Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
CH 301 Unit 2 Exam-Solutions
Caricato da
brunosipodCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
CH 301 Unit 2 Exam-Solutions
Caricato da
brunosipodCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Version 396 Unit 2 Exam vandenbout (51335) This print-out should have 31 questions.
ns. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page nd all choices before answering. 001 2.6 points Which of the following statements is true regarding electromagnetic radiation? 1. Electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength of 400 nm has a frequency that is lower than that with a wavelength of 600 nm. 2. Electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength of 400 nm travels faster than that with a wavelength of 600 nm. 3. Electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength of 600 nm travels faster than that with a wavelength of 400 nm. 4. Electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength of 600 nm has a frequency that is lower than that with a wavelength of 400 nm. correct 5. The frequency of electromagnetic radiation determines how fast it travels. Explanation: 1 . Higher wavelengths corf respond to lower frequencies, and vice versa. v = f , so = 3e8 / 500e-9 = 6e14
003 2.6 points Which color in the rainbow has the shortest wavelength? 1. green 2. blue correct 3. orange 4. red 5. yellow Explanation: Ordered by wavelengths, blue < green < yellow < orange < red 004 2.6 points An orbital with n = 4 and = 2 would be described as 1. 4s. 2. 2p. 3. 4d. correct 4. 2s. 5. 4p. Explanation: = 2 refers to the d orbital, so the orbital is 4d. 005 2.6 points Rank the following species from smallest to largest atomic radius: K, Mg, Rb, Ca. 1. Mg < Rb < K < Ca 2. Mg < Ca < Rb < K 3. Mg < K < Ca < Rb 4. Mg < Ca < K < Rb correct
002 2.6 points What is the frequency of a 500 nm photon? 1. 9.0 1017 Hz 2. 15 Hz 3. 4.0 107 Hz 4. 5.0 106 Hz 5. 1.5 1016 Hz 6. 6.0 1014 Hz correct Explanation: frequency = speed of light / wavelength =
Version 396 Unit 2 Exam vandenbout (51335) 5. Rb < K < Ca < Mg Explanation: Atomic radii increase down and to the left. 006 2.6 points When two H atoms are brought together from large distances they can make H2 . As the bond begins to form, the force between the atoms becomes more (attractive, repulsive) and the potential energy (increases, stays the same, decreases). 1. attractive; increases 2. attractive; decreases correct 3. attractive; stays the same 4. repulsive; increases 5. repulsive; decreases 6. repulsive; stays the same Explanation: 007 2.6 points In a pure covalent bond, electrons are 1. uncharged. 2. shared equally. correct 3. transferred. 4. shared unequally. Explanation: 008 2.6 points In which compound is the bond the LEAST polar? 1. HCl 2. HBr 3. HF 4. HI correct Explanation:
009 2.6 points The number of single bonds, double bonds, triple bonds, and unshared (lone) pairs on the central atom in the sulte ion (SO2 3 ) is 1. 3,0,0,1 correct 2. 2,1,0,0 3. 1,1,0,2 4. 1,2,0,1 5. 2,1,0,1 Explanation: To draw the dot structure for SO2 3 we must rst calculate the number of valence electrons available from the atoms: A = 6 1 (S atom) + 6 3 (O atoms) + 2 (from 2 charge) = 26 e We choose the least electronegative element as the central atom (sulfur in this case) and place the other atoms symmetrically around it. The correct dot structure for the molecule should show a complete octet (8 electrons) around each atom and a total of 26 valence electrons for the entire structure: 2 O S O O As can be seen above, there is one lone pair on the central atom. (If using the S = N A rule to determine the dot structure, N = (81)+(83) = 32 e and S = 32 26 = 6 e . This would indicate 3 bonds and correspond to the structure shown above.) 010 2.6 points The carbon and oxygen in carbon monoxide
Version 396 Unit 2 Exam vandenbout (51335) (CO) are joined by what type of bond or bonds? 1. two double bonds 2. one triple bond correct 3. one single bond 4. one double bond 5. four single bonds Explanation: The total number of valence electrons is C O 1 4 e = 4 e 1 6 e = 6 e 10 e C O 1. 5 2. 3 3. 7 4. 8 correct 5. 9
Explanation: To draw the dot structure for SO3 we must rst calculate the number of valence electrons available from the atoms: A = 6 1(S atom) + 6 3(O atoms) = 24 e We choose the least electronegative element as the central atom (sulfur in this case) and place the other atoms symmetrically around it. The correct dot structure for the molecule should show a complete octet (8 electrons) around each atom and a total of 24 valence electrons for the entire structure: O S O O As can be seen above, there are 8 lone pairs on the oxygen atoms. (If using the S = N A rule to determine the dot structure, N = 8 1 + 8 3 = 32 e and S = 32 24 = 8 e . This would indicate 4 bonds and correspond to the structure shown above.) Alternate Solution: SO3 has 24 valence electrons. 6 of these come from S, and the remaining 18 come from O (3 atoms at 6 electrons each). In drawing the Lewis structure for SO3 , three resonance forms must be depicted for S to obey the octet rule. Ultimately, 8 of the available 24 electrons are used to form the three S O bonds, and the remaining 16 electrons (8 pairs) exist as lone pairs on oxygen.
