Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Fluid Mechanics Take Home 2
Caricato da
Michael VillameDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Fluid Mechanics Take Home 2
Caricato da
Michael VillameCopyright:
Formati disponibili
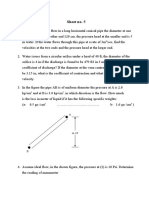
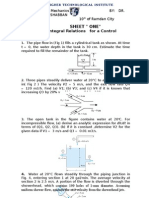
FLUID MECHANICS PROBLEM SETS 1.
MARCH 23, 2012
Water flows steadily up the vertical 1-in.-diameter pipe and out the nozzle, which is 0.5 in. in diameter, discharging to atmospheric pressure. The stream velocity at the nozzle exit must be 30 ft/s. Calculate the minimum gage pressure required at section (1). If the device were inverted, what would be the required minimum pressure at section (1) to maintain the nozzle exit velocity at 30 ft/s?
2.
Water flows from a very large tank through a 5-cm-diameter tube. The dark liquid in the manometer is mercury. Estimate the velocity in the pipe and the rate of discharge from the tank. (assume the flow is frctionless)
3.
A jet of air from a nozzle is blown at right angles against a wall in which two pressure taps are located. A manometer connected to the tap directly in from of the jet shows a head of 25 mm of mercury above atmospheric. Determine the approximate speed of the air leaving the nozzle if it is at -10deg C and 200 Kpa. At the second tap a manometer indicates a head of 5 mm of mercury above atmospheric; what is the approximate speed of the air there? The pump shown creates a 20deg C water jet oriented to travel a maximum horizontal distance. System friction head losses are 6.5 m. The jet may be approximated by the trajectory of frictionless particles. What power must be delivered by the pump?
4.
5.
A free liquid jet shown, has constant ambient pressure and small losses; hence from Bernoullis equation is constant along the jet. For the fire nozzle in the figure, what are a.) the minimum and b.) the maximum values of for which the water jet will clear the corner of the building? For which case will the jet velocity be higher when it strikes the roof the building?
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Problems ؤا 5Documento4 pagineProblems ؤا 5Abdalla MemeNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial Bernoulli Equation Part 2Documento2 pagineTutorial Bernoulli Equation Part 2Muhamad Hazim ZaabaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid Mechanics - ProblemsDocumento4 pagineFluid Mechanics - ProblemsClement Chima50% (2)
- Soal Tugas BernoulliDocumento7 pagineSoal Tugas BernoulliAnnisaNurulFadilahNessuna valutazione finora
- PS 3Documento9 paginePS 3naverfallNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid Mechanics AssignmentsDocumento3 pagineFluid Mechanics AssignmentsSahil DevNessuna valutazione finora
- Che 222 Tutorial 2Documento15 pagineChe 222 Tutorial 2naverfallNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid LabDocumento2 pagineFluid LabShahidulHoqueSohelNessuna valutazione finora
- Flow of Fluids QuizDocumento2 pagineFlow of Fluids QuizJhon Oliver De JoseNessuna valutazione finora
- Fayoum University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Department Fluid Mechanics (1), SheetDocumento2 pagineFayoum University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Department Fluid Mechanics (1), SheetMo 16Nessuna valutazione finora
- Compri QuestionsDocumento2 pagineCompri QuestionsCheryl ChaudhariNessuna valutazione finora
- Sheet (7) Viscous Flow in PipesDocumento4 pagineSheet (7) Viscous Flow in PipesABDELRHMAN ALINessuna valutazione finora
- Week 10 of Aqs110 Fluid Mechanics PDFDocumento16 pagineWeek 10 of Aqs110 Fluid Mechanics PDFGeva GarradoNessuna valutazione finora
- GeologyDocumento41 pagineGeologyNamara TemesgenNessuna valutazione finora
- Sheet 5Documento3 pagineSheet 5Hussien El-masryNessuna valutazione finora
