Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Weather and Climate Unit Flashcards
Caricato da
api-169639475Descrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Weather and Climate Unit Flashcards
Caricato da
api-169639475Copyright:
Formati disponibili
Cut squares along dotted line then fold in half and staple / tape to make flashcard.
Start learning a few and then add some in once you have mastered those few.
What is weather?
The state of the atmosphere at a given time and place.
- Temperature - Moisture - Wind - Air Pressure
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
What is Climate?
The average weather of a particular part of the world at different times of the year. The layer of gases surrounding Earth; composed mainly of nitrogen and oxygen.
What is the atmosphere?
Troposphere
Lowest layer of the atmosphere. Weather occurs in this layer.
Stratosphere
Second layer of the atmosphere - Jets fly through, ozone found here. Middle layer of the atmosphere. Meteors burn up here.
Mesosphere
Thermosphere
Upper layer of the atmosphere. Northern Lights. Space Shuttle.
Exosphere
Layer of the atmosphere that merges with space.
Air pollution can be
Global Regional Local
Ozone Layer
Layers of atmosphere - Gas made of 3 oxygen atoms (O3) - Absorbs 99% of suns harmful UVB rays
---Dont sunbathe. The sun is radiation ---Tanning also increases your risk ----Avoid the sun, especially between 10-4PM ----Seek shade ----Wear a shirt (thicker and darker) ----Wear sunglasses ---Be especially wary fair skinned people
Ways to avoid skin cancer
Air Pressure
The pressure caused by the weight of the atmosphere.
As elevation ___________, air pressure decreases
As elevation increases, air pressure ______________
Barometer
An instrument that measures air pressure.
Warm air ______, cool air sinks.
Warm air rises, cool air _____.
Wind
Travels from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure!
Cold Front
Form where cold air moves towards warm air. Creates rain storms.
Warm Front
Form where warm air moves towards cold air.
Stationary Front
When cold and warm cannot overtake each other (tie)
Global Winds
Polar Easterlies Prevailing Westerlies Horse Latitudes Trade Winds Doldrums Trade Winds Horse Latitude Prevailing Westerlies Polar Easterlies
Coriolis Force
Caused by the rotating of the earth. A rotating body deflects.
Jet Stream
Any of the high-speed, highaltitude air currents that circle
the Earth in a westerly direction.
Wind Chill
The cooling effect of wind and temperature combined. The higher the wind, the cooler it gets.
Albedo
The reflectiveness of a surface. Black absorbs all colors while white reflects all colors.
A measure of the average kinetic energy (motion) of individual molecules in matter. 100 degreew Celsius = Water Boils 0 degrees Celsius = Water Freezes
Temperature
Thermometer
A device that measures the heat from expanding and contracting liquids or coils.
The seasons are caused by the
The tilt of the earths axis 23.5 degrees
The Water Cycle (Hydrologic Cycle)
The continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface of the Earth.
Evaporation
Substance changes from a liquid state to gas state (requires energy).
Condensation
Water vapor (gas) turns back to a liquid. (energy required / cold) -cloud formation.
Precipitation
Water that is so heavy it falls as liquid / solid.
Dew
Moisture condensed from the atmosphere, esp. at night, and deposited in the form of small drops upon any cool surface.
Cloud
A visible body of very fine water droplets or ice particles suspended in the atmosphere at different altitudes.
Cirrus
High altitude wispy clouds made of ice crystals.
Cumulus
White puffy clouds
Stratus
Low lying layered clouds. Usually grey and dull.
Cumulonimbus
Very tall Dense, heavy, dark massive thunderstorms hard showers, explosive top, great vertical development
Meteorology
The study of atmosphere that focuses on weather process and forecasting.
Weather Tools
-Thermometer -Wind Vane Wind direction -Anemometer Wind speed -Barometer Measures air pressure -Rain Gauge: Measures rainfall. -Satellites: Provide larger view of weather. A line drawn on a weather map or chart linking all points of equal or constant temperature.
Isotherm
Climate Change
The gradual warming of the Earth caused by the greenhouse effect and manmade emission of greenhouse gases.
Biome
A large, distinctive complex of plant communities created and maintained by climate.