and the Lewis dot structure is
The 3 lines represent a triple bond between the C and O. 011 2.6 points Which of the following is the correct Lewis structure of ethynol (C2 H2 O)? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. H H H H H C C C C C C C C C C O O O O O H H H H correct H
Explanation: All of the other choices have octet rule violations, and because Carbon and Oxygen are Period 2 elements, they cannot form hypervalent compounds. 012 2.6 points Draw the Lewis electron dot structure for SO3 . What is the total number of lone pairs of electrons on the three oxygen atoms?
Version 396 Unit 2 Exam vandenbout (51335) 013 2.6 points Which one of the following compounds does NOT obey the octet rule? 1. CH4 2. BF3 correct 3. NaCl 4. H2 O Explanation: 014 2.6 points How many lone pairs are on the central atom of AsF5 ? 1. 4 2. 0 correct 3. 1 4. 2 5. 3 Explanation: The Lewis dot structure for AsF5 is F F As F F F , H 016 2.6 points In the following molecule H C H C
O
H
H C H C
1. the carbon/oxygen bonds have two distinct bond strengths and all carbon/hydrogen bonds have two distinct bond strengths 2. all the carbon/hydrogen bonds have the same strength but the carbon/oxygen bonds are found to have two distinct bond strengths 3. all the carbon/oxygen bonds have the same strength but the carbon/hydrogen bonds are found to have two distinct bond strengths 4. all the carbon/oxygen bonds have the same strength and all the carbon/hydrogen bonds have the same strength correct Explanation: Resonance is when there are two equivalent ways of drawing a Lewis structure, so you draw both, as the true structure is somewhere in between. The true structure is not switching back and forth but is essentially the average of these two structures. Thus the carbon/oxygen bonds are both 1.5 bonds. The molecule does not have two types of carbon/oxygen bonds. The dicult is with our drawings not the molecule. Because we insist on having Lewis structure with only single and double bonds the only way we can capture this idea of a 1.5 bond is to draw two equivalent resonance structures. 017 2.6 points
015 2.6 points The chemical formula for potassium sulfate is 1. K3 (SO4 )2 2. KSO4 3. K(SO4 )2 4. K2 SO4 correct Explanation: K+ and SO2 4 forms K2 SO4 : 2(+1) + 1(2) = 0
For an ionic compound, the lattice energy is the energy associated with 1. generating the ionic compound from the neutral elements
Version 396 Unit 2 Exam vandenbout (51335) 2. dissolving the compound in water to form aqueous ions. 3. moving a pair of ions to innite separation. 4. breaking up the solid crystal into gas phase ions. CORRECT Explanation: The lattice energy is the energy associated with taking the ions from the solid crystalline structure and separating them into ions in the gas phase. The energy associated with simply separating two isolated ions is the Coulomb energy. The energy for dissolving the compound to for aqueous ions is the enthalpy of solution. And the energy for forming the ionic compound from neutral elements is the enthalpy of formation. 