa EverandCoating and Drying Defects: Troubleshooting Operating ProblemsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsDa EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Piping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationDa EverandPiping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (18)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction in the Science of Everyday LifeDa EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction in the Science of Everyday LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (9)
- Trevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationDa EverandTrevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationNessuna valutazione finora
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsDa EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (146)
- The Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableDa EverandThe Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (22)
- The Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionDa EverandThe Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolDa EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNessuna valutazione finora
- Nuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressDa EverandNuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsDa EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (3)
- Advanced Process Control: Beyond Single Loop ControlDa EverandAdvanced Process Control: Beyond Single Loop ControlNessuna valutazione finora
- Guidelines for Asset Integrity ManagementDa EverandGuidelines for Asset Integrity ManagementValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Essential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilDa EverandEssential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Napoleon's Buttons: 17 Molecules That Changed HistoryDa EverandNapoleon's Buttons: 17 Molecules That Changed HistoryValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (25)
- Chemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesDa EverandChemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (14)
- An Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksDa EverandAn Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Process Engineering for a Small Planet: How to Reuse, Re-Purpose, and Retrofit Existing Process EquipmentDa EverandProcess Engineering for a Small Planet: How to Reuse, Re-Purpose, and Retrofit Existing Process EquipmentNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeDa EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (14)
- Introduction to Strategies for Organic SynthesisDa EverandIntroduction to Strategies for Organic SynthesisNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableDa EverandChemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableNessuna valutazione finora