Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Physics 7
Caricato da
Wayne TeoDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Physics 7
Caricato da
Wayne TeoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Laser (read the notes) Coherent: In phase Collimated: Same dir Monochromatic: 1 wavelength
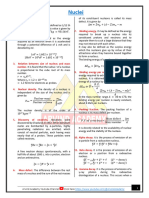
Isotopes: Nuclei that have the same proton number but different number of neutrons. u: atomic mass unit; 1/12th of the mass of a 12C atom. Mass Defect m: The difference between the sum of the masses of the nucleon and the mass of the actual nucleus.
m = ( Zm p + Nmn ) m nucleus = ( Zm p + Nm n ) (m A Zme ) = Zm H + Nmn m A
BE = ( m ) c 2
Fe Coulomb repulsion > nuclear force U BE per nucleon
Conservation of Charge Momentum Mass-Energy Mass number
Fusion H
Fission
Radioactivity is the random and spontaneous decay of an unstable nucleus to a more stable one by emission of particles and/or radiation. Random: Dont know which and when a nucleus will decay Spontaneous: Not affected by other environmental factors Background radiation is systematic error.
Mass no, A
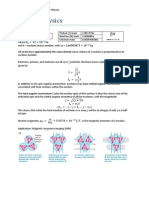
particlesHelium-4 nuclei High Ionising PowerAir range of 3 - 4cm Stopped by paper Low L hazard unless ingestedModerate Ionising Power High speeds (0.5c)Stopped by 5mm of Al Stopped by surface tissuesProduced when excited nuclei returns to ground S state Weak Ionising PowerStopped by few cm of lead Main radiation hazard due to deep penetration Cancer, leukemia, cataracts, hereditary defectsStore in lead containers when C not in use. Handle with a pair of tongs. H
dN = N dt N = N 0 e t A=
Decay Constant is the probability of decay of a nucleus per unit time. Where N is the no. of undecayed nuclei. N Constant half-life
dN = N = A0 e t Activity A, is the rate of decay. (Bq) Where A0 is the activity at t = 0. dt ln 2 t 12 = Half-life is the time it takes for half of N 1 = N0 2
n
a given no. of nuclei to decay.
Where n is the number of half-lives.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Solid-State Circuits: Electrical Engineering DivisonDa EverandSolid-State Circuits: Electrical Engineering DivisonValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (4)
- Physics 08 NuclearDocumento32 paginePhysics 08 NuclearPiotr NowakNessuna valutazione finora
- Nuclear Techniques in Analytical Chemistry: International Series of Monographs on Analytical ChemistryDa EverandNuclear Techniques in Analytical Chemistry: International Series of Monographs on Analytical ChemistryNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 12 Physics Revision Notes Atoms (1) LEARN WITH GIGACHADSDocumento20 pagineClass 12 Physics Revision Notes Atoms (1) LEARN WITH GIGACHADSBlurry FaceNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1Da EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (5)
- 7.1 Discrete Energy and Radioactivity NotesDocumento6 pagine7.1 Discrete Energy and Radioactivity Noteskoksoon chongNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic NucleusDocumento15 pagineAtomic Nucleussreenivas1990100% (1)
- Nuclei - Short Notes - VIJETA SERIES CLASS-12THDocumento2 pagineNuclei - Short Notes - VIJETA SERIES CLASS-12THAbhishek KumarNessuna valutazione finora
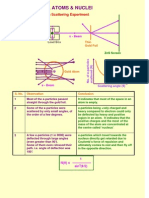
- Atoms & Nuclei: Rutherford's Alpha Scattering ExperimentDocumento9 pagineAtoms & Nuclei: Rutherford's Alpha Scattering ExperimentNathanianNessuna valutazione finora
- Radioactivity: Physical Chemistry by Prince SirDocumento25 pagineRadioactivity: Physical Chemistry by Prince SirAbhijeetNessuna valutazione finora
- Radioactivity & Radionuclide ProductionDocumento92 pagineRadioactivity & Radionuclide Productionvex2rex100% (2)
- NuclearDocumento5 pagineNuclearmargaretwambui294Nessuna valutazione finora
- Atoms and NucleiDocumento12 pagineAtoms and NucleiBablu ChaudharyNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem101 Ho5Documento5 pagineChem101 Ho5nairbatnabamNessuna valutazione finora
- MathematicalDocumento31 pagineMathematicalmohammed1998Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nuclei For CBSE Physics Class XII Revision NotesDocumento4 pagineNuclei For CBSE Physics Class XII Revision NotesKuldeep HoodaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 13 NucleiDocumento2 pagineChap 13 NucleiV MohithNessuna valutazione finora
- Nuclear DecayDocumento20 pagineNuclear DecayAli SalamehNessuna valutazione finora
- Nuclear Physics A Level RevisionDocumento32 pagineNuclear Physics A Level Revisionsupniggas80% (5)
- Nuclear PhysicsDocumento28 pagineNuclear PhysicsSatish Kumar100% (1)