018 2.6 points Consider the rst three energy levels for an electron in a helium ion. 1st energy level : 6.41 1019 J 2nd energy level : 1.60 1019 J 3rd energy level : 0.72 1019 J A 413 nm photon interacts with the ion. What might happen as a result of this interaction? 1. An electron could be excited from the 2nd to 3rd energy level. 2. An electron could be excited from the 1st to 3rd energy level. 3. None of the transitions listed would occur. 4. An electron could be excited from the 1st to 2nd energy level. correct Explanation: 019 2.6 points 2. 3. 4. 5. phosphorus pentachloride PCl5 sulfur trioxide SO3 carbon tetrachloride CCl4 dinitrogen pentoxide N2 O5
Explanation: SeO2 is selenium dioxide. The prex lable di is misplaced in the answer indicating a ratio of 2:1 Se to O. 020 2.6 points
The oxygen/oxygen bond in O2 is stronger than in HOOH because 1. the oxygen/oxygen bond in O2 is more polar than in HOOH. 2. O2 has a oxygen/oxygen double bond and HOOH has a oxygen/oxygen single bond. CORRECT 3. O2 has only one structure, while HOOH has a resonance structure that weakens the bond. 4. O2 has an oxygen/oxgyen triple bond where HOOH has an oxygen/oxygen double bond. 5. O2 has a resonance structure that provides extra stability compared to the HOOH which has only one contributing structure. 6. the oxygen/oxygen bond in O2 is less polar than in HOOH. Explanation: The Lewis dot structure of O2 shows it has a oxygen/oxygen double bond. HOOH only has a oxygen/oxygen single bond. 021 2.6 points Which of the following species is isoelectronic with S2 ? 1. Br 2. As3 3. Rb+ 4. Mg2+
Which of the following is NOT correctly matched name to formula 1. diselenium oxide SeO2 CORRECT
Version 396 Unit 2 Exam vandenbout (51335) 5. None of these 5. Ar correct Explanation: Isoelectronic means has the same number of electrons as. Locate each element in the Periodic Table. The atomic number will give the number of protons, which equals the number of electrons for the neutral atom; for an ion, you will have to add or subtract from this value. 022 2.6 points Let X be a hypothetical element. Which of the following would be largest? 1. X2+ 2. X 3. X2 correct 4. X 5. X+ Explanation: X2 would be largest as it has 2 more electrons than protons, and the protons here would be at the greatest disadvantage when trying to draw the electrons towards the nucleus. 2.6 points Cobalt-60 is an articial radioisotope that is produced in a nuclear reactor for use as a gamma-ray source in the treatment of certain types of cancer. If the wavelength of the gamma radiation from a cobalt-60 source is 1.00 103 nm, calculate the energy of a photon of this radiation. (60 27 Co) 1. 2.0 1013 J correct 2. 2.0 1016 J 3. 2.0 1019 J 4. 6.4 1014 J 023 6. 6.63 1034 J 7. 6.4 1010 J Explanation: = 1.00 103 nm Ephoton = h =
Ephoton = ?
