Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Specific Gravity Formulas
Caricato da
rrj44Descrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Specific Gravity Formulas
Caricato da
rrj44Copyright:
Formati disponibili
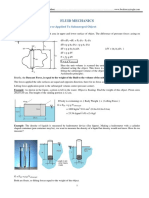
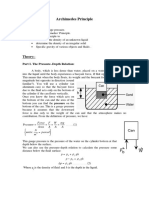
SpecificGravity(RelativeDensity)Calculations ThefollowingvaluesarerecordedaspartofASTMC127: A=massofovendrytestsampleinair,g B=ofsaturatedsurfacedrytestsampleinair,g C=apparentmassofsaturatedtestsampleinwater,g According to the principle of buoyancy, the apparent mass of the aggregate particles
suspended in water(C)isequaltotheirovendrymassinair(A)lessthemassofwatertheydisplacewhensubmerged. Thelatteristheproductofthemassdensityofwater(w)andthenetvolumeoftheaggregateparticles (i.e.,thevolumeoftheaggregateparticlesexcludingtheirpermeablepores),so C=AwVnet AC=wVnet
The apparent specific gravity is defined as the ratio of the mass of the particles to the mass of a volume ofwaterequaltothenetvolumeoftheparticles,sotheapparentspecificgravitycanbecalculatedas:
Gapp A A w Vnet A C
whichistheformulagivenintheASTMspecification. The SSD mass of the particles (B) is equal to their ovendry mass (A) plus the mass of water needed to completely fill their pores. The latter is the product of the mass density of water and the volume of the permeablepores,so B=A+wVpore BA=wVpore
The bulk specific gravity (SSD) is defined as the ratio of the SSD mass of the particles to the mass of a volume of water equal to the gross volume of the particles (i.e., the volume including the permeable pores),so
SSD Gbulk
B B B B w Vgross w Vnet w Vpores A C B A B C
whichistheformulagivenintheASTMspecification. Finally, the bulk specific gravity (OD) is the ratio of the ovendry mass of the particles to the mass of a volumeofwaterequaltothegrossvolumeoftheparticles:
OD Gbulk
A A A A w Vgross w Vnet w Vpores A C B A B C
which,again,istheformulagivenintheASTMspecification.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Specific GravityDocumento7 pagineSpecific GravityAj MinaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Mechanics of Water-Wheels - A Guide to the Physics at Work in Water-Wheels with a Horizontal AxisDa EverandThe Mechanics of Water-Wheels - A Guide to the Physics at Work in Water-Wheels with a Horizontal AxisNessuna valutazione finora
- Results and Discussion Report4Documento3 pagineResults and Discussion Report4Aisha AleneziNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid Mechanics 1 Mark QuestionsDocumento81 pagineFluid Mechanics 1 Mark QuestionsYashwant RajeshirkeNessuna valutazione finora
- University of The East College of Engineering Civil Engineering Department Caloocan Construction Materials and TestingDocumento11 pagineUniversity of The East College of Engineering Civil Engineering Department Caloocan Construction Materials and TestingPATRICIA NICOLE DIZONNessuna valutazione finora
- Standard Test Method For The Determination of SPECIFIC Gravity of Coarse AggregateDocumento5 pagineStandard Test Method For The Determination of SPECIFIC Gravity of Coarse AggregateAbdul MueedNessuna valutazione finora
- Bulik, SSD, Apparent Specific GravityDocumento2 pagineBulik, SSD, Apparent Specific GravityMd.Towhidul IslamNessuna valutazione finora
- SampDocumento2 pagineSampMat Eugine Paul ComiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid Mechanics Questions and AnswersDocumento118 pagineFluid Mechanics Questions and AnswersRam Ac100% (1)
- Specific Gravity of Coarse AggregateDocumento8 pagineSpecific Gravity of Coarse AggregateTariq HasanNessuna valutazione finora
- Random All TogetherDocumento7 pagineRandom All Togethermav7812Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrostatics PDFDocumento13 pagineHydrostatics PDFNsBhasinNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid Mechanics: BUOYANCY-The Lifting Force Applied To Submerged ObjectDocumento5 pagineFluid Mechanics: BUOYANCY-The Lifting Force Applied To Submerged ObjectYakup TasalıNessuna valutazione finora
- Aggregate Specific Gravity Test: Mechanics of Materials Laboratory NotesDocumento9 pagineAggregate Specific Gravity Test: Mechanics of Materials Laboratory NotesHaroon RashidiNessuna valutazione finora
- Specific Gravity: Introductory Mechanics Experimental LaboratoryDocumento3 pagineSpecific Gravity: Introductory Mechanics Experimental LaboratoryHussein BeqaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Cbe350 2013 HW01Documento3 pagineCbe350 2013 HW01Aarati SriramNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal and Physical Properties of AggregatesDocumento13 pagineThermal and Physical Properties of Aggregateslolenlenn100% (2)