- Introduction To RadioactivityDocumento21 pagineIntroduction To Radioactivity413 YASH MANENessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry NotesDocumento24 pagineChemistry NotesTaylor HuangNessuna valutazione finora
- Portal For CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and TricksDocumento5 paginePortal For CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and TricksAshish PalaiNessuna valutazione finora
- (NIT Rourkela) Nuclear PhysicsDocumento46 pagine(NIT Rourkela) Nuclear PhysicsAditya JagadalaNessuna valutazione finora
- QB Lecture 14-2014Documento16 pagineQB Lecture 14-2014Hashir SaeedNessuna valutazione finora
- Radioactive Decay Experiment Deniz BilgiliDocumento12 pagineRadioactive Decay Experiment Deniz BilgiliDeniz BilgiliNessuna valutazione finora
- Fisika DasarDocumento5 pagineFisika DasarBulan NiaNessuna valutazione finora
- RevisionDocumento13 pagineRevisionrajayush67780Nessuna valutazione finora
- CH 12Documento82 pagineCH 12SylviaNessuna valutazione finora
- Revision Notes For NucleationDocumento7 pagineRevision Notes For Nucleationsumakodipaka938Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nuclear Decay Applications of Nuclear PhysicsDocumento19 pagineNuclear Decay Applications of Nuclear PhysicspfmlerNessuna valutazione finora
- RP PDFDocumento71 pagineRP PDFGAZI SALAH UDDINNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical Work 10Documento11 paginePractical Work 10Achraf RabadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 ing - - نسخةDocumento11 pagineChapter 3 ing - - نسخةThë Nãüght RayenëNessuna valutazione finora
- RadioactivityDocumento103 pagineRadioactivityMuhammad ShahzaibNessuna valutazione finora
- Neutron InteractionDocumento47 pagineNeutron InteractionSamu SimamesaNessuna valutazione finora
- NucleiDocumento32 pagineNucleiGDGGFGFNessuna valutazione finora
- Answers To Examination-Style Questions: Answers Marks Examiner's TipsDocumento7 pagineAnswers To Examination-Style Questions: Answers Marks Examiner's TipsjasbirsinghNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 17 - Nuclear PhysicsDocumento37 pagineCH 17 - Nuclear PhysicsOKAY JAROD PUGNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.nuclear PhysicsDocumento8 pagine3.nuclear PhysicsFarjana KabirNessuna valutazione finora
- Nuclear Physics: An OverviewDocumento29 pagineNuclear Physics: An OverviewabdulbaseerNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To RadioactivityDocumento80 pagineIntroduction To RadioactivityKaranam.Ramakumar100% (4)
- Nuclear Chemistry: RadioactivityDocumento11 pagineNuclear Chemistry: RadioactivityMilton Dels RosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nuclear ChemistryDocumento32 pagineNuclear ChemistrypotassiumNessuna valutazione finora
- Particle Interaction Matter UploadDocumento79 pagineParticle Interaction Matter UploadvictorNessuna valutazione finora
- Nuclear Physics: Basic Properties of NucleusDocumento17 pagineNuclear Physics: Basic Properties of NucleusSK. NAFISH SADIQUE AYON 1903043Nessuna valutazione finora
- Electron Scattering and DiffractionDocumento27 pagineElectron Scattering and Diffractionshubhang2392Nessuna valutazione finora
- Radioactivity 1Documento10 pagineRadioactivity 1subhajana646Nessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Nuclear Properties: Particle and Nuclear PhysicsDocumento27 pagineBasic Nuclear Properties: Particle and Nuclear PhysicsAmartya BeuriaNessuna valutazione finora
- PNP Handout3Documento62 paginePNP Handout3Anil HirparaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nuclear Physics NotesDocumento8 pagineNuclear Physics NotesCai Peng Fei100% (1)
- Nuclear Physics PrimerDocumento10 pagineNuclear Physics PrimerAnthony AffulNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 4 Nuclear ChemistryDocumento7 pagineLesson 4 Nuclear ChemistrySheilora DagusNessuna valutazione finora
- NucleiDocumento22 pagineNucleivaishnavpatil2458Nessuna valutazione finora
- Radiation Physics and Dosimetry: Institute of Radiation Safety, Sudan Atomic Energy CommissionDocumento51 pagineRadiation Physics and Dosimetry: Institute of Radiation Safety, Sudan Atomic Energy CommissionOmar A. MohammadNessuna valutazione finora
- Ss - 26092020110000 - Final Nuclear Chemistry - Complete ModuleDocumento16 pagineSs - 26092020110000 - Final Nuclear Chemistry - Complete Moduleketan sumanNessuna valutazione finora
- Review 402Documento50 pagineReview 402Serdar CharyyevNessuna valutazione finora
- Anleitung Ab eDocumento21 pagineAnleitung Ab eChristian Contreras CastroNessuna valutazione finora