hc (6.626 1034 J s)(3.0 108 m/s) = (1.00 103 nm)(109 m/nm) = 2.0 1013 J
024 2.6 points An electron in a hydrogen atom moves from the n = 2 to n = 5 level. What is the wavelength of the photon that corresponds to this transition and is the photon emitted or absorbed during this process? 1. 276 nm; absorbed 2. 1875 nm; absorbed 3. 1875 nm; emitted 4. 434 nm; emitted 5. 434 nm; absorbed correct 6. 276 nm; emitted Explanation: 025 2.6 points Which of the following is correct with respect to the photoelectric eect? 1. A plot of the kinetic energy of the ejected electrons versus the frequency of the incident radiation has a slope that is equal to the value of the work function. 2. The kinetic energy of the ejected electrons increases with the intensity of the incident radiation. 3. A plot of the kinetic energy of the ejected
Version 396 Unit 2 Exam vandenbout (51335) electrons versus the frequency of the incident radiation is linear. correct 4. All metals have the same work function. Explanation: The photoelectric eect is summarized by KE = h , which ts the standard equation for a line : y = mx c, where is the work function of the metal, and varies for dierent metals. The intensity of the incident radiation does not show here as it is just the number of photons hitting a surface in a given time. 026 2.6 points You shine white light through a sample of neon atoms and then through a holographic diraction grating. From this experiment, you would expect to observe 1. mostly black space with thin lines of color. 2. a continuous spectrum broken by thin black lines. correct 3. a continuous spectrum. Explanation: 027 2.6 points Phosphorus has a higher ionization energy than silicon because 1. False; phosphorus has a lower ionization energy than silicon. 2. the outer orbitals of phosphorus are located closer to the nucleus than the outer orbitals of silicon. 3. the eective nuclear charge of phosphorus is less than that of silicon. 4. the outer orbitals of phosphorus are located farther from the nucleus than the outer orbitals of silicon. Explanation:
5. the eective nuclear charge of silicon is less than that of phosphorus. correct
: [Ne] 3s 3p 14 Si : [Ne] 3s 3p
15 P
In both cases, the valence electrons are located in 3s and 3p orbitals. However, P has a greater nuclear charge due to its greater number of protons, so more energy is required to remove an electron from P relative to Si. 028 2.6 points Which of the following will not have ionic bonds? 1. NaCl 2. methane (CH4 ) correct 3. calcium oxide 4. KBr 5. magnesium chloride
Explanation: All of the options except CH4 have ionic bonds, which are formed between metals and nonmetals. CH4 has only covalent (nonmetal-nonmetal) bonds. 029 2.6 points The graph shows the radial distribution plots for the 1s wavefunctions for H, He, and He+ .
Version 396 Unit 2 Exam vandenbout (51335) A B 4r 22 C
radius Which plot is the 1s wavefunction for the He+ ion? 1. A correct 2. C 3. There is no way to know 4. B Explanation: H has one electron and one proton. He has two electrons and two protons. He+ has one electron and two protons. Therefore the electron will have the greatest attraction to the the nuclei with two protons. In He there will be a slight reduction in the eective nuclear charge due to the electron-electron repulsion. In He+ , there is only one electron so the radius will be the smallest. Plot A is peaked closest to the nucleus so it will be the smallest. 030 2.6 points Any neutral atom having an odd (i.e., uneven) atomic number must be 1. metallic. 2. non-magnetic. 3. paramagnetic. correct 4. inert. 5. a transition element. Explanation:
Version 396 Unit 2 Exam vandenbout (51335) 031 22.0 points
This question is merely a placeholder for the points in the hand-graded portion of the exam. Explanation: This question is merely a placeholder for the points in the hand-graded portion of the exam.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Electron Transfer Reactions of Complex Ions in SolutionDa EverandElectron Transfer Reactions of Complex Ions in SolutionNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 3 Exam-SolutionsDocumento8 pagineUnit 3 Exam-SolutionsbrunosipodNessuna valutazione finora
- Enzymes: A Practical Introduction to Structure, Mechanism, and Data AnalysisDa EverandEnzymes: A Practical Introduction to Structure, Mechanism, and Data AnalysisValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (2)
