Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
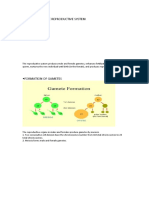
Proliferative Phase: Proliferation of Granulosa Cells, Growth
Caricato da
Chng Wei QiangTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Proliferative Phase: Proliferation of Granulosa Cells, Growth
Caricato da
Chng Wei QiangCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Actions of sex hormones MALES Testosterone 1.
Fetal differentiation of the internal male genital tract: epipidymis, vas deferens and seminal vesicles 2. Puberty: increased muscle mass, growth spurt, closure of epiphyseal plates, growth of penis + seminal vesicles, voicebreaking, spermatogenesis and increased libido 1. Fetal differentiation of external male genitalia: penis, scrotum and prostate 2. Male hair distribution 3. Sebaceous gland activity 4. Growth of prostate (5a-reductase inhibitors treat benign prostatic hypertrophy)
Dihydrotestosterone
FEMALES Estrogen Menstruation & Puberty Proliferative phase: proliferation of granulosa cells, growth of endometrium + glands + stroma, elongation of spiral arteries, cervical mucus becomes watery and elastic to allow sperm to penetrate Proliferation and development of granulosa cells Upregulation of estrogen, progesterone and LH receptors Breast development estrogen stimulate growth of areolar, lobular ducts and adipose tissue Maturation and maintenance of internal female genitalia: uterus, fallopian tubes, cervix and upper 1/3 of vagina Decrease LDL cholesterol Anti-osteoporotic Growth of myometrium Growth of ductal system in breasts Stimulation of prolactin secretion Enlargement of external genitalia Blocks action of prolactin on breasts Decreases uterine threshold to contractile stimuli Secretory phase: proliferation of endometrium slows, uterine glands become tortuous, glycogen vacuoles increase, mucus secretion increase, stroma of endometrium becomes edematous, spiral arteries grow and coil, cervical mucus decrease, becoming thick and non-elastic Progesterone coordinate with estrogen to stimulate secretion in mammary ducts Maintains endometrial lining of uterus Increases uterine threshold to contractile stimuli
Pregnancy
Progesterone
Menstruation & Puberty
Pregnancy
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Chapter 5 - MCN ReviewerDocumento12 pagineChapter 5 - MCN ReviewerPrincess Queenie OlarteNessuna valutazione finora
- Function of Male and Female Reproductive SystemDocumento41 pagineFunction of Male and Female Reproductive SystemCelestineNessuna valutazione finora
- Ana Physio Menstrual Cycle For StudentsDocumento45 pagineAna Physio Menstrual Cycle For StudentsChelsea Mariette AndradeNessuna valutazione finora
- Primary Hormones of ReproductionDocumento3 paginePrimary Hormones of ReproductionMohd AriffNessuna valutazione finora
- MCN ReviewerDocumento10 pagineMCN ReviewergreinabelNessuna valutazione finora
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOgyDocumento17 pagineANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOgyadriancalprNessuna valutazione finora
- Reproductive System: Lecture by DR M. Sohaib FOR Ms Medical PhysicsDocumento11 pagineReproductive System: Lecture by DR M. Sohaib FOR Ms Medical PhysicsislamNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec 2Documento14 pagineLec 2Tabark AliNessuna valutazione finora
- OB ReviewDocumento257 pagineOB ReviewRosemaryCastro100% (1)
- ACTIVITY 3 BIOMEDICAL PERSPECTIVE IN GENDER AND SEXUALiTYDocumento9 pagineACTIVITY 3 BIOMEDICAL PERSPECTIVE IN GENDER AND SEXUALiTYMASTER CLINTONNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas Module 4 Lesson 1Documento3 pagineGas Module 4 Lesson 1MARK 2020Nessuna valutazione finora
- Male Reproductive SystemDocumento26 pagineMale Reproductive SystemRahil PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiology of ReproductionDocumento3 pagineAnatomy and Physiology of ReproductionAstorias Jayv B.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Maternal Nursing: Anatomy and PhysiologyDocumento60 pagineMaternal Nursing: Anatomy and PhysiologyAmazingMindNessuna valutazione finora
- 1a ReproductiveAndSexualHealthDocumento2 pagine1a ReproductiveAndSexualHealthKenjie Palaganas CentenoNessuna valutazione finora
- Reproductive System A& PDocumento17 pagineReproductive System A& PCrystal MerchantNessuna valutazione finora
- Test #5 Notes 2Documento29 pagineTest #5 Notes 2api-3723612Nessuna valutazione finora
- GE9 Module Lesson 3Documento6 pagineGE9 Module Lesson 3agnesNessuna valutazione finora
- Nle Notes MCNDocumento38 pagineNle Notes MCNAngela CamilleNessuna valutazione finora
- Maternal Ob NotesDocumento37 pagineMaternal Ob NotesO.r. CadzNessuna valutazione finora
- GENSOC M2 Lesson 4Documento7 pagineGENSOC M2 Lesson 4cassy margaNessuna valutazione finora
- Maternal/Ob NotesDocumento45 pagineMaternal/Ob NotesJoanne Christina Buenafe100% (1)
- Obstetric Nursing Review (NLE)Documento48 pagineObstetric Nursing Review (NLE)'jmark Francia100% (4)
- Reproductive System Development: Ob NotesDocumento2 pagineReproductive System Development: Ob NotesLykee PadillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gender & Society 2Documento20 pagineGender & Society 2Anna Rose T. MarcelinoNessuna valutazione finora
- ANAPHYSIODocumento5 pagineANAPHYSIOCarol Lopez DauagNessuna valutazione finora
- Male & Female Reproductive SystemDocumento211 pagineMale & Female Reproductive SystemDanica Marie SibayNessuna valutazione finora
- Gender and Society CompileDocumento32 pagineGender and Society Compileクイーンクイーン ロペスNessuna valutazione finora
- Gender and Society 2Documento27 pagineGender and Society 2Kent Ian InfanteNessuna valutazione finora
- 8.7.10 REPRODUCTION IN HUMANS My CS NotesDocumento13 pagine8.7.10 REPRODUCTION IN HUMANS My CS NotesAndre KachigambaNessuna valutazione finora
- Inbound 4525214668487640543Documento12 pagineInbound 4525214668487640543Neña Bautista PagalNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 TransDocumento10 pagine1 TranssenecabheNessuna valutazione finora
- Reproductive SystemDocumento11 pagineReproductive Systemcasandra moranteNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 3Documento8 pagineCH 3api-288494741Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reproductive SystemDocumento11 pagineReproductive SystemMID IMRANNessuna valutazione finora
- Antenatal Lec. 3Documento112 pagineAntenatal Lec. 3Jesusa AbanesNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Ii: Biochemical Perspective in Gender and Sexuality Lesson 1: Anatomy and Physiology of ReproductionDocumento10 pagineChapter Ii: Biochemical Perspective in Gender and Sexuality Lesson 1: Anatomy and Physiology of ReproductionDevin Jake Maylas FeoNessuna valutazione finora
- Obstetric NursingDocumento36 pagineObstetric NursingpauchanmnlNessuna valutazione finora
- Pretender PubisDocumento28 paginePretender Pubiskhaye_35100% (1)
- Pemeriksaan Dalam VTDocumento24 paginePemeriksaan Dalam VTFauzi Al-IslamiNessuna valutazione finora
- HP Repro 2Documento4 pagineHP Repro 2Rhzyl Moira CadapNessuna valutazione finora
- Socsci Lesson 4Documento19 pagineSocsci Lesson 4wendellkun1Nessuna valutazione finora
- GonadsDocumento21 pagineGonadsTanya SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 125Documento18 pagineChapter 125Saloni SaloniNessuna valutazione finora
- All MCN MidtermDocumento207 pagineAll MCN MidtermInah SaritaNessuna valutazione finora
- Reproduction in HumansDocumento14 pagineReproduction in HumansarnoldnsondojrNessuna valutazione finora
- Science 3rd QuarterDocumento22 pagineScience 3rd QuarterBethel AquinoNessuna valutazione finora
- 41) Sex Hormones (C. Patho)Documento33 pagine41) Sex Hormones (C. Patho)Haider AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 4 PresentationDocumento78 pagineGroup 4 PresentationMissy YatnapgamNessuna valutazione finora
- Male Sex HormonesDocumento7 pagineMale Sex Hormonesحسن اليوسفNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Reproduction 22-23 CorrectedDocumento11 pagineHuman Reproduction 22-23 Correctedhi100% (1)
- Class 10 Biology 8.9.20Documento11 pagineClass 10 Biology 8.9.20Shruti MahtoNessuna valutazione finora
- Rodriguez LecDocumento2 pagineRodriguez LecRAZELLE JOY CATIAN RODRIGUEZNessuna valutazione finora
- Male and Female Reproductive SystemDocumento105 pagineMale and Female Reproductive Systemjanmic100% (3)
- Bachelor of Science in Nursing: Care of Mother, Child and ADOLESCENT (Well Clients)Documento9 pagineBachelor of Science in Nursing: Care of Mother, Child and ADOLESCENT (Well Clients)Jerica Mae VenoyaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Reproductive SystemDocumento5 pagineThe Reproductive SystemPak LypNessuna valutazione finora
- The Illustrated Book of Medicine: The Making of MeDa EverandThe Illustrated Book of Medicine: The Making of MeNessuna valutazione finora
- Preclinical Anatomy Review 2023: For USMLE Step 1 and COMLEX-USA Level 1Da EverandPreclinical Anatomy Review 2023: For USMLE Step 1 and COMLEX-USA Level 1Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)