Tropical Rainforest
This biome is very wet with warm temperatures. This biome has the most plants and animals
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Weather Study GuideDocumento2 pagineWeather Study Guideapi-296852092100% (1)
- Sci Cheat SHeet For MOAT (Text)Documento1 paginaSci Cheat SHeet For MOAT (Text)whatthefailNessuna valutazione finora
- Weather Systems Vocab Updated 12-31-14Documento5 pagineWeather Systems Vocab Updated 12-31-14api-260201978Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mass 369104ngsDocumento5 pagineMass 369104ngsPhftNessuna valutazione finora
- Atmospheric MotionDocumento35 pagineAtmospheric Motionselah100% (1)
- Interactive Textbook 2 2 Air Masses and Fronts13Documento8 pagineInteractive Textbook 2 2 Air Masses and Fronts13api-240094705Nessuna valutazione finora
- Weather Watch Study NotesDocumento5 pagineWeather Watch Study Notesapi-336664994Nessuna valutazione finora
- 18 Air Masses and Fronts Notes - TeacherDocumento4 pagine18 Air Masses and Fronts Notes - Teacherapi-251355123Nessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Global WarmingDocumento11 pagineWhat Is Global Warmingali3800Nessuna valutazione finora
- GW ExplainedDocumento10 pagineGW ExplainedFaisal AwanNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Impact Graphic OrganizerDocumento2 pagineHuman Impact Graphic Organizerapi-398648522Nessuna valutazione finora
- Renewable Energy Basics BGDocumento6 pagineRenewable Energy Basics BGErwin NurrizkiNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes TeacherenergyunitDocumento15 pagineNotes Teacherenergyunitapi-213591933Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 9Documento16 pagineChapter 9anil.gelra5140Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 20 The Earths EcosystemsDocumento24 pagineChapter 20 The Earths EcosystemsBily roriguesNessuna valutazione finora
- Processes and Landforms Along Plate Boundaries PDFDocumento39 pagineProcesses and Landforms Along Plate Boundaries PDFJe Lly Ann100% (1)
- Weather and Climate (KQ1)Documento9 pagineWeather and Climate (KQ1)Ice Cream C0ne100% (1)
- Ecological Succession Worksheet: Pond ADocumento3 pagineEcological Succession Worksheet: Pond AJamileth Bonilla CanalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Biophysical Environments: The AtmosphereDocumento5 pagineBiophysical Environments: The AtmosphereAnanya UppalNessuna valutazione finora
- How Organisms Adapt to Their HabitatsDocumento4 pagineHow Organisms Adapt to Their HabitatsEman Fatima GulnawazNessuna valutazione finora
- 5th Grade Quiz Week 1Documento2 pagine5th Grade Quiz Week 1api-254428474Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biology AdaptationDocumento2 pagineBiology Adaptation• LyaMew •Nessuna valutazione finora
- Earth's Energy BudgetDocumento4 pagineEarth's Energy BudgetSunay MehtaNessuna valutazione finora
- Longman Science Biology 11 To 14 Page 2 SampleDocumento5 pagineLongman Science Biology 11 To 14 Page 2 SampleErdi FushekatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Aquatic Adaptations in Animals: A) Aquatic Adaptations in FishDocumento7 pagineAquatic Adaptations in Animals: A) Aquatic Adaptations in FishSiri YerneniNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 1 VocabDocumento1 paginaWeek 1 Vocabapi-254428474Nessuna valutazione finora
- Earth Sun and Moon SystemsDocumento23 pagineEarth Sun and Moon Systemsapi-257978541100% (1)
- Concepts of Environmental Science Hand-Out # 4: Environmental Systems: Biomes, Marine Environment, and Freshwater EcosystemsDocumento3 pagineConcepts of Environmental Science Hand-Out # 4: Environmental Systems: Biomes, Marine Environment, and Freshwater EcosystemsTRICIA PANGILINANNessuna valutazione finora
- Weather Fronts Foldable NotesDocumento2 pagineWeather Fronts Foldable NotesKeith JosephsNessuna valutazione finora