- Assign - 5 (Fluid Flow)Documento4 pagineAssign - 5 (Fluid Flow)Mahmoud AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 4Documento10 pagineAssignment 4mahmoud EissaNessuna valutazione finora
- Venturi MetersDocumento16 pagineVenturi Metersengineer63Nessuna valutazione finora
- Homework No. 2Documento3 pagineHomework No. 2Albasir Tiang Sedik REENessuna valutazione finora
- Problem Set 1Documento1 paginaProblem Set 1Rj PangaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid B SheetDocumento7 pagineFluid B SheetmustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- Integral Analysis of Flow (Applications On Energy Equation)Documento6 pagineIntegral Analysis of Flow (Applications On Energy Equation)ABDELRHMAN ALINessuna valutazione finora
- Section 5Documento5 pagineSection 5Aduchelab AdamsonuniversityNessuna valutazione finora
- Solution To HW5Documento23 pagineSolution To HW5minervini markNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercises - Ii 13-12-2022Documento5 pagineExercises - Ii 13-12-2022Gãlväñ FôxNessuna valutazione finora
- HW 3Documento4 pagineHW 3Alwyn KalapuracanNessuna valutazione finora
- Sheet No - 5 - Fluid Dynamics.Documento3 pagineSheet No - 5 - Fluid Dynamics.AHMED BAKRNessuna valutazione finora
- Extra Momentum Transfer QuestionsDocumento5 pagineExtra Momentum Transfer QuestionsaNessuna valutazione finora
- ENG243 F Final Examination: Luid MechanicsDocumento10 pagineENG243 F Final Examination: Luid MechanicsNobel FahadNessuna valutazione finora
- HydraulicsDocumento5 pagineHydraulicsMark Daryl Lopez Billedo100% (1)
- PipeFlow PracticeProblemsDocumento23 paginePipeFlow PracticeProblemsFawaz PartoNessuna valutazione finora
- VR 17 FM and HM HA Questions - Part 1Documento5 pagineVR 17 FM and HM HA Questions - Part 1bhanu tejaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid Dynamics - Class ExamplesDocumento3 pagineFluid Dynamics - Class Examplesrobynmae17Nessuna valutazione finora
- BernoulliDocumento2 pagineBernoullilllllNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercicios 2Documento10 pagineExercicios 2Julio NunesNessuna valutazione finora
- Taller 3Documento3 pagineTaller 3Juan Pablo TangarifeNessuna valutazione finora
- Sheet (2) Fluid Spring 2017Documento5 pagineSheet (2) Fluid Spring 2017Mohammed SobhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid B SheetDocumento7 pagineFluid B SheetAmr Mustafa MohammedNessuna valutazione finora
- Sheet3 3Documento3 pagineSheet3 3Jasmine KhaledNessuna valutazione finora
- SIE 2002 Tutorial 3Documento4 pagineSIE 2002 Tutorial 3lightsoul91Nessuna valutazione finora
- Homework SolutionDocumento25 pagineHomework SolutionHirman De NovaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 1 Viscous Flow in PipesDocumento5 pagineTutorial 1 Viscous Flow in PipesAcap AliasNessuna valutazione finora
- TCW3101200904 HydraulicsDocumento3 pagineTCW3101200904 HydraulicsTinashe Mazokera100% (1)
- FMH201 AS2019 SetADocumento6 pagineFMH201 AS2019 SetAJampel kun TsheringNessuna valutazione finora
- Royal University of BhutanDocumento6 pagineRoyal University of BhutanJampel kun TsheringNessuna valutazione finora
- B Tech Mechanical QuestionsDocumento11 pagineB Tech Mechanical QuestionsAnkita VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Exercises Part3Documento3 pagineChapter 2 Exercises Part3Carolina Herrera0% (1)
- One Dimensional FlowsDocumento2 pagineOne Dimensional FlowsUSHANAND vermaNessuna valutazione finora
- EXERCISEDocumento6 pagineEXERCISEJerico Enriquez CacaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignement 3 FMDocumento3 pagineAssignement 3 FMREVANTH KUMAR KNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 2 Fluid FlowDocumento3 pagineAssignment 2 Fluid FlowNicolHernandezNarvaezNessuna valutazione finora