- Prepared By: S.C.EDocumento8 paginePrepared By: S.C.EJeth LawNessuna valutazione finora
- M15 Knig9404 Ism C15 PDFDocumento31 pagineM15 Knig9404 Ism C15 PDFnorma_jeannNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid StaticsDocumento40 pagineFluid StaticsAbdul AhadNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Chess RevisionDocumento51 paginePhysics Chess RevisionZyad MâğdyNessuna valutazione finora
- Aggregates - Relative Density For StudentsDocumento35 pagineAggregates - Relative Density For StudentsRania FitouriNessuna valutazione finora
- Specific Gravity For C.A and F.A New2Documento7 pagineSpecific Gravity For C.A and F.A New2Ali M. ChehadehNessuna valutazione finora
- Specific GravityDocumento5 pagineSpecific GravityVenkiteshNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid Mechanics SanfoundaryDocumento277 pagineFluid Mechanics Sanfoundaryengineersalam786Nessuna valutazione finora
- Air Content of WaterDocumento11 pagineAir Content of WaterabhishekNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermodynamics: Physics SF 016Documento39 pagineThermodynamics: Physics SF 016Muhammad SolehinNessuna valutazione finora
- Archimedas PrincipleDocumento4 pagineArchimedas PrinciplewaqasNessuna valutazione finora
- Pressure: Unit 2Documento14 paginePressure: Unit 2Sumit ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch13 SSMDocumento18 pagineCh13 SSMJuanca AbadNessuna valutazione finora
- ESandEPS162 Homework 1Documento17 pagineESandEPS162 Homework 1SISTLA SUNDARA RAMA SARMANessuna valutazione finora
- Thermodynamics Fundamentals For ApplicationsDocumento7 pagineThermodynamics Fundamentals For ApplicationsMohamed Sayed AbdoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Pore-Pressure Coefficients A and B: A (Ao, - AU,) ) Est Mentally B Are Given. BDocumento5 pagineThe Pore-Pressure Coefficients A and B: A (Ao, - AU,) ) Est Mentally B Are Given. BdaveNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQsDocumento5 pagineMCQsebrahem khalidNessuna valutazione finora
- Surface Tension ExperimentDocumento11 pagineSurface Tension ExperimentnileshugemugeNessuna valutazione finora
- Exchap 02 AnsDocumento11 pagineExchap 02 AnsMewnEProwtNessuna valutazione finora
- Archimedes Principle: ObjectivesDocumento7 pagineArchimedes Principle: ObjectivesVicente Armones IVNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 5 PDFDocumento5 pagineLesson 5 PDFDjonraeNarioGalvezNessuna valutazione finora
- QpaperDocumento6 pagineQpaperRandeep Iyyad N CNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit Weight of Aggregate ASTM C 29Documento4 pagineUnit Weight of Aggregate ASTM C 29YasirNessuna valutazione finora
- MidtermDocumento3 pagineMidtermMohamed AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5 - The Gas Phase List ALL Basic QuestionsDocumento45 pagineChapter 5 - The Gas Phase List ALL Basic QuestionsSara Al SaeedNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit WeightDocumento6 pagineUnit WeightEnas S RadaidehNessuna valutazione finora
- Physical Properties of WaterDocumento4 paginePhysical Properties of WaterAshokNessuna valutazione finora
- Sheet PDFDocumento8 pagineSheet PDFEman MousaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrostatic Force On A Submerged SurfaceDocumento11 pagineHydrostatic Force On A Submerged Surfaceum4alltravel100% (1)
- ThermoDocumento67 pagineThermoapoorva jainNessuna valutazione finora
- Specific Gravity For C.A and F.A2Documento6 pagineSpecific Gravity For C.A and F.A2Ali M. ChehadehNessuna valutazione finora
- Palestine Technical University Engineering Department Building EngineeringDocumento4 paginePalestine Technical University Engineering Department Building EngineeringMaram M HaseebaNessuna valutazione finora
- CLT4 Recitation Worksheet Fall 2022 Solutions PDFDocumento3 pagineCLT4 Recitation Worksheet Fall 2022 Solutions PDFotlacasNessuna valutazione finora
- Drdo Examination Question Paper Year 2009Documento19 pagineDrdo Examination Question Paper Year 2009Gaurav AgarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid Mechanics Objective Type QuestionsDocumento223 pagineFluid Mechanics Objective Type Questionshello17Nessuna valutazione finora
- Buoyancy Problem Example For Fluid MechanicsDocumento2 pagineBuoyancy Problem Example For Fluid Mechanicsab100% (1)