- Coastal Processes and LandformsDocumento55 pagineCoastal Processes and Landformsthirumangai6100% (1)
- Lecture 9 Desert Features and Landforms PDFDocumento4 pagineLecture 9 Desert Features and Landforms PDFaliNessuna valutazione finora
- EnSci Reviewer #1 - Ecosystem ReviewerDocumento2 pagineEnSci Reviewer #1 - Ecosystem ReviewerJohn PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- FDFDSFSDFDocumento2 pagineFDFDSFSDFapi-254428474100% (1)
- Coastal Erosion: Christa Lee Spurrell and Katie-Marie BrownDocumento17 pagineCoastal Erosion: Christa Lee Spurrell and Katie-Marie BrownChrista Lee Spurrell0% (1)
- Sustainable EcosystemsDocumento5 pagineSustainable EcosystemsbobNessuna valutazione finora
- Volcanoes!: Introduction Unit by Ms. GreenDocumento15 pagineVolcanoes!: Introduction Unit by Ms. GreenErikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Solar System Unit Cover PageDocumento6 pagineSolar System Unit Cover Pageapi-382675034Nessuna valutazione finora
- 5th Grade Earth Systems Week 1Documento9 pagine5th Grade Earth Systems Week 1api-254428474Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biomes ActivityDocumento3 pagineBiomes ActivitybabyduckiezNessuna valutazione finora
- Bcsci 10 - Unit 1 - Topic1 - 3Documento26 pagineBcsci 10 - Unit 1 - Topic1 - 3DemisNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5Documento25 pagineChapter 5homamunfatNessuna valutazione finora
- DecomposingDocumento2 pagineDecomposingapi-254428474100% (1)
- Latitude Affects ClimateDocumento8 pagineLatitude Affects ClimateAngelyn Dechino SigayleNessuna valutazione finora
- Earth's Atmosphere LayersDocumento5 pagineEarth's Atmosphere LayersShawn SriramNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 Guided NotesDocumento5 pagineUnit 1 Guided Notesapi-280725048Nessuna valutazione finora
- Landforms PowerpointDocumento21 pagineLandforms PowerpointJhaypee SorianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio1 EcosystemsUDocumento30 pagineBio1 EcosystemsUlen16328Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biomes Kinds of EcosystemDocumento4 pagineBiomes Kinds of EcosystemDesiree G. SacasanNessuna valutazione finora
- Untitleddocument 6Documento1 paginaUntitleddocument 6api-254428474Nessuna valutazione finora
- Movement of Ocean WatersDocumento31 pagineMovement of Ocean WatersAnime_King100% (3)
- Earth Moon Sun RelationshipDocumento12 pagineEarth Moon Sun RelationshipMichelle Raquil100% (1)
- Biome Speed DatingDocumento4 pagineBiome Speed DatingPuck718187Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lady Ann E. Murillo III- BEEd Principles of Ecology Vocabulary ListDocumento3 pagineLady Ann E. Murillo III- BEEd Principles of Ecology Vocabulary ListLady Ann Enanoria MurilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Impact Study Guide TableDocumento2 pagineHuman Impact Study Guide Tableapi-187507090Nessuna valutazione finora
- How Environmental Pollution Affects Balance in NatureDocumento10 pagineHow Environmental Pollution Affects Balance in Nature秀珍100% (1)
- What are longitudes and latitudesDocumento2 pagineWhat are longitudes and latitudesClaudene GellaNessuna valutazione finora
- Comets and AsteroidsDocumento42 pagineComets and AsteroidsEd TapuroNessuna valutazione finora
- Guided Notes - Cycles in Ecosystems 1Documento6 pagineGuided Notes - Cycles in Ecosystems 1Yassine Koot33% (3)
- McConnell 3e PPT Ch14Documento66 pagineMcConnell 3e PPT Ch14Ken AguilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Meteorology NotesDocumento5 pagineMeteorology Notesapi-330037580Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Intro MoonDocumento25 pagine1 Intro Moonapi-169639475Nessuna valutazione finora