- Solutions Manual Chapter8 PDFDocumento54 pagineSolutions Manual Chapter8 PDFKwan-Soo ParkNessuna valutazione finora
- Sat Boot Camp #2 Sig Figs, Conversions, Density ... Score:: 2.148 2.15 2.1 2.2 None of The AboveDocumento7 pagineSat Boot Camp #2 Sig Figs, Conversions, Density ... Score:: 2.148 2.15 2.1 2.2 None of The Aboveapi-233552637Nessuna valutazione finora
- UT CH 301 UNIT 1 EXAM-SolutionsDocumento7 pagineUT CH 301 UNIT 1 EXAM-SolutionsbrunosipodNessuna valutazione finora
- 02 Petrucci10e CSMDocumento33 pagine02 Petrucci10e CSMAlexNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry - Mccord - Exam 1Documento9 pagineChemistry - Mccord - Exam 1Miguel MartinezNessuna valutazione finora
- 25 Petrucci10e CSMDocumento25 pagine25 Petrucci10e CSMAlexNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5 WorksheetDocumento6 pagineChapter 5 WorksheetJules BrunoNessuna valutazione finora
- 06 Petrucci10e CSMDocumento54 pagine06 Petrucci10e CSMAlexNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 Practice Test 4u1Documento4 pagineChapter 4 Practice Test 4u1helloblargNessuna valutazione finora
- GRE Sub 化学题 (太傻整理)Documento30 pagineGRE Sub 化学题 (太傻整理)Alisa100% (1)
- Rate LawsDocumento20 pagineRate LawsReginal MoralesNessuna valutazione finora
- 07 Petrucci10e CSMDocumento43 pagine07 Petrucci10e CSMPhương Ngân HồNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 4: Bonding 4.2: Covalent BondingDocumento30 pagineTopic 4: Bonding 4.2: Covalent Bondingapi-546066323Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Final Exam 1 - 2012Documento11 pagineChemistry Final Exam 1 - 2012Alex HwangNessuna valutazione finora
- Acid Base 15Documento36 pagineAcid Base 15Imranzo HsnNessuna valutazione finora
- 28 Petrucci10e CSMDocumento35 pagine28 Petrucci10e CSMAlexNessuna valutazione finora
- CAIE Chemistry A-Level: 24: ElectrochemistryDocumento8 pagineCAIE Chemistry A-Level: 24: ElectrochemistryahumanbeinginearthNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7 Practice TestDocumento2 pagineChapter 7 Practice TesthelloblargNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 7 Practice Test AnswersDocumento1 paginaCH 7 Practice Test AnswershelloblargNessuna valutazione finora
- Intermolecular Forces - Chemistry PracticeDocumento1 paginaIntermolecular Forces - Chemistry Practicewjahx8eloo ly100% (1)
- Problem Set On ElectrochemistryDocumento2 pagineProblem Set On ElectrochemistryMark Cliffton BadlonNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch123 Exam II Practice Exam Spring2011Documento7 pagineCh123 Exam II Practice Exam Spring2011christopher92530% (1)
- 1 IntroductoryDocumento45 pagine1 IntroductoryTuhin Sahu100% (1)
- Acid Base WorksheetDocumento5 pagineAcid Base WorksheetOmar IjazNessuna valutazione finora
- Faraday's Law WorksheetDocumento4 pagineFaraday's Law WorksheetBrianna MalcolmNessuna valutazione finora
- WS10!1!1a Finding The Oxidation StateDocumento1 paginaWS10!1!1a Finding The Oxidation StatejupiterlNessuna valutazione finora
- CHM 101 Complete - LNDocumento80 pagineCHM 101 Complete - LNSimon Adediran100% (1)
- Chemistry 12: Solutions Manual Part ADocumento44 pagineChemistry 12: Solutions Manual Part ADerrick JamesNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinetics Homework 3Documento4 pagineKinetics Homework 3RizkiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4Documento30 pagineChapter 4helloblargNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 R DPBui QMF ZPUq Exc 6 JFDocumento53 pagine5 R DPBui QMF ZPUq Exc 6 JFBhfjsukNessuna valutazione finora
- Last Name - Read Directions Last Name 1st On Scantron & Exam Read Directions Read DirectionsDocumento5 pagineLast Name - Read Directions Last Name 1st On Scantron & Exam Read Directions Read DirectionsJared BurkeNessuna valutazione finora
- Stoichiometry Questions & AnswersDocumento2 pagineStoichiometry Questions & Answersnosirat aladeNessuna valutazione finora
- Percent Yield: Chemfile Mini-Guide To Problem SolvingDocumento11 paginePercent Yield: Chemfile Mini-Guide To Problem SolvingdhavaleshNessuna valutazione finora
- Mini Mock Unit 4 4 To 4 11 A2 Organic Chemistry and Structure DeterminationDocumento15 pagineMini Mock Unit 4 4 To 4 11 A2 Organic Chemistry and Structure DeterminationSahanNivanthaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2Documento11 pagineChapter 2helloblargNessuna valutazione finora
