Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Cellular Respiration Notes - Anaerobic Cellular Respiration2
Caricato da
api-199560874Descrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Cellular Respiration Notes - Anaerobic Cellular Respiration2
Caricato da
api-199560874Copyright:
Formati disponibili
Cellular Respiration Notes- Anaerobic Cellular Respiration (7.
4)
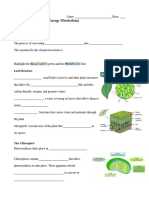
Anaerobic = _____________ During Glycolysis, energy is obtained without oxygen. This type of energy production is called _________________ Fermentation occurs ___________ oxygen. Bacteria species engage in a host of specific fermentation processes. Eukaryotic organisms engage in 2 types of fermentation. (Eukaryotes: have a nucleus) Both methods of eukaryotic fermentation have 2 steps. Step 1: Glycolysis. Step 2: fermentation (accomplished by recycling the products of glycolysis). Alcohol Fermentation Common in ___________. Acetaldehyde is produced when carbon dioxide was removed from pyruvate by the enzyme pyruvate decarboxylase. NADH (product of glycolysis) passes Hydrogen Atoms to acetaldehyde. This generates carbon dioxide, ____________, and NAD+. The alcohol ethanol is produced as a result (alcohol found in alcoholic drinks.) The process recycles NAD+, therefore, _________ can continue. _____ ATP produced in glycolysis satisfy energy needs. Ethanol and Carbon dioxide are released as wastes. Alcohol Fermentation is commonly used to produce breads, pastries, beer, liquor and soy sauce. Bread Yeast is added which will undergo fermentation. The bread will rise due to the release of __________. Alcohol is also produced Wine Yeast ferments sugar of fruit juice (Grape juice). Mixture bubbles due to carbon dioxide. At 12% alcohol concentration yeast cells die.
Lactic Acid Fermentation During ________________, the muscles energy demands are greater than aerobic respiration can supply. Additional ATP is supplied by lactic acid fermentation NADH made in glycolysis transfers H atoms to pyruvate to make __________ and NAD+ Formation of NAD+ allows glycolysis to continue. Accumulation of lactic acid leads to muscle stiffness/ soreness, and fatigue.
Lactic acid is transported to the liver and converted to pyruvate when vigorous exercise ceases. Pyruvates then go through ______________. Extra oxygen in necessary to process lactic acid. (oxygen debt) ___________ accompanying hard exercise is the bodies way to pay off the oxygen debt.
Exercise Physiology The branch of biology that studies the bodies biological responses to exercise. Most common problem encountered by athletes? ___________
___________- Maximum volume of oxygen that the cells can remove from the bloodstream in 1 min/kg of body mass at maximum exertion. (Measured in mL/kg/min) High VO2 max = better ______________. 2 components- Exercise and Genetics (age to some extent). Lactic Acid Threshold Value of exercise intensity at which lactic acid production __________. Leads to sore muscles, increased pain, and fatigue. Exercising below lactic acid threshold = longer duration of exercise Untrained person has a lactic acid threshold at about _____% of VO2 max Trained person has a lactic acid threshold at about ______% of VO2 max.