- Billnye Planets Moons Worksheet and QuizDocumento2 pagineBillnye Planets Moons Worksheet and Quizapi-169639475Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tides-2015 LectureDocumento17 pagineTides-2015 Lectureapi-169639475Nessuna valutazione finora
- Phases Eclipses and TidesDocumento31 paginePhases Eclipses and Tidesapi-169639475Nessuna valutazione finora
- Totally Tourist Tour of Solar SystemDocumento3 pagineTotally Tourist Tour of Solar Systemapi-169639475Nessuna valutazione finora
- Creating A Travel Brochure GuidelinesDocumento6 pagineCreating A Travel Brochure Guidelinesapi-169639475100% (1)
- Nasa Moon Survival ExerciseDocumento4 pagineNasa Moon Survival Exerciseapi-169639475Nessuna valutazione finora
- Phases of Matter WebquestDocumento6 paginePhases of Matter Webquestapi-169639475Nessuna valutazione finora
- World of Plants WebquestDocumento4 pagineWorld of Plants Webquestapi-169639475100% (1)
- Totally Tourist Tour of Solar System 2Documento3 pagineTotally Tourist Tour of Solar System 2api-169639475Nessuna valutazione finora
- Facts About The Solar SystemDocumento2 pagineFacts About The Solar Systemapi-169639475Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Solar SystemDocumento11 pagineThe Solar Systemapi-169639475Nessuna valutazione finora
- 95 Worlds and Counting Video HandoutDocumento2 pagine95 Worlds and Counting Video Handoutapi-1696394750% (1)
- Planets of Our Solar SystemDocumento5 paginePlanets of Our Solar Systemapi-169639475Nessuna valutazione finora
- Planets of Our Solar SystemDocumento5 paginePlanets of Our Solar Systemapi-169639475Nessuna valutazione finora
- Facts About The Solar SystemDocumento2 pagineFacts About The Solar Systemapi-169639475Nessuna valutazione finora
- Literacy Article Soil Composting WKSTDocumento2 pagineLiteracy Article Soil Composting WKSTapi-169639475Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nebular Gas Theory Literacy ArticleDocumento2 pagineNebular Gas Theory Literacy Articleapi-169639475Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture SoilsDocumento24 pagineLecture Soilsapi-169639475Nessuna valutazione finora
- Soil Notes-StudentDocumento3 pagineSoil Notes-Studentapi-169639475Nessuna valutazione finora
- Plant-Review-Foldable Instructions and NotesDocumento17 paginePlant-Review-Foldable Instructions and Notesapi-169639475Nessuna valutazione finora
- Creating A Travel Brochure GuidelinesDocumento6 pagineCreating A Travel Brochure Guidelinesapi-169639475100% (1)
- Composting Fact SheetDocumento2 pagineComposting Fact Sheetapi-169639475Nessuna valutazione finora
- Types of RocksDocumento18 pagineTypes of Rocksapi-169639475Nessuna valutazione finora
- Angiosperms Textbook ChapterDocumento7 pagineAngiosperms Textbook Chapterapi-169639475Nessuna valutazione finora
- Questions For Angiosperms BookletDocumento1 paginaQuestions For Angiosperms Bookletapi-169639475Nessuna valutazione finora
- 033 Plant Reproduction Text Book ChapterDocumento32 pagine033 Plant Reproduction Text Book Chapterapi-169639475Nessuna valutazione finora
- 030 Plants Text Book ChapterDocumento34 pagine030 Plants Text Book Chapterapi-169639475100% (2)
- 031 Parts of Plants Text Book ChapterDocumento14 pagine031 Parts of Plants Text Book Chapterapi-169639475Nessuna valutazione finora
- Survival Tactics of Plants 6 L 2 2Documento12 pagineSurvival Tactics of Plants 6 L 2 2api-169639475Nessuna valutazione finora
- KIRAN PPT-unit 3Documento54 pagineKIRAN PPT-unit 3RED EYENessuna valutazione finora
- Centrifugal Pump Selection ProcessDocumento5 pagineCentrifugal Pump Selection ProcessAnanthNessuna valutazione finora