- Ques202 295bon2mcDocumento13 pagineQues202 295bon2mcMuhammad HaneefNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter: 1 Stoichiometric Relationships: SubtopicsDocumento108 pagineChapter: 1 Stoichiometric Relationships: SubtopicsBNessuna valutazione finora
- Name Jurico A. Marges: Chem 1-General Chemistry Final ExamDocumento10 pagineName Jurico A. Marges: Chem 1-General Chemistry Final ExamGina Ann MaderaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8Documento31 pagineChapter 8helloblarg100% (4)
- H2 Atomic Structure, Stiochiometry QuestionsDocumento8 pagineH2 Atomic Structure, Stiochiometry QuestionskitoniumNessuna valutazione finora
- 19 Petrucci10e CSMDocumento52 pagine19 Petrucci10e CSMPhạm Hoàng NamNessuna valutazione finora
- AP Chemistry Study Guide: Chapter 14: Acids and Bases and Chapter 15, 16.1 and 21.3: Aqueous and Acid-Base EquilibriaDocumento8 pagineAP Chemistry Study Guide: Chapter 14: Acids and Bases and Chapter 15, 16.1 and 21.3: Aqueous and Acid-Base Equilibrialorraine_cuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fill in The Table Below:: Empirical Formula WorksheetDocumento2 pagineFill in The Table Below:: Empirical Formula WorksheetSherida GibbsNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes Chapter 8 Transition ChemistryDocumento17 pagineNotes Chapter 8 Transition ChemistryGauravRajNessuna valutazione finora
- 01 1350977450 79497 PDFDocumento83 pagine01 1350977450 79497 PDFArya ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- SCH4C Organic Chem Test Cheat SheetDocumento1 paginaSCH4C Organic Chem Test Cheat SheetSteve M Hall50% (2)
- Unit 5 Part BDocumento84 pagineUnit 5 Part BFaye CaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Complexation and Precipitation Reactions and TitrationsDocumento53 pagineComplexation and Precipitation Reactions and TitrationsDivya TripathyNessuna valutazione finora
- 20 Petrucci10e CSMDocumento66 pagine20 Petrucci10e CSMAlexNessuna valutazione finora
- Lect 18 - Examples On ElectrolysisDocumento12 pagineLect 18 - Examples On ElectrolysisSalem GarrabNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8 Practice Test 4u1Documento1 paginaChapter 8 Practice Test 4u1helloblargNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 ElectrochemistryTheoryDocumento29 pagine1 ElectrochemistryTheoryEdon Bedi100% (1)
- PDFDocumento155 paginePDFHifza shairwani100% (1)
- In Class Practice On Periodic Trends WsDocumento3 pagineIn Class Practice On Periodic Trends WsFern HofileñaNessuna valutazione finora
- IR Spectroscopy Problem Set 1Documento0 pagineIR Spectroscopy Problem Set 1Jules BrunoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem 155 ElectrochemistryDocumento12 pagineChem 155 Electrochemistryapi-318921527Nessuna valutazione finora
- CHEM 301 Unit 3 SoluionDocumento9 pagineCHEM 301 Unit 3 SoluionbrunosipodNessuna valutazione finora
- History Additive ManufacturingDocumento7 pagineHistory Additive ManufacturingbrunosipodNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics 303K Test 3 SolutionsDocumento11 paginePhysics 303K Test 3 SolutionsbrunosipodNessuna valutazione finora
- PHY 303K Test 2 SolutionsDocumento11 paginePHY 303K Test 2 SolutionsbrunosipodNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4 Exam-SolutionsDocumento7 pagineUnit 4 Exam-SolutionsbrunosipodNessuna valutazione finora
- PHY 303K Test 4 SolutionsDocumento10 paginePHY 303K Test 4 Solutionsbrunosipod100% (1)
- Lect07 Ch5 Steady State Sinusoidal AnalysisDocumento27 pagineLect07 Ch5 Steady State Sinusoidal AnalysisbrunosipodNessuna valutazione finora
- M427L Homework 1Documento1 paginaM427L Homework 1brunosipodNessuna valutazione finora
- Wrangling WebinarDocumento151 pagineWrangling WebinarbrunosipodNessuna valutazione finora
- Boot Camp Installation & Setup GuideDocumento11 pagineBoot Camp Installation & Setup GuidebrunosipodNessuna valutazione finora
- Runge Kutta MethodDocumento2 pagineRunge Kutta MethodbrunosipodNessuna valutazione finora
- Developing Visual LiteracyDocumento28 pagineDeveloping Visual LiteracybrunosipodNessuna valutazione finora
- PHY 303L MT4 SolutionsDocumento9 paginePHY 303L MT4 SolutionsbrunosipodNessuna valutazione finora
- 2011 Fall Midterm1 Soln CS439Documento8 pagine2011 Fall Midterm1 Soln CS439brunosipodNessuna valutazione finora