- Physics-Part Test-3 SolutionDocumento5 paginePhysics-Part Test-3 SolutionRaju SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- ENGR207 - Assignment#1Documento4 pagineENGR207 - Assignment#1Mohamed KhairyNessuna valutazione finora
- Mass Volume - Mod3Documento3 pagineMass Volume - Mod3vivekNessuna valutazione finora
- IIIC1and2 IntegralForms ContinuityandEnergyDocumento64 pagineIIIC1and2 IntegralForms ContinuityandEnergyKenneth KnowlesNessuna valutazione finora
- DRDO 2009 Section - A: (O Entering The Process-O Required)Documento18 pagineDRDO 2009 Section - A: (O Entering The Process-O Required)RaghuNessuna valutazione finora
- Buoyancy Problem SolutionsDocumento3 pagineBuoyancy Problem SolutionsKeiole86% (7)
- Tutorial 08 Probabilistic AnalysisDocumento24 pagineTutorial 08 Probabilistic Analysisrrj44Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 05 Water Pressure GridDocumento17 pagineTutorial 05 Water Pressure Gridrrj44Nessuna valutazione finora
- Custom GraphDocumento1 paginaCustom Graphrrj44Nessuna valutazione finora
- Shallow Foundation (Bearing Capacity) TERZAGHI's Bearing Capacity FormulaDocumento3 pagineShallow Foundation (Bearing Capacity) TERZAGHI's Bearing Capacity Formularrj44Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fhwa Ed 88 053Documento42 pagineFhwa Ed 88 053rshaghayan100% (1)
- Phys 2012 Exam 1 Equations and Constants Constants: Electric Flux, Gauss' LawDocumento1 paginaPhys 2012 Exam 1 Equations and Constants Constants: Electric Flux, Gauss' Lawrrj44Nessuna valutazione finora
- Table 1 Angular DependenceDocumento1 paginaTable 1 Angular Dependencerrj44Nessuna valutazione finora
- Trig RefDocumento2 pagineTrig Refrrj44Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Sheet CHM256 Exp 3Documento3 pagineLab Sheet CHM256 Exp 3iwana dirayatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Template-Chill Summer BeachDocumento35 pagineTemplate-Chill Summer BeachAwan LangNessuna valutazione finora
- Color: A Coloring Book byDocumento19 pagineColor: A Coloring Book byMarta Pérez Madrid50% (2)
- How A Photon Is Created or AbsorbedDocumento5 pagineHow A Photon Is Created or AbsorbedLucia LopezNessuna valutazione finora
- Pipeline Corrosion Management CapabilityDocumento2 paginePipeline Corrosion Management CapabilityMajdi Abdulrahman Mohamed RahamaNessuna valutazione finora
- IB Biology - Respiration SL Quiz 2.8Documento5 pagineIB Biology - Respiration SL Quiz 2.8Ameen amediNessuna valutazione finora
- Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology: An Earth System PerspectiveDocumento20 paginePaleoceanography and Paleoclimatology: An Earth System PerspectivejohnwcaragNessuna valutazione finora
- 9702 Quantum Physics AllDocumento13 pagine9702 Quantum Physics AllSwifty SpotNessuna valutazione finora
- Ashby Deformation Mechanism MapsDocumento232 pagineAshby Deformation Mechanism MapsDaniel Eduardo Lescano100% (1)
- fourtyYearsOfcgiInChina PDFDocumento7 paginefourtyYearsOfcgiInChina PDFfdcarazoNessuna valutazione finora
- Polyacetal (POM) : Polyplastics Co., LTDDocumento19 paginePolyacetal (POM) : Polyplastics Co., LTDPhuoc Thinh TruongNessuna valutazione finora
- Insulect Specification PDFDocumento10 pagineInsulect Specification PDFThuan NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Construction of Ag - AgCl Reference Electrode and ApplicationDocumento3 pagineConstruction of Ag - AgCl Reference Electrode and ApplicationValentin-AngeloUzunovNessuna valutazione finora
- Prepared By: Julkarnain Ahemad. L&T-QA/QC-DDIP-SambalpurDocumento26 paginePrepared By: Julkarnain Ahemad. L&T-QA/QC-DDIP-SambalpurKarna Satish KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Batch To Continuous ProcessingDocumento7 pagineBatch To Continuous ProcessingChem.EnggNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity Coefficients of Acids, Bases, and SaltsDocumento2 pagineActivity Coefficients of Acids, Bases, and SaltsJessi EkaNessuna valutazione finora
- Reaction Engineering EP 319/EP 327: Chapter 4 (Part Ii) Multiple ReactionsDocumento25 pagineReaction Engineering EP 319/EP 327: Chapter 4 (Part Ii) Multiple ReactionsWoMeiYouNessuna valutazione finora
- Ethacure® 90 - AlbemarleDocumento2 pagineEthacure® 90 - Albemarlesriatul2006Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lavanya (20065-CH-009) VSP PPT-1Documento21 pagineLavanya (20065-CH-009) VSP PPT-1Yogesh BuradaNessuna valutazione finora
- Water Requirement in Chemical Process IndustriesDocumento145 pagineWater Requirement in Chemical Process IndustriesKAUSTAV ROYNessuna valutazione finora
- Positioning Techniques - Horizontal Vertical PDFDocumento34 paginePositioning Techniques - Horizontal Vertical PDFMuhd Zuhairi100% (1)