Environmental Factors (Supplements and Toxins) ___________: counteract the acidic nature of lactic acid and will allow an athlete to have enhanced performance for a short period of time. ___________: contains a phosphate that is donated to ADP to allow for the creation of more ATP. Net effect: more energy available for the muscles to use. ________________ binds at the oxygen receptor sites of the bodies hemoglobin, so oxygen is not available to drive the ETC. Cell Death follows. Cyanide and hydrogen sulfide act directly on a specific reaction within the respiration pathway. Summary
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Physiology of Cell Energy Production: CPTIPS.COM MonographsDa EverandThe Physiology of Cell Energy Production: CPTIPS.COM MonographsNessuna valutazione finora
- Corrina Pledger - Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Guided NotesDocumento4 pagineCorrina Pledger - Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Guided NotesCorrina PledgerNessuna valutazione finora
- Atp Cloze NotesDocumento4 pagineAtp Cloze Notesapi-260690009Nessuna valutazione finora
- Section 2-The Process of Cellular RespirationDocumento31 pagineSection 2-The Process of Cellular RespirationPDX FrostNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Lesson 9.1 WorksheetDocumento3 pagineBiology Lesson 9.1 WorksheetAbhay MonNessuna valutazione finora
- Cellular Respiration Guided NotesDocumento4 pagineCellular Respiration Guided NotesRangerbackNessuna valutazione finora
- Cellular RespirationDocumento36 pagineCellular RespirationWillow ItchiroNessuna valutazione finora
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Aerobic Respiration and FermentationDocumento3 pagineAdvantages and Disadvantages of Aerobic Respiration and FermentationChrislyn Eds Javier AcobNessuna valutazione finora
- Study Guide For QuestDocumento4 pagineStudy Guide For Questapi-352384491Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cellular Respiration 1Documento28 pagineCellular Respiration 1Maria Flor PabeloniaNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Fermentation?: Table of ContentDocumento6 pagineWhat Is Fermentation?: Table of ContentDanish AmozNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 3 - Cell Energy Guided NotesDocumento3 pagineUnit 3 - Cell Energy Guided NotesKaylee Lopez Student - KnightdaleHSNessuna valutazione finora
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Fermentation and Aerobic RespirationDocumento10 pagineAdvantages and Disadvantages of Fermentation and Aerobic RespirationIan Gabriel MayoNessuna valutazione finora
- Name: - Chapter 7 RespirationDocumento3 pagineName: - Chapter 7 RespirationGhanapathi RamanathanNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation 5Documento15 paginePresentation 5Rahanie Gadungan PajijiNessuna valutazione finora
- Cellular RespirationDocumento49 pagineCellular RespirationJohn Paul RoaNessuna valutazione finora
- GB1 Q2 Week-3bDocumento10 pagineGB1 Q2 Week-3bAnnejhel Mae PoralanNessuna valutazione finora
- 06 Lecture Presentation PDFDocumento23 pagine06 Lecture Presentation PDFJavier CorralNessuna valutazione finora
- Anaerobic RespirationDocumento10 pagineAnaerobic Respirationnadya munawwarohNessuna valutazione finora
- Aerobic Respiration Power PointDocumento35 pagineAerobic Respiration Power PointJeremy WongNessuna valutazione finora
- 15 Ferementation Study Guide PDFDocumento4 pagine15 Ferementation Study Guide PDFGhostNessuna valutazione finora
- Fermentationprocess 150129034150 Conversion Gate02Documento14 pagineFermentationprocess 150129034150 Conversion Gate02skNessuna valutazione finora