- 2011 Fall Midterm2 Soln CS 439Documento6 pagine2011 Fall Midterm2 Soln CS 439brunosipodNessuna valutazione finora
- Tech - Info, Tensile TestingDocumento6 pagineTech - Info, Tensile TestingbrunosipodNessuna valutazione finora
- Y86 Programmer-Visible StateDocumento14 pagineY86 Programmer-Visible StatebrunosipodNessuna valutazione finora
- Graph Theory, Part 2: 7 ColoringDocumento23 pagineGraph Theory, Part 2: 7 ColoringbrunosipodNessuna valutazione finora
- PHYSICS 303L EXAM 2 SolutionsDocumento10 paginePHYSICS 303L EXAM 2 SolutionsbrunosipodNessuna valutazione finora
- Tech-1.Info. Hardness TestingDocumento6 pagineTech-1.Info. Hardness TestingbrunosipodNessuna valutazione finora
- CS 439 2011 Fall Final SolnDocumento9 pagineCS 439 2011 Fall Final SolnbrunosipodNessuna valutazione finora
- Google Zeitgeist 2012 enDocumento125 pagineGoogle Zeitgeist 2012 enPavan WaniNessuna valutazione finora
- M427K Fall '10 Differential Equations Test SolutionsDocumento5 pagineM427K Fall '10 Differential Equations Test SolutionsbrunosipodNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer Key - Introductory Calculations I - UncertaintyDocumento2 pagineAnswer Key - Introductory Calculations I - Uncertaintybrunosipod100% (1)
- Biotechnology For Beginners Chapter 1 Reinhard RennebergDocumento27 pagineBiotechnology For Beginners Chapter 1 Reinhard RennebergnekojcoNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer Key - Introductory Calculations I - UncertaintyDocumento2 pagineAnswer Key - Introductory Calculations I - Uncertaintybrunosipod100% (1)
- SuperconductivityDocumento7 pagineSuperconductivityGopinathan MNessuna valutazione finora
- Viva QuestionsDocumento3 pagineViva Questionssainandhakumaar86% (7)
- Temephos WHODocumento24 pagineTemephos WHOMochHabibEl-Huseiny0% (1)
- 10.37 Spring 2007 Homework 1 Due Wednesday, Feb. 14Documento6 pagine10.37 Spring 2007 Homework 1 Due Wednesday, Feb. 14ÅdnAn MehmOodNessuna valutazione finora
- FP-Lect10 - Water PropertiesDocumento34 pagineFP-Lect10 - Water PropertiesMohamed SadekNessuna valutazione finora
- Rapid Method For Determining Moisture Content in Crude Palm Oil by Fourier Transform Infrared SpectrosDocumento7 pagineRapid Method For Determining Moisture Content in Crude Palm Oil by Fourier Transform Infrared SpectrosnaseemNessuna valutazione finora
- Document Shaista Fareen Third PDFDocumento3 pagineDocument Shaista Fareen Third PDFSha Far97Nessuna valutazione finora
- Universe Question Bank (Introduction) : Physics PhysicsDocumento2 pagineUniverse Question Bank (Introduction) : Physics Physicsanon_50109362Nessuna valutazione finora
- Excel Work Book For Heat ExchangersDocumento88 pagineExcel Work Book For Heat Exchangerspk dasNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermodynamics (SI Units) Sie 6E - CengelDocumento157 pagineThermodynamics (SI Units) Sie 6E - CengelMatt HarrisNessuna valutazione finora
- Sulfur and Sulfuric AcidDocumento24 pagineSulfur and Sulfuric AciddhavalNessuna valutazione finora
- E - Pfaudler Glass Linings 614 4EDocumento18 pagineE - Pfaudler Glass Linings 614 4Edevang asherNessuna valutazione finora
- Movie Review of Interstellar by Christopher Nolan Plot Characters and VisualsDocumento3 pagineMovie Review of Interstellar by Christopher Nolan Plot Characters and VisualsRekha DhoundiyalNessuna valutazione finora
- Paint and Coatings Industry OverviewDocumento3 paginePaint and Coatings Industry OverviewYash VasantaNessuna valutazione finora
- Photocure TXR 10 TDSDocumento2 paginePhotocure TXR 10 TDSjm sanchezNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrostatic Pressure: ICP A ChemistryDocumento14 pagineHydrostatic Pressure: ICP A ChemistryselniNessuna valutazione finora
- Stem 006 Day 3Documento10 pagineStem 006 Day 3Caryl Ann C. SernadillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Learning Resource - Physical and Chemical Properties of MineralsDocumento8 pagineLearning Resource - Physical and Chemical Properties of MineralsKatrina JulianesNessuna valutazione finora
- EPA 608 Certification Test QuestionsDocumento96 pagineEPA 608 Certification Test Questionslanzea91% (65)
- HeatecDocumento10 pagineHeatecMogtaba Osman100% (1)
- Study PLANNER XII (Second Step) - JEE Main & Advanced 2020-21 (Phase-1) - April To DecemberDocumento30 pagineStudy PLANNER XII (Second Step) - JEE Main & Advanced 2020-21 (Phase-1) - April To DecemberBharat GelotNessuna valutazione finora