- PHYS1210 Particle Physics and Cosmology: DR Michael Gladys PhysicsDocumento41 paginePHYS1210 Particle Physics and Cosmology: DR Michael Gladys PhysicssamNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 11 Economics Unit #3: Government Intervention Practice Test and Answer KeyDocumento8 pagineGrade 11 Economics Unit #3: Government Intervention Practice Test and Answer KeyWayne TeoNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.1 Indirect TaxesDocumento4 pagine3.1 Indirect TaxesmuskaanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 11Documento25 pagineChapter 11Wayne TeoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 9Documento14 pagineChapter 9Wayne TeoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8Documento20 pagineChapter 8Wayne TeoNessuna valutazione finora
- Wayne Teo - Scharffen Berge Case Study PDFDocumento1 paginaWayne Teo - Scharffen Berge Case Study PDFWayne TeoNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategy, Organization Design, and Effectiveness GoalsDocumento2 pagineStrategy, Organization Design, and Effectiveness GoalsWayne TeoNessuna valutazione finora
- Monday: 4E4 - LC RM2 4E4 - Blab2 - Plab2 4E4 - E2Documento1 paginaMonday: 4E4 - LC RM2 4E4 - Blab2 - Plab2 4E4 - E2Wayne TeoNessuna valutazione finora
- GeogDocumento1 paginaGeogWayne TeoNessuna valutazione finora
- Health Editorial On Healthcare CostDocumento3 pagineHealth Editorial On Healthcare CostWayne TeoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Household-Consumption Sector: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocumento44 pagineThe Household-Consumption Sector: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinWayne TeoNessuna valutazione finora
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseDa EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (69)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesDa EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (2193)
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceDa EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (51)
- Giza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyDa EverandGiza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyNessuna valutazione finora
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldDa EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (64)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldDa EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (60)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayDa EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (125)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessDa EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (6)
- The Beauty of Falling: A Life in Pursuit of GravityDa EverandThe Beauty of Falling: A Life in Pursuit of GravityNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingDa EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (5)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterDa EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (410)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidDa EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1396)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldDa EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (54)
- Let There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessDa EverandLet There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (57)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowDa EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (49)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Da EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (157)
- A Natural History of Color: The Science Behind What We See and How We See itDa EverandA Natural History of Color: The Science Behind What We See and How We See itValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (13)
- Chasing Heisenberg: The Race for the Atom BombDa EverandChasing Heisenberg: The Race for the Atom BombValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (8)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceDa EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (5)
- Black Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseDa EverandBlack Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (13)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeDa EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- AP Physics 1 Premium, 2024: 4 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeDa EverandAP Physics 1 Premium, 2024: 4 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeNessuna valutazione finora