- Chemistry: Free Web Support in EducationDocumento30 pagineChemistry: Free Web Support in EducationsakshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Using Empower Systemsqt Qualification Tool For Waters Modular HPLC SystemsDocumento8 pagineUsing Empower Systemsqt Qualification Tool For Waters Modular HPLC SystemsПетр КрасновNessuna valutazione finora
- First Monography Operation in The AlchemDocumento4 pagineFirst Monography Operation in The AlchemahmNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid and Thermal Systems, Ch.2, Properties of Fluids, Lec2Documento16 pagineFluid and Thermal Systems, Ch.2, Properties of Fluids, Lec2Mohamed EmamNessuna valutazione finora
- SOM (4th) May2022Documento1 paginaSOM (4th) May2022Simarjeet SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics HeatDocumento6 paginePhysics Heatsiba padhyNessuna valutazione finora
- Find Your Way Around The SkiesDocumento3 pagineFind Your Way Around The SkiesgamangabrielNessuna valutazione finora
- CHEM Form5 Chapter 5Documento10 pagineCHEM Form5 Chapter 5MOK MOKNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is A Fuel CELL?Documento49 pagineWhat Is A Fuel CELL?raveendrareddyeeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingDa EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (5)
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceDa EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (51)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesDa EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (2193)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldDa EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (64)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseDa EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (69)
- Giza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyDa EverandGiza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyNessuna valutazione finora
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Da EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (157)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessDa EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (6)
- The 60 Minute Quantum Physics Book: Science Made Easy For Beginners Without Math And In Plain Simple EnglishDa EverandThe 60 Minute Quantum Physics Book: Science Made Easy For Beginners Without Math And In Plain Simple EnglishValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (4)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterDa EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (410)
- The Beauty of Falling: A Life in Pursuit of GravityDa EverandThe Beauty of Falling: A Life in Pursuit of GravityNessuna valutazione finora
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeDa EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeNessuna valutazione finora
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldDa EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (60)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayDa EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (125)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldDa EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (54)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceDa EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (5)
- The Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityDa EverandThe Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (78)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowDa EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (49)
- Hyperspace: A Scientific Odyssey Through Parallel Universes, Time Warps, and the 10th DimensionDa EverandHyperspace: A Scientific Odyssey Through Parallel Universes, Time Warps, and the 10th DimensionValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- The Illustrated Theory of Everything: The Origin and Fate of the UniverseDa EverandThe Illustrated Theory of Everything: The Origin and Fate of the UniverseValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- AP Physics 1 Premium, 2024: 4 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeDa EverandAP Physics 1 Premium, 2024: 4 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeNessuna valutazione finora
- Vibration and Frequency: How to Get What You Want in LifeDa EverandVibration and Frequency: How to Get What You Want in LifeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (13)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeDa EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)