- Pressure Loss Major LossDocumento2 paginePressure Loss Major Lossvictor.sNessuna valutazione finora
- E 698 - 99 - Rty5oc1sruqDocumento10 pagineE 698 - 99 - Rty5oc1sruqtam daoNessuna valutazione finora
- Light Metals and Their AlloysDocumento55 pagineLight Metals and Their Alloysmurari100% (1)
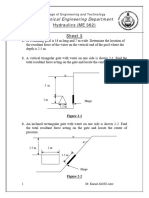
- Sheet 3Documento6 pagineSheet 3Keroles SabryNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Design GuideDocumento44 pagineEngineering Design GuideMohamed NouzerNessuna valutazione finora
- 5990 4547enDocumento16 pagine5990 4547enHoanghanh LequangNessuna valutazione finora
- Problems For Computational ChemistryDocumento15 pagineProblems For Computational ChemistryMohamed Ayman MoshtohryNessuna valutazione finora
- Stream Flow Measurement Sample Report 069BCE16Documento21 pagineStream Flow Measurement Sample Report 069BCE16Gaurab TimilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tin Mill Products, Electrolytic Tin Plate, Single Reduced: Standard Specification ForDocumento5 pagineTin Mill Products, Electrolytic Tin Plate, Single Reduced: Standard Specification Forist93993Nessuna valutazione finora
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesDa EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (2193)
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceDa EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (51)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseDa EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (69)
- The Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectDa EverandThe Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (20)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessDa EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (6)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingDa EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (5)
- The Beauty of Falling: A Life in Pursuit of GravityDa EverandThe Beauty of Falling: A Life in Pursuit of GravityNessuna valutazione finora
- The Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityDa EverandThe Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (76)
- Giza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyDa EverandGiza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyNessuna valutazione finora
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldDa EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (64)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidDa EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1395)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterDa EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (410)
- Let There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessDa EverandLet There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (57)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismDa EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (500)
- Chernobyl 01:23:40: The Incredible True Story of the World's Worst Nuclear DisasterDa EverandChernobyl 01:23:40: The Incredible True Story of the World's Worst Nuclear DisasterValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (264)
- Chasing Heisenberg: The Race for the Atom BombDa EverandChasing Heisenberg: The Race for the Atom BombValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (8)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldDa EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (60)
- Strange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsDa EverandStrange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (94)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowDa EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (49)
- Too Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldDa EverandToo Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (8)
- Why Time Flies: A Mostly Scientific InvestigationDa EverandWhy Time Flies: A Mostly Scientific InvestigationValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (17)
- Vibration and Frequency: How to Get What You Want in LifeDa EverandVibration and Frequency: How to Get What You Want in LifeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (13)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Da EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (157)