- LacticDocumento10 pagineLacticapi-282066626Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8 Learn Smart: Chapter 8 Microbial MetabolismDocumento2 pagineChapter 8 Learn Smart: Chapter 8 Microbial MetabolismSajjad Hossain ShuvoNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbohydrate Metabolism PathwaysDocumento28 pagineCarbohydrate Metabolism PathwaysIvy JoyceNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.2.5 Respiration WorksheetDocumento7 pagine2.2.5 Respiration WorksheeterikabeltranNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 6 WorksheetDocumento6 pagineUnit 6 WorksheetMarta YantiNessuna valutazione finora
- Anaerobic RespirationDocumento6 pagineAnaerobic Respirationzain ahmedNessuna valutazione finora
- How cells harvest energy from foodDocumento18 pagineHow cells harvest energy from foodrhaineNessuna valutazione finora
- Glycolysis and Fermentation: Harvesting Chemical Energy from GlucoseDocumento4 pagineGlycolysis and Fermentation: Harvesting Chemical Energy from GlucoseJulia ZouNessuna valutazione finora
- What is Fermentation? - Anaerobic Process Converts Glucose to EnergyDocumento4 pagineWhat is Fermentation? - Anaerobic Process Converts Glucose to EnergyRider 006Nessuna valutazione finora
- Autotrophs and Heterotrophs: Photosynthesis & Cellular RespirationDocumento7 pagineAutotrophs and Heterotrophs: Photosynthesis & Cellular Respirationapi-319819727Nessuna valutazione finora
- Science Daily Lesson l44Documento48 pagineScience Daily Lesson l44Audie Nocedo MontecastroNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio Lesson 21 RespiDocumento48 pagineBio Lesson 21 RespiChlzy ArdienteNessuna valutazione finora
- H O P E: Ealth Ptimizing Hysical Ducation 3Documento4 pagineH O P E: Ealth Ptimizing Hysical Ducation 3Florence50% (2)
- Edited Activity 1 8 4Documento4 pagineEdited Activity 1 8 4Karl Mathew PajarillagaNessuna valutazione finora
- 4-4 Anaerobic RespirationDocumento7 pagine4-4 Anaerobic Respirationapi-265907602Nessuna valutazione finora
- Place Homework Into The Basket. 2. Pick Up Powerpoint GuideDocumento52 paginePlace Homework Into The Basket. 2. Pick Up Powerpoint GuideADR GARDIOLANessuna valutazione finora
- Aerobic Anaerobic RespirationDocumento29 pagineAerobic Anaerobic RespirationAnonymous e0TdsoxUNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.8 Cell Respiration SL: Chapter 2 Molecular Biology p.98-103Documento46 pagine2.8 Cell Respiration SL: Chapter 2 Molecular Biology p.98-103PaolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic Compounds Lecture on AlcoholsDocumento11 pagineOrganic Compounds Lecture on AlcoholsBenoniNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Energy: Accessing Energy Stored byDocumento15 pagineCell Energy: Accessing Energy Stored bylemoniadelisNessuna valutazione finora
- Cellular Respiration Notes--student copy (1)Documento3 pagineCellular Respiration Notes--student copy (1)joisbastaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 4 Human Physiology Enzymes StudentDocumento6 pagineLecture 4 Human Physiology Enzymes StudentAlfonso RobertNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Notes: Chapter 16: Cellular RespirationDocumento24 pagineBiology Notes: Chapter 16: Cellular RespirationhakimNessuna valutazione finora
- Fermentation:: BY Aqsa ErajDocumento9 pagineFermentation:: BY Aqsa ErajHira NoorNessuna valutazione finora
- Respiration PowerpointDocumento14 pagineRespiration Powerpointmmpanjwani4Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Respiration: ATP from GlucoseDocumento11 pagineCell Respiration: ATP from GlucoseNiña Jennifer Potter Vergara100% (2)
- Final BiochemistryDocumento6 pagineFinal BiochemistryHuyen Tram NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Fermentation Processes and Their Application PDFDocumento8 pagineFermentation Processes and Their Application PDFninasabelita100% (9)
- biologydictionary.net-Cellular Respiration DefinitionDocumento6 paginebiologydictionary.net-Cellular Respiration Definitionsumeshp664Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7 Cellular RespirationDocumento47 pagineChapter 7 Cellular Respirationwickedbiology101Nessuna valutazione finora