- Taller 5 FluidosDocumento5 pagineTaller 5 FluidosManuel OlayaNessuna valutazione finora
- ENGR207 Assignment4 Energyeq Linearmomentum 2019sDocumento2 pagineENGR207 Assignment4 Energyeq Linearmomentum 2019sOmnia KhattabNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydraulics 2 Plate No. 1Documento1 paginaHydraulics 2 Plate No. 1Charm GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bernoulli Venturi NozzleDocumento4 pagineBernoulli Venturi NozzleFrank PingolNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 in Fluid MechanicsDocumento1 paginaChapter 3 in Fluid MechanicsRegineDagumanFuellasNessuna valutazione finora
- MEM311 Manual 09192014Documento77 pagineMEM311 Manual 09192014Sam Yang SunNessuna valutazione finora
- FLuid Mechs ExercisesDocumento8 pagineFLuid Mechs ExercisesMark Andrew TabucanonNessuna valutazione finora
- Exam 1 Study Guide Problems PDFDocumento32 pagineExam 1 Study Guide Problems PDFS. GreenNessuna valutazione finora
- Base Module For Experiments in Fluid MechanicsDocumento5 pagineBase Module For Experiments in Fluid MechanicsMichael VillameNessuna valutazione finora
- Immigration CertificationDocumento5 pagineImmigration CertificationMichael VillameNessuna valutazione finora
- VCU Form 1Documento2 pagineVCU Form 1Michael VillameNessuna valutazione finora
- Digest #01Documento2 pagineDigest #01Michael VillameNessuna valutazione finora
- Name of Agency Verification and Certification UnitDocumento3 pagineName of Agency Verification and Certification UnitMichael VillameNessuna valutazione finora
- Certification Request For Travel Records: ReceivedDocumento2 pagineCertification Request For Travel Records: ReceivedMichael Villame100% (1)
- RS Form 1Documento2 pagineRS Form 1Michael VillameNessuna valutazione finora
- EDMT 201 - 2ndsem12Documento6 pagineEDMT 201 - 2ndsem12Michael VillameNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 4 Power SeriesDocumento4 pagineModule 4 Power SeriesMichael VillameNessuna valutazione finora
- Bi Clearance CertificationDocumento3 pagineBi Clearance CertificationMichael VillameNessuna valutazione finora
- Criminal Law-People vs. Genosa: Facts of The CaseDocumento3 pagineCriminal Law-People vs. Genosa: Facts of The CaseMichael VillameNessuna valutazione finora
- Special Power of AttorneyDocumento1 paginaSpecial Power of AttorneyMaricel Caranto FriasNessuna valutazione finora
- Scilab TutorialDocumento55 pagineScilab TutorialMichael Villame100% (1)
- Judicial EthicsDocumento4 pagineJudicial EthicsMichael VillameNessuna valutazione finora
- Combating Trafficking in Persons: A Handbook For ParliamentariansDocumento140 pagineCombating Trafficking in Persons: A Handbook For ParliamentariansMichael VillameNessuna valutazione finora
- Republic Act No. 386 An Act To Ordain and Institute The Civil Code of The PhilippinesDocumento230 pagineRepublic Act No. 386 An Act To Ordain and Institute The Civil Code of The PhilippinesMichael VillameNessuna valutazione finora
- April Lynn L. Ursal: If Lawyers Act As Executor and Administrator, Can They Charge For Legal Fees?Documento18 pagineApril Lynn L. Ursal: If Lawyers Act As Executor and Administrator, Can They Charge For Legal Fees?Michael VillameNessuna valutazione finora
- KSB Etabloc Jelleggorbe 50hzDocumento172 pagineKSB Etabloc Jelleggorbe 50hzUmar MajeedNessuna valutazione finora
- M-P-A 2000-X: Liquid Antisettling Agent For Solvent-Borne SystemsDocumento2 pagineM-P-A 2000-X: Liquid Antisettling Agent For Solvent-Borne SystemsさいとはちこNessuna valutazione finora
- Moment of ForceDocumento5 pagineMoment of ForceSahrul RamdanNessuna valutazione finora
- 30RB - RQ - Carrier - ManualzzDocumento19 pagine30RB - RQ - Carrier - ManualzzmelodyNessuna valutazione finora