- Water and Its Forms: Name: - DateDocumento2 pagineWater and Its Forms: Name: - DateNutrionist Preet PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Chute Design and Problems-Causes and SolutionDocumento19 pagineChute Design and Problems-Causes and SolutionThakaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Analyzing Projectile Motion with Capstone SoftwareDocumento5 pagineAnalyzing Projectile Motion with Capstone SoftwarepatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Electroplating of PlasticsDocumento4 pagineElectroplating of PlasticsislammughalNessuna valutazione finora
- Impact Test RequirementDocumento6 pagineImpact Test RequirementmansurNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 17 Cat A (Jan 18)Documento2 pagineModule 17 Cat A (Jan 18)Shaheed ChirayinkeezhuNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 - Engesser's Theorem and Truss Deflections by Virtual Work PrinciplesDocumento14 pagine6 - Engesser's Theorem and Truss Deflections by Virtual Work PrinciplesFrans Alen SarmientoNessuna valutazione finora
- June 2018 MS - Paper 1 OCR (A) Chemistry AS-LevelDocumento18 pagineJune 2018 MS - Paper 1 OCR (A) Chemistry AS-LevelRunNessuna valutazione finora
- B. Real GasesDocumento57 pagineB. Real GasesRayanna WardNessuna valutazione finora
- UFC 3-570-06 - Cathodic Protection - (Draft)Documento63 pagineUFC 3-570-06 - Cathodic Protection - (Draft)Johnny WalkerNessuna valutazione finora
- Jee MainsDocumento32 pagineJee Mainsjhaayushbhardwaj9632Nessuna valutazione finora
- States of Matter (Gaseous & Liquid) : Gaseous State: Measurable Properties of Gases Gas Laws - Boyle's LawDocumento6 pagineStates of Matter (Gaseous & Liquid) : Gaseous State: Measurable Properties of Gases Gas Laws - Boyle's LawIhtisham Ul HaqNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermodynamics Lab Report - Application of The Perfect Gas Laws in The Determination of Adiabatic Index of AirDocumento9 pagineThermodynamics Lab Report - Application of The Perfect Gas Laws in The Determination of Adiabatic Index of Airqiaunus69% (13)
- Handbook of Hydrophone Element Design TechnologyDocumento2 pagineHandbook of Hydrophone Element Design TechnologyBrendon SoongNessuna valutazione finora
- 2DOF System Free Vibration AnalysisDocumento42 pagine2DOF System Free Vibration Analysismohanrajjercy71Nessuna valutazione finora
- Units and Unit Conversions Mcgraw HillDocumento5 pagineUnits and Unit Conversions Mcgraw HillParvezNessuna valutazione finora
- Cu-ETP: C11000 Industrial RolledDocumento4 pagineCu-ETP: C11000 Industrial Rolledsrsivaraman81Nessuna valutazione finora
- retention volumes chromatographyDocumento2 pagineretention volumes chromatographyMohd Sukri DaudNessuna valutazione finora
- IctionDocumento7 pagineIctionFullo Flores MarviloneNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Sheet: In-Line Proportional Chemical FeedersDocumento2 pagineData Sheet: In-Line Proportional Chemical FeedersChancedaniels EmunaNessuna valutazione finora
- Characterization TechniquesDocumento8 pagineCharacterization TechniquesAyush SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Lang MuirDocumento7 pagineLang MuirLao ZhuNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical ProperitiesDocumento66 pagineElectrical ProperitiesGabito EssienNessuna valutazione finora
- Product Data Sheet DRE80 EPDM Rubber SheetDocumento1 paginaProduct Data Sheet DRE80 EPDM Rubber Sheetvivashwanth paiNessuna valutazione finora
- NanoCoat Leaflet PDFDocumento1 paginaNanoCoat Leaflet PDFProsun RoyNessuna valutazione finora
- 1011 Chapter 3Documento38 pagine1011 Chapter 3Eman Sarmiento0% (1)
- Chapter 1 (Part 2) Process VariablesDocumento41 pagineChapter 1 (Part 2) Process VariablesMuhammad FawwazNessuna valutazione finora
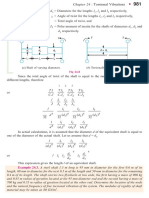
- Chapter 24: Torsional Vibrations: (A) Shaft of Varying Diameters. (B) Torsionally Equivalent ShaftDocumento8 pagineChapter 24: Torsional Vibrations: (A) Shaft of Varying Diameters. (B) Torsionally Equivalent ShaftNazmus Sakib100% (1)