- Group4 BIology Presentation 1Documento13 pagineGroup4 BIology Presentation 1Junjun GwapoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cellular Respiration DefinitionDocumento9 pagineCellular Respiration Definitionmaria genioNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Respiration Cornell Notes TeacherDocumento5 pagineCell Respiration Cornell Notes TeacherErik Artur100% (1)
- Unit 2B Guided Notes 2022Documento6 pagineUnit 2B Guided Notes 2022Victoria WarrenNessuna valutazione finora
- Forum 1 - OCT 2023Documento3 pagineForum 1 - OCT 2023arvinp89Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cellular Respiration Webquest - 2009Documento8 pagineCellular Respiration Webquest - 2009Juz IveneNessuna valutazione finora
- Cellular Respiration Guide - Aerobic vs AnaerobicDocumento5 pagineCellular Respiration Guide - Aerobic vs AnaerobicYuri Andre CustodioNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7KSSM FORM 4 BIODocumento6 pagineChapter 7KSSM FORM 4 BIOYEO MING HUI MoeNessuna valutazione finora
- GofishDocumento1 paginaGofishapi-199560874Nessuna valutazione finora
- Roll and Read Unit 13Documento1 paginaRoll and Read Unit 13api-199560874Nessuna valutazione finora
- TPGPDocumento3 pagineTPGPapi-199560874Nessuna valutazione finora
- RhymesDocumento3 pagineRhymesapi-199560874Nessuna valutazione finora
- Snakes and Ladders General TemplateDocumento1 paginaSnakes and Ladders General Templateapi-199560874Nessuna valutazione finora
- Slide For Ike AkeDocumento4 pagineSlide For Ike Akeapi-199560874Nessuna valutazione finora
- Wheel AmeDocumento2 pagineWheel Ameapi-199560874Nessuna valutazione finora
- Long Range OnlineDocumento16 pagineLong Range Onlineapi-199560874Nessuna valutazione finora
- AbcorderDocumento3 pagineAbcorderapi-199560874Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sounds of y Vowel SortDocumento6 pagineSounds of y Vowel Sortapi-199560874Nessuna valutazione finora
- ConcentrationDocumento1 paginaConcentrationapi-199560874Nessuna valutazione finora
- 4km and 4kj Blog Permission Note 2013 td8cz1Documento1 pagina4km and 4kj Blog Permission Note 2013 td8cz1api-199560874Nessuna valutazione finora
- Flipbooksfreebie 1Documento48 pagineFlipbooksfreebie 1api-199560874100% (1)
- Abcdefg Hijklmn Opq R ST U V W Xy Z: Aa BB CC DD Ee FF GGDocumento1 paginaAbcdefg Hijklmn Opq R ST U V W Xy Z: Aa BB CC DD Ee FF GGapi-199560874Nessuna valutazione finora
- Allison Groenenboom: EmailDocumento2 pagineAllison Groenenboom: Emailapi-199560874Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ed 4767 Final ProjectDocumento11 pagineEd 4767 Final Projectapi-199560874Nessuna valutazione finora
- PofsDocumento49 paginePofsapi-199560874Nessuna valutazione finora
- 4km and 4kj Blog Information Note 2013 Zp3yujDocumento2 pagine4km and 4kj Blog Information Note 2013 Zp3yujapi-199560874Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bio Unit PlanDocumento12 pagineBio Unit Planapi-199560874Nessuna valutazione finora
- Twitter Cheat Sheet For CdntchrsDocumento1 paginaTwitter Cheat Sheet For Cdntchrsapi-199560874Nessuna valutazione finora
- Space Module-Allison GroenenboomDocumento24 pagineSpace Module-Allison Groenenboomapi-199560874Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit Plan-Allison GroenenboomDocumento11 pagineUnit Plan-Allison Groenenboomapi-199560874Nessuna valutazione finora
- Psiigrowthplantemplate-Allison Groenenboom2Documento2 paginePsiigrowthplantemplate-Allison Groenenboom2api-199560874Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fermentation ProtocolDocumento4 pagineFermentation Protocolcharles mepaniaNessuna valutazione finora
- Final PDFDocumento96 pagineFinal PDFAbhinav GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Producing bioethanol from coconut shellsDocumento16 pagineProducing bioethanol from coconut shellsmomo connorNessuna valutazione finora