- Power and Distribution Transformers Sizing Calculations - Part Nine Electrical KnowhowDocumento11 paginePower and Distribution Transformers Sizing Calculations - Part Nine Electrical KnowhowRodel PelimianoNessuna valutazione finora
- How The Human Eye FocusesDocumento8 pagineHow The Human Eye FocusesCucută Alexandru-DanielNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 9 2nd Quarter Periodical Test SY 2022 2023 40 ITEMS FinalDocumento3 pagineGrade 9 2nd Quarter Periodical Test SY 2022 2023 40 ITEMS FinalSAN JOSE LITEX SHS 342566100% (1)
- Three Rods On A Ring and The Triangular BilliardDocumento5 pagineThree Rods On A Ring and The Triangular BilliardCesar RosalesNessuna valutazione finora
- 9th Class English S.A-1 Model PaperDocumento5 pagine9th Class English S.A-1 Model Paperasudhakar21520Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Reactions and Chemical EquationsDocumento34 pagineChemical Reactions and Chemical EquationsIvy Joyce BuanNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics A Level P 5 Yearly Worked Soluti PDFDocumento21 paginePhysics A Level P 5 Yearly Worked Soluti PDFIqra Hameed KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Muster PDFDocumento36 paginePhysics Muster PDFMarlon FariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Vibration Analysis of Steel Pedestrian BridgesDocumento35 pagineVibration Analysis of Steel Pedestrian BridgesYasela100% (1)
- NBC Rule 7 & 8 Step by Step v1.2 Sep2016Documento2 pagineNBC Rule 7 & 8 Step by Step v1.2 Sep2016Andrea EstiponaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial Sheet 1 - KeyDocumento11 pagineTutorial Sheet 1 - KeyRobert SimazuoNessuna valutazione finora
- Low-Cost Autonomous Power Factor Controlling Device: Bs-Ee Final Year Project ProposalDocumento17 pagineLow-Cost Autonomous Power Factor Controlling Device: Bs-Ee Final Year Project ProposalShazaib SanaullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Oleg Pankov مهم مهم مهمDocumento115 pagineOleg Pankov مهم مهم مهمAmr ElDisoukyNessuna valutazione finora
- Mass Transfer Slides - CHE304 - Chapter 27Documento50 pagineMass Transfer Slides - CHE304 - Chapter 27RehabNessuna valutazione finora
- 6-Screw and Gear MeasurementDocumento50 pagine6-Screw and Gear MeasurementRohit BhangaleNessuna valutazione finora
- LTA320HN02 W SamsungDocumento28 pagineLTA320HN02 W SamsungRavi SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 Direct SensingDocumento3 pagine12 Direct SensingPooja MehraNessuna valutazione finora
- V20 Op Instr 1019 en-US PDFDocumento426 pagineV20 Op Instr 1019 en-US PDFAlex BocanceaNessuna valutazione finora
- Uantum Physics Simplicity AND Beauty: M M - T A PDocumento3 pagineUantum Physics Simplicity AND Beauty: M M - T A PKeepy FamadorNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Vena Contracta - How Vena Contracta Formed in Fluid Flow - Mecholic PDFDocumento3 pagineWhat Is Vena Contracta - How Vena Contracta Formed in Fluid Flow - Mecholic PDFAmrut Raj PurohitNessuna valutazione finora
- Friction and Heat Transfer Coefficients in Smooth and Rough PipesDocumento255 pagineFriction and Heat Transfer Coefficients in Smooth and Rough PipesAnderson AndradeNessuna valutazione finora
- Scanning MRI Full BodyDocumento1 paginaScanning MRI Full BodyHabtamu WorkuNessuna valutazione finora
- 5.2 Method of JointsDocumento37 pagine5.2 Method of Jointsnisa erinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tunneling-Like Wave Transmission in Non-Hermitian Lattices With Mirrored NonreciprocityDocumento6 pagineTunneling-Like Wave Transmission in Non-Hermitian Lattices With Mirrored Nonreciprocitydonniedarko817Nessuna valutazione finora
- Packet SLG WS123TR 2014 CoreDocumento8 paginePacket SLG WS123TR 2014 CoreMeera SoniNessuna valutazione finora
- Grounding & Lighting Prot-Grounding BarDocumento2 pagineGrounding & Lighting Prot-Grounding BarAlifia AiniNessuna valutazione finora