- Ethanol Production Process From Molasses PDFDocumento2 pagineEthanol Production Process From Molasses PDFPamela0% (1)
- Original Article Elaboration of A Fruit Wine From Cocoa (Theobroma Cacao L.) PulpDocumento11 pagineOriginal Article Elaboration of A Fruit Wine From Cocoa (Theobroma Cacao L.) PulpWilliam Rolando Miranda ZamoraNessuna valutazione finora
- BINAKAYAN NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL Fermentation LessonDocumento5 pagineBINAKAYAN NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL Fermentation LessonNheng M. BlancoNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio Ethanol I ToDocumento301 pagineBio Ethanol I Togeopradhana100% (1)
- Fruit Wine Production: A Review: July 2014Documento9 pagineFruit Wine Production: A Review: July 2014SEPTIA SRI EKA PUTRINessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Lab ReportDocumento7 pagineSample Lab ReportPutri Syalieyana0% (1)
- 3040010Documento44 pagine3040010Mark Anthony CaroNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment - Rate of Fermentation of Fruit JuicesDocumento5 pagineExperiment - Rate of Fermentation of Fruit JuicesBenedick Jayson MartiNessuna valutazione finora
- FermentationDocumento14 pagineFermentationSandeep SamuelNessuna valutazione finora
- N-10012-4-OPM-1301-0 Operation and Maintenace Manual Fermentation Section PDFDocumento105 pagineN-10012-4-OPM-1301-0 Operation and Maintenace Manual Fermentation Section PDFmario feuilladeNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 Cellular EnergeticsDocumento67 pagine5 Cellular EnergeticsFransche BeukesNessuna valutazione finora
- The Microbiology of Cocoa Fermentation and Its Role inDocumento18 pagineThe Microbiology of Cocoa Fermentation and Its Role inJose Miguel Castillo0% (1)
- Cellular Respiration in Yeast LabDocumento2 pagineCellular Respiration in Yeast LabLeslie Samuel0% (1)
- Fermentation of Carrot Juice, Wheat Flour, Gram Flour EtcDocumento17 pagineFermentation of Carrot Juice, Wheat Flour, Gram Flour EtcGowNik SahPav88% (134)
- Ethanol Production Prospects and Cost Analysis from SugarcaneDocumento36 pagineEthanol Production Prospects and Cost Analysis from SugarcaneAjay guptaNessuna valutazione finora
- KATZEN - Bioetanol ProcessDocumento91 pagineKATZEN - Bioetanol Processjpaz2000Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sandhana KalpanaDocumento30 pagineSandhana KalpanaVasaviNessuna valutazione finora
- Visit Report to Sugar Fermentation IndustryDocumento11 pagineVisit Report to Sugar Fermentation IndustrysysiddhiyadavNessuna valutazione finora
- The Kinetics of Alcoholic Fermentation B PDFDocumento5 pagineThe Kinetics of Alcoholic Fermentation B PDFTysir SarhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Yeast Fermentation LabDocumento6 pagineYeast Fermentation LabDana Porter100% (1)
- Aswin Chemistry New ProjectDocumento32 pagineAswin Chemistry New ProjectVartikaNessuna valutazione finora
- It Cannot Be Used Without Prior Permission: Prof. Vaibhav V. GoudDocumento176 pagineIt Cannot Be Used Without Prior Permission: Prof. Vaibhav V. GoudshubhamNessuna valutazione finora
- Boonsiri, Journal Manager, 19990402p3 PDFDocumento9 pagineBoonsiri, Journal Manager, 19990402p3 PDFNesya Dinasarah (Napitupulu)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nuruk Microbiology BreakdownDocumento7 pagineNuruk Microbiology Breakdownfwewrew asddsfNessuna valutazione finora
- Acknowledgement: A Report On Visiting Carew & Co. (BD), Bsri and Ibn Sina Phamaceuticals LTDDocumento13 pagineAcknowledgement: A Report On Visiting Carew & Co. (BD), Bsri and Ibn Sina Phamaceuticals LTDlkokodkodNessuna valutazione finora
- Biofuels of IndiaDocumento18 pagineBiofuels of IndiaNishant GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Worksheet On Act#3 Alcoholic FermentationDocumento4 pagineWorksheet On Act#3 Alcoholic FermentationKrizia CabayacruzNessuna